MTA Security Fundamentals Exam Questions and Answers

Preparing for a technical certification in the field of IT requires a solid understanding of key principles, practices, and concepts. The process often involves studying various subjects related to system protection, risk management, and effective threat mitigation. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to enhance your knowledge, this guide will help you navigate the essential areas for success.
Comprehensive knowledge of network defense, encryption techniques, access control, and overall system integrity is crucial. It is not only about memorizing facts, but also about understanding how these concepts interact within real-world scenarios. By familiarizing yourself with potential challenges, you’ll be better equipped to approach your preparation methodically and with confidence.
In this article, we focus on the most critical aspects you need to grasp, emphasizing both theory and practical applications. This approach will support your readiness for certification, ensuring that you not only pass but understand the material deeply. With the right strategy, you can achieve success and be well-prepared to handle complex situations in professional environments.
Understanding Core IT Protection Concepts
To excel in a certification focused on system integrity, it’s essential to comprehend the broad spectrum of protective measures, risk management strategies, and methods for safeguarding data. A solid foundation in these areas helps professionals design, implement, and monitor secure environments. This section delves into key principles you must understand, providing the groundwork for more advanced topics.
Core Principles of Protection
One of the most critical aspects of the certification is understanding the different types of protection mechanisms that can be applied to IT infrastructure. These include various layers of defense, ranging from user access controls to data encryption and network security strategies. By grasping these core principles, you can start building a comprehensive approach to system protection.
Risk Management and Threat Detection
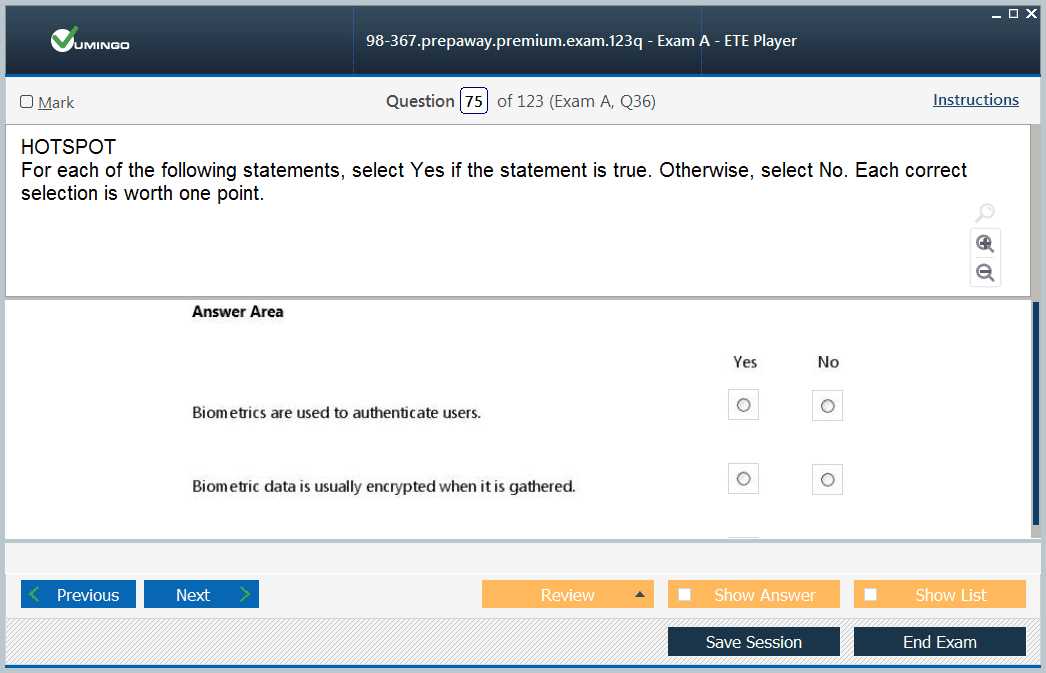
Another fundamental concept in the field is risk management. Being able to identify potential threats, assess their impact, and deploy mitigating controls is essential for maintaining a resilient system. Alongside this, understanding how to detect and respond to security incidents forms a core part of the knowledge required for certification.
| Core Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|
| User Access Control | Limiting access to sensitive data and systems based on user roles and permissions. |
| Data Encryption | Transforming information into a secure format to prevent unauthorized access. |
| Network Defense | Protecting internal networks from external threats through firewalls, VPNs, and other tools. |
| Incident Response | Methods for detecting and reacting to potential breaches or system failures. |
By mastering these foundational concepts, you’ll be well-positioned to approach more advanced material and prepare for real-world scenarios in the field of IT protection.
Key Concepts for Certification Preparation
To succeed in a certification process focused on protecting IT systems, it is crucial to grasp the essential principles that form the backbone of the industry. These concepts cover a wide range of topics, from basic system protection techniques to advanced strategies for managing risks and safeguarding sensitive data. Mastery of these areas ensures that individuals are prepared to meet the challenges posed by evolving technological threats.
Understanding the importance of layering defenses and applying various tools to prevent unauthorized access is fundamental. The ability to identify and mitigate risks, alongside knowledge of encryption and monitoring tools, will empower professionals to create secure environments that can withstand potential attacks.
Furthermore, familiarity with the different compliance standards and regulations ensures that those pursuing a career in IT protection adhere to industry best practices and legal requirements. By focusing on these core concepts, individuals can build a strong foundation that is essential for both passing certification and performing effectively in real-world situations.
What to Expect in the Certification Process
Preparing for a technical certification involves understanding the structure of the assessment and knowing what topics will be covered. The process typically involves a series of challenges designed to test your understanding of core principles, technical skills, and practical application. The content will focus on ensuring that candidates are equipped to handle common scenarios they may encounter in professional environments.
During the evaluation, you will encounter various types of challenges, ranging from multiple-choice questions to scenario-based assessments. These will test both theoretical knowledge and your ability to apply concepts to real-world situations. Time management will also be an essential factor, as you will need to efficiently answer a range of questions within the given timeframe.
It’s important to understand that the assessment isn’t solely focused on memorization, but rather on demonstrating an in-depth grasp of key topics. Expect a balanced mix of questions that cover areas such as data protection, risk management, and system defenses.
Top Security Topics to Study
When preparing for a certification focused on IT system protection, it’s essential to prioritize the most critical topics. These subjects not only form the foundation of the field but also represent the areas most likely to be tested. By focusing on the core elements, you can build a strong understanding and ensure you’re well-prepared for any assessment.
Network Defense Techniques
Understanding how to safeguard networks from external threats is one of the most vital aspects of IT protection. Key areas to study include firewall configurations, intrusion detection systems, and virtual private networks (VPNs). You’ll also need to understand how to monitor network traffic and identify potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors.
Access Control and Authentication
Effective management of user access is crucial for maintaining a secure system. Study methods of authentication, including multi-factor and biometric techniques, as well as access control models like role-based and discretionary systems. A solid grasp of these topics will help you design systems that ensure only authorized users have access to sensitive data and resources.
Common Mistakes in Certification Assessments
As with any technical assessment, there are common errors that candidates make during their preparation and evaluation. Recognizing these pitfalls can help you avoid them and improve your chances of success. Many of these mistakes stem from a lack of focus on critical topics, misunderstanding the assessment format, or not managing time effectively during the test.
Relying Too Much on Memorization
One of the most frequent mistakes is relying too heavily on memorizing information rather than understanding core concepts. While remembering key facts is essential, the ability to apply knowledge in real-world scenarios is often tested. It’s crucial to focus on grasping the underlying principles and how they connect, rather than just memorizing answers.
Misinterpreting Complex Scenarios

Another common error is misinterpreting scenario-based questions. These challenges often require you to apply your knowledge to a practical situation, which can be difficult if you don’t thoroughly understand the material. Take the time to read each scenario carefully and identify the key points before answering. Context matters, and understanding the specifics of the question will help guide your response.
How to Prepare Effectively
Effective preparation is key to mastering the material and achieving success in any technical certification. The goal is not just to memorize facts but to deeply understand the concepts and be able to apply them in practical situations. By creating a structured plan and focusing on the most critical areas, you can significantly increase your chances of performing well.
Start by reviewing the core topics and identifying the areas where you need more practice. Break down complex subjects into smaller, manageable sections and tackle them one at a time. Make use of various study materials, including textbooks, online resources, and practice tests, to reinforce your learning. Additionally, simulate real-world scenarios to better understand how to apply your knowledge under pressure.
Time management is also an important factor. Allocate specific periods for study and stick to your schedule. Avoid cramming at the last minute, as this can lead to confusion and reduce retention. Consistent, focused practice over time will ensure you’re well-prepared when the time comes.
Exam Format and Question Types
Understanding the structure of the assessment and the types of challenges you will face is a crucial part of your preparation. The format is designed to test both your theoretical knowledge and your practical application of key concepts. Familiarizing yourself with the layout and types of tasks will help you approach the assessment with confidence and efficiency.
Typically, you will encounter multiple-choice questions that assess your understanding of specific topics, as well as scenario-based questions that require you to apply your knowledge to real-world situations. These tasks will test your ability to analyze situations, make informed decisions, and select the most appropriate solutions based on your knowledge.
Additionally, there may be questions that focus on identifying best practices or troubleshooting common issues. These types of tasks are intended to evaluate your practical experience and your ability to think critically under time pressure. Being comfortable with different question formats will help you respond accurately and efficiently during the assessment.
Importance of Network Security Basics
Having a solid understanding of the basic principles of network protection is essential for anyone working in IT infrastructure. Network security serves as the first line of defense against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other malicious activities. Without a firm grasp of these fundamental concepts, it’s difficult to build effective, resilient systems that can withstand evolving threats.
Protection of Sensitive Information
The primary objective of network defense is to ensure that sensitive data remains secure from external and internal threats. By implementing strong protective measures, such as firewalls, encryption, and secure authentication protocols, you reduce the risk of data loss or exposure. Understanding these basic protections is crucial for maintaining confidentiality and integrity across all connected systems.
Minimizing Vulnerabilities
Another critical aspect of network protection is identifying and minimizing system vulnerabilities. Networks are often targets for hackers due to weak points in their configuration. By learning how to assess risks and apply protective measures, you can ensure that systems are properly safeguarded against potential attacks. This includes recognizing common vulnerabilities and taking proactive steps to prevent exploitation.
Understanding Risk Management Principles
Risk management is a critical aspect of protecting IT systems and data. It involves identifying potential threats, assessing their likelihood and impact, and implementing measures to mitigate those risks. A strong understanding of these principles helps organizations prioritize their resources and safeguard their assets from various vulnerabilities.
Identifying and Assessing Risks
The first step in effective risk management is to identify potential threats to the system, such as cyberattacks, natural disasters, or human errors. Once threats are identified, it’s essential to assess both the likelihood of their occurrence and the potential consequences. This assessment helps determine which risks need immediate attention and which can be addressed with less urgency.
Mitigation Strategies and Controls

Once risks are identified and assessed, the next step is implementing strategies to reduce or eliminate their impact. This can include adopting preventive measures, such as firewalls and encryption, or developing contingency plans for responding to incidents when they occur. The goal is to create a comprehensive approach that minimizes vulnerabilities while maintaining operational efficiency.
Security Threats and Mitigation Techniques
In today’s digital landscape, various threats jeopardize the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of systems and data. These risks can stem from external sources, such as cybercriminals, or internal factors, like employee negligence. Identifying these threats and employing effective mitigation strategies is crucial to maintaining a resilient IT environment.
Common Security Threats
Several types of risks can compromise the safety of networks and data. Here are some of the most common threats:
- Malware: Malicious software designed to damage, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to systems.
- Phishing: A technique where attackers impersonate legitimate entities to steal sensitive information.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: Attacks that overwhelm a system or network to make it unavailable to users.
- Insider Threats: Risks posed by employees or contractors with access to systems who misuse their privileges.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: Intercepting and altering communication between two parties without their knowledge.
Effective Mitigation Techniques
To minimize the risks associated with these threats, several mitigation techniques can be employed:
- Antivirus and Anti-malware Software: Installing and regularly updating security software to detect and remove harmful programs.
- Firewalls: Configuring firewalls to block unauthorized access and monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic.
- Employee Training: Educating staff about security best practices, including recognizing phishing attempts and maintaining strong passwords.
- Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data to ensure it is unreadable to unauthorized users, both in transit and at rest.
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Requiring multiple verification methods to strengthen user authentication and reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Identity and Access Management Overview
Managing user identities and controlling their access to resources is a fundamental aspect of any organization’s IT infrastructure. Proper management ensures that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data, systems, and applications. This process includes verifying users’ identities, determining their level of access, and ensuring that security policies are enforced consistently across all systems.
Effective identity and access management (IAM) reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches by ensuring that only the right people have the right level of access to the right resources. By leveraging IAM tools and best practices, organizations can establish a secure environment that supports both security and operational efficiency.
Key Components of IAM
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| User Authentication | The process of verifying the identity of a user, often through credentials like usernames, passwords, or biometrics. |
| Authorization | Determining what resources or actions a user is allowed to access based on their identity and roles. |
| Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) | A method of restricting system access based on users’ roles within an organization. |
| Single Sign-On (SSO) | A mechanism that allows a user to authenticate once and gain access to multiple systems without needing to log in repeatedly. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Using more than one form of verification to enhance the authentication process, such as combining passwords with biometrics or security tokens. |
Implementing Cryptography Essentials
Cryptography plays a crucial role in ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of data in modern computing environments. By transforming information into unreadable formats, cryptography protects sensitive data from unauthorized access, tampering, or interception. Implementing cryptographic methods effectively can safeguard communication, authenticate users, and provide assurances against various security risks.
To successfully implement cryptographic practices, it is essential to understand the underlying techniques and algorithms that make data protection possible. These methods can be used for data encryption, secure communication, and digital signatures, each with its own set of benefits and use cases. The proper implementation of cryptographic protocols can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and maintain the privacy of users and organizations alike.
Key Cryptographic Techniques

The following are fundamental cryptographic techniques commonly used to protect data:
- Symmetric Encryption: Uses a single key to both encrypt and decrypt data. It is fast and efficient, but key management can be challenging.
- Asymmetric Encryption: Utilizes two keys, a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption, ensuring secure communication over open networks.
- Hashing: Converts data into a fixed-length value or hash, which is used to verify data integrity without revealing the original information.
- Digital Signatures: Provides a means of verifying the authenticity and integrity of a message or document, ensuring that it has not been altered.
- Key Management: Involves the generation, distribution, and storage of encryption keys in a secure manner to ensure that only authorized parties can access the encrypted data.
Best Practices for Cryptography Implementation
To ensure cryptography is implemented effectively and securely, consider the following best practices:
- Use strong encryption algorithms and keys to prevent unauthorized decryption attempts.
- Regularly update cryptographic keys to protect against evolving threats.
- Store encryption keys securely, preferably using hardware security modules (HSMs) or secure key management systems.
- Employ multi-factor authentication (MFA) in conjunction with cryptographic methods to provide additional layers of security.
- Stay informed about vulnerabilities in cryptographic algorithms and patch them as necessary.
Study Resources for MTA Exam
Preparing for a certification that validates your understanding of IT concepts requires access to reliable study materials. Whether you are new to the field or looking to strengthen your knowledge, utilizing the right resources can greatly improve your chances of success. These resources provide a well-rounded approach, covering everything from basic concepts to more complex topics and practical applications.
Various study tools are available to help you review essential topics. Books, online courses, practice tests, and forums offer diverse methods of learning. It’s important to explore a variety of these materials to get a comprehensive understanding and gain confidence in the subject matter. Below are some of the most effective resources to consider when preparing for your certification journey:
Recommended Study Materials
- Official Guides: These are textbooks or eBooks specifically designed to cover all the topics included in the certification. They often include practice exercises and sample tests.
- Online Learning Platforms: Websites like Udemy, Pluralsight, and LinkedIn Learning offer structured courses taught by experts in the field. These platforms provide video tutorials and interactive content.
- Practice Tests: Taking practice exams is an essential part of the preparation process. These tests simulate real certification assessments and help you familiarize yourself with the format and types of questions.
- Discussion Forums and Study Groups: Engaging with online communities such as Reddit, Stack Overflow, or dedicated forums can provide valuable insights, tips, and answers to challenging topics.
- Flashcards: Tools like Quizlet and Anki can help reinforce your knowledge through spaced repetition, focusing on key terms and definitions.
Additional Resources for Better Understanding
- Blogs and Websites: Many IT professionals share their knowledge through blogs and personal websites, offering explanations of complex concepts and up-to-date trends.
- YouTube Channels: Video content can make learning more engaging. Channels like Professor Messer and CBT Nuggets provide free tutorials that cover exam topics in detail.
- Virtual Labs: Hands-on experience is crucial in IT. Virtual labs allow you to practice real-world scenarios without the need for physical hardware.
- Study Apps: Mobile apps offer convenience for on-the-go learning, helping you review key concepts whenever you have free time.
By utilizing a combination of these resources, you can ensure a thorough preparation strategy and increase your chances of passing the certification with confidence.
Time Management Strategies for Exams
Effective time management plays a crucial role in achieving success during any certification process. By organizing study sessions and allocating appropriate time to each topic, you can approach the test with confidence. Balancing study time and rest, prioritizing key areas, and ensuring that you don’t run out of time on the day of the assessment are all essential factors for optimal performance.
With the right strategies, you can ensure that every minute spent preparing is productive. The following methods can help you improve your efficiency and maximize your readiness for the test:
Effective Planning Techniques
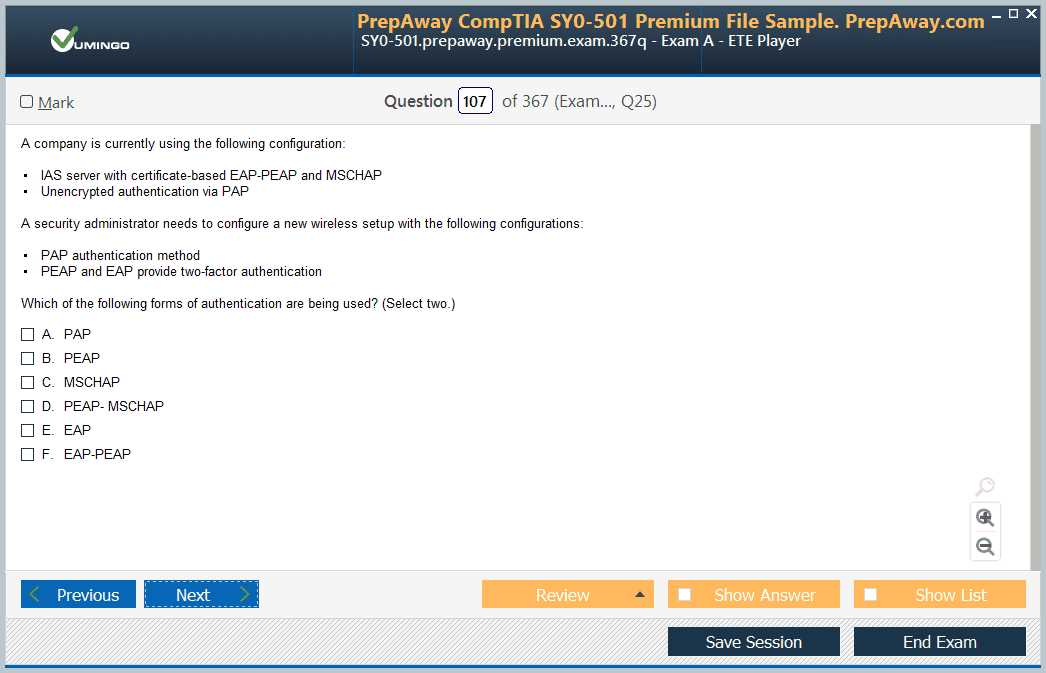
- Create a Study Schedule: Plan your study sessions in advance. Break your learning into manageable chunks and allocate time for each topic based on its complexity and your familiarity with it.
- Prioritize Weak Areas: Focus more on topics that you find challenging. Spending additional time on these areas will help build your confidence and reduce the chances of encountering difficulties during the test.
- Use a Timer: Practice with timed quizzes and exercises. Setting a timer helps simulate the actual test conditions, allowing you to gauge how long you need to complete each section.
- Set Milestones: Break down your preparation into smaller tasks and set specific deadlines for completing each. This will keep you on track and prevent procrastination.
During the Test: Managing Your Time
- Read Instructions Carefully: Before you begin, quickly read through the instructions to avoid confusion and ensure you understand the format and requirements of the test.
- Don’t Spend Too Much Time on One Question: If a particular question is taking too long, move on and come back to it later. Prioritize answering questions you know well.
- Monitor Your Time: Keep track of the time left. This will prevent you from rushing towards the end and give you the opportunity to review your answers.
- Leave Some Time for Review: Reserve the last 5-10 minutes to go over your responses. This will allow you to correct any mistakes and ensure you haven’t overlooked anything important.
By incorporating these time management strategies into your study routine and test-taking approach, you can enhance your focus, reduce stress, and ultimately improve your chances of success.
Tips for Answering Multiple-Choice Questions
Multiple-choice questions often appear in assessments and can be challenging if not approached strategically. The key to mastering these types of questions is to remain calm, read each option carefully, and employ methods to rule out incorrect choices. With the right techniques, you can increase your accuracy and ensure that you are selecting the best possible answer.
Here are some useful strategies for tackling multiple-choice items efficiently:
Approach Each Question Methodically
- Read the Question Thoroughly: Before looking at the available options, make sure you fully understand what the question is asking. This will help prevent confusion and keep you focused.
- Eliminate Obvious Incorrect Answers: Quickly eliminate choices that are clearly wrong. This narrows down your options and increases your chances of selecting the correct answer.
- Look for Keywords: Pay attention to keywords in both the question and the answer choices. Words like “always,” “never,” or “most likely” can provide clues about the right response.
- Check for Similar Answers: If two options are nearly identical, one of them is likely the correct answer. Compare these closely and choose the one that aligns best with the question.
Dealing with Uncertainty
- Make an Educated Guess: If you’re unsure about the correct response, try to use logic and any relevant information you’ve studied to make an educated guess. Don’t leave any questions unanswered unless you’re absolutely certain.
- Don’t Overthink: Trust your first instinct. Overanalyzing a question can lead to second-guessing and mistakes.
- Be Cautious with “All of the Above” and “None of the Above”: These options can be tricky. If you know that at least one option is correct, “All of the Above” might be a good choice. However, if one is incorrect, “All of the Above” can be ruled out.
- Review Your Choices: Once you have selected an answer, double-check it. Ensure it makes sense in the context of the question. If you’re still uncertain, consider how each option fits with the question.
By applying these tips, you’ll be better prepared to navigate multiple-choice sections, increase your confidence, and improve your overall performance during assessments.
How to Use Practice Tests Effectively

Practice tests are a powerful tool for preparation, offering a simulated experience of the real assessment. By completing these exercises, you can familiarize yourself with the format, identify areas for improvement, and refine your time-management skills. However, the key to success lies in using these tests strategically, making them a key component of your study routine.
Here are some strategies to maximize the benefits of practice tests:
Strategic Preparation
- Start Early: Begin using practice tests early in your preparation process. This will give you a sense of where you stand and what areas require more attention. Early testing can also highlight gaps in your knowledge, allowing you to focus your efforts effectively.
- Simulate Real Conditions: Take practice tests under conditions that mirror the actual situation. Set a time limit and avoid distractions to get an accurate assessment of your readiness.
- Focus on Specific Areas: Use practice tests to target weak areas. If you struggle with particular topics, take multiple tests that emphasize those subjects to reinforce your understanding and boost confidence.
Review and Learn from Mistakes
- Analyze Your Results: After completing a practice test, carefully review your answers. Pay close attention to incorrect responses and understand why you made those mistakes. This reflection will help you avoid similar errors in the future.
- Identify Patterns: Look for recurring patterns in your mistakes. Are there certain topics you consistently struggle with? Focus more time on those areas to improve your overall performance.
- Track Your Progress: As you continue to take practice tests, track your scores and improvement over time. This can help you measure your readiness and motivate you to keep pushing forward.
Final Preparation Phase
- Use Practice Tests as a Confidence Builder: In the final phase of preparation, use practice tests to build your confidence. The more tests you complete successfully, the more assured you’ll feel when facing the real assessment.
- Review Key Concepts: After finishing several practice tests, go back to your study materials and review key concepts, especially those that appear frequently in the tests. This final review can help solidify your knowledge and ensure you’re fully prepared.
By incorporating practice tests into your study plan with these strategies, you can increase your preparedness, reduce anxiety, and improve your performance when it matters most.