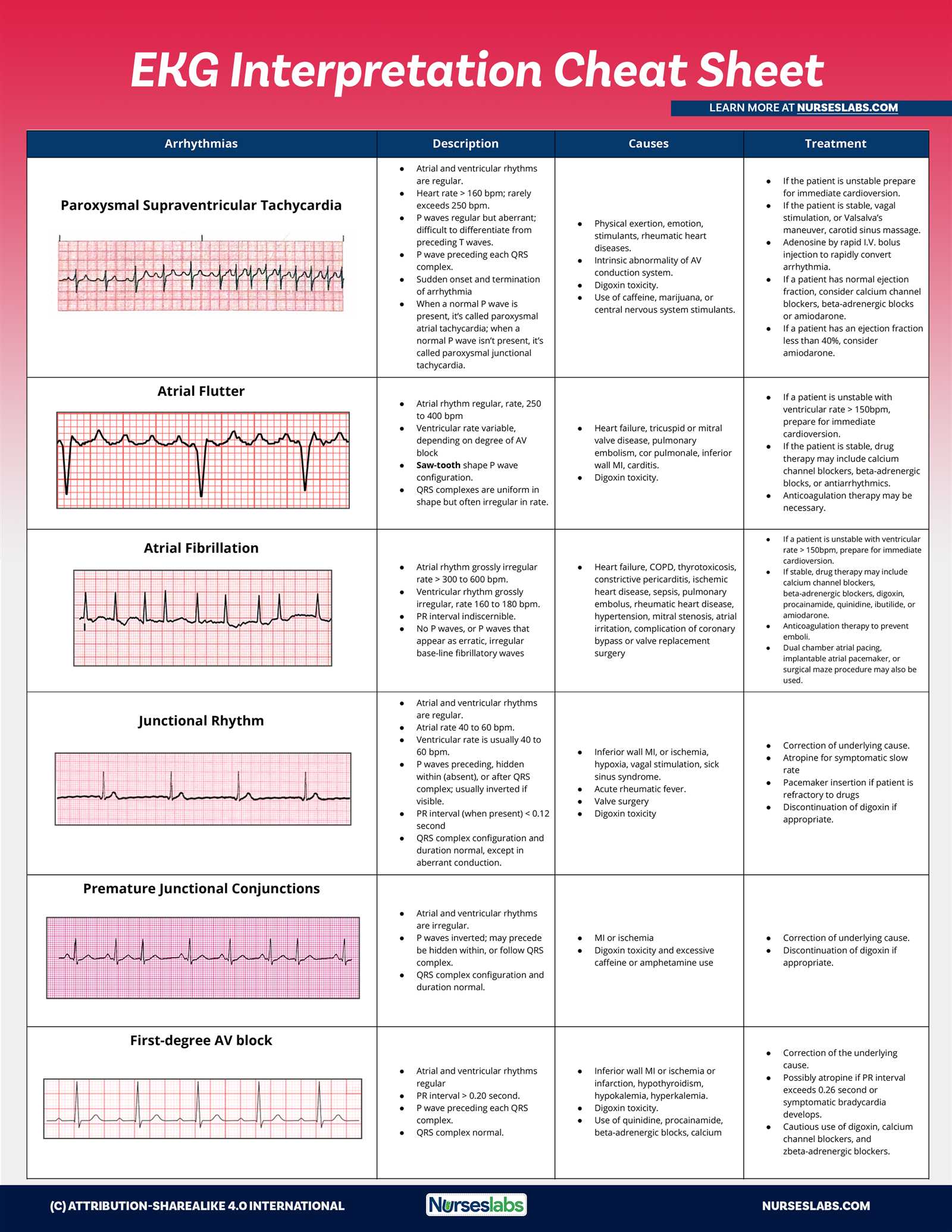
Healthstream Pharmacology Exam Answers and Tips

Achieving success in medical-related assessments requires a strong understanding of essential concepts that govern the use and administration of various therapeutic agents. With numerous topics and complex details to grasp, preparation becomes crucial for mastering the material and excelling in testing environments.
Effective study techniques combined with careful review of relevant material can significantly enhance your ability to tackle these challenging assessments. Familiarizing yourself with key categories of medications, their effects on the body, and how they interact with one another is essential for long-term success.
In this guide, we will focus on providing you with the tools to navigate this content efficiently, ensuring you’re well-prepared for any upcoming challenges. Understanding the core principles, recognizing patterns, and practicing strategic test-taking will set you on the path to success.
Healthstream Pharmacology Exam Answers
Successfully navigating assessments in the field of medical studies requires more than just memorizing facts. It involves understanding key principles, recognizing patterns, and applying knowledge in practical scenarios. Grasping the fundamentals of medication usage, the body’s response, and the interactions between different substances is essential for performing well in these evaluations.
Focusing on the critical components that appear most frequently in these assessments, such as drug classifications, mechanisms of action, and potential side effects, will help you feel more confident and prepared. By reviewing common questions and focusing on the most relevant topics, you can boost your chances of success.
Mastering these key areas ensures a comprehensive understanding of the material, providing a solid foundation for answering questions accurately and effectively. In this section, we will cover essential tips and strategies for approaching these tests with confidence and clarity.
Key Concepts for Pharmacology Success
To excel in medical assessments involving drugs and their effects, it’s crucial to have a solid understanding of the fundamental principles that govern therapeutic agents. Mastering key concepts can enhance your ability to recognize how different substances interact with the body and help you apply this knowledge in real-world situations.
Essential Areas to Focus On
Focusing on the following topics will strengthen your grasp of the material and improve your performance:
- Drug classifications: Understanding how medications are grouped based on their effects or chemical structure is vital for quick recall during tests.
- Mechanisms of action: Knowing how drugs work in the body helps you answer questions about their therapeutic effects and side effects.
- Side effects and adverse reactions: Recognizing common side effects of medications is critical for both clinical and test situations.
- Drug interactions: Being aware of how different substances may affect each other is key to understanding potential risks in treatment.
Study Tips for Mastering Key Concepts
To retain critical information and apply it successfully, consider these study strategies:
- Active recall: Regularly quiz yourself on key terms and drug classifications to improve retention.
- Practice with case studies: Reviewing real-life scenarios helps solidify your understanding and aids in applying theoretical knowledge.
- Use mnemonics: Create memory aids for remembering complex drug names, side effects, and classifications.
Mastering these key concepts not only improves your ability to perform well in tests but also ensures that you can apply your knowledge in practical healthcare settings.
Understanding Common Drug Classifications
One of the core aspects of mastering medical assessments is having a clear understanding of how medications are grouped. Drug classifications allow healthcare professionals to categorize substances based on their effects, chemical structure, or therapeutic use. Recognizing these categories enables more efficient identification and use of medications in practice.
Types of Drug Classifications
Drugs are typically grouped into broad categories to help distinguish their functions and applications. Here are some of the most common classifications:
- Analgesics: Medications designed to relieve pain, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or opioids.
- Antibiotics: Used to treat bacterial infections by inhibiting or killing bacteria, such as penicillin or tetracycline.
- Antihypertensives: Drugs that help manage high blood pressure, including ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers.
- Diuretics: Medications that help reduce excess fluid in the body, commonly used for conditions like heart failure or kidney disease.
- Antidepressants: Used to treat mood disorders, these medications regulate brain chemicals to improve emotional well-being.
Importance of Understanding Classifications
Having a thorough understanding of these categories not only helps in the identification of medications but also aids in predicting their effects, side effects, and potential interactions with other substances. For instance, knowing that certain drugs fall under a specific classification can provide insight into how they may work in the body and their expected outcomes.
As you progress through your studies, familiarizing yourself with the major drug classifications will help you answer questions with confidence and accuracy. This knowledge is essential for applying your understanding in real-world medical settings, where proper drug selection is crucial for patient care.
Essential Pharmacology Terms to Know
To succeed in any medical-related evaluation, a strong grasp of key terminology is essential. Understanding common terms related to medications, their effects, and how they interact with the body will help improve comprehension and retention of critical information. Familiarity with these terms will also assist in answering complex questions and applying knowledge effectively in practice.
Key Terms and Definitions
Here are some fundamental terms you should be familiar with when studying medications and their mechanisms:
- Absorption: The process by which a drug enters the bloodstream after being administered.
- Bioavailability: The proportion of a drug that enters the circulation when introduced into the body and is made available for use.
- Half-life: The time it takes for the concentration of a drug in the blood to reduce by half, indicating how long a drug stays active in the body.
- Therapeutic index: The ratio between the minimum effective dose and the minimum toxic dose of a drug, helping to determine its safety margin.
- Metabolism: The process by which the body breaks down and converts drugs into active or inactive substances.
- Excretion: The process through which drugs are eliminated from the body, typically via the kidneys or liver.
Understanding Drug Interactions
Recognizing how drugs interact with each other and with food or alcohol is also critical. These interactions can affect a drug’s effectiveness, cause adverse effects, or lead to toxicity. Key terms related to drug interactions include:
- Synergistic effect: When two drugs work together to produce a greater effect than the sum of their individual effects.
- Antagonistic effect: When one drug reduces or blocks the effect of another drug.
- Cumulative effect: When the effects of a drug increase with repeated administration due to accumulation in the body.
- Potentiation: When one drug enhances the effect of another, even though the second drug alone may not have much effect.
Mastering these terms not only helps with understanding the materials for tests but also improves your ability to work effectively in healthcare settings, ensuring the proper use of medications.
How to Prepare for Healthstream Exams
Preparing for assessments in the medical field requires a strategic approach to mastering key topics and understanding the underlying principles. Effective preparation goes beyond simple memorization and involves a deep comprehension of critical concepts, the ability to apply knowledge in different contexts, and the development of test-taking strategies that maximize your performance.
Steps to Effective Preparation
To ensure success, follow these essential steps when preparing for medical assessments:
- Review core topics: Focus on the main categories of study, such as drug classifications, side effects, and therapeutic uses.
- Break down complex material: Divide large sections of content into manageable parts and tackle them one by one to avoid feeling overwhelmed.
- Create study aids: Use flashcards, diagrams, and mind maps to reinforce important terms and concepts.
- Practice application: Work through case studies or practice scenarios to better understand how theoretical knowledge translates into real-world situations.
Test-Taking Strategies
In addition to mastering the material, consider these strategies to perform better on the actual assessment:
- Time management: During the test, pace yourself to ensure you have enough time to address every question.
- Read questions carefully: Pay attention to details in each question, especially when multiple answers seem correct. Look for keywords that help identify the best option.
- Eliminate incorrect answers: If unsure, rule out clearly wrong answers to increase the odds of selecting the correct one.
- Stay calm and focused: Approach each question with a clear mind, avoiding stress or panic during the test.
By following these steps and using effective strategies, you can prepare thoroughly for the assessment, ensuring a confident and informed approach to answering questions.
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics Overview
Understanding how substances move through the body and how they produce their effects is essential for effective treatment planning. Two core concepts in this field are how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted by the body (pharmacokinetics), and how drugs affect the body at the molecular level (pharmacodynamics). Both play crucial roles in determining the proper dosage, administration, and potential side effects of medications.
Key Phases of Drug Action
The journey of a drug through the body involves several phases, each of which influences its effectiveness and duration of action. The following table outlines these phases and their significance:
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Absorption | The process by which a drug enters the bloodstream, typically after oral ingestion or injection. |
| Distribution | How the drug spreads through the body, reaching its target areas, including organs and tissues. |
| Metabolism | The breakdown of the drug, primarily in the liver, into active or inactive forms. |
| Excretion | The elimination of the drug from the body, usually via the kidneys, feces, or sweat. |
Drug Effects on the Body
Pharmacodynamics explores how drugs interact with receptors, enzymes, or other biological targets to produce therapeutic effects. The body’s response to a drug can vary based on factors like dosage, genetic factors, and the presence of other substances. Understanding this interaction helps predict both the desired and potential adverse effects of a drug.
- Agonists: Drugs that bind to receptors and activate them to produce a desired effect.
- Antagonists: Drugs that block receptors and prevent them from being activated by other substances.
- Potentiation: When one drug enhances the effect of another, often leading to an amplified response.
These two concepts–how a drug is processed in the body and how it exerts its effects–are integral to understanding treatment protocols and ensuring both safety and efficacy in medication use.
Study Strategies for Pharmacology Tests
Preparing for assessments in the medical field requires not only memorization but also an understanding of complex concepts. Effective study strategies focus on mastering critical terms, recognizing patterns, and applying knowledge in practical scenarios. By using the right techniques, you can boost retention, reduce anxiety, and perform well on tests.
Effective Study Techniques
To maximize your study sessions, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Active recall: Instead of passively reviewing notes, test yourself regularly on key concepts. This helps reinforce memory and identify areas that need more attention.
- Spaced repetition: Break your study sessions into intervals, gradually increasing the time between reviews. This technique helps cement long-term retention of material.
- Visual aids: Use diagrams, charts, and flashcards to visualize complex concepts. Visualizing information often makes it easier to understand and remember.
- Group study: Collaborating with peers can provide new insights and help reinforce your knowledge through discussion and teaching others.
- Summarize material: After each study session, write a brief summary in your own words. This exercise helps reinforce learning and clarifies difficult concepts.
Time Management Tips
Proper time management is key to effective studying. Here are some tips to help you stay organized and focused:
- Create a study schedule: Break your study time into manageable blocks, focusing on one topic at a time. This keeps you organized and prevents feeling overwhelmed.
- Prioritize difficult topics: Focus on the most challenging material early in your study session when you have the most energy and focus.
- Avoid cramming: Spread your study sessions out over several days or weeks. Last-minute cramming often leads to poor retention and unnecessary stress.
By combining these strategies and managing your time wisely, you can enhance your preparation and feel confident on test day. Consistent study and practice are the keys to mastering complex material and achieving success in your assessments.
Common Medication Errors to Avoid
Medication errors are a significant concern in healthcare, as they can lead to serious health complications or ineffective treatment. These mistakes can occur at various stages, from prescribing and dispensing to administration and monitoring. Understanding the most common errors and how to avoid them is crucial for ensuring patient safety and treatment success.
Some frequent medication mistakes stem from misunderstandings of dosage, incorrect drug interactions, or confusion between similar-looking medications. Other errors may arise due to inadequate communication between healthcare providers or insufficient patient education about proper medication use. Preventing these errors requires vigilance, attention to detail, and a systematic approach to medication management.
Below are a few common medication errors that should be avoided:
- Incorrect dosage: Administering too much or too little of a drug can result in either toxicity or insufficient therapeutic effect. Always double-check dosages, especially for medications with narrow therapeutic windows.
- Drug interactions: Some medications can interact with each other, leading to harmful side effects. Always verify potential interactions before prescribing or dispensing drugs.
- Look-alike, sound-alike medications: Confusing one medication for another due to similar names or packaging is a common error. Use clear labeling, and confirm the drug with patients before administration.
- Failure to educate patients: Not informing patients about how and when to take their medications, or the potential side effects, can lead to improper use or non-compliance.
- Inadequate patient history: Failing to assess a patient’s medical history thoroughly can result in prescribing drugs that are contraindicated for that individual.
By remaining vigilant, utilizing available resources, and fostering clear communication, healthcare providers can minimize the risk of medication errors and improve patient outcomes.
Top Resources for Test Preparation Help
Effective preparation for any assessment in the medical field requires access to high-quality resources that help you grasp complex concepts and strengthen your knowledge. A variety of tools, including study guides, online platforms, and practice materials, can assist you in mastering the essential content. By utilizing these resources, you can enhance your learning experience and boost your confidence as you prepare for your assessments.
The following table highlights some of the top resources that can aid in your study and provide valuable assistance as you prepare:
| Resource | Purpose | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Online Learning Platforms | Interactive courses, practice tests, and quizzes | Access to comprehensive study materials and the ability to track progress |
| Study Guides and Textbooks | In-depth explanations of key concepts and terms | Detailed coverage of topics, essential for understanding foundational principles |
| Flashcards | Quick review of important terms and definitions | Ideal for memorization and active recall techniques |
| Peer Study Groups | Collaborative learning and discussion of complex topics | Shared insights and clarification of difficult concepts |
| Practice Quizzes | Simulation of test conditions with multiple-choice questions | Helps familiarize with the format and improves test-taking skills |
Incorporating a combination of these resources into your study routine can ensure a well-rounded approach and increase the likelihood of success. Whether you prefer independent learning, group discussions, or interactive platforms, there is a resource tailored to fit your preferred study style.
Important Drug Interactions to Remember
Understanding drug interactions is essential for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of treatment. Some medications can affect the absorption, metabolism, or elimination of others, leading to reduced efficacy or dangerous side effects. Being aware of these interactions is critical for both healthcare professionals and patients to prevent adverse outcomes.
Here are several important drug interactions that should always be considered when prescribing or taking medications:
- Anticoagulants and NSAIDs: Using blood thinners along with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can increase the risk of bleeding. Careful monitoring is necessary to avoid complications.
- Antibiotics and Birth Control Pills: Certain antibiotics can reduce the effectiveness of hormonal birth control. It’s important to use additional methods of contraception when taking these medications together.
- SSRIs and MAOIs: Combining selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) can lead to serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition. Avoid this combination unless closely monitored by a healthcare provider.
- Statins and Grapefruit: Grapefruit can inhibit the enzymes that metabolize statins, leading to elevated drug levels in the bloodstream and an increased risk of muscle damage.
- Diuretics and Lithium: Diuretics can increase the levels of lithium in the body, potentially leading to toxicity. Monitoring lithium levels is crucial when these drugs are used together.
These are just a few examples of how drugs can interact with one another, causing unintended effects. It’s vital to consult with healthcare providers about potential drug interactions and always read labels for any warnings. When in doubt, ask a pharmacist for advice before starting a new medication or supplement.
Managing Time During the Exam
Time management is a critical skill that can significantly impact performance during any assessment. Without a clear strategy for allocating time, it’s easy to become overwhelmed, rush through questions, or leave sections incomplete. To maximize success, it’s essential to approach the assessment with a plan that allows you to manage your time efficiently and effectively.
Here are some key strategies to help you manage your time during the test:
1. Allocate Time to Each Section
Before beginning the assessment, take a moment to read through the instructions and understand how much time is available. Divide this time according to the number of sections or questions. If there are multiple-choice questions, allocate less time to each, and spend more time on essays or open-ended questions. Stick to your plan as closely as possible to avoid spending too much time on any single part.
2. Prioritize Easier Questions
If you encounter questions that are particularly difficult or time-consuming, move on and return to them later if time permits. Starting with easier questions helps you build momentum, boosts confidence, and ensures you get as many answers as possible. Leave complex questions for the end, when you have a better sense of how much time remains.
By using these strategies, you can improve your ability to complete the test in the allotted time while maintaining accuracy. Proper time management not only helps you finish the assessment but also reduces stress and enhances your overall performance.
Commonly Tested Pharmacology Questions
Understanding the key concepts and topics often covered in assessments is crucial for effective preparation. Many questions focus on core aspects of drug action, classifications, mechanisms, and safety precautions. Knowing what to expect and familiarizing yourself with frequently asked questions can give you an edge in achieving success.
Here are some types of questions that often appear in assessments related to medication knowledge:
1. Drug Classifications and Uses
Questions in this category typically ask about the therapeutic uses of specific drug classes or how a particular drug works within the body. Understanding the mechanism of action for common drugs and their corresponding effects is essential for answering these types of questions accurately.
- What is the primary function of ACE inhibitors?
- Which drug class is commonly prescribed for pain relief?
2. Drug Interactions and Side Effects
Questions regarding interactions between medications, as well as their potential side effects, are frequently tested. It’s important to be aware of both common and rare interactions that could lead to complications when drugs are combined.
- What potential side effect may occur when combining aspirin with warfarin?
- Which medications should be avoided when taking antidiabetic drugs?
By reviewing these types of questions and focusing on the most commonly tested topics, you can better prepare yourself for assessments and increase your chances of success.
Exam-Taking Tips for Healthstream Exams
Effective strategies for taking any assessment can make a significant difference in your performance. It’s not just about what you know, but also how you approach the test. Proper planning, staying calm under pressure, and using specific tactics during the assessment can help you maximize your score. Here are some essential tips to keep in mind when preparing for and taking your next test.
1. Read Instructions Carefully
Before you start answering questions, take the time to read all instructions thoroughly. Many tests provide specific guidelines on how to answer questions or which sections to focus on. Skipping this step can lead to mistakes, especially if there are unique rules or time constraints.
2. Stay Calm and Focused

Test anxiety can negatively impact your performance, so it’s important to stay calm and focused throughout the assessment. Practice deep breathing and visualization techniques to reduce stress. If you feel overwhelmed, take a short break, close your eyes, and refocus.
| Tip | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Read instructions first | Avoid confusion and mistakes |
| Manage time effectively | Ensure you complete the test |
| Answer easier questions first | Build confidence and momentum |
By following these tips, you can boost your confidence and performance, turning the testing process into a more manageable and less stressful experience. Remember that preparation and mindset are just as important as knowledge when it comes to achieving success in any assessment.
Reviewing Drug Mechanisms of Action
Understanding how medications work in the body is fundamental to mastering their effects and uses. Every drug interacts with the body in a specific way, targeting particular receptors, enzymes, or biological pathways to bring about a therapeutic effect. Reviewing these mechanisms is crucial for both safe medication administration and understanding the rationale behind treatment choices. Familiarity with these processes helps in predicting possible outcomes and side effects, allowing for better clinical decision-making.
Below are some of the primary mechanisms through which drugs exert their effects:
- Receptor Binding: Many medications work by binding to specific receptors on cell surfaces, influencing cellular activity. This process is central to drugs like beta-blockers, which target beta-adrenergic receptors to reduce heart rate.
- Enzyme Inhibition: Certain drugs inhibit enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions in the body. For example, ACE inhibitors block the enzyme that converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II, lowering blood pressure.
- Ion Channel Modulation: Some medications affect the movement of ions across cell membranes, which can modify nerve signaling or muscle contraction. Calcium channel blockers, for example, prevent calcium ions from entering cells, helping to manage hypertension.
Having a deep understanding of these mechanisms allows healthcare professionals to tailor treatments effectively, anticipate potential interactions, and manage patient care with greater confidence. Whether you’re studying for assessments or seeking to enhance clinical practice, reviewing these mechanisms is a key component of mastering drug therapy.
Pharmacology Case Studies and Scenarios
Case studies and practical scenarios are invaluable tools for understanding how theoretical knowledge applies in real-world situations. These exercises help deepen understanding of drug actions, interactions, and side effects in the context of actual patient care. By reviewing cases, healthcare professionals can develop critical thinking skills, improve clinical judgment, and learn how to adapt treatment plans based on individual patient needs.
Below are a few examples of scenarios that illustrate the application of drug knowledge in clinical settings:
Case Study 1: Managing Hypertension
A 60-year-old male patient with a history of hypertension presents with high blood pressure readings despite taking medication. The patient is also experiencing dizziness and mild swelling in his ankles. Reviewing his medication regimen reveals that he is on a calcium channel blocker and an ACE inhibitor. After conducting a thorough assessment, the healthcare provider considers whether the dosage of his current medications should be adjusted or if a new drug class is needed to control his blood pressure effectively.
Case Study 2: Managing Type 2 Diabetes
A 45-year-old female patient with type 2 diabetes reports difficulty maintaining stable blood glucose levels, despite taking her prescribed medications regularly. Her current regimen includes a combination of insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents. After reviewing her case, the healthcare provider explores potential causes for the fluctuation in blood sugar, such as improper insulin administration or a change in her diet or physical activity level. The provider also considers introducing a new class of drugs to help with insulin resistance.
By engaging with such case studies, individuals can practice diagnosing potential issues and determining appropriate interventions. These scenarios allow healthcare professionals to reflect on drug therapies and how they can be applied effectively in patient care.
How to Stay Calm During the Exam
Staying composed during a high-stakes assessment can significantly impact performance. The pressure to perform well often leads to anxiety, which can cloud judgment and hinder recall. However, by employing strategies to remain calm, individuals can manage their stress levels and approach the test with confidence and clarity. These techniques can help improve focus and ensure that knowledge is applied effectively during the assessment.
One of the most effective ways to manage anxiety is through deep breathing exercises. Taking slow, deep breaths helps lower the heart rate and calm the nervous system. Practice this technique for a few minutes before the test or when feeling overwhelmed during the assessment.
Preparation is Key
Proper preparation is one of the most important factors in feeling confident and calm. When you know the material thoroughly, the test will feel less daunting. Make sure to review key concepts, practice with mock tests, and understand the format of the questions. The more familiar you are with the content, the more relaxed you will feel during the assessment.
Stay Positive and Focused
Maintaining a positive mindset is crucial for managing test-related stress. Remind yourself that the purpose of the assessment is to evaluate your knowledge, not to judge your abilities. If you encounter a challenging question, stay calm, take a deep breath, and move on to the next one. Returning to the tough question later with a clear mind can often lead to a more accurate answer.
By using these techniques and maintaining a calm, focused attitude, you can approach any test with the confidence needed to succeed.
Post-Assessment Review and Retake Strategies
After completing an important evaluation, it’s essential to reflect on the experience and identify areas of improvement. Reviewing performance can provide valuable insights into strengths and weaknesses, helping you to refine your approach for future assessments. Whether you’ve passed or need to retake the test, understanding where you went wrong and addressing those gaps can significantly enhance your preparation moving forward.
Taking the time to go over each question, especially the ones you struggled with, can help solidify your understanding of key concepts. It also allows you to recognize patterns in the types of mistakes you made, so you can avoid them in the future. This process is crucial for continuous improvement and ensuring success in future evaluations.
Review Mistakes and Analyze Patterns
One of the best ways to prepare for a retake is to focus on the questions you found most difficult. Consider why you missed them–was it a misunderstanding of the material, a careless mistake, or time management issues? Understanding the root cause can help you address the problem and ensure you’re better prepared next time.
| Category | Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Understanding Material | Review relevant resources, textbooks, or notes | Better grasp of concepts and terms |
| Time Management | Practice answering questions under time constraints | Improved pacing and confidence |
| Study Techniques | Try different study methods such as flashcards or group study | Increased retention and engagement with content |
Retake Preparation Tips
If a retake is necessary, it’s important to use the time wisely. Break down the study material into smaller sections and focus on the areas where you struggled the most. Use practice tests to simulate the exam environment, and consider working with a tutor or study group to gain different perspectives on the material. The key is to stay positive, stay persistent, and treat the retake as an opportunity for growth.
With these strategies, you can ensure that the post-assessment period becomes a productive phase for improving and succeeding in future evaluations.
Additional Resources for Mastery
Achieving mastery in any field requires consistent learning and access to high-quality resources. Whether you are looking to deepen your understanding of complex topics or strengthen foundational knowledge, a variety of tools can help you on your educational journey. Utilizing multiple learning materials and platforms can provide diverse perspectives and enhance comprehension of the subject matter.
From textbooks and online courses to mobile apps and study groups, there is a wealth of information available to aid your studies. These resources offer interactive learning experiences and are designed to cater to different learning styles, whether you prefer reading, listening, or hands-on practice.
Books and Textbooks
Books remain one of the most reliable sources of in-depth knowledge. A well-chosen textbook can provide structured and comprehensive coverage of the material. Look for highly recommended titles by professionals or educators in the field. Many books also offer practice questions and explanations that can help reinforce concepts.
Online Platforms and Courses
For a more dynamic learning experience, online courses and platforms offer video lectures, interactive quizzes, and discussion forums. These can be particularly useful for visual learners or those who prefer structured modules. Websites like Khan Academy, Coursera, and Udemy provide specialized courses that allow you to learn at your own pace, often with the option to interact with instructors or peers.
Mobile Applications
Mobile apps are a convenient way to study on the go. Many apps provide flashcards, practice questions, and mini-quizzes that you can use whenever you have a few spare minutes. Apps like Anki and Quizlet are popular among learners for their ease of use and ability to create custom study sets tailored to specific needs.
Study Groups and Peer Learning
Sometimes, collaborating with others can accelerate your learning. Joining or forming study groups allows you to engage in discussions, share insights, and challenge your understanding. Peer learning fosters a supportive environment where everyone can contribute their knowledge and ask questions that might not be addressed in individual study.
By combining these various resources, you can develop a well-rounded approach to mastering the material and improving your understanding. The key is to remain consistent, stay curious, and explore different avenues of learning that suit your style and preferences.