California Food Handlers Answers and Guidelines

Ensuring safety and health standards in the service industry is crucial for both staff and customers. Understanding the proper regulations and protocols is key to maintaining a hygienic and efficient environment. Employees involved in food preparation, handling, and distribution must be well-versed in the requirements to prevent risks and maintain a high level of sanitation.
Training and certification are vital components in ensuring compliance with local laws. These programs equip workers with the necessary skills to manage their responsibilities effectively while adhering to strict health guidelines. Having knowledgeable staff leads to a safer and more reliable service, reducing the likelihood of contamination or violations.
In this guide, we explore essential topics and offer practical advice on how workers and employers can navigate the complexities of health regulations. From understanding the basic rules to avoiding common mistakes, this information will help build a solid foundation for achieving the highest standards in safety practices.
California Food Handlers Answers
In any industry that involves direct interaction with consumables, understanding and complying with hygiene standards is paramount. It’s essential to know the key principles that guide sanitation and ensure the safety of those consuming the products. This section addresses common queries regarding regulations, certifications, and best practices to promote a clean and safe environment for all.
The following are frequently asked questions that shed light on critical aspects of working in this sector:
- What are the basic requirements for certification? Certification involves completing an accredited training course, followed by passing a test that confirms your understanding of hygiene protocols and safety standards.
- How long is the certification valid? The validity of your certification typically ranges from one to three years, after which recertification is required to stay current with updated laws and practices.
- Are there different requirements for different job roles? Yes, depending on whether you’re handling ingredients, managing food preparation areas, or interacting with customers, the regulations and necessary training can vary.
- What should I do in case of contamination? Immediate action is required to contain the situation. Contaminated items must be disposed of, and affected areas should be thoroughly sanitized to prevent further risks.
- Can I complete the training online? Many accredited programs offer online courses that allow flexibility while ensuring that participants gain the required knowledge to meet industry standards.
These answers provide a starting point for anyone involved in preparing, serving, or handling consumables. Adhering to these standards not only ensures compliance but also safeguards public health by reducing risks associated with contamination and poor hygiene practices.
Requirements for Food Handler Certification
To work in environments where consumables are handled or prepared, individuals must meet specific certification requirements. These qualifications ensure that workers have the necessary knowledge and skills to maintain a hygienic and safe atmosphere. The certification process typically includes training on key health regulations, sanitation practices, and food safety protocols.
General Certification Criteria
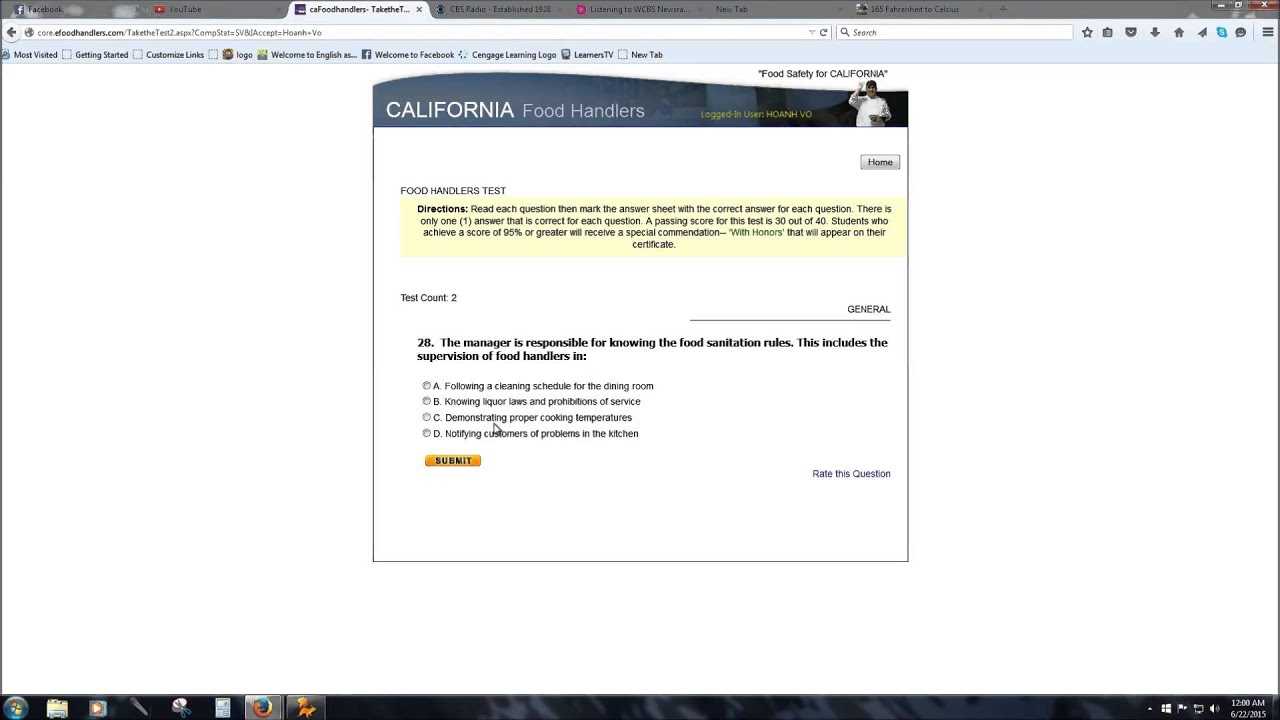
The requirements for obtaining certification vary slightly depending on the region, but generally, the following steps must be completed:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Training | Completion of an accredited program covering basic safety, hygiene, and health protocols in a food service or production setting. |
| Exam | Passing a written test to demonstrate knowledge of health standards, contamination prevention, and proper handling techniques. |
| Application | Submitting an application along with any necessary documents or proof of training for official certification. |
| Fees | Paying any applicable fees for certification and recertification as required by the regulatory authority. |
Additional Considerations
Beyond completing the required training and passing the exam, workers must also adhere to ongoing health guidelines. Regular updates and refresher courses may be necessary to ensure compliance with evolving health standards. It’s also important to note that some areas may have additional regulations based on the nature of the establishment or the type of products being handled.
Common Questions About Food Safety
Ensuring proper hygiene and safety in environments where consumables are handled is crucial to preventing contamination and protecting public health. Many workers and employers have questions regarding the best practices for maintaining a safe and clean environment. In this section, we address some of the most frequently asked questions to help clarify common concerns.
How do I prevent cross-contamination? Cross-contamination can be avoided by keeping raw ingredients separate from ready-to-eat products, using separate utensils, and properly cleaning surfaces and equipment after each use.
What are the correct storage temperatures? Different items require different temperatures to prevent bacterial growth. Generally, perishable goods should be stored at or below 40°F (4°C), while hot items should be kept at temperatures above 140°F (60°C).
How often should I wash my hands? Hands should be washed before and after handling any consumables, after using the restroom, and after touching potentially contaminated surfaces. Use soap and warm water for at least 20 seconds.
When should gloves be worn? Gloves should be worn when handling ready-to-eat items, working with raw ingredients, or touching items that will be served directly to consumers. Gloves should be changed regularly, especially when switching tasks.
What should I do if an item becomes contaminated? Contaminated items should be immediately discarded to prevent any risk of illness. Surfaces and tools that came into contact with the contaminated item must be thoroughly cleaned and sanitized.
How to Get a Food Handler Card
Obtaining certification for working in environments where consumables are handled is a crucial step for ensuring safety and hygiene standards are met. The process of acquiring a certification typically involves completing a training program followed by a test to assess knowledge of key practices. This section outlines the steps involved in obtaining the necessary certification.
Steps to Obtain Certification
While the exact process may vary depending on location, there are common steps that individuals must follow to receive certification. Below is a general overview of the typical process:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Choose an Accredited Program | Find a program recognized by local authorities. Many options are available online or through in-person classes. |
| 2. Complete Training | Undergo training that covers the necessary topics, such as sanitation procedures, contamination prevention, and proper storage methods. |
| 3. Pass the Exam | Take and pass an exam that tests knowledge of the materials covered during training. This is typically a multiple-choice test. |
| 4. Submit Application | Submit your application along with proof of training completion and exam results to the relevant regulatory authority. |
| 5. Receive Certification | Once approved, you will receive your certification card, which is valid for a specified period before renewal is required. |
Renewal and Maintenance

Certification typically expires after a few years, depending on local regulations. To maintain your credentials, you may need to take a refresher course and pass a new exam. Be sure to check local requirements to ensure timely renewal and avoid any lapses in certification.
Understanding Health Codes
Health regulations are put in place to ensure the safety and well-being of consumers and workers in establishments where consumables are prepared, stored, and served. These codes outline the requirements for proper sanitation, hygiene practices, and safety protocols that must be followed to prevent contamination and illness. Understanding these codes is essential for anyone working in these environments to maintain a clean and safe atmosphere.
The health codes address a wide range of practices, including proper handling of ingredients, equipment sanitation, employee hygiene, and the safe storage of items. Below are some key areas covered by health regulations:
- Sanitation Standards: Guidelines for cleaning and disinfecting surfaces, utensils, and equipment to prevent the spread of harmful bacteria.
- Temperature Control: Rules for storing perishable goods at the proper temperatures to prevent spoilage and contamination.
- Employee Hygiene: Requirements for workers to maintain personal cleanliness, including hand washing and wearing appropriate clothing and gloves.
- Food Storage: Specifications for the safe storage of raw and cooked items, ensuring they are kept separate to avoid cross-contamination.
- Waste Management: Proper disposal of waste materials to maintain cleanliness and avoid attracting pests.
By following these regulations, businesses can not only comply with legal standards but also ensure the health and safety of their customers and employees. Regular inspections are conducted to verify compliance, and violations can result in penalties or suspension of operations.
Food Safety Practices for Restaurants
Maintaining a high standard of cleanliness and safety is critical in any dining establishment. Proper sanitation practices, along with effective prevention measures, help ensure that customers enjoy safe meals while reducing the risk of contamination. These practices are essential for maintaining both the reputation of the restaurant and the health of its patrons.
Restaurants should implement rigorous safety protocols at every stage of preparation and service. Below are key areas of focus for ensuring a safe dining environment:
- Cross-Contamination Prevention: Separate raw and cooked items, and use distinct cutting boards, utensils, and storage containers to prevent harmful bacteria from spreading.
- Proper Handwashing: Employees must wash their hands frequently, especially after handling raw ingredients, using the restroom, or touching shared surfaces.
- Temperature Control: Ensure that perishable items are stored at the correct temperature, and that hot dishes are served at safe, high temperatures while cold items remain chilled.
- Sanitizing Surfaces: All food preparation surfaces, equipment, and utensils should be sanitized regularly to eliminate germs and bacteria that may cause illness.
- Regular Employee Training: All staff members should be trained on best practices for hygiene, safety protocols, and emergency procedures to keep operations running smoothly.
By strictly following these practices, restaurants can significantly reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses and provide a safe dining experience for all customers.
Handling Allergens in Food Service
Managing allergens effectively is a critical component of providing safe and enjoyable dining experiences. As allergies to specific ingredients can be severe, it is essential for food service establishments to have procedures in place that minimize the risk of cross-contamination and ensure that customers are informed about potential allergens in their meals.
Identifying Common Allergens
Common allergens include ingredients such as dairy, nuts, gluten, soy, eggs, shellfish, and certain fruits. It is vital for restaurant staff to be able to identify which allergens are present in menu items and communicate this clearly to customers. Establishments should also keep an up-to-date list of ingredients for all dishes to help quickly identify potential allergens.
Preventing Cross-Contamination

To prevent cross-contamination, it’s essential to implement strict guidelines for food preparation and storage. Here are some key practices:
- Separate Storage: Store allergenic ingredients separately from others, ideally in clearly marked containers to prevent accidental mixing.
- Dedicated Equipment: Use separate utensils, cutting boards, and cooking tools when preparing allergenic items.
- Cleaning Procedures: Ensure thorough cleaning of surfaces, equipment, and utensils between uses to remove any traces of allergens.
By adopting these practices and educating staff on the importance of allergen management, restaurants can reduce the risk of allergic reactions and create a safer environment for all patrons.
Role of a Food Handler in California
Individuals working in environments where consumables are prepared and served play a vital role in ensuring safety, hygiene, and quality. Their primary responsibility is to follow proper procedures to prevent contamination, maintain cleanliness, and ensure that all meals served are safe for consumption. This role involves a mix of knowledge, skill, and attention to detail to meet the regulatory requirements set by local health authorities.
Key Responsibilities:
- Maintaining Personal Hygiene: Workers must keep themselves clean, wash hands regularly, and wear proper clothing, such as gloves and hairnets, to avoid contamination.
- Sanitizing Equipment: Ensuring that all utensils, surfaces, and cooking equipment are properly sanitized to eliminate harmful bacteria.
- Proper Storage and Handling: Ensuring that all ingredients are stored at correct temperatures and handled in ways that minimize the risk of spoilage or contamination.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Keeping track of the conditions and safety protocols in the workplace, reporting any issues to management for resolution.
By fulfilling these responsibilities, individuals help create a safer environment for both staff and customers, reducing the risk of illness and ensuring that all operations comply with health regulations.
How Often Should Certifications Be Renewed
Certifications for working in environments where consumables are prepared and served are not permanent and need to be renewed periodically. Regular renewal ensures that individuals remain up to date with the latest safety standards, protocols, and regulations. The renewal frequency can vary based on local requirements and the type of certification obtained, but maintaining current certification is essential for continued compliance and safety.
Here are the general guidelines regarding the renewal of certifications:
- Typical Renewal Period: Most certifications require renewal every 2 to 5 years, depending on local laws and the specific certification program.
- Mandatory Refresher Courses: In many cases, individuals must complete a refresher course before renewing their certification to stay informed on new practices or changes in health regulations.
- Continuing Education: Some jurisdictions may require ongoing education or workshops to stay updated on industry standards, even if the certification itself does not need to be renewed immediately.
- Renewal Fees: There may be a fee involved in the renewal process, which varies by location and certification provider.
It’s important to keep track of the expiration date and start the renewal process well in advance to avoid any lapses in certification that could affect employment or operations.
Food Safety Training for Employees
Training staff on safety practices is essential for preventing health risks and maintaining a hygienic environment in establishments where consumables are prepared and served. Educating employees on the proper handling, storage, and sanitation techniques ensures that they understand their responsibilities in protecting both themselves and customers from foodborne illnesses and contamination.
Effective training programs cover a variety of key areas, such as:
- Personal Hygiene Practices: Emphasizing the importance of handwashing, wearing appropriate attire, and maintaining personal cleanliness to prevent contamination.
- Cross-Contamination Prevention: Teaching employees how to avoid mixing raw and cooked ingredients, and how to use separate equipment for different food types.
- Temperature Control: Educating staff on the correct temperatures for storing and serving perishable items to prevent spoilage and bacterial growth.
- Safe Food Preparation: Providing guidance on how to safely prepare and handle ingredients to minimize the risk of contamination during cooking or serving.
Regularly updating training materials and holding refresher courses helps ensure that all employees are well-prepared to handle their duties safely and efficiently, creating a safer environment for everyone involved.
Common Violations and How to Avoid Them
In any establishment where consumables are prepared and served, certain violations can undermine safety standards and pose significant risks to public health. These mistakes often arise from lack of training, negligence, or misunderstanding of best practices. However, by understanding the most common violations and adopting proactive strategies, businesses can ensure a safer environment and avoid costly fines or reputational damage.
Improper Temperature Control
One of the most frequent violations occurs when perishable items are not stored or served at the correct temperature. Failing to keep items either too hot or too cold can promote the growth of harmful bacteria, leading to potential contamination.
- How to Avoid: Regularly check the temperature of refrigerators, freezers, and hot holding units. Use calibrated thermometers to ensure that food stays within the recommended temperature ranges.
- Best Practices: Maintain proper temperature logs and train staff to quickly identify and address temperature issues.
Improper Handling and Cross-Contamination
Improper handling of raw and cooked items can lead to cross-contamination, which is a major contributor to foodborne illnesses. This can occur when utensils, surfaces, or hands are not adequately cleaned between handling different ingredients.
- How to Avoid: Establish clear guidelines for using separate utensils and cutting boards for raw and cooked foods. Ensure employees are trained in proper handwashing techniques.
- Best Practices: Use color-coded tools for different types of food and regularly sanitize surfaces to minimize the risk of contamination.
By staying vigilant and adhering to safety protocols, businesses can prevent these common violations and foster a safe dining environment for all customers.
Steps to Prevent Cross-Contamination

Preventing cross-contamination is critical in maintaining a safe and hygienic environment in any establishment where consumables are prepared and served. This process involves keeping harmful microorganisms from transferring from one surface or food item to another, which can lead to foodborne illnesses. Proper practices and vigilance are necessary to minimize this risk and ensure the safety of customers.
Here are key steps to effectively prevent cross-contamination:
- Use Separate Equipment: Always designate specific cutting boards, knives, and utensils for raw and cooked items. This helps avoid the transfer of harmful bacteria between different types of ingredients.
- Regular Handwashing: Ensure that all workers wash their hands thoroughly before and after handling different types of food, especially when switching from raw to ready-to-eat items.
- Proper Storage: Store raw ingredients, especially meats, in separate containers or on lower shelves to prevent any drips or contact with other food items.
- Clean and Sanitize Surfaces: Regularly sanitize countertops, prep tables, and other surfaces that come in contact with raw ingredients. Use appropriate cleaners to kill bacteria and other pathogens.
- Training and Awareness: Educate staff about the importance of cross-contamination prevention, ensuring they understand the steps to take and the risks involved.
By following these steps and ensuring everyone in the workplace is properly trained, cross-contamination risks can be significantly reduced, ensuring a safe environment for both staff and customers.
Importance of Personal Hygiene in Food Handling

Personal hygiene plays a crucial role in preventing contamination and ensuring the safety of items prepared for consumption. When individuals working in environments where ingredients are handled maintain cleanliness, it significantly reduces the risk of harmful pathogens being introduced into the preparation process. Proper hygiene is essential not only for the health of those consuming the items but also for the well-being of the staff involved in the production process.
Key Hygiene Practices
To prevent contamination and maintain a safe environment, employees must adopt several essential hygiene practices:
- Frequent Handwashing: Hands should be washed thoroughly with soap and warm water before handling any ingredients, after using the restroom, or after touching non-food surfaces like phones or cleaning equipment.
- Proper Attire: Wearing clean uniforms, hairnets, and gloves (when necessary) helps minimize the risk of contamination. Long hair should always be tied back, and jewelry should be avoided to ensure it does not come into contact with food.
- Covering Coughs and Sneezes: Ensuring that employees cover their mouths and noses when coughing or sneezing prevents droplets from contaminating surfaces or products.
Why Hygiene Matters
Good hygiene practices are not just a matter of personal responsibility but also legal and ethical obligations for those working in the preparation of consumables. By minimizing the risk of contamination, staff contribute directly to the overall health and safety of consumers. Maintaining high hygiene standards helps establish trust and ensures compliance with health regulations.
California’s Food Safety Regulations Explained
In order to protect public health and ensure the safety of consumables prepared for consumption, strict guidelines are established for establishments that deal with ingredients and prepared items. These regulations are designed to prevent contamination, ensure proper handling, and enforce cleanliness standards in all aspects of production, from storage to serving. Understanding these rules is crucial for anyone working in such environments, as they are directly responsible for maintaining a safe environment for both employees and customers.
Key Elements of Food Safety Regulations
The regulations surrounding hygiene, temperature control, and safe ingredient handling are critical components in preventing illness caused by pathogens. Below are some of the key regulations:
- Temperature Control: Ensuring that perishables are stored at the right temperature to prevent the growth of harmful bacteria. Both hot and cold items should be kept within the required ranges to reduce the risk of contamination.
- Cross-Contamination Prevention: Regulations require the use of separate equipment for raw and cooked items. This minimizes the risk of harmful microorganisms being transferred from one product to another.
- Hygiene Standards: Employees are mandated to wash their hands regularly and wear appropriate attire, including gloves and hair coverings, to reduce the chances of contaminating prepared items.
Compliance and Enforcement
Compliance with these regulations is essential for avoiding penalties and ensuring the safety of consumers. Regular inspections by health authorities are conducted to verify adherence to the set guidelines. Establishments found in violation may face fines or, in severe cases, closure until conditions are corrected. Following these regulations not only ensures public safety but also helps build consumer trust in the services provided.
Safe Food Temperatures for Handling
Maintaining proper temperature controls is one of the most critical aspects of safe ingredient management in any environment. Incorrect temperatures can encourage the growth of harmful microorganisms, leading to potential health risks. Establishing and following temperature guidelines ensures that prepared items are kept at safe levels throughout the handling process, from storage to cooking to serving.
Temperature Ranges for Safe Handling
Different types of items require specific temperature ranges to prevent bacterial growth. Below is a general guideline for safe temperature handling:
| Temperature Range | Type of Product | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| 40°F (4°C) or lower | Perishable ingredients and prepared items | Store in refrigeration |
| 140°F (60°C) or higher | Hot ready-to-eat items | Maintain at serving temperature |
| 41°F – 135°F (5°C – 57°C) | Danger zone for bacterial growth | Avoid leaving items in this range for extended periods |
| 165°F (74°C) or higher | Cooked meats, poultry, seafood | Ensure internal temperature reaches this level before serving |
Ensuring Consistency in Temperature
To maintain the integrity of temperature-sensitive items, it is crucial to use reliable thermometers and regularly check the temperature of storage units, cooking equipment, and serving areas. Regular monitoring ensures that potential risks are avoided and that all items are handled safely, minimizing the risk of contamination or foodborne illnesses.
Penalties for Violating Food Handling Laws
Ensuring compliance with health and safety regulations is crucial in any establishment. Failing to adhere to the required guidelines can lead to serious consequences. Violations of hygiene standards, improper storage, or negligence in temperature controls can not only endanger public health but also result in significant legal penalties and fines. Understanding the potential repercussions is key to maintaining a safe and compliant operation.
Types of Violations and Their Penalties
Common violations that may lead to penalties include but are not limited to:
- Failure to maintain proper hygiene standards, such as unclean work surfaces and improper hand washing practices.
- Storing perishable goods at incorrect temperatures, which can lead to bacterial contamination.
- Serving undercooked or improperly prepared dishes that could cause foodborne illnesses.
- Failure to label allergens and other critical ingredients correctly, increasing the risk of allergic reactions.
- Not obtaining necessary permits or certifications for operating in a regulated environment.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
The penalties for non-compliance can vary depending on the severity of the violation and local regulations. These consequences may include:
- Imposition of fines, ranging from minor to substantial amounts.
- Temporary suspension or closure of the establishment until violations are corrected.
- Mandatory retraining for staff to ensure proper practices are followed.
- Criminal charges in extreme cases, particularly in instances of negligence or intentional misconduct.
By staying informed about and adhering to the necessary safety protocols, businesses can avoid these penalties and ensure the well-being of their customers, while maintaining a trustworthy reputation in the industry.