AHA Basic Life Support Exam A Answers

When it comes to handling medical emergencies, having the right knowledge and skills can make all the difference. The ability to act quickly and efficiently in critical situations requires a solid understanding of fundamental procedures and techniques that can save lives. Whether you’re preparing for a certification or simply looking to refresh your knowledge, mastering these essential methods is crucial for anyone involved in healthcare or emergency response.
In this guide, we’ll walk through key concepts and practices that are vital for responding to various medical crises. From managing breathing difficulties to performing resuscitation, each section is designed to enhance your confidence and competence. Knowing what to do in an emergency is not just about memorizing steps, but about developing the muscle memory and mental clarity to react decisively.
Focus will be placed on the most important skills, ensuring you’re prepared to handle real-life situations with the confidence of someone who’s trained and informed. These steps are designed to provide clarity and structure, breaking down complex scenarios into simple, actionable tasks. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned professional, this guide will equip you with the tools necessary to perform in high-pressure situations.
AHA Basic Life Support Exam A Answers
In emergency response situations, knowledge of critical techniques is essential. The ability to perform life-saving procedures correctly and swiftly can mean the difference between life and death. This section focuses on common scenarios and key concepts that are often tested in certification assessments. By familiarizing yourself with these, you can improve both your skills and your confidence in handling high-stress medical situations.
Here are the primary topics to focus on when preparing for the test:
- Recognizing signs of cardiac arrest and breathing problems.
- Understanding the correct sequence of actions to take during an emergency.
- Performing chest compressions and rescue breathing effectively.
- Using an automated external defibrillator (AED) safely and efficiently.
Each concept involves specific techniques that need to be mastered. The following questions are designed to assess your understanding of these life-saving actions:
- What is the first step to take when you find an unresponsive patient?
- How do you determine if a person needs chest compressions?
- What is the appropriate compression depth for an adult during CPR?
- What should you do after using an AED on a patient?
These questions are typically structured to evaluate your response time and accuracy in performing each step. Answering them correctly demonstrates a clear understanding of how to react in an emergency and confirms your readiness to perform the necessary actions when required.
Understanding BLS Exam Structure
When preparing for a certification assessment in emergency response, it’s important to understand the framework and organization of the test. The structure is designed to evaluate your ability to perform essential procedures under pressure. The format typically consists of multiple sections, each focusing on different aspects of emergency care. Knowing what to expect and how the questions are structured will help you approach the test with confidence and clarity.
Components of the Assessment
The assessment is divided into several segments that test your practical skills, theoretical knowledge, and decision-making abilities. Each part is carefully crafted to ensure that you can handle real-life situations effectively. The key components often include:
- Multiple-choice questions on emergency protocols and medical conditions.
- Scenario-based questions that simulate real-world situations.
- Practical demonstrations of skills such as CPR and the use of medical equipment.
Preparing for Each Section
Each section requires a different type of preparation. The theoretical questions are designed to test your understanding of emergency procedures and medical knowledge. The practical portion assesses your physical ability to perform tasks accurately and efficiently. Focusing on both areas will ensure you are ready for the assessment and equipped to respond effectively in any emergency.
Key Concepts for Life Support Success
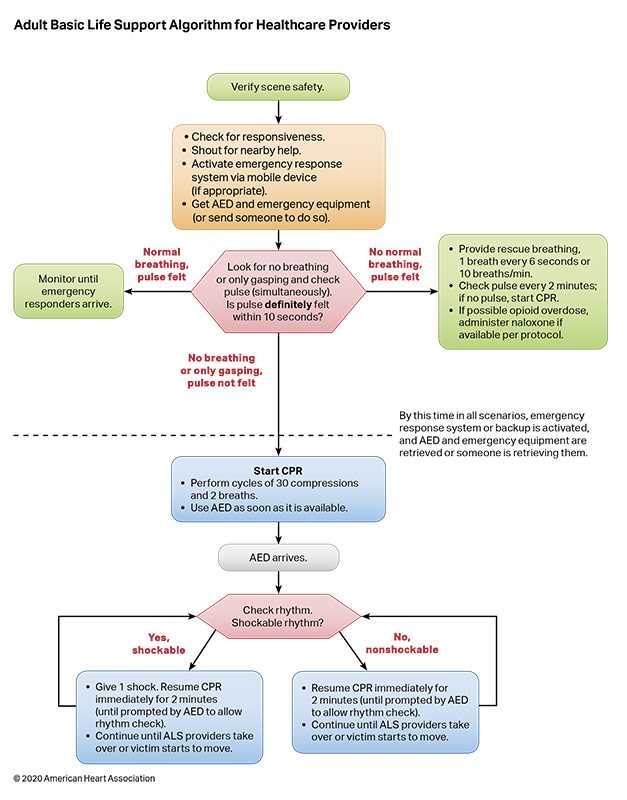
Mastering the essential principles of emergency response is crucial for anyone looking to excel in a certification assessment. The success of providing immediate care hinges on understanding the core concepts that guide life-saving procedures. These principles are not only about knowing what to do, but also about reacting swiftly and accurately when faced with high-pressure situations. By focusing on these key concepts, you ensure that you can perform effectively in real-world emergencies.
Critical concepts to grasp include:
- Prioritizing actions in emergency scenarios based on severity.
- Recognizing signs of distress, such as unresponsiveness and difficulty breathing.
- Performing chest compressions and rescue breathing with proper technique.
- Using defibrillation devices effectively to restore a normal heartbeat.
Understanding these concepts allows you to approach any situation with confidence. It’s not only about performing steps in a certain order, but also about maintaining composure and adapting to the specific needs of each emergency. These principles form the foundation of successful emergency response and play a significant role in ensuring positive outcomes during critical moments.
Essential Skills for BLS Certification
To successfully complete a certification in emergency care, individuals must master several vital skills that are fundamental in responding to medical crises. These abilities are not only tested during assessments but also serve as the foundation for real-life interventions. The goal is to ensure you can react swiftly and correctly, using the proper techniques to stabilize a patient and potentially save lives.
The key skills required for certification include:
- Effective chest compressions – Understanding the correct depth, speed, and technique is essential for maintaining circulation during cardiac emergencies.
- Rescue breathing – Knowing when and how to administer breaths, as well as how to assess whether the patient is breathing adequately.
- Use of an automated external defibrillator (AED) – Properly operating an AED can significantly increase a patient’s chance of survival after a sudden cardiac arrest.
- Airway management – Being able to clear and secure the airway to ensure that the patient is able to breathe properly.
- Rapid decision-making – Assessing the situation quickly to determine the appropriate response and adjusting as conditions change.
These skills are not only about following protocols but also about practicing them until they become second nature. Mastery of these techniques ensures that, when faced with an emergency, you can act with precision and confidence, maximizing the chances of a positive outcome.
CPR Techniques and Best Practices
When responding to a cardiac emergency, performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) correctly is one of the most crucial skills you can have. Effective CPR can significantly increase the chances of survival for a person experiencing cardiac arrest. This section focuses on the key techniques and best practices that ensure CPR is performed efficiently and effectively, maximizing the chances of a successful outcome.
Key Techniques for CPR
There are several fundamental techniques to follow when performing CPR, and each step is essential to maintaining circulation and oxygenating the patient’s vital organs. The most important aspects include:
- Chest Compressions – Provide deep, fast compressions at a rate of 100-120 per minute, ensuring the chest returns to its normal position between compressions.
- Rescue Breathing – Deliver two rescue breaths after every 30 chest compressions, ensuring the airway is open and air enters the lungs effectively.
- Minimize Interruptions – Limit pauses in chest compressions to ensure blood flow is continuous and oxygen is supplied to the brain and heart.
Best Practices for CPR

While mastering the basic techniques is essential, implementing best practices can make all the difference in an emergency situation. These practices will help you stay calm and organized while maximizing the patient’s chances of survival.
- Check responsiveness first – Before starting CPR, ensure the person is unresponsive and not breathing or only gasping.
- Ensure proper hand placement – For adults, place your hands in the center of the chest, ensuring you apply firm pressure without causing injury.
- Use an AED if available – If an automated external defibrillator (AED) is available, use it as soon as possible to analyze the heart rhythm and deliver a shock if necessary.
- Stay calm and focused – Consistency and composure are key during CPR. Stay focused on the task at hand and do not hesitate to ask for assistance if available.
By mastering these techniques and best practices, you can ensure that you’re prepared to respond effectively in any emergency where CPR is required. Proper training and regular practice are essential to becoming proficient and ensuring the best possible outcome for the patient.
How to Approach Certification Test Questions
Preparing for a certification assessment in emergency care involves more than just memorizing procedures; it’s about learning how to think critically and apply knowledge to real-life scenarios. The key to performing well in such tests is developing a strategy for understanding and answering the questions effectively. By mastering this approach, you can increase your chances of success and demonstrate your ability to perform under pressure.
Breaking Down Each Question
When faced with a test question, it’s important to take a moment to analyze and break it down. Instead of rushing to an answer, carefully consider the scenario or the information provided. Follow these steps for a more organized approach:
- Read the question carefully – Understand what is being asked before jumping to any conclusions.
- Identify key details – Focus on crucial information, such as the patient’s condition or the required action.
- Eliminate obviously wrong answers – Narrow down the options by excluding responses that don’t align with established protocols.
- Think about the best outcome – Consider the most effective action that ensures the patient’s safety and follows proper guidelines.
Managing Time and Staying Calm
One of the biggest challenges during a certification test is managing time effectively. It’s easy to get bogged down by difficult questions, but it’s essential to stay calm and pace yourself. If you’re stuck on a question, don’t waste too much time. Move on and come back to it later with a fresh perspective. Trust in your preparation and don’t let stress affect your performance.
By breaking down each question and managing your time well, you can approach the test with a clear strategy. These techniques not only help with answering questions correctly but also build your confidence in handling real-world emergency situations.
Common Mistakes in BLS Exams

When preparing for an assessment in emergency medical response, many candidates make similar errors that can negatively impact their performance. These mistakes often stem from a lack of attention to detail or insufficient practice with key procedures. Understanding these common pitfalls and how to avoid them is crucial for improving your skills and increasing your chances of success during the test.
Some of the most frequent errors include:
- Improper chest compression depth – Failing to push deeply enough during chest compressions can reduce blood circulation, impacting the chances of survival.
- Incorrect hand placement – Positioning your hands too high or too low on the chest can make compressions less effective and may cause injury.
- Skipping rescue breaths – Some candidates skip the vital step of delivering breaths, which can hinder oxygen flow to the lungs and brain.
- Not using the AED early enough – Delaying the use of an automated external defibrillator (AED) can lower the effectiveness of defibrillation during cardiac arrest.
- Long pauses between compressions – Interrupting chest compressions for too long reduces the flow of oxygenated blood to critical organs.
- Failure to reassess the patient’s condition – Neglecting to check the patient’s status regularly during the procedure can result in missed opportunities to adjust the approach as needed.
Being aware of these common mistakes is the first step toward avoiding them. With careful attention to the correct techniques, regular practice, and a calm approach, you can improve your performance and be better prepared to handle emergency situations.
Important Life Support Protocols

When responding to a medical emergency, following established protocols is crucial for ensuring the best possible outcome. These guidelines outline the steps to take in critical situations, providing a clear course of action that helps responders deliver effective care. Knowing and adhering to these protocols ensures that life-saving measures are implemented correctly and efficiently, increasing the chances of survival for those in need.
Some of the most important protocols to follow include:
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) – A fundamental protocol for patients in cardiac arrest, focusing on chest compressions and rescue breathing to maintain circulation and oxygenation.
- Use of automated external defibrillator (AED) – A protocol for applying a defibrillator when a person experiences a sudden cardiac arrest, aiming to restore a normal heart rhythm.
- Airway management – Ensuring that the patient’s airway is clear and open to facilitate proper breathing, using techniques such as head-tilt-chin-lift or jaw thrust.
- Choking intervention – Administering the Heimlich maneuver or back blows to clear an airway obstruction in a conscious patient.
- Bleeding control – Applying pressure, using dressings, or using a tourniquet to control severe bleeding and prevent shock.
- Recovery position – Placing an unconscious, breathing patient in a side-lying position to maintain an open airway and prevent choking or aspiration.
These protocols serve as a framework for managing emergencies in a calm and organized manner. They provide clarity in moments of high stress, ensuring that critical steps are followed and the patient receives the appropriate care. Mastery of these procedures is essential for anyone looking to perform confidently and competently in an emergency situation.
How to Interpret BLS Exam Scenarios
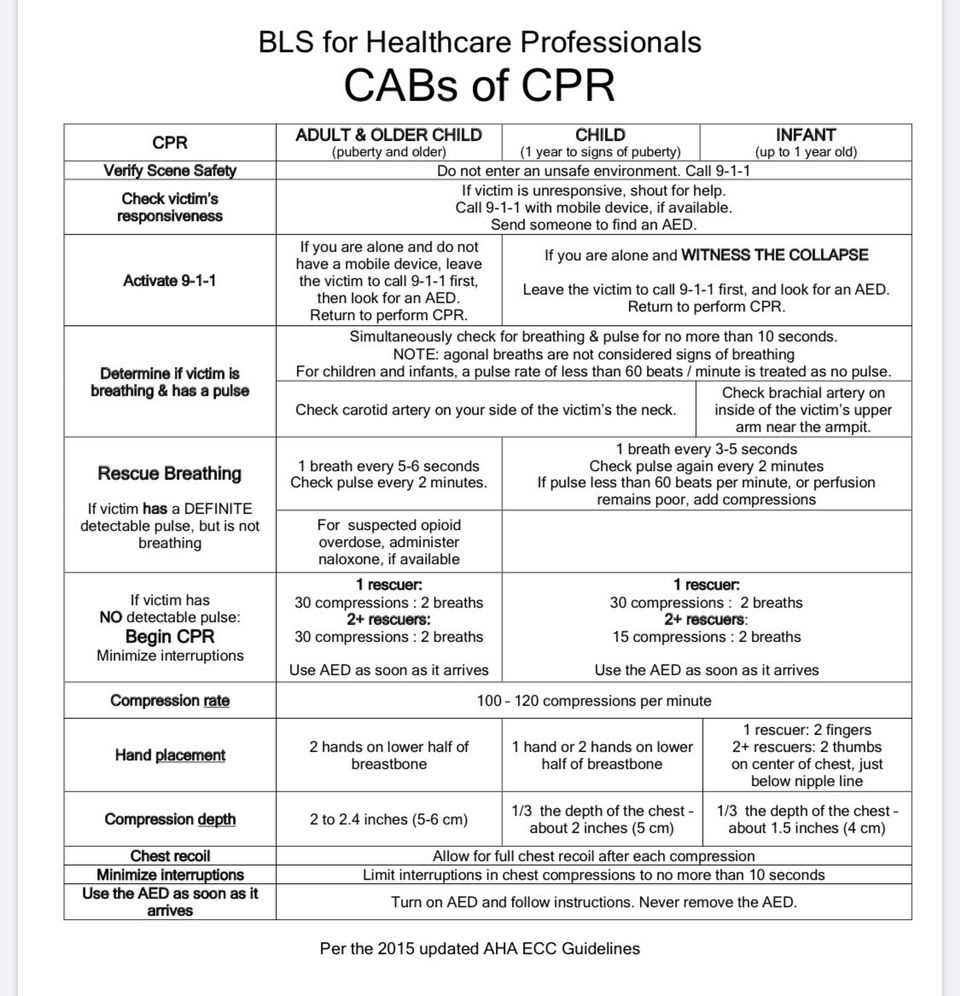
Interpreting scenarios in emergency care assessments requires a clear understanding of the context and the appropriate response. When faced with a scenario, it’s important to focus on the details provided and determine the most effective course of action based on the situation. The ability to analyze these scenarios critically and apply knowledge under pressure is key to performing well in any assessment related to emergency response procedures.
To interpret scenarios effectively, follow these steps:
- Identify the key issue – Pay close attention to the patient’s condition, such as signs of breathing difficulties, unconsciousness, or other critical factors that indicate the severity of the situation.
- Assess the environment – Consider the surroundings, any potential hazards, and available resources, like the presence of an AED or the proximity of medical professionals.
- Determine the priority actions – Based on the scenario, decide which actions need to be taken first. This could include starting chest compressions, providing rescue breaths, or using an AED.
- Stay calm and focused – Clear thinking is essential for interpreting any scenario. Avoid rushing, and make sure your decisions are based on established guidelines and protocols.
By practicing scenario-based thinking and applying established protocols, you’ll be able to quickly and accurately assess any emergency situation. This skill is essential not only for testing purposes but also for real-life situations where every second counts.
Heart Attack Response in BLS Exam
Recognizing and responding to a heart attack during an emergency care assessment is critical. When a patient shows signs of a heart attack, it’s essential to remain calm and follow the correct sequence of actions to maximize the chances of survival. Understanding the proper procedures and prioritizing interventions can make a significant difference in the outcome of the situation. This section highlights the key steps to take when responding to a suspected heart attack during an emergency medical situation.
Immediate Actions for Suspected Heart Attack
When confronted with a person showing signs of a heart attack, it is important to take the following actions:
- Call for help immediately – Ensure that emergency services are contacted as soon as possible. Early medical intervention can significantly improve survival chances.
- Assess the patient’s condition – Look for symptoms such as chest pain, difficulty breathing, nausea, or sweating. These signs can help confirm a heart attack.
- Administer aspirin (if applicable) – If the patient is conscious and not allergic to aspirin, offer them a single dose to help reduce blood clotting, but only if recommended by medical guidelines.
- Monitor the patient’s breathing – If the person becomes unresponsive and stops breathing, initiate CPR immediately while awaiting professional assistance.
Using an AED for Cardiac Arrest
If the patient loses consciousness and stops breathing, it may indicate that a cardiac arrest has occurred. In such cases, using an automated external defibrillator (AED) as soon as possible is essential. Here’s what to do:
- Turn on the AED – Follow the instructions provided by the device. AEDs are designed to be user-friendly and can guide you through the steps.
- Attach the AED pads – Place the pads on the patient’s bare chest as instructed by the AED device.
- Deliver the shock – If advised by the AED, deliver the shock to help restore a normal heart rhythm.
- Continue CPR if needed – After the shock, continue performing chest compressions until emergency services arrive or the patient begins to show signs of life.
By acting quickly and following the appropriate steps, you can significantly improve the patient’s chances of survival during a heart attack. Proper preparation and knowledge of these steps are vital for any emergency responder, ensuring that immediate and effective care is provided in critical moments.
Managing Airway Obstruction During CPR

During cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), ensuring that the airway remains clear is a critical aspect of providing effective care. When a person experiences cardiac arrest, it’s essential to maintain an open airway to allow for proper ventilation. Obstructions, whether caused by the tongue, food, or other foreign objects, can significantly hinder the flow of air into the lungs, reducing the effectiveness of the resuscitation effort. Knowing how to quickly identify and address these blockages can make the difference between life and death.
Here are key steps to manage airway obstruction during CPR:
- Check for visible obstructions – Before starting chest compressions or rescue breathing, check the victim’s mouth for any obvious obstructions. If a foreign object is visible and easy to remove, clear it immediately.
- Open the airway – Use the head-tilt-chin-lift maneuver to open the airway. If a neck injury is suspected, use the jaw-thrust technique instead to avoid further harm.
- Attempt rescue breaths – After opening the airway, give two rescue breaths. If the chest does not rise after the first breath, this may indicate an obstruction. If the chest does rise, continue with CPR.
- Use abdominal thrusts (Heimlich maneuver) – For conscious victims who are choking, administer abdominal thrusts to force the object out. If the person becomes unconscious, begin CPR immediately, starting with chest compressions.
- Continue CPR if needed – If the victim does not regain consciousness or breathing after the attempt to clear the airway, continue chest compressions and rescue breaths as needed until help arrives.
It is essential to remain calm and focused when dealing with airway obstructions. Immediate action can help prevent further complications, such as brain damage due to lack of oxygen. By using the appropriate techniques and staying composed, you can significantly increase the chances of a successful resuscitation in an emergency situation.
Defibrillation Guidelines in BLS

Defibrillation is a critical intervention when responding to certain cardiac emergencies, especially when the heart’s electrical activity becomes irregular, leading to life-threatening arrhythmias. In such situations, applying an electrical shock through a defibrillator can help restore a normal rhythm and increase the chances of survival. Understanding when and how to use this technique effectively is crucial for anyone involved in emergency care. Following the proper defibrillation guidelines ensures that the treatment is applied at the right time, maximizing its potential benefits.
Here are the key guidelines for performing defibrillation during resuscitation efforts:
- Ensure safety first – Before using a defibrillator, make sure the area around the patient is clear of any hazards. Never touch the person while the device is analyzing or delivering a shock.
- Use an automated external defibrillator (AED) – AEDs are designed for ease of use and provide clear step-by-step instructions. Turn on the device and follow the prompts carefully.
- Attach the electrodes – Place the AED pads on the patient’s bare chest, ensuring proper contact with the skin. The device will guide you in positioning the pads correctly.
- Allow the AED to analyze the heart rhythm – The device will assess whether a shock is needed. Avoid touching the patient during this analysis phase.
- Deliver the shock if instructed – If the AED indicates that a shock is required, press the button to administer the shock. Afterward, continue CPR with chest compressions until further assistance arrives or the person starts to show signs of life.
- Continue monitoring – If the person remains unresponsive, repeat the steps as advised by the AED. Perform CPR and defibrillation cycles until emergency responders take over or the individual regains consciousness.
Defibrillation, when used correctly, can be a lifesaving intervention in cases of cardiac arrest. By following these guidelines and using the device properly, responders can significantly improve the patient’s chances of survival during a critical event.
Assessing Breathing and Circulation
Evaluating a person’s ability to breathe and the circulation of blood through the body is a fundamental part of emergency care. These two vital functions are essential for survival, and identifying any abnormalities quickly can make the difference in providing effective treatment. In an emergency situation, it’s crucial to act fast and assess whether the person is breathing properly and if blood is circulating as it should. This process helps guide the responder’s next steps in delivering the appropriate care.
The following table summarizes key steps for assessing breathing and circulation:
| Assessment Step | Action | Signs of Concern |
|---|---|---|
| Check for breathing | Look for chest rise, listen for breath sounds, and feel for airflow. Perform this for no more than 10 seconds. | Absence of chest rise, no breath sounds, or no airflow. Breathing may be irregular or labored. |
| Assess circulation | Check for a pulse by feeling for it at the neck or wrist. Observe skin color and temperature. | No pulse felt, pale or bluish skin, cold extremities. Lack of circulation indicates potential shock or cardiac arrest. |
| Evaluate responsiveness | Gently tap or shout to see if the person responds. Assess whether they are conscious or unconscious. | Unresponsiveness or confusion is a strong indicator that immediate intervention is needed. |
If breathing or circulation is not detected, immediate action must be taken, such as performing CPR or using a defibrillator if indicated. Assessing these vital signs regularly throughout the emergency care process ensures that appropriate interventions are applied at the right time, maximizing the chances of a positive outcome for the individual in distress.
Role of Rescuers in Life Support
In emergency situations, the role of rescuers is crucial to ensuring the survival of individuals who are experiencing medical crises. Rescuers must be prepared to perform a series of actions quickly and efficiently, focusing on maintaining essential functions like breathing and circulation. The effectiveness of their response can significantly impact the outcome of the situation. Rescuers often work in teams, where each person has a specific responsibility to ensure timely and accurate interventions.
Key Responsibilities of Rescuers
- Initial Assessment: Identifying signs of distress and determining the immediate needs of the patient, such as breathing problems or loss of consciousness.
- Immediate Action: Administering necessary procedures, such as chest compressions or airway management, to stabilize the individual.
- Team Coordination: Effective communication with other rescuers to ensure all actions are carried out in a coordinated and timely manner.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Continuously evaluating the patient’s condition and adjusting actions as needed until professional help arrives.
Collaboration and Communication
Clear communication among rescuers is essential for success in emergency situations. Each person must be aware of their role and how their actions support others in the team. Whether it’s sharing information about the patient’s condition or delegating tasks such as calling emergency services or retrieving equipment, teamwork is a vital component of effective care.
Rescuers must also be adaptable, as situations can change rapidly. The ability to shift focus, improvise when necessary, and stay calm under pressure is vital to providing effective assistance in critical moments.
How to Study for BLS Exams
Preparing for a certification test in emergency response requires focus, practice, and a deep understanding of key principles. Successful preparation involves mastering theoretical knowledge, such as protocols and procedures, as well as developing hands-on skills like CPR and airway management. To achieve success, candidates should develop a study plan that combines reading, practice scenarios, and timed tests to simulate the conditions of an actual assessment.
Start by reviewing the core guidelines and best practices for responding to medical emergencies. Understanding the sequence of actions to take in critical situations is essential. Additionally, it’s important to focus on the reasoning behind each procedure so that you can apply the knowledge effectively when faced with real-life challenges.
Another key component is practicing practical skills. Ensure you are comfortable performing techniques such as chest compressions, use of defibrillators, and proper airway clearance. Hands-on training in these areas helps to reinforce your understanding and builds confidence for the assessment.
Lastly, consider using study materials such as practice questions, flashcards, and mock tests to evaluate your readiness. These tools can help you identify areas that require further attention and enhance your ability to recall information under pressure.
Emergency Situations in BLS Training
Training for emergency response involves more than just learning techniques; it also requires understanding how to react effectively in various critical scenarios. Whether it’s a cardiac arrest, choking, or severe trauma, knowing how to assess and manage these situations can mean the difference between life and death. This section covers some of the most common emergency scenarios that practitioners must be prepared for during training.
In emergency response education, simulations are often used to mimic real-life events, providing learners with the opportunity to practice in a controlled, yet realistic environment. Each scenario challenges trainees to think quickly, act decisively, and apply the appropriate procedures. By practicing these situations, individuals are better equipped to respond confidently during actual emergencies.
| Scenario | Key Actions | Common Mistakes |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiac Arrest | Immediate chest compressions, followed by defibrillation if needed | Delaying CPR or not using an AED promptly |
| Choking | Perform Heimlich maneuver or back blows | Not checking for the object after each attempt |
| Severe Bleeding | Apply direct pressure, elevate if possible | Ignoring the need for pressure or waiting too long to act |
In each case, the responder must be familiar with the correct protocol and ready to adapt to the situation’s specific needs. Consistent training in emergency response situations ensures that individuals are able to maintain composure and deliver effective aid when every second counts.
Reviewing BLS Guidelines and Updates

Staying up-to-date with the latest protocols and standards is essential for anyone involved in emergency response. Guidelines in this field are periodically updated to reflect new research, technologies, and best practices. These updates ensure that responders are well-equipped to provide the most effective and efficient care in critical situations. This section focuses on key updates and revisions to existing procedures, highlighting changes that impact daily practice.
Regularly reviewing these guidelines helps ensure that individuals remain informed and prepared for real-world scenarios. New recommendations often emerge following studies, trials, and expert consensus, making it crucial to incorporate these changes into training and response strategies. Here, we examine some of the major updates in emergency care protocols.
| Update | Description | Impact on Practice |
|---|---|---|
| Chest Compression Depth | Recent studies recommend deeper compressions, about 2.4 inches for adults | Improves blood circulation to vital organs during CPR |
| Compression-to-Ventilation Ratio | For untrained bystanders, compression-only CPR is now advised | Simplifies response for laypersons, improving chances of survival |
| Automated External Defibrillators (AED) | New guidelines stress the importance of early AED use, even for children | Reduces mortality by delivering shocks early in cases of cardiac arrest |
Adhering to updated guidelines ensures that responders are following the most effective practices, which in turn leads to better patient outcomes. It is essential that professionals and trainees alike revisit these standards regularly to ensure their readiness in the event of an emergency.