Complete Guide to Telemetry Competency Exam Answers

Successfully completing proficiency assessments in health monitoring requires a solid understanding of key concepts and practices. These evaluations assess your ability to handle critical data, interpret readings accurately, and respond appropriately in clinical settings. Preparing for these evaluations involves mastering a variety of topics, from heart rhythms to patient monitoring systems.
Comprehensive preparation is essential for anyone aiming to excel in this field. By focusing on relevant knowledge and practicing with real-life scenarios, you can ensure that you are well-equipped to demonstrate your skills. The goal is not only to pass the assessment but to be confident in your ability to perform under pressure when it matters most.
Whether you are just starting or looking to improve your existing skills, understanding the fundamental principles behind these tests is key. A strategic approach to learning will help you focus on the most important aspects, ensuring that you are ready to handle any challenge that comes your way during the evaluation process.
Telemetry Competency Exam Answers Guide
Successfully navigating proficiency assessments in health monitoring requires more than just basic knowledge–it demands a strategic understanding of the tools and techniques used in critical care environments. Preparing for such evaluations involves mastering a broad range of skills, including data interpretation, patient observation, and troubleshooting when issues arise with monitoring systems.
One of the best ways to ensure success is to familiarize yourself with common scenarios you might face. By practicing with mock tests and real-world examples, you can gain confidence and improve your problem-solving abilities. Pay attention to the types of challenges that are frequently tested, such as recognizing heart rhythms, responding to alarms, and understanding system outputs.
In addition to theoretical knowledge, it is essential to have hands-on practice with the equipment. Understanding how to operate monitoring devices under various conditions will help you troubleshoot quickly and effectively during the assessment. With the right preparation, you will not only perform well but be equipped to handle real-time situations with competence and calmness.
Understanding Telemetry Competency Requirements
To excel in the field of patient monitoring and critical care assessment, it is essential to understand the core skills and knowledge expected. These requirements are designed to ensure that individuals can handle complex systems, interpret vital signs, and respond to emergency situations effectively. Meeting these standards requires a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical experience.
The primary areas covered in these assessments include:
- Understanding physiological data and its interpretation
- Familiarity with various monitoring systems and devices
- Knowledge of heart rhythms and arrhythmias
- Proficiency in responding to alarms and system malfunctions
- Effective communication with healthcare teams in critical situations
In addition to mastering these topics, it is important to be able to demonstrate practical application in real-world scenarios. This includes troubleshooting equipment, understanding system outputs, and managing patient data under stress. Preparing for such evaluations requires thorough study, hands-on practice, and familiarity with the tools used in daily patient care.
Key Topics Covered in the Assessment
When preparing for proficiency evaluations in patient monitoring, it’s essential to understand the critical topics that are often covered. These areas are designed to test both theoretical knowledge and practical application of skills in healthcare environments. Mastering these topics ensures that candidates can respond effectively to medical data and use monitoring equipment proficiently.
Fundamental Concepts
These topics lay the groundwork for understanding patient monitoring systems and their operation. Key concepts include:
- Basic physiological parameters (heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels)
- Heart rhythm identification and interpretation
- Recognizing signs of abnormalities or critical conditions
- Understanding the role of different monitoring devices in patient care
Practical Skills
In addition to theoretical knowledge, candidates must demonstrate hands-on abilities, such as:
- Properly using monitoring equipment
- Responding to equipment alarms and troubleshooting issues
- Effectively communicating patient data with healthcare teams
- Managing multiple monitoring systems simultaneously
Focusing on these key areas will ensure that you are well-prepared for the assessment, with the ability to handle a range of real-world situations confidently and efficiently.
How to Prepare for Testing

Effective preparation for proficiency assessments in patient monitoring requires a focused approach that combines theoretical knowledge with practical experience. A strong foundation in medical concepts, along with hands-on practice, ensures that you are ready to handle real-world scenarios and demonstrate your skills under pressure.
Study the Key Concepts
Start by reviewing the essential topics that are often included in the assessment. Key concepts to master include:
- Understanding basic physiological measurements (heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation)
- Familiarity with common heart rhythms and their interpretation
- Recognizing life-threatening conditions and how to respond
- Knowing how to use and troubleshoot different monitoring devices
Practice with Real Equipment
Theoretical knowledge alone is not enough; hands-on practice with monitoring systems is equally important. Make sure to:
- Familiarize yourself with the equipment you will be using during the test
- Practice interpreting data from various devices
- Simulate emergency scenarios to develop a quick and effective response
- Review troubleshooting techniques for common issues
By combining both study and practice, you will be well-prepared to succeed in your proficiency testing and demonstrate your ability to manage patient care effectively in high-pressure situations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in the Assessment
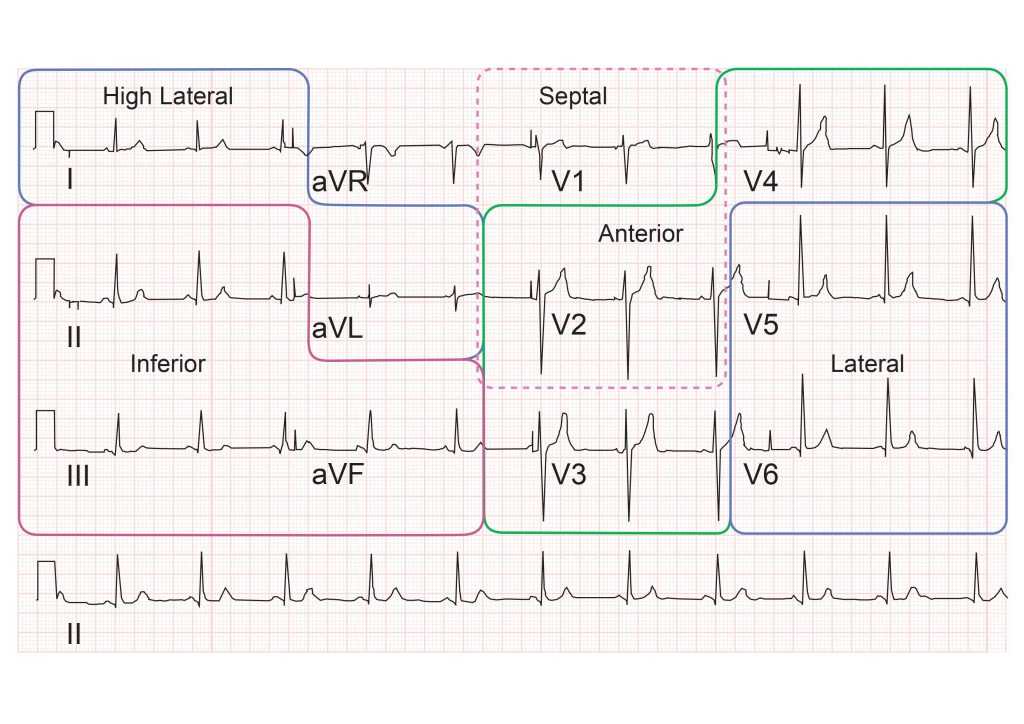
During proficiency assessments for health monitoring, there are several common pitfalls that can undermine performance. Being aware of these mistakes and actively working to avoid them can significantly improve your chances of success. Preparation is key to understanding both the material and the testing environment, allowing you to perform confidently when it matters most.
Overlooking Key Concepts
One of the most frequent errors is neglecting to fully grasp essential topics. Ensure you are comfortable with the following:
- Basic physiological parameters and their normal ranges
- Recognizing different types of arrhythmias and irregular heart rhythms
- Understanding the operation of monitoring equipment
- Being able to respond to critical conditions and emergencies
Failing to Manage Time Effectively

Another common mistake is poor time management. During the assessment, make sure to:
- Allocate enough time to review all questions or tasks
- Stay calm and focused to avoid rushing through key steps
- Prioritize critical issues when troubleshooting equipment
- Allow time for thorough analysis of data before making decisions
By avoiding these common errors, you can increase your chances of success and demonstrate your readiness to manage real-world monitoring situations confidently.
Study Tips for Success
Effective preparation is essential for succeeding in proficiency assessments that test your skills in patient monitoring and critical care. With the right study strategies, you can sharpen your understanding of key concepts, improve your practical skills, and build confidence in your abilities. Below are some practical tips to help you prepare effectively and perform at your best.
Focus on Core Concepts
Before diving into specific scenarios, make sure you have a solid understanding of the foundational topics. These include:
- Basic understanding of vital signs and their significance
- Heart rhythm recognition and interpretation
- Knowledge of monitoring systems and how they function
- Identification of critical conditions and appropriate responses
Practice with Mock Scenarios
Simulating real-world situations will help you improve your problem-solving skills and become more comfortable in high-pressure environments. Consider the following:
- Work with practice questions or mock tests
- Recreate emergency scenarios to test your response time
- Review past cases to understand common challenges
- Perform hands-on practice with monitoring devices
Stay Organized and Manage Your Time
Effective time management and staying organized are crucial during preparation. Keep track of your study sessions and progress by:
- Setting clear goals for each study session
- Creating a study schedule to balance theory and practice
- Prioritizing areas where you feel less confident
- Reviewing your work regularly to reinforce key concepts
By following these tips and staying consistent in your preparation, you will be well-equipped to demonstrate your skills and succeed in your proficiency assessment.
What You Need to Know About ECG
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a crucial tool for monitoring heart activity and diagnosing various cardiac conditions. Understanding how to interpret ECG readings is essential for healthcare professionals, as it allows for the detection of abnormalities such as arrhythmias, ischemia, and other heart-related issues. Familiarity with the components of an ECG waveform and the ability to accurately assess these patterns is key to providing effective patient care.
The ECG waveform consists of several key components that represent the electrical impulses traveling through the heart. These include:
- P wave: Represents atrial depolarization.
- QRS complex: Represents ventricular depolarization, which is the largest and most prominent part of the waveform.
- T wave: Represents ventricular repolarization, or the recovery phase.
- U wave: A less common feature that can be seen in some ECGs, often associated with repolarization of the papillary muscles.
In addition to recognizing these key components, it is important to understand the significance of various rhythm abnormalities. Some common issues detected through ECG include:
- Bradycardia and tachycardia, which refer to slow and fast heart rates, respectively.
- Arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation, ventricular fibrillation, and heart block.
- Signs of ischemia or infarction, which may appear as ST segment elevation or depression.
Being able to interpret these patterns accurately enables healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about patient care and treatment. Consistent practice and study are essential for mastering ECG interpretation and understanding the clinical significance of various waveforms.
Important Terminology to Master
To effectively navigate the world of patient monitoring and critical care, it is essential to become familiar with key terms that describe various systems, conditions, and procedures. Mastering the terminology used in this field will help you interpret data accurately, communicate with the healthcare team efficiently, and ensure quality care for patients. Below are some fundamental terms and concepts you should understand:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Bradycardia | A slower-than-normal heart rate, typically less than 60 beats per minute. |
| Tachycardia | Abnormally fast heart rate, usually greater than 100 beats per minute. |
| Arrhythmia | Irregular or abnormal heart rhythms, such as atrial fibrillation or ventricular fibrillation. |
| ECG (Electrocardiogram) | A recording of the electrical activity of the heart, used to diagnose heart conditions. |
| Pulse Oximetry | A non-invasive method to monitor oxygen saturation levels in the blood. |
| ST Elevation | Elevation of the ST segment on an ECG, often indicating a heart attack or ischemia. |
| Defibrillation | The process of delivering an electric shock to the heart to restore a normal rhythm during life-threatening arrhythmias. |
Being proficient in these terms will help you communicate effectively within the healthcare setting, interpret vital signs correctly, and provide optimal care for patients. Mastery of this terminology is critical for ensuring accurate decision-making and efficient patient monitoring.
Resources for Exam Preparation
Preparing for proficiency assessments in health monitoring and patient care requires access to a variety of reliable resources. These materials can help deepen your understanding of key concepts, improve practical skills, and increase confidence as you approach your evaluation. Below are some valuable resources that can assist in your preparation:
- Textbooks and Study Guides: Comprehensive texts covering the fundamentals of heart rhythms, monitoring techniques, and emergency protocols can serve as the foundation for your studies. Look for books that provide detailed explanations, practice questions, and case studies.
- Online Courses and Tutorials: Platforms offering specialized courses can provide structured learning experiences. Many of these courses include video tutorials, interactive quizzes, and real-time feedback to help reinforce your knowledge.
- Practice Tests and Quizzes: Mock exams or practice quizzes are essential for familiarizing yourself with the format and types of questions you may encounter. These can help you assess your strengths and areas for improvement.
- Workshops and Hands-On Training: Participating in workshops or simulation labs provides real-world practice in operating monitoring equipment, interpreting data, and responding to critical scenarios.
- Peer Study Groups: Collaborative study sessions with colleagues or other candidates can be extremely beneficial. Discussing complex topics and sharing insights can help clarify concepts and promote better retention of information.
Utilizing these resources effectively will allow you to approach your assessment with a well-rounded understanding, enhancing your ability to perform under pressure and make informed decisions during critical situations.
How to Improve Your Confidence
Building confidence before a high-stakes assessment is crucial for performing at your best. A calm and assured mindset can help you approach questions methodically, recall information more easily, and respond to challenges without hesitation. Confidence comes from preparation, practice, and mental strategies that help reduce anxiety and boost self-belief. Here are some key approaches to help strengthen your confidence as you prepare:
- Thorough Preparation: The more prepared you are, the more confident you will feel. Study consistently, review key concepts, and practice with mock scenarios. Familiarity with the material allows you to enter the assessment with less uncertainty.
- Simulate Real-Life Situations: Recreating realistic situations will build your confidence in responding to unexpected challenges. Practice handling different monitoring equipment, interpreting data, and managing critical care scenarios to gain more control over your reactions.
- Positive Self-Talk: Shift your mindset by replacing negative thoughts with positive affirmations. Remind yourself of your strengths, past successes, and the hard work you have put into your preparation.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Stress and anxiety can interfere with your performance. Practice mindfulness exercises, deep breathing, and relaxation techniques to calm your nerves before and during the assessment.
- Learn from Mistakes: Instead of dwelling on errors, use them as learning opportunities. Understanding what went wrong allows you to make adjustments and improve. This will build resilience and further enhance your confidence for future assessments.
By incorporating these techniques into your preparation, you will foster a sense of self-assurance and approach the assessment with a clear, focused mindset.
Monitoring Systems You Should Know

Understanding the various systems used for patient monitoring is essential for anyone working in critical care environments. These systems help healthcare professionals track a patient’s vital signs, detect potential issues, and make informed decisions about treatment. Familiarity with different types of monitoring equipment and their functions will help you operate effectively and respond quickly in emergency situations. Below are some of the key monitoring systems you should be well-versed in:
- Heart Rate Monitors: These systems measure the heart’s rhythm and rate, alerting healthcare providers to potential irregularities like bradycardia or tachycardia. They are commonly used in ICU and emergency care settings.
- Blood Pressure Monitors: Automated or manual blood pressure systems are critical for tracking a patient’s cardiovascular health. They help identify hypertension or hypotension, which may signal underlying health problems.
- Pulse Oximeters: These devices measure the oxygen saturation levels in the blood. Low oxygen levels can be indicative of respiratory distress or other serious conditions that require immediate attention.
- ECG Machines: Electrocardiograms track the electrical activity of the heart and are crucial for diagnosing heart attacks, arrhythmias, and other cardiac conditions. Understanding how to interpret an ECG is essential for effective patient management.
- Capnography Systems: These devices monitor the concentration of carbon dioxide in the exhaled breath, providing valuable information on a patient’s ventilation and respiratory function.
- Invasive Pressure Monitoring: Used for critically ill patients, these systems track pressures in the arteries, veins, and heart chambers, providing insights into the patient’s circulatory system and guiding medical interventions.
- Temperature Monitors: These systems track the body’s core temperature, helping identify fever, hypothermia, or other conditions that could impact patient recovery.
Proficiency in using and interpreting the data from these monitoring systems is crucial for providing high-quality care in clinical settings. Being familiar with the technology and its applications can greatly enhance your ability to respond to critical situations effectively.
Time Management During the Assessment
Effective time management is a crucial skill for performing well in any high-stakes evaluation. Properly allocating time to each section ensures that you can thoroughly answer all questions, avoid rushing, and reduce stress. With the right strategies, you can stay on track and maximize your performance. Here are some time management techniques to consider:
- Familiarize Yourself with the Structure: Before beginning, take a moment to understand the layout and format of the assessment. Knowing how many sections there are and how much time is allocated to each will allow you to plan accordingly.
- Set Time Limits for Each Section: Break down the available time into manageable segments. Assign a specific amount of time to each part of the assessment, ensuring that you don’t spend too much time on any one section. This will help prevent you from running out of time.
- Prioritize Easy Questions: Start with the questions you are most confident in. This will help you build momentum and secure easy points quickly, leaving more time for difficult ones.
- Don’t Get Stuck on Difficult Questions: If you encounter a challenging question, move on and come back to it later. Spending too much time on one question can cost you valuable time for others.
- Monitor Your Progress: Keep an eye on the clock as you work through the assessment. Regularly check your progress to ensure you’re staying on track and adjusting your pace as needed.
- Leave Time for Review: Allocate the last few minutes of the assessment to review your answers. Check for any missed questions, ensure all responses are complete, and correct any mistakes you might have made in haste.
By using these time management strategies, you can approach the assessment with a clear plan, stay focused throughout, and ensure that you make the most of the time available.
Understanding Heart Rhythms in Monitoring
Heart rhythms are critical indicators of a patient’s cardiac health, and understanding their variations is essential for anyone working with patient monitoring systems. The rhythm of the heart can reveal important information about the patient’s condition, helping healthcare professionals identify potential issues such as arrhythmias, ischemia, or other life-threatening conditions. Recognizing these patterns and anomalies is key to effective monitoring and timely intervention.
Types of Heart Rhythms
There are several types of heart rhythms that healthcare providers need to be familiar with. Each rhythm can tell a different story about the health of the heart and the individual’s overall well-being. Some common heart rhythms include:
- Normal Sinus Rhythm: This is the standard rhythm of a healthy heart, characterized by regular intervals between beats and a consistent rate of 60-100 beats per minute.
- Bradycardia: A slower-than-normal heart rate, typically below 60 beats per minute. This can be a sign of underlying conditions, such as heart block or other heart problems.
- Tachycardia: An abnormally fast heart rate, generally over 100 beats per minute, which could indicate stress, fever, or more serious issues like atrial fibrillation.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats, which can be caused by a variety of factors. These may include atrial fibrillation, ventricular fibrillation, or premature ventricular contractions, all of which require medical attention.
- Atrial Fibrillation: A type of arrhythmia where the atria (upper chambers of the heart) beat erratically, leading to poor blood flow and an increased risk of stroke.
- Ventricular Fibrillation: A life-threatening condition where the lower chambers of the heart quiver instead of contracting properly, leading to a loss of effective blood circulation.
Recognizing and Responding to Abnormal Rhythms
Early recognition of abnormal heart rhythms is critical for timely intervention. Monitoring devices play a key role in detecting these irregularities, but healthcare providers must be trained to interpret the data accurately. When an abnormal rhythm is detected, it is important to assess the patient’s overall condition and provide appropriate treatment based on the type and severity of the irregularity.
Understanding the fundamentals of heart rhythms and being able to differentiate between normal and abnormal patterns is vital for anyone involved in patient monitoring. This knowledge helps to ensure that any cardiac issues are addressed promptly and effectively, improving patient outcomes and safety.
Interpreting Monitoring Data Accurately
Accurate interpretation of data collected through monitoring devices is crucial for healthcare professionals. The data provides real-time insights into a patient’s condition, allowing medical staff to make informed decisions and take immediate action when necessary. Misreading or misunderstanding the information can lead to incorrect diagnoses, delayed treatments, and potentially serious outcomes. Therefore, understanding how to read and interpret this data with precision is a vital skill in patient care.
Different parameters such as heart rate, respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, and blood pressure can be tracked using monitoring systems. Each of these metrics provides valuable insights, and interpreting them correctly requires both technical knowledge and clinical judgment. Here are some key points to remember when interpreting monitoring data:
| Parameter | Normal Range | Indication of Abnormality |
|---|---|---|
| Heart Rate | 60-100 beats per minute | Bradycardia (under 60 bpm), Tachycardia (over 100 bpm) |
| Blood Pressure | 120/80 mmHg | Hypertension (over 140/90 mmHg), Hypotension (below 90/60 mmHg) |
| Oxygen Saturation | 95-100% | Hypoxemia (below 90%) |
| Respiratory Rate | 12-20 breaths per minute | Bradypnea (below 12 bpm), Tachypnea (above 20 bpm) |
It is also important to consider the patient’s history and current condition when interpreting this data. For instance, a slight deviation from the normal range may not be alarming in a well-known case, but it could indicate a serious issue in a critically ill patient. Always cross-reference the data with the patient’s symptoms and overall health status for a complete assessment.
Accurate data interpretation can be improved by practicing pattern recognition, staying updated on medical standards, and using technology tools effectively. Regular training and hands-on experience help build the confidence needed to interpret monitoring information quickly and reliably.
Mock Exams and Practice Questions
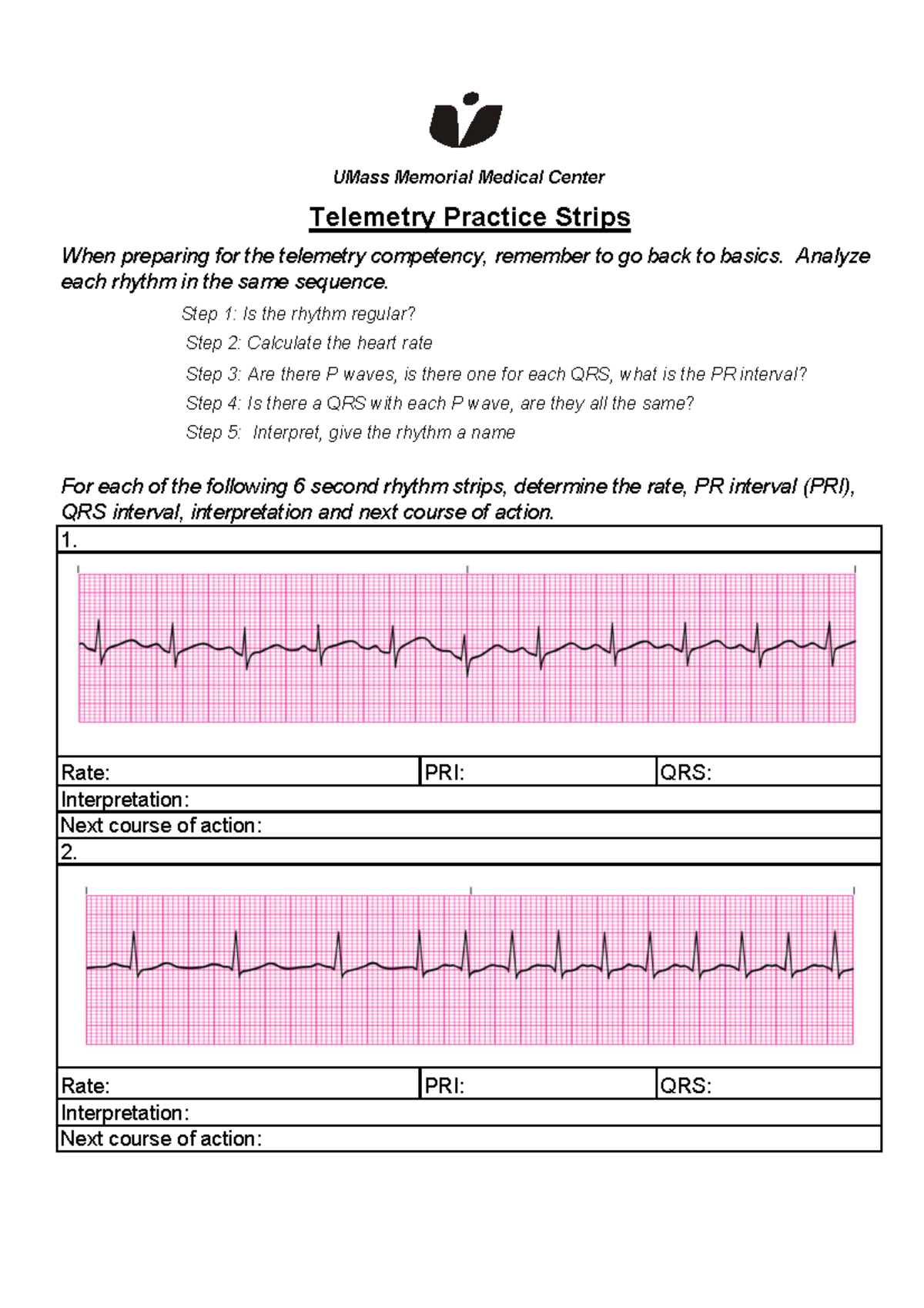
One of the most effective ways to prepare for assessments is through practice. Mock tests and sample questions provide a valuable opportunity to familiarize yourself with the format and types of questions you may encounter. They help you gauge your understanding of the material, identify areas of weakness, and boost your confidence ahead of the actual evaluation. By regularly engaging with practice content, you can refine your knowledge and improve your response time under pressure.
Benefits of Practice Tests
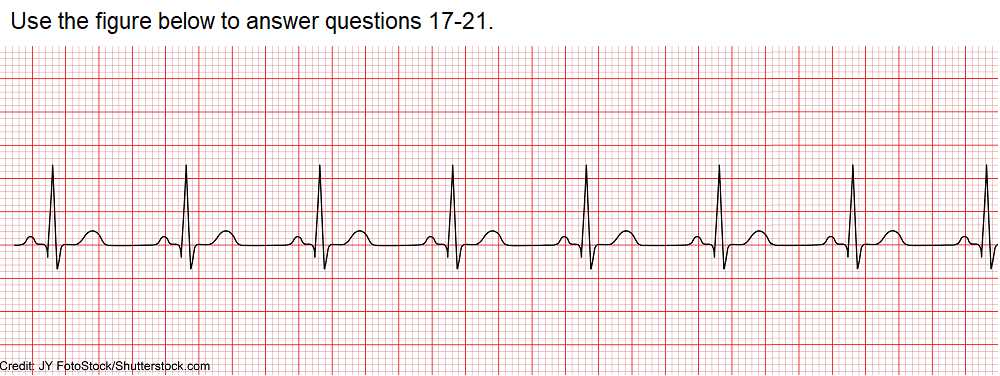
- Helps identify knowledge gaps
- Enhances time management skills
- Boosts confidence and reduces test anxiety
- Improves familiarity with question formats
- Reinforces learning and retention
Where to Find Mock Questions
Mock exams and practice questions can be found in various sources. Below are some common places to look:
- Online Resources: Websites and platforms often offer free or paid practice tests tailored to the subject matter.
- Study Guides: Many textbooks or digital study guides include sample questions at the end of chapters or as supplementary material.
- Professional Training Programs: Specialized courses or workshops may provide access to practice tests designed to simulate the actual assessment environment.
- Peer Groups: Joining study groups or forums can provide an opportunity to exchange questions and test each other.
By using a combination of these resources, you can create a comprehensive study plan that incorporates mock exams and practice questions. The more you practice, the more prepared you will be for the real test.
Tips for Reviewing Key Concepts
Effective revision is essential when preparing for any type of assessment. Understanding the core principles and their applications is critical for achieving success. This section provides practical strategies for reviewing essential concepts, helping you reinforce your knowledge and boost your readiness. Whether you are revisiting foundational material or focusing on more complex topics, these tips will guide you in retaining key information and applying it accurately when needed.
Strategies for Effective Review
- Focus on Core Principles: Identify the most critical concepts and ensure you understand their basic principles and how they are applied in different scenarios.
- Break Down Complex Topics: If a subject feels overwhelming, break it into smaller sections. Tackle each piece one at a time and build your understanding gradually.
- Use Visual Aids: Diagrams, charts, and other visual tools can simplify complex ideas and help you remember key details.
- Practice with Examples: Apply what you’ve learned by working through examples. This will solidify your understanding and allow you to recognize patterns.
- Review Past Mistakes: Look at any past assessments, quizzes, or practice exercises. Identify where you went wrong and revisit those areas for improvement.
Creating a Study Schedule
Building a study schedule that includes time for regular reviews can ensure you cover all necessary topics without feeling rushed. Here’s a simple approach to structuring your study time:
| Time Block | Activity |
|---|---|
| Morning | Review core concepts and foundational knowledge |
| Afternoon | Work through practice problems and case studies |
| Evening | Test your knowledge with mock exercises or quizzes |
By following a well-planned schedule, you’ll ensure that you’re consistently reinforcing your understanding and addressing any weak points in your knowledge.
What to Do After the Assessment
Once you’ve completed the assessment, it’s essential to focus on what comes next. This phase is just as important as preparation, as it helps you reflect on your performance, identify areas for improvement, and plan your next steps. Whether you pass or need to retake the test, how you respond afterward plays a crucial role in your long-term success and growth.
Steps to Take Immediately After Completion
- Review Your Performance: Take a few moments to evaluate your experience. What sections did you feel confident about? Which areas were more challenging? This reflection will guide your future preparations.
- Relax and Recover: If the process was intense, allow yourself time to unwind. Stress can affect your mental clarity, so it’s important to recharge and approach any follow-up tasks with a fresh mindset.
- Check for Results: Understand the process for receiving your results. Be sure you know when and how to expect feedback, and avoid unnecessary worry by giving it time.
- Seek Feedback: If available, request feedback from the assessors or review any reports you received. Constructive criticism is valuable for improving your skills and understanding of the material.
If You Need to Retake the Assessment

If the results aren’t what you hoped for, don’t be discouraged. Use this opportunity to learn from any mistakes and refine your approach. Here are some steps to consider:
| Action | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Analyze Mistakes | Identify which areas you struggled with and focus on improving those topics. |
| Review Resources | Revisit study materials, additional resources, and practice exercises to reinforce your understanding. |
| Seek Additional Help | Consider enrolling in review sessions or seeking guidance from experts in areas you find difficult. |
| Revisit Study Schedule | Adjust your study routine to ensure adequate time for revision and preparation. |
By reflecting on your performance and taking deliberate steps toward improvement, you’ll be better equipped for the next opportunity. Keep a positive attitude and remember that setbacks are part of the learning journey.