Microeconomics Exam 1 Study Guide for Success

Preparing for a fundamental economics test requires a solid understanding of core principles and their practical applications. By focusing on key concepts, you can build the foundation needed to tackle a range of questions efficiently and accurately. Gaining a deep grasp of essential theories will help you approach any challenge with confidence.
Success in the subject comes down to mastering the major topics such as market dynamics, consumer behavior, and the effects of various economic forces. It’s crucial to approach your preparation with a strategic mindset, organizing your time and resources wisely. This will not only help you retain important information but also enhance your ability to apply it in different scenarios.
Effective preparation goes beyond memorization–it’s about developing a comprehensive understanding of how economic principles interact. This will allow you to think critically and respond to problems with clarity and precision.
Microeconomics Exam 1 Study Guide
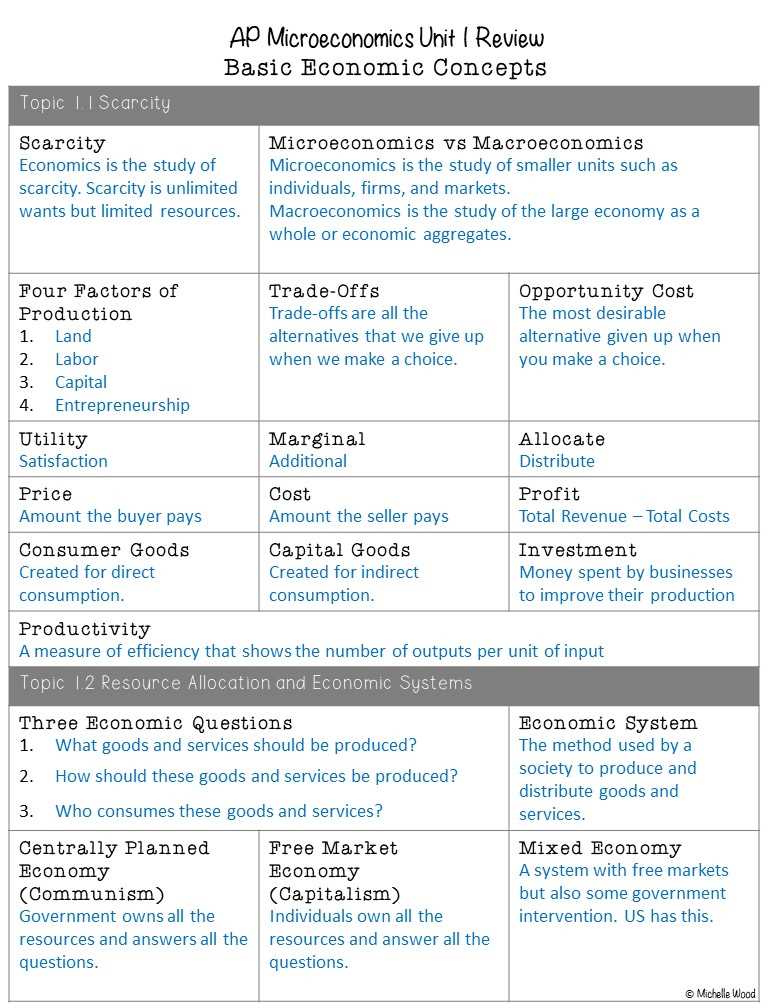
Approaching your first test in economics requires more than just a surface-level understanding. It’s about connecting fundamental concepts and applying them to real-world situations. In this section, we will explore the core topics, helpful strategies, and practical tools to help you perform at your best.
Key Concepts to Focus On
Concentrating on the most essential concepts will ensure a stronger grasp of the material. Here are the key areas to review:
- Market structures and their characteristics
- Supply and demand fundamentals
- Consumer choice theory
- Elasticity and its applications
- Production and cost analysis
Strategies for Effective Preparation
Effective preparation is essential to success. Consider the following methods to optimize your review sessions:
- Organize study time: Break down each topic into manageable sections.
- Focus on problem-solving: Practice applying concepts to different scenarios.
- Review past questions: Understanding the types of questions asked can help guide your preparation.
By focusing on these areas and using these strategies, you will be well-prepared to handle the material with confidence. Make sure to manage your time efficiently and ensure that all major topics are covered. With thoughtful preparation, you’ll be ready to excel in your first assessment.
Understanding Key Economic Principles

Grasping the fundamental principles of economics is essential to navigating the subject effectively. These foundational ideas serve as the building blocks for more complex concepts and practical applications. A clear understanding of these core principles will allow you to analyze real-world scenarios and make informed decisions.
At the heart of economics are the concepts that govern how resources are allocated, how markets function, and how individuals and firms make choices. By familiarizing yourself with these concepts, you will be able to better understand the mechanisms that drive economic activity and shape market outcomes.
- Scarcity: The concept that resources are limited, forcing individuals and societies to make choices about their usage.
- Opportunity Cost: The cost of forgoing the next best alternative when making a decision.
- Marginal Analysis: The evaluation of the additional benefits and costs of a decision.
- Incentives: The factors that motivate individuals and firms to make certain economic decisions.
Mastering these principles will help you better understand how various elements of the economy interact, from consumer behavior to government policy. By applying these ideas, you can develop a deeper insight into how markets operate and why certain economic decisions are made.
Essential Topics to Focus On
To perform well in your upcoming test, it’s crucial to prioritize the most significant topics that are likely to appear. Concentrating on these core areas will ensure you have a strong grasp of the key concepts and are prepared for any question type. These subjects form the foundation of the material and are central to understanding how economic principles are applied.
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Structures | Understand the different types of market systems, including perfect competition, monopolies, and oligopolies. |
| Supply and Demand | Study how price and quantity are determined in markets, and the effects of shifts in supply and demand. |
| Elasticity | Focus on how the responsiveness of quantity demanded or supplied changes with price variations. |
| Production and Costs | Examine how firms produce goods and services, including the role of fixed and variable costs. |
| Consumer Behavior | Learn how individuals make purchasing decisions based on preferences, budget constraints, and utility maximization. |
By dedicating time to these crucial areas, you will ensure that you are well-prepared to tackle the various questions that can appear on your assessment. Understanding these topics will allow you to think critically and apply your knowledge effectively in different economic scenarios.
Tips for Effective Study Sessions
Maximizing the effectiveness of your preparation requires a strategic approach to your review sessions. It’s important to manage your time efficiently, stay focused, and use methods that enhance your retention and understanding of the material. Well-organized study habits can make a significant difference in how well you perform when it counts.
Time Management and Organization
Breaking your preparation into structured sessions will help you stay on track and prevent feeling overwhelmed. Here are a few tips:
- Create a schedule: Set aside specific times each day to review, and prioritize topics based on their importance and complexity.
- Set goals: Establish clear, measurable objectives for each session, such as mastering a specific concept or completing a set of practice questions.
- Take breaks: Avoid burnout by taking short, regular breaks to recharge your focus.
Active Learning Techniques
Active learning will help you engage with the material more deeply. Here are a few techniques that can boost your comprehension:
- Teach others: Explaining concepts to a study partner or even to yourself reinforces your understanding.
- Use flashcards: Create cards for key concepts or terms to test your memory and improve recall.
- Practice problems: Regularly solving problems related to key topics will solidify your skills and help you identify areas that need further review.
By incorporating these strategies, you’ll be better equipped to manage your time effectively, stay motivated, and ensure you’re ready for the test. Stay consistent and focused to maximize your preparation efforts.
Commonly Tested Economic Theories
Understanding the most frequently tested economic theories is essential for success in any assessment. These theories form the foundation of economic analysis and are crucial for answering a wide range of questions. By focusing on these key ideas, you can better understand the underlying principles that govern market behavior and decision-making processes.
Some of the most important theories you’ll encounter revolve around how individuals, firms, and governments make choices in the face of scarcity and resource allocation. Mastering these concepts will allow you to apply your knowledge to real-world scenarios and theoretical questions with greater ease and accuracy.
- Law of Demand and Supply: Explains how the quantity of goods demanded and supplied changes with variations in price, creating market equilibrium.
- Price Elasticity: Describes how the quantity demanded or supplied changes in response to price changes, a crucial concept in understanding consumer behavior.
- Consumer and Producer Surplus: Focuses on the benefits consumers and producers receive from engaging in transactions at market prices.
- Perfect Competition: A market structure where many firms sell identical products, and no single firm can influence the market price.
- Monopoly: A market structure where a single firm controls the entire supply of a product or service, allowing it to set prices unilaterally.
By mastering these essential theories, you will be prepared to tackle a wide variety of questions and develop a deeper understanding of how economic forces shape individual and market behavior.
How to Analyze Market Structures
Analyzing different types of market environments is essential for understanding how businesses and consumers interact. Each market structure has distinct characteristics that influence pricing, competition, and the availability of goods and services. By familiarizing yourself with these structures, you can assess the behavior of firms and predict how changes in the market will affect overall outcomes.
Identifying Market Types
There are several key market types that every economic analysis should include. Understanding these structures will allow you to differentiate between them and apply the right analytical tools:
| Market Type | Key Characteristics | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Perfect Competition | Many firms, identical products, no barriers to entry, and price takers. | Farming, small agricultural markets |
| Monopoly | One firm controls the market, high barriers to entry, unique product. | Utility companies, railroads |
| Oligopoly | Few firms, significant barriers to entry, products may be differentiated or identical. | Telecommunications, airline industry |
| Monopolistic Competition | Many firms, differentiated products, low barriers to entry. | Restaurants, clothing brands |
Analyzing Behavior and Pricing
Each market structure influences how firms set prices, produce goods, and compete. Understanding these behaviors is essential to predicting outcomes and evaluating efficiency in various market scenarios. Pay close attention to factors such as:
- Pricing strategies: How firms determine prices based on market control and competition.
- Barriers to entry: The obstacles that prevent new firms from entering the market, which affects competition.
- Product differentiation: The extent to which products are perceived as unique, which impacts consumer choice and pricing.
By carefully analyzing these structures, you can better understand the forces that shape pricing, production decisions, and market efficiency in different industries.
Mastering Supply and Demand Concepts
Understanding the relationship between supply and demand is fundamental to analyzing how markets operate. These two forces determine the price and quantity of goods in any economy. By grasping the dynamics of supply and demand, you can better predict market outcomes and the effects of various economic shifts.
The law of supply and demand is at the core of market analysis, as it explains how prices fluctuate based on changes in supply and demand levels. When demand increases and supply remains constant, prices tend to rise. Conversely, if supply exceeds demand, prices typically fall. Recognizing these patterns helps in understanding not only market behavior but also broader economic trends.
- Supply Curve: Represents the quantity of a good that producers are willing to offer at different prices. As the price rises, the supply usually increases.
- Demand Curve: Shows the quantity of a good that consumers are willing to buy at different prices. Typically, as the price decreases, demand increases.
- Market Equilibrium: The point where supply and demand curves intersect, indicating the price and quantity where the market clears.
- Shifts in Curves: Factors such as income, preferences, or technology can shift the supply and demand curves, affecting prices and quantities.
Mastering these concepts allows you to understand not only how individual markets function but also how government policies, changes in consumer behavior, and other external factors can affect overall economic performance.
Understanding Elasticity and its Applications
Elasticity measures the responsiveness of one variable to changes in another. In economic terms, it refers to how the quantity demanded or supplied of a good or service changes when its price changes. By understanding elasticity, you can analyze how sensitive consumers and producers are to price changes, which has important implications for pricing strategies, revenue generation, and overall market behavior.
There are several types of elasticity that are crucial for understanding market dynamics:
- Price Elasticity of Demand (PED): This measures how much the quantity demanded of a good changes in response to a change in its price. If demand is highly responsive to price changes, the good is considered elastic; if it’s less responsive, it’s inelastic.
- Price Elasticity of Supply (PES): Similar to PED, but it measures how much the quantity supplied of a good changes in response to a price change. Goods with high elasticity of supply can be produced more quickly as prices rise.
- Income Elasticity of Demand (YED): This refers to how demand for a good changes as consumer income changes. Normal goods see an increase in demand as income rises, while inferior goods see a decrease.
Understanding elasticity is valuable for businesses and policymakers alike. For instance, businesses can use elasticity to set optimal prices that maximize their revenue, while governments may use this knowledge to forecast the impact of taxation or subsidies on consumer behavior. By analyzing how elasticity affects demand and supply, you can gain deeper insights into market efficiency and the economic forces at play.
Examining Consumer and Producer Behavior
Understanding how individuals and firms make decisions in the marketplace is fundamental to analyzing economic activity. Consumers and producers each play critical roles in determining how resources are allocated, goods are distributed, and prices are set. Their decisions are influenced by factors such as prices, preferences, and available technology, shaping the overall functioning of the market.
Consumer Decision-Making
Consumers make purchasing decisions based on their preferences, income, and the prices of goods and services. These decisions are influenced by the concept of utility, which refers to the satisfaction or benefit derived from consuming a good or service. Consumers aim to maximize their total utility given their budget constraints. Several factors influence their choices:
- Price Sensitivity: Consumers often respond to price changes by altering their purchasing behavior. Goods that are more elastic see a greater change in demand when prices fluctuate.
- Income Effects: An increase in income typically leads to higher demand for normal goods, while demand for inferior goods may decrease as consumers’ financial situations improve.
- Substitution and Complementarity: Consumers may substitute one good for another if the price of the former rises, or increase their consumption of complementary goods if the price of one decreases.
Producer Decision-Making
Producers, on the other hand, decide how much of a good to supply based on production costs, technology, and the price at which the good can be sold. Their goal is typically to maximize profit, which is the difference between total revenue and total costs. Several key factors drive producer behavior:
- Production Costs: The cost of raw materials, labor, and other inputs directly impacts the amount a producer is willing to supply at a given price.
- Technology: Advances in technology can reduce production costs and increase the efficiency with which goods are produced, affecting supply levels.
- Market Conditions: Producers adjust their output based on market demand, competition, and potential for profit in different market structures.
By understanding the behaviors of both consumers and producers, you can better analyze how markets function and how changes in external factors, such as government policies or technological innovations, might affect overall economic outcomes.
Strategies for Solving Graph-Based Questions
Graph-based questions are a common and effective way to assess your understanding of key economic concepts. These questions require interpreting and analyzing visual representations of data, such as supply and demand curves, production possibilities frontiers, or cost structures. The ability to correctly interpret these graphs is essential for explaining economic outcomes and drawing meaningful conclusions from data.
Key Steps to Approach Graph-Based Problems
When tackling graph-based questions, it’s crucial to follow a structured approach to ensure that you correctly identify the key elements and relationships. Here are some helpful strategies:
- Label the Axes: Always start by checking the labels of the axes. Understand what each axis represents, as this will guide your interpretation of the graph. The horizontal axis typically represents quantity, while the vertical axis represents price or cost.
- Identify Curves and Lines: Pay attention to the various curves, lines, and shifts in the graph. For example, identify supply and demand curves, and understand what each curve represents. Note if any curves shift and consider the factors that might cause this shift.
- Check for Equilibrium: Many graphs, especially in market analysis, will show equilibrium points where supply and demand meet. Recognizing this point is crucial for understanding price determination and quantity exchanged in a market.
Common Graph Types and Analysis Tips
Different graph types are used to visualize various economic relationships. Here are some common types you may encounter and tips for analyzing them:
- Supply and Demand Graphs: In these graphs, pay attention to the intersection point, as it represents the market equilibrium. Changes in factors such as consumer preferences or production costs will shift these curves, leading to new equilibrium prices and quantities.
- Cost Curves: In production cost graphs, look for key points such as the minimum of the average cost curve or the point where marginal cost equals marginal revenue. These points are critical for understanding profit-maximizing output levels.
- Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF): This graph shows the trade-offs between the production of two goods. Understand the concept of opportunity cost as you interpret shifts along or outside the frontier, which can indicate efficiency or inefficiency in resource allocation.
By following these strategies, you can improve your ability to interpret and solve graph-based questions. Understanding the key elements of the graph and how changes in variables affect the graph’s outcome is crucial for successfully answering these types of questions in an academic setting.
Time Management for Exam Preparation
Effective time management is essential when preparing for any assessment. With limited time and a broad range of topics to cover, it’s crucial to plan and organize your preparation. Properly allocating time ensures that you can review all key concepts, practice problem-solving, and avoid last-minute cramming.
Steps to Plan Your Time Effectively
To maximize your study sessions, it’s important to have a clear strategy. Below are steps to help you allocate your time wisely:
- Set Clear Goals: Define what you need to accomplish during each study session. Break down the material into manageable chunks and focus on mastering one concept at a time.
- Create a Schedule: Develop a study schedule that fits your personal life. Block off specific times for review, practice, and rest. Stick to this plan to maintain consistency.
- Prioritize Topics: Identify the most important topics or those that you find more challenging. Allocate more time to these areas to ensure you are well-prepared.
Techniques to Maximize Your Time
Once you have a schedule, applying effective techniques will help you optimize your preparation. Consider the following approaches:
- Use Active Recall: Instead of passively reading notes, test yourself on the material. This will reinforce your understanding and improve retention.
- Practice Problem-Solving: Work through practice questions or past papers to apply the concepts you’ve learned. This will help you identify weak spots and build confidence.
- Take Regular Breaks: Study in focused intervals (e.g., 25-30 minutes), followed by short breaks. This helps prevent burnout and maintains high levels of focus.
By following these time management strategies, you can approach your preparation with a clear plan, making the most of the available time and enhancing your ability to perform well. Consistent effort, combined with a well-organized schedule, is key to achieving success in any assessment.
How to Tackle Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple choice questions often test a broad understanding of key concepts. With several options to choose from, these questions require careful consideration and strategic thinking. To answer them accurately, it’s important to understand the structure of the question and evaluate each option methodically.
Steps to Approach Multiple Choice Questions
When you encounter a multiple choice question, follow these steps to ensure you make the right choice:
- Read the Question Carefully: Before looking at the options, make sure you fully understand the question. Look for keywords and phrases that can guide you toward the correct answer.
- Eliminate Obvious Incorrect Answers: Start by ruling out the answers that are clearly wrong. This increases your chances of selecting the correct option from the remaining choices.
- Consider Each Option: Go through each remaining option one by one. Don’t rush; consider how each one relates to the question and whether it fits with the concepts you’ve studied.
- Look for Qualifiers: Words like “always,” “never,” “only,” and “most” can give you clues about the validity of an answer. Be cautious with absolute terms as they are often incorrect.
Tips for Maximizing Your Performance
To further enhance your ability to tackle multiple choice questions, consider these additional tips:
- Trust Your First Instinct: If you’re unsure of an answer but feel confident about an initial choice, go with your first instinct. Often, your gut feeling is based on your understanding of the material.
- Don’t Overthink: If you’re stuck, avoid spending too much time on a single question. Move on and come back to it later if needed. It’s better to make an educated guess than to waste valuable time.
- Check for Patterns: If multiple questions seem similar, check for patterns in the answers. This can sometimes give you hints or reinforce the idea behind a concept.
By using these strategies, you can improve your chances of answering multiple choice questions accurately. Careful analysis, elimination, and confidence in your knowledge are the keys to success.
Practice Problems to Improve Skills
Consistent practice is one of the most effective ways to strengthen your understanding and sharpen your problem-solving abilities. By actively engaging with practice questions, you can reinforce the concepts you’ve learned, identify areas for improvement, and increase your confidence in applying theories to real-world scenarios. The more you practice, the better equipped you become to tackle complex questions when it matters most.
Working through a variety of problems allows you to experience different types of questions and challenges, improving both your speed and accuracy. Here are some strategies to help you get the most out of practice problems:
- Start with the Basics: Begin by solving simpler problems that focus on foundational concepts. This helps build a strong understanding before tackling more complicated questions.
- Mix Problem Types: Practice a mix of question types to ensure you are well-prepared for all possible scenarios. Include both conceptual questions and those requiring calculations or graph analysis.
- Track Your Progress: Keep track of your performance over time. Identify patterns in the types of questions you struggle with and focus your efforts on improving those areas.
- Time Yourself: Simulate timed conditions to improve your efficiency. This will help you get used to working under time constraints and increase your confidence in solving problems quickly.
By incorporating these practices into your routine, you will enhance your ability to tackle difficult questions, improve your critical thinking skills, and increase your overall readiness for assessments. Regular practice not only solidifies your knowledge but also boosts your problem-solving speed and accuracy.
Revising Economic Models and Diagrams

Understanding and revising economic models and diagrams is essential for grasping the core concepts of any theory. These visual tools serve as representations of how various economic forces interact, helping to simplify complex ideas. By mastering these models, you can better visualize the relationships between different variables, such as supply and demand, market equilibrium, or production costs. A solid grasp of these tools not only aids in understanding but also improves your ability to apply concepts in various scenarios.
Key Models and Diagrams to Review
As you revise, focus on the most common models and diagrams, which often form the basis for questions. Here are a few important ones to keep in mind:
| Model/Diagram | Key Concepts | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Supply and Demand Curve | Equilibrium, Price determination, Shifts in curves | Market analysis, Price changes, Government policies |
| Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) | Scarcity, Opportunity cost, Efficiency | Resource allocation, Economic trade-offs |
| Cost Curves (AC, MC) | Short-run and long-run cost, Marginal cost | Firm analysis, Profit maximization |
| Indifference Curve | Consumer preferences, Substitution effect | Consumer choice, Budget constraint |
Effective Revision Strategies
When revising these models, it is helpful to break down the process into smaller steps. Focus on the key variables, understand the shifts and movements within the diagrams, and think critically about the factors that could lead to changes in these models. Reviewing real-life examples where these models apply can also enhance your understanding.
- Practice Drawing: Repeatedly draw the diagrams to get comfortable with labeling and identifying key components. This will help reinforce your understanding.
- Understand the Shifts: Focus on understanding the reasons behind shifts in curves or movements along the axes, as these are commonly tested areas.
- Connect to Real-World Examples: Try to relate theoretical models to current economic situations to deepen your understanding of their practical applications.
By systematically revising and practicing economic models and diagrams, you’ll be better prepared to analyze and apply these concepts when needed. Mastery of these tools provides a solid foundation for tackling more advanced topics and complex problem-solving scenarios.
Avoiding Common Exam Mistakes
When preparing for any assessment, it’s easy to overlook certain details that can affect your performance. While understanding the material is important, avoiding common errors can make the difference between a good and great result. Many students find themselves making simple mistakes that could have been avoided with a little more attention to detail. This section will highlight the most frequent pitfalls and offer strategies to ensure you’re fully prepared to tackle any challenge effectively.
One of the most frequent mistakes is misinterpreting the questions or instructions. It’s crucial to carefully read the problem before answering, as even small misunderstandings can lead to incorrect responses. Another common issue is rushing through the answer sheet. While time pressure is inevitable, skipping steps or failing to double-check your work can result in easily avoidable errors.
- Skipping Key Details: Always ensure that you understand every part of the question. Pay close attention to words like “except,” “only,” or “most likely,” which can change the meaning entirely.
- Rushing Through Answers: While it may be tempting to move quickly, taking a moment to think through your response can help avoid careless mistakes.
- Not Reviewing Work: Once you’ve completed the questions, take a few minutes to go over your answers. It’s easy to overlook minor errors that can affect your score.
- Overcomplicating Simple Problems: Sometimes students add unnecessary steps or overthink a question, leading to confusion. Stick to the basics and keep it simple.
By avoiding these mistakes, you can approach any assessment with more confidence and clarity. Practicing mindful reading, staying calm under pressure, and reviewing your answers can help you avoid pitfalls that many students face.
Boosting Confidence Before the Exam
Confidence plays a crucial role in performing well when facing any type of evaluation. Preparing thoroughly is only one part of the equation; the mental aspect–feeling self-assured–can be just as important. Many students experience anxiety and doubt as the day approaches, but there are practical strategies to build confidence and remain focused. This section will offer effective techniques to boost your morale and ensure you’re in the right mindset to excel.
Key Strategies to Enhance Confidence
- Visualize Success: Take a few moments each day to visualize yourself succeeding. Imagine yourself confidently answering questions and recalling key concepts. This mental exercise can help reduce stress and increase self-belief.
- Review and Reinforce: Go over the material that you’ve already studied. Revisiting key points and concepts that you’re comfortable with can provide a sense of mastery and remind you of how much you’ve already learned.
- Practice Under Timed Conditions: Simulate real test conditions by practicing with a timer. This can help you get used to managing time effectively and prevent panic on the day of the assessment.
- Relaxation Techniques: Taking a few minutes for deep breathing, meditation, or stretching can help calm the nerves. A relaxed mind is more effective at recalling information.
Maintaining a Positive Mindset
- Avoid Negative Thinking: Focus on your strengths and past successes. Avoid dwelling on what you haven’t mastered yet. A positive mindset can help reduce anxiety and improve overall performance.
- Stay Organized: A clear study schedule and proper planning allow you to feel in control, minimizing last-minute stress. Knowing exactly what to focus on can ease your mind and boost your confidence.
- Celebrate Small Wins: Recognize and celebrate the progress you’ve made during your preparation. Every bit of knowledge gained adds up, and acknowledging this progress can provide motivation.
By integrating these strategies, you can build a resilient mindset that keeps you calm, focused, and confident. Remember, confidence isn’t about knowing everything–it’s about trusting yourself and your preparation.