Basic Life Support Exam A 2016 Answer Key

When it comes to handling critical situations, knowing the correct methods to intervene can make all the difference. Effective training ensures that individuals are prepared to respond promptly and appropriately to medical emergencies, saving lives in moments of crisis. This section provides insights into key procedures and strategies necessary for handling such situations efficiently.
Preparedness is crucial for anyone involved in healthcare, whether in a professional setting or as a bystander. The ability to assess a scenario, make informed decisions, and take action quickly is vital. This guide offers a clear understanding of the concepts and techniques that are fundamental to passing any certification related to emergency interventions.
As you go through the following content, you’ll find important details that will help clarify common questions and address areas where many individuals might struggle. Understanding the procedures, practicing the necessary steps, and becoming familiar with the right answers to key questions will enhance your readiness when faced with urgent situations.
Basic Life Support Exam A Overview
In emergency situations, knowing the right procedures and being able to act quickly can be the difference between life and death. This section provides a broad look at the essential concepts that are tested in emergency response training programs. It focuses on assessing one’s knowledge of critical interventions in cases such as cardiac arrest, choking, and respiratory failure, ensuring that responders are ready to handle any emergency efficiently.
Key Skills Tested in the Assessment
The evaluation process examines a range of practical skills and theoretical knowledge. It covers vital techniques like performing chest compressions, operating an automated external defibrillator (AED), and providing rescue breaths. Responders are tested on their ability to recognize symptoms, initiate the correct actions, and maintain a calm, effective approach under pressure. The goal is to ensure that individuals can confidently provide assistance until professional help arrives.
What to Expect During the Evaluation
Candidates will encounter multiple-choice questions designed to assess their understanding of emergency procedures. These questions simulate real-life scenarios, testing both theoretical knowledge and the ability to apply skills in a variety of critical situations. The format allows for a comprehensive evaluation of the responder’s ability to act appropriately in different emergency contexts, ensuring they are prepared for any unexpected challenge.
Importance of BLS Certification
Obtaining certification in emergency response techniques is crucial for anyone who might be called upon to assist in critical situations. This training ensures individuals are equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to respond effectively in the event of a medical emergency. With the proper certification, individuals not only gain confidence but also play a vital role in saving lives during moments of crisis.
Enhancing Preparedness for Emergencies
Having formal certification ensures that individuals are ready to take quick and effective action when faced with urgent medical conditions such as cardiac arrest or severe choking. By mastering key skills like performing chest compressions or using an automated external defibrillator (AED), certified responders can stabilize individuals until professional help arrives. This level of preparedness can significantly improve survival outcomes in critical situations.
Building Confidence and Trust
Certification in emergency procedures also fosters a sense of confidence, both for the responder and those around them. When someone is trained and certified, it instills trust in their abilities, allowing others to rely on them during emergencies. This can be especially important in public spaces, workplaces, or in healthcare settings, where knowing that help is available can make all the difference.
Understanding the BLS Exam Structure
The process of assessing emergency response abilities is designed to test an individual’s knowledge and practical skills in handling life-threatening situations. This section breaks down the components of the assessment, explaining how the test is organized to evaluate both theoretical understanding and hands-on proficiency. The structure of the assessment ensures that candidates are thoroughly prepared to act confidently in high-pressure environments.
Types of Questions and Assessments
The evaluation typically includes a combination of multiple-choice questions and practical scenarios. Multiple-choice questions are designed to test theoretical knowledge, such as understanding the correct steps to take in various emergency situations. Practical assessments focus on evaluating hands-on skills, such as performing CPR, using defibrillators, and assessing a patient’s condition accurately.
Scoring and Requirements
In many cases, candidates are required to score a minimum percentage to pass the assessment, demonstrating their ability to respond effectively in an emergency. The practical portion usually involves a direct evaluation of actions taken in simulated scenarios, where candidates must follow proper protocols. Achieving a passing score ensures that the individual is ready to perform critical interventions when needed.
Key Concepts in Emergency Response

In critical situations, understanding the essential techniques for providing immediate care can significantly improve the chances of survival. The most fundamental concepts involve recognizing signs of distress, performing vital interventions such as chest compressions, and using equipment like defibrillators. This section highlights the core principles that every responder should master to act swiftly and effectively when confronted with medical emergencies.
Essential Procedures and Interventions
The following table outlines some of the core procedures and interventions that are vital in emergency situations:
| Procedure | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| Chest Compressions | Performing compressions to maintain circulation in a patient with no pulse | When the patient is unresponsive and not breathing |
| Rescue Breathing | Providing breaths to assist in oxygenating the patient | When the patient is not breathing but has a pulse |
| Automated External Defibrillator (AED) | Using an AED to restore a normal rhythm to the heart | In cases of sudden cardiac arrest |
| Choking Relief | Using the Heimlich maneuver or back blows to clear an airway obstruction | When a person is choking and cannot breathe or speak |
Developing Competency in Critical Skills
Mastering these concepts requires practice and familiarity with the protocols. Responders must be able to perform each technique effectively under pressure, ensuring the best possible outcomes. Continuous training and certification renewals ensure that individuals remain prepared for any emergency scenario, reinforcing their ability to provide timely and life-saving care.
CPR Techniques for Adult Patients

When an adult suffers from a sudden cardiac arrest, immediate action is critical. The goal of performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is to restore circulation and oxygenation to vital organs until professional medical help arrives. Understanding the proper techniques for administering chest compressions and rescue breaths can significantly increase the chances of survival. This section outlines the steps involved in performing CPR on adult patients, focusing on effective and efficient methods.
The most important aspect of CPR is delivering chest compressions at the right depth and rate. For adults, compressions should be firm and at least two inches deep, with a rhythm of 100 to 120 compressions per minute. The hands should be placed on the center of the chest, just below the sternum, while keeping the arms straight to use the body’s weight effectively. Properly timed compressions maintain blood flow to the brain and other vital organs until more advanced care can take over.
Along with compressions, providing rescue breaths is necessary to deliver oxygen to the patient’s lungs. After every 30 compressions, two breaths should be given. It’s important to ensure that the patient’s airway is open by tilting their head back and lifting the chin. The breaths should be slow and steady, ensuring the chest rises with each breath, indicating that the air is reaching the lungs.
CPR should be continued until either the patient shows signs of recovery, such as breathing or movement, or until emergency medical personnel arrive. If an automated external defibrillator (AED) is available, it should be used as soon as possible to assess the heart rhythm and administer a shock if necessary. CPR and AED use together provide the best chance of survival for adults experiencing sudden cardiac events.
Child and Infant CPR Guidelines
In cases of cardiac or respiratory emergencies, performing resuscitation on children and infants requires specific techniques tailored to their smaller, more delicate bodies. Unlike adults, children and infants require less force and a more gentle approach to ensure safety while maintaining effectiveness. This section outlines the proper steps and considerations when performing resuscitation on younger patients.
CPR for Children (1 Year to Puberty)
When providing resuscitation to a child, the technique is similar to that used for adults but with modifications to suit their size. The following steps should be followed:
- Chest Compressions: Use one or two hands, depending on the child’s size. Compress the chest at least 2 inches deep at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute.
- Rescue Breaths: Give two breaths after every 30 compressions. Ensure that the child’s airway is open by tilting the head back and lifting the chin. Each breath should be given slowly, enough to make the chest rise.
- Duration: Continue the process until the child shows signs of life, or emergency help arrives.
CPR for Infants (Under 1 Year Old)
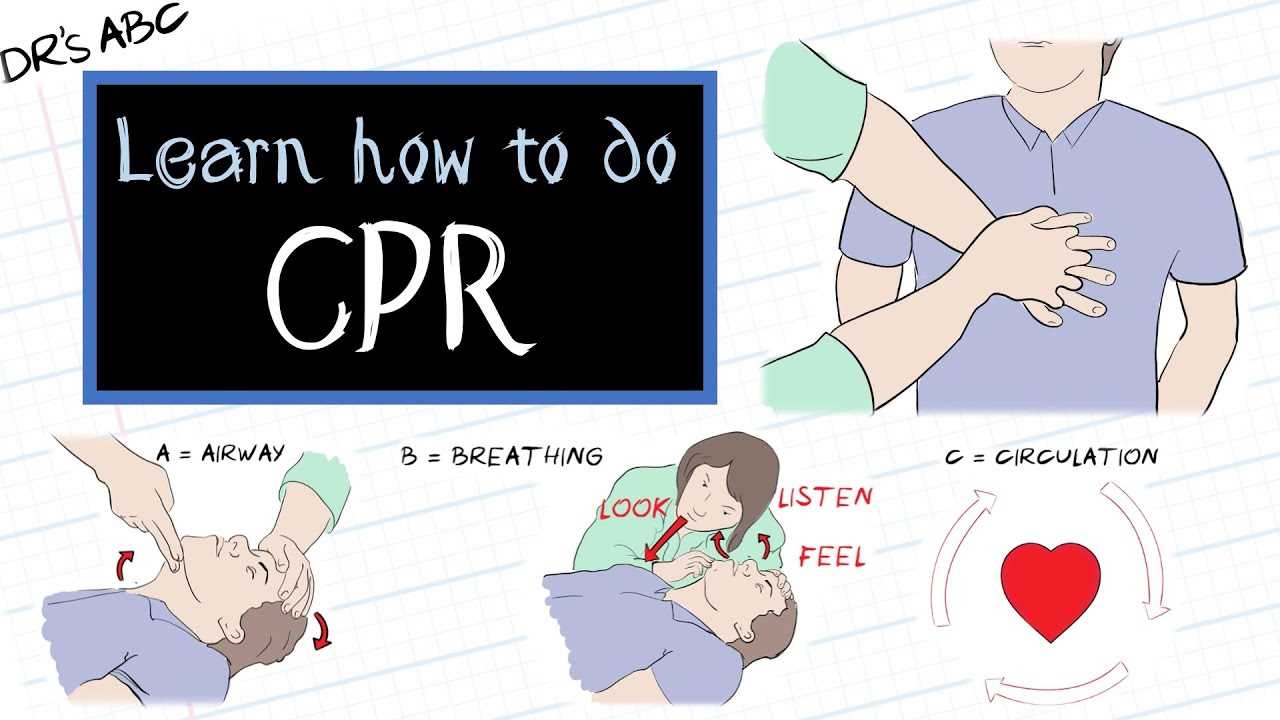
Infants require a more delicate approach due to their smaller size and fragile chest. The following steps are essential for performing CPR on an infant:
- Chest Compressions: Use two fingers placed just below the nipple line to compress the chest about 1.5 inches deep. Perform compressions at a rate of 100-120 per minute.
- Rescue Breaths: Place your mouth over the infant’s nose and mouth to give two gentle breaths. Ensure that the chest rises with each breath. The breaths should be slower and more controlled to avoid over-inflating the lungs.
- Duration: Continue CPR until the infant starts breathing, or emergency responders arrive.
It is crucial to remember that the effectiveness of CPR depends on quick and correct action. In both children and infants, it’s vital to minimize interruptions in chest compressions and to maintain a rhythm that maximizes blood circulation to vital organs.
Common Questions on the BLS Exam
Many individuals preparing for the certification process often have questions about what to expect and how to best approach the test. This section addresses some of the most frequently asked questions to help candidates better understand the process and ensure they are well-prepared for the assessment. From the structure of the test to the most common challenges, knowing what to expect can make a big difference in your preparation and confidence level.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What topics are covered on the assessment?
The assessment typically focuses on key emergency response skills, including CPR techniques for adults, children, and infants, as well as the use of defibrillators and airway management. Additionally, candidates may be tested on how to respond to choking and other life-threatening situations. - How long does the assessment take?
The length of the test varies depending on the specific course or certification program, but most tests take between 30 minutes and 1 hour to complete. The practical portion, where you demonstrate your skills, may take additional time. - What is the passing score?
Typically, candidates must achieve a passing score of around 80% or higher to receive certification. The exact score required may vary depending on the certifying organization, so it is important to review the guidelines beforehand. - Is there a time limit for each section?
While there may be time limits for answering multiple-choice questions, the practical skills section is usually performed at your own pace, though you should aim to demonstrate proficiency in a timely manner. - Do I need to retake the test periodically?
Yes, certification is usually valid for 2 years. After this period, you will need to renew your certification by retaking the assessment or completing a refresher course. - Can I take the test online?
Some programs offer online or blended learning options that allow you to complete the written portion of the test remotely. However, the practical skills section must typically be completed in person with an instructor present.
Being well-informed about these common questions can help you feel more prepared and confident going into the certification process. Understanding the structure and requirements of the assessment ensures you can focus on mastering the essential skills needed for effective emergency response.
Answering Multiple-Choice Questions Effectively
Multiple-choice questions are a common format in many certification assessments. These questions test your understanding of key concepts by offering several possible answers, from which you must select the correct one. To perform well on these types of questions, it’s important to approach them strategically. This section offers tips and techniques to help you answer multiple-choice questions accurately and efficiently.
Strategies for Success
Effective strategies can improve your performance on multiple-choice tests. Here are some key tips to consider:
- Read Each Question Carefully: Before choosing an answer, make sure you fully understand what the question is asking. Look for keywords that specify what is being tested.
- Eliminate Incorrect Answers: Often, you can rule out one or more incorrect options immediately. This narrows down your choices and increases your chances of selecting the correct answer.
- Look for Clues in the Question: Sometimes, the wording of the question or the other answer options can provide clues to the correct choice. Pay attention to subtle hints or phrases that might indicate the right response.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While multiple-choice questions can be straightforward, there are some common mistakes you should try to avoid:
- Don’t Rush: Take your time to think through each question. Rushing can lead to careless mistakes.
- Avoid Overthinking: Trust your initial instincts unless you have a strong reason to change your answer. Overthinking can cause confusion and increase the likelihood of selecting an incorrect option.
- Read All Answer Choices: Even if you think you know the answer right away, always read all options before making your final choice. Sometimes the correct answer is hidden among seemingly similar options.
By employing these strategies and avoiding common mistakes, you can improve your chances of selecting the correct answers and increase your overall score. Taking a careful, methodical approach to answering multiple-choice questions is key to performing well in any assessment.
Handling Difficult BLS Scenarios
In real-life emergencies, you may encounter situations that challenge your ability to respond effectively. These scenarios can range from unpredictable patient conditions to limited resources, making it crucial to remain calm and use your training to adapt quickly. This section provides guidance on how to handle the most difficult situations you may face when providing emergency care, ensuring you can perform efficiently even under pressure.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Emergency situations often come with unexpected obstacles. Here are some common challenges and strategies for overcoming them:
- Unresponsive Victims with No Bystanders: In cases where you are alone and unable to call for help, immediately begin CPR. If the victim is an adult, start chest compressions and continue until help arrives or the victim shows signs of life. If you are alone with an infant or child, perform CPR for about 2 minutes before calling emergency services.
- Multiple Casualties: When confronted with multiple patients, prioritize care based on the severity of their condition. Use the triage approach to identify those who need immediate attention and those who can wait for help.
- Lack of Equipment: In some situations, necessary tools like a defibrillator or airway management devices may be unavailable. In these cases, continue to provide the best care possible with what you have, such as performing high-quality chest compressions and rescue breaths until advanced help arrives.
- Physical or Emotional Stress: High-pressure scenarios can cause stress, but it’s important to stay focused. Take a deep breath, follow your training, and break down tasks into manageable steps. Stay calm and methodical, ensuring that your actions are deliberate and effective.
Key Considerations for High-Stress Situations

While dealing with challenging situations, consider these essential points to enhance your performance:
- Stay Calm: In stressful situations, maintaining composure is critical. Panicking can impair your judgment and response time, so focus on staying calm and thinking clearly.
- Adapt to the Situation: Every emergency is different. While your training provides a foundation, you may need to adapt based on the unique circumstances you are facing.
- Use Teamwork: If you are working with others, communicate clearly and delegate tasks to maximize efficiency. If possible, work as a team to provide care until professional responders arrive.
Handling difficult scenarios in emergency situations requires a balance of knowledge, calmness, and adaptability. By preparing for a variety of challenges, you’ll be better equipped to deliver effective care no matter the circumstances.
Step-by-Step Guide to BLS Procedures
Knowing how to respond quickly and effectively in emergencies can make all the difference when it comes to saving lives. The following guide outlines the key steps you need to take when providing emergency care to an individual who is unresponsive or not breathing. These steps are designed to help you deliver the appropriate care while maintaining calm and efficiency, ensuring the best possible outcome.
Initial Assessment
When you first encounter a person in need, it’s important to assess their condition before taking action. Follow these steps:
- Check Responsiveness: Gently tap or shake the person to see if they respond. If they don’t respond, move on to the next step.
- Call for Help: If the person is unresponsive, immediately call emergency services. If possible, ask someone nearby to do this while you begin care.
- Check for Breathing: Look, listen, and feel for breathing. If there is no breathing or irregular breathing, start the next steps.
Chest Compressions and Rescue Breaths
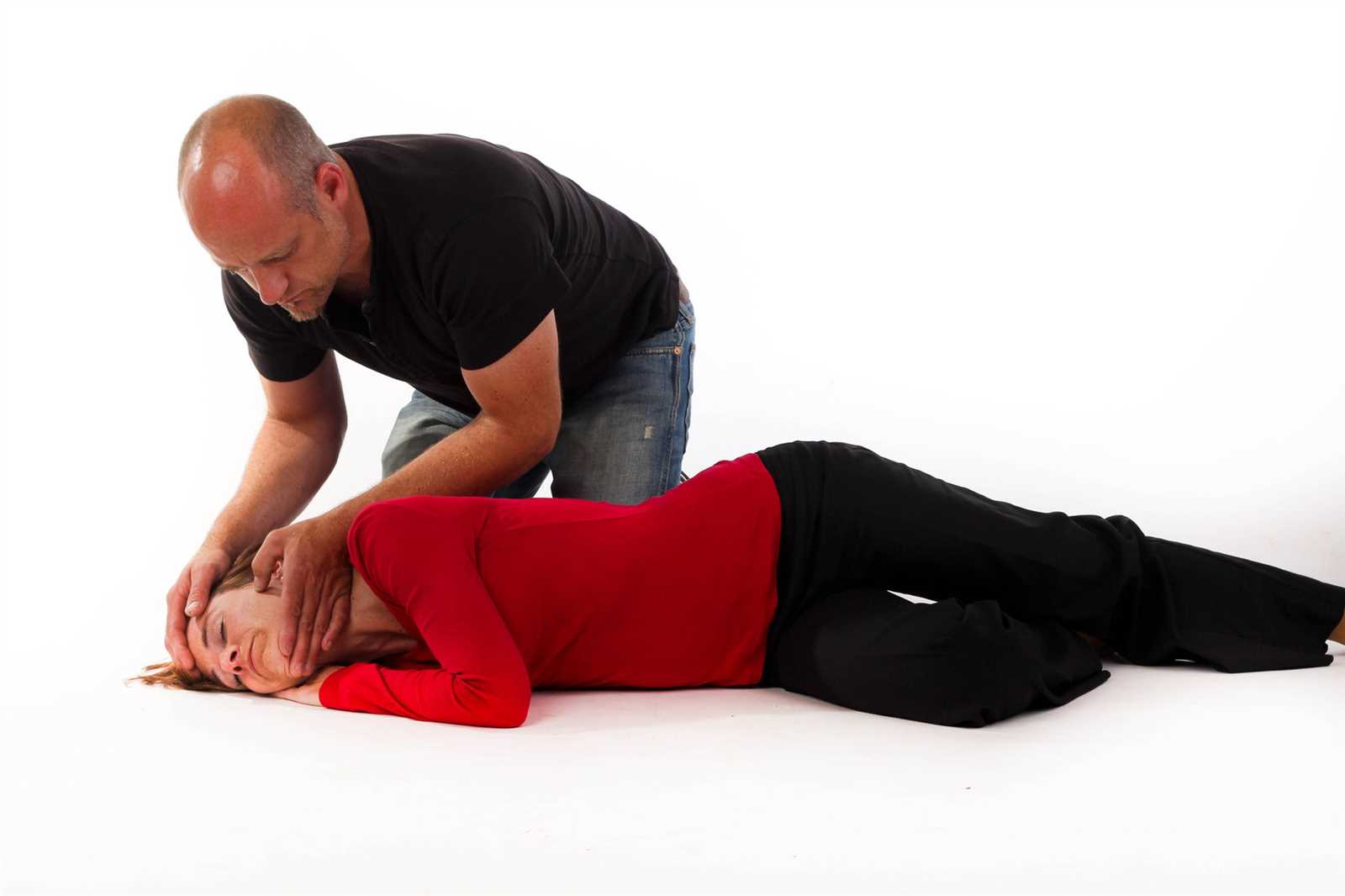
If the person is unresponsive and not breathing, it’s critical to start chest compressions and rescue breaths. Here’s how:
- Position the Person: Place the person on their back on a firm surface. Kneel beside them and ensure their airway is open by tilting the head back slightly and lifting the chin.
- Start Chest Compressions: Place the heel of one hand on the center of the chest, just below the breastbone. Place your other hand on top and interlace your fingers. Use your body weight to press down hard and fast, aiming for a depth of at least 2 inches and a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute.
- Give Rescue Breaths: After 30 chest compressions, give 2 rescue breaths. Pinch the person’s nose shut, create a seal over their mouth with yours, and breathe in until the chest rises. Continue alternating between 30 compressions and 2 breaths until help arrives or the person starts breathing on their own.
Using a Defibrillator
If available, a defibrillator can greatly improve the chances of survival. Here’s how to use one:
- Turn on the Defibrillator: Follow the device’s instructions carefully. The defibrillator will analyze the person’s heart rhythm and recommend whether a shock is needed.
- Apply the Pads: Place the electrode pads on the person’s chest as directed by the device. Make sure the area is clear of any obstructions or clothing.
- Deliver a Shock: If instructed, press the button to deliver a shock. Afterward, immediately resume chest compressions and continue until emergency services take over.
By following these clear and concise steps, you can provide critical care that significantly enhances the chances of survival. Always remember that staying calm and focused is just as important as knowing the right procedures to follow.
Recognizing Cardiac Arrest Symptoms
Identifying the signs of a sudden, life-threatening event is crucial for initiating the proper response. In many emergency situations, time is of the essence, and the ability to recognize these symptoms early can greatly improve the chances of survival. When an individual’s heart stops functioning effectively, it is essential to act swiftly to provide immediate care and seek help.
Signs of Cardiac Arrest
When a person experiences a cardiac arrest, they exhibit several key symptoms that indicate the need for urgent intervention. The most common signs include:
- Unresponsiveness: The individual will not respond to any form of physical stimuli, such as shouting their name or tapping them.
- No Pulse: The person will not have a detectable pulse, and you may feel no blood flow in their arteries.
- Irregular or Absent Breathing: Breathing may stop entirely, or it may become erratic and shallow. Gasping or snoring sounds are also signs that normal breathing is not occurring.
- Loss of Consciousness: The individual will be completely unconscious and unable to react to their environment in any way.
Key Actions When Cardiac Arrest Occurs
Recognizing the symptoms early is the first step, but immediate action is vital. Here’s what to do if you observe these signs:
- Call Emergency Services: Alert emergency medical professionals immediately, as they will provide further assistance and life-saving interventions.
- Begin Chest Compressions: Start performing chest compressions to help circulate blood and oxygen to the brain and vital organs.
- Use a Defibrillator if Available: If you have access to an automated external defibrillator (AED), follow the device’s instructions to administer a shock if needed.
Recognizing cardiac arrest symptoms quickly and taking immediate action can significantly improve outcomes. Every second counts, and prompt intervention can make a life-saving difference.
Using an AED Correctly
When a person experiences a sudden cardiac event, using the right equipment quickly can make all the difference in survival. An Automated External Defibrillator (AED) is a critical tool that helps restore normal heart rhythm during a life-threatening situation. Knowing how to operate this device properly is essential for anyone who might be in a position to help.
It is important to follow the steps in the correct sequence when using an AED. The device is designed to be user-friendly, with prompts that guide you through each phase of the process. The key is to act promptly and confidently, without hesitation, to give the person the best chance of recovery.
Here’s how to use an AED effectively:
- Turn on the AED: Most AEDs have a simple power button. As soon as you turn it on, the device will give audible instructions and guide you through the process.
- Place the Pads: The AED will have electrode pads that need to be placed on the chest of the person. One pad goes on the upper right side of the chest, just below the collarbone, and the other on the lower left side, below the ribcage.
- Follow the Instructions: Once the pads are attached, the AED will analyze the heart’s rhythm. The device will inform you whether a shock is needed. If it prompts, stand clear of the patient and ensure no one is touching them before delivering the shock.
- Resume Chest Compressions: After delivering the shock, continue performing chest compressions until medical help arrives or the person shows signs of life.
Properly using an AED is simple but effective. It’s a life-saving skill that everyone should know, especially those in environments where sudden cardiac arrest is a possibility. The device itself is intuitive, but understanding its function and being prepared to use it at a critical moment can make all the difference.
Exam Strategies for Success
Successfully completing a certification test requires more than just knowledge–it involves strategic preparation and a clear approach during the assessment. Whether you are testing your skills for a professional requirement or personal growth, understanding how to approach the process effectively can significantly improve your performance.
Adopting the right strategies before, during, and after the test is key to achieving a positive outcome. By organizing your preparation and staying focused, you can maximize your chances of success. The following guidelines will help you develop a winning approach to your next assessment.
Effective Study Techniques
Preparation is the foundation of any successful outcome. Start by reviewing all relevant materials, focusing on key topics, and understanding the concepts thoroughly. Use various study tools such as flashcards, practice tests, and summary notes to reinforce your knowledge. Additionally, scheduling regular study sessions can help maintain a steady pace and prevent last-minute cramming.
Time Management During the Test

Once you’re in the test environment, managing your time becomes crucial. Begin by quickly scanning through all the questions and identify those that you feel most confident about. Tackle these first to secure easy points and build momentum. For more challenging questions, don’t spend too much time on them initially–mark them and return later if you have time left. Staying calm and managing your time effectively will reduce anxiety and help you stay on track.
Incorporating these strategies into your preparation will allow you to approach your certification test with confidence. Focus on understanding the material, managing your time well, and maintaining a positive mindset throughout the process.
Time Management During the BLS Test
Efficient time management is essential when taking any test, especially when evaluating critical skills under pressure. Managing your time wisely ensures that you complete all sections of the assessment while avoiding unnecessary stress. By prioritizing tasks and pacing yourself effectively, you can maximize your performance and maintain composure throughout the process.
The key to success lies in balancing thoroughness with speed. Start by allocating enough time for the most important questions and sections, while leaving some buffer for more challenging or detailed tasks. The following strategies will help you optimize your time and ensure you stay on track during the test.
Prioritizing Questions
When faced with a variety of questions, it’s important to prioritize. Begin with those you know best. This allows you to secure points quickly and builds confidence. If you encounter difficult questions, it’s wise to skip them temporarily and return after completing easier ones. Don’t let any single question consume too much of your time.
Monitoring Time Progress
Keeping an eye on the clock helps you stay mindful of your pace. Set mini-goals to track progress throughout the test. For example, aim to finish the first set of questions by a certain time, and adjust your pace if necessary. This ensures that you have sufficient time to review and finalize your responses.
| Task | Estimated Time | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Read through instructions | 5 minutes | Make sure to understand the guidelines |
| Answer easy questions | 15-20 minutes | Quickly secure easy points |
| Answer difficult questions | 20-25 minutes | Return to these after easier questions |
| Review answers | 5-10 minutes | Double-check responses for accuracy |
By planning your approach and staying aware of time limits, you can navigate the test with confidence. The goal is not only to complete the test but to do so in a way that reflects your best performance under the time constraints.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When assessing critical skills in emergency situations, it’s important to approach the process with accuracy and focus. However, many individuals make avoidable mistakes that can impact their performance or understanding. These errors are often a result of misjudgment, misunderstanding, or inadequate preparation. Being aware of these common pitfalls can help you navigate the process more effectively and achieve better outcomes.
The following list highlights some of the most frequent mistakes that individuals make during the assessment. By recognizing and addressing these issues, you can ensure that your responses are both accurate and confident. Avoiding these errors will allow you to demonstrate your knowledge and preparedness effectively.
1. Skipping Key Steps
In high-pressure situations, it’s easy to overlook essential procedures or steps. Rushing through tasks may cause you to miss important elements that are critical for success. Take the time to follow each step carefully, even if it seems obvious or redundant. Skipping any critical steps can lead to poor performance or incomplete answers.
2. Overthinking or Second-Guessing
Overthinking answers or second-guessing yourself can waste valuable time and reduce confidence. Trust your initial judgment based on your preparation and experience. Avoid getting caught up in unnecessary details or complexities that may distract you from the correct response. Confidence in your knowledge is key to managing the task efficiently.
3. Not Reading Instructions Thoroughly
Failing to read the instructions thoroughly before beginning can lead to misunderstandings or mistakes in how you approach certain tasks. Ensure that you fully understand what is being asked of you before proceeding. Misinterpreting the guidelines or directions can result in incorrect actions or responses that affect your overall performance.
4. Poor Time Management
Time management plays a crucial role in completing the assessment effectively. Rushing through the questions or spending too much time on a single task can hinder your ability to finish within the time limit. Plan your approach ahead of time, allocate your minutes wisely, and remember to leave time for review.
5. Inconsistent Technique
Consistency in applying techniques is essential, especially when demonstrating critical skills. Fluctuations in your approach can lead to errors or missed steps. Practice the necessary techniques repeatedly until they become second nature, ensuring you execute each action with precision and confidence.
By avoiding these common mistakes and staying focused on the task at hand, you can significantly improve your chances of success. Preparation, attention to detail, and a calm, methodical approach are the best ways to ensure that you perform to the best of your ability.
Preparing for Certification Renewal
Renewing your certification is a crucial part of staying updated on the latest protocols and maintaining your readiness to respond in critical situations. As standards evolve, it’s important to refresh your knowledge and skills to ensure that you are always prepared. Whether you are nearing the expiration of your current certification or simply aiming to stay current, effective preparation is key to passing the renewal process with confidence.
There are several steps you can take to ensure that you are fully prepared for the certification renewal process. These steps not only help you review essential information but also give you the opportunity to enhance your skills and stay updated on any changes in the guidelines. Below are some important actions to consider when preparing for the renewal:
1. Review Updated Guidelines
Certification programs often update their training materials and protocols. Ensure that you are familiar with the latest guidelines and recommendations. These updates may involve changes in procedures, techniques, or recommended devices, so reviewing the new material is essential.
2. Complete a Refresher Course
Many certification organizations offer refresher courses to help individuals prepare for the renewal process. These courses can be completed online or in-person and often include both theoretical knowledge and hands-on practice. Participating in a refresher course is an excellent way to reinforce your skills and stay sharp.
3. Practice Hands-On Skills
Practical skills are critical in emergency situations, and they need to be practiced regularly. Whether it’s performing chest compressions, using an AED, or handling airway management, ensure that you practice these skills until they become second nature. Most renewal programs will include a practical component, so hands-on preparation is essential.
4. Take Practice Quizzes
To assess your knowledge, take practice quizzes that mirror the certification renewal test. These quizzes will help you become familiar with the types of questions you will encounter and identify areas where you may need additional study. Consistent practice will improve both your knowledge retention and test-taking confidence.
5. Stay Calm and Confident
During the renewal process, remember that confidence and calmness are just as important as knowledge. Take your time during practical assessments, think through each step, and focus on performing each task correctly. A calm approach ensures you don’t miss critical steps and allows you to demonstrate your competence effectively.
6. Review Important Concepts
- Recognizing signs of cardiac arrest and other emergencies
- Understanding how to use an AED effectively
- Performing CPR with the correct compression depth and rate
- Ensuring proper airway management techniques
By following these steps, you can ensure that you are well-prepared for your certification renewal and that you remain ready to respond effectively in emergency situations. Continuous education and practice are essential in maintaining your certification and confidence as a healthcare provider.