Food Handler Questions and Answers for Safe Practices

Ensuring safety in food preparation environments is crucial for both health and compliance. From managing hygiene to understanding proper techniques, there are numerous practices that professionals must follow to maintain a safe space for meal creation. Clear knowledge of these protocols helps prevent contamination and promotes well-being among consumers.
Maintaining a clean and organized workspace is one of the first steps in reducing the risk of illness. Proper training equips workers with the necessary skills to handle all aspects of the process, from storing ingredients to serving the final dish. Understanding what measures to take when an issue arises is equally important to avoid potential harm.
By addressing common challenges in the kitchen environment, individuals can create a culture of safety that benefits both the workforce and those they serve. These insights help clarify the key actions required for effective management and reduce the occurrence of avoidable mistakes.
Food Handler Questions and Answers

Proper knowledge of best practices is essential for maintaining a safe environment in any kitchen or dining establishment. There are several key points that individuals must be familiar with to ensure hygiene, minimize risks, and handle challenges effectively. Addressing common uncertainties helps strengthen overall safety protocols and ensures that all necessary precautions are taken at every step.
When it comes to preventing contamination, understanding the proper techniques for handling raw materials and cooked items is vital. Common inquiries often focus on the safest ways to store, prepare, and serve meals without compromising quality or health standards. Identifying the appropriate times for cleaning, sanitizing, and personal hygiene practices also plays a central role in maintaining an effective, hazard-free space.
By addressing these crucial aspects, workers can feel more confident in their daily tasks, knowing they are following essential safety guidelines. The ability to quickly respond to potential issues ensures smoother operations and reduces the chances of serious health risks to consumers.
Understanding the Role of Food Handlers
Professionals working in meal preparation play a key part in ensuring the safety and quality of what is served. Their responsibilities extend beyond simple cooking tasks and include maintaining a clean environment, following safety standards, and preventing potential hazards. Their actions impact the health of those consuming the meals and the overall reputation of the establishment.
Core Responsibilities in the Kitchen
One of the primary duties of these individuals is to adhere to hygiene protocols at every stage of the process, from the arrival of ingredients to the final dish being served. This includes proper storage, handling, and sanitization practices to minimize any risk of contamination. Their role also involves staying informed about the latest safety regulations and ensuring that all procedures are followed to protect both consumers and staff.
Training and Knowledge Requirements
Proper training is essential for anyone in this line of work. Understanding food safety principles, such as temperature control, allergen awareness, and cross-contamination prevention, is critical. Workers are often required to undergo certification or continuous education to stay current with industry standards, ensuring they are equipped to handle any challenges that may arise in the kitchen.
Essential Food Safety Practices to Follow
Maintaining a safe environment during meal preparation is critical for preventing contamination and ensuring the well-being of consumers. There are key practices that must be followed to minimize the risk of illness, from proper hygiene to correct temperature management. These actions are crucial at every stage of the process, from receiving raw ingredients to serving the final dish.
One of the most important aspects of safety is ensuring that all surfaces, tools, and utensils are kept clean and sanitized. This prevents the spread of harmful bacteria and pathogens. Equally important is the proper storage of ingredients, keeping perishable items at the right temperature to avoid spoilage and contamination. Regular monitoring of temperature in both cooking and refrigeration processes helps to ensure that food remains safe to consume.
Personal hygiene is another vital component of safety. Workers must wash their hands regularly and wear protective clothing, such as gloves or aprons, to prevent direct contact with food. Avoiding cross-contamination by using separate equipment for raw and cooked items further reduces health risks. Training all involved in meal preparation ensures that everyone is knowledgeable and capable of adhering to these essential guidelines.
Handling Contaminated Food Properly
When harmful substances or bacteria contaminate ingredients, it is crucial to manage the situation quickly and efficiently to prevent the spread of illness. The proper response involves immediate action, including discarding or isolating the affected items, and ensuring that no further contamination occurs. Understanding the right procedures can make the difference in maintaining a safe environment for both staff and consumers.
Steps to Take When Contamination is Identified
Proper identification and action are essential when contaminated items are discovered. Follow these steps to ensure safety:
- Immediately isolate the affected products to prevent cross-contamination.
- Dispose of any items that cannot be salvaged according to safety guidelines.
- Clean and sanitize all surfaces, equipment, and utensils that may have come into contact with the contaminated items.
- Monitor storage areas to ensure that no other items have been compromised.
Preventing Future Contamination
Once the situation has been handled, it’s vital to take steps to avoid a recurrence. This includes:
- Implementing stronger monitoring systems to identify potential risks early.
- Training staff regularly on proper handling techniques and contamination prevention methods.
- Maintaining high standards of cleanliness in all areas where raw materials are prepared or stored.
By following these steps, individuals can minimize the risk of contamination and maintain a safer, healthier environment for everyone involved.
Common Foodborne Illnesses and Prevention

Illnesses caused by contaminated ingredients or improper handling can lead to serious health risks. Understanding the types of common infections and knowing how to prevent them is essential for maintaining a safe environment. These diseases are typically transmitted through improper handling, storage, or preparation, making awareness and proactive measures critical to avoid outbreaks.
Some of the most frequent illnesses are caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites. These pathogens can be present in raw materials or can spread through contaminated surfaces, utensils, or even improper personal hygiene. By recognizing these risks and applying proper safety protocols, individuals can significantly reduce the chance of contamination and illness.
Common Pathogens and Their Effects

- Salmonella: Often found in raw meat and eggs, this bacterium can cause severe stomach cramps, diarrhea, and vomiting.
- E. coli: Typically found in undercooked meat, particularly beef, it can lead to serious gastrointestinal illness and kidney failure.
- Norovirus: A highly contagious virus that spreads through contaminated water or surfaces, causing nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Listeria: This bacterium is often present in unpasteurized dairy products and ready-to-eat meats, leading to fever and muscle aches.
Preventive Measures to Reduce Risk
Implementing safety practices at every stage of meal preparation is essential to prevent these illnesses. Some of the most effective prevention strategies include:
- Always wash hands thoroughly before handling ingredients or preparing meals.
- Ensure all utensils, surfaces, and equipment are cleaned and sanitized regularly.
- Store perishable items at the correct temperature and avoid leaving them out for extended periods.
- Cook raw ingredients to the recommended internal temperature to kill harmful microorganisms.
- Avoid cross-contamination by using separate cutting boards and utensils for raw and cooked items.
By adhering to these guidelines, the risk of foodborne illnesses can be greatly minimized, ensuring the health and safety of all individuals involved in the meal preparation and consumption process.
Personal Hygiene Tips for Food Handlers
Maintaining a high standard of cleanliness is essential for anyone involved in meal preparation. Proper personal hygiene not only protects individuals from illness but also helps prevent contamination of ingredients and surfaces. Simple habits and practices can greatly reduce the risk of harmful bacteria or viruses spreading during the preparation and serving process.
Key Hygiene Practices to Follow

Adopting the following habits is crucial to ensure safety in the kitchen:
- Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water before handling any items, after using the restroom, and after touching surfaces or waste.
- Keep fingernails clean and trimmed to avoid harboring bacteria.
- Wear clean clothing and protective gear, such as gloves or aprons, to prevent direct contact with ingredients.
- Cover cuts or wounds with bandages and gloves to prevent contamination.
Maintaining Clean Work Areas
In addition to personal cleanliness, keeping the work environment tidy is just as important. Ensure all tools, equipment, and work surfaces are cleaned and sanitized regularly to avoid the spread of harmful microorganisms. Store items in clean, dry areas, and avoid leaving ingredients out for long periods to reduce exposure to contaminants.
How to Store Food Safely

Proper storage techniques are vital for preventing contamination and ensuring ingredients remain safe to use. Whether it’s raw materials, prepared dishes, or leftovers, the way items are stored can have a significant impact on their longevity and safety. By following basic principles, you can avoid the growth of harmful bacteria and preserve the quality of what is being prepared or served.
Best Practices for Refrigeration
Keeping perishable items at the right temperature is crucial for reducing the risk of spoilage and foodborne illnesses. Here are key guidelines for proper refrigeration:
- Ensure the refrigerator is set to the correct temperature, typically between 32°F and 40°F (0°C – 4°C).
- Store raw items, such as meat or seafood, on the bottom shelf to prevent juices from contaminating other ingredients.
- Label and date items before storing to ensure older products are used first, following the FIFO (First In, First Out) method.
- Keep the refrigerator clean and free of mold, excess moisture, or spoiled items to avoid cross-contamination.
Safe Practices for Dry Storage
Not all items require refrigeration, but proper dry storage is just as important. To maintain the safety and quality of non-perishable ingredients, follow these steps:
- Store dry goods, such as grains and canned products, in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area.
- Avoid storing items near heat sources or in areas with high humidity, as this can lead to spoilage or pest infestation.
- Keep ingredients in airtight containers to prevent contamination and preserve freshness.
The Importance of Food Temperature Control
Maintaining the right temperature during meal preparation, storage, and serving is essential for preventing the growth of harmful microorganisms. Proper temperature management ensures that ingredients are cooked thoroughly and stored safely, reducing the risk of illness. Whether keeping items hot or cold, temperature control plays a key role in safeguarding health and preserving quality.
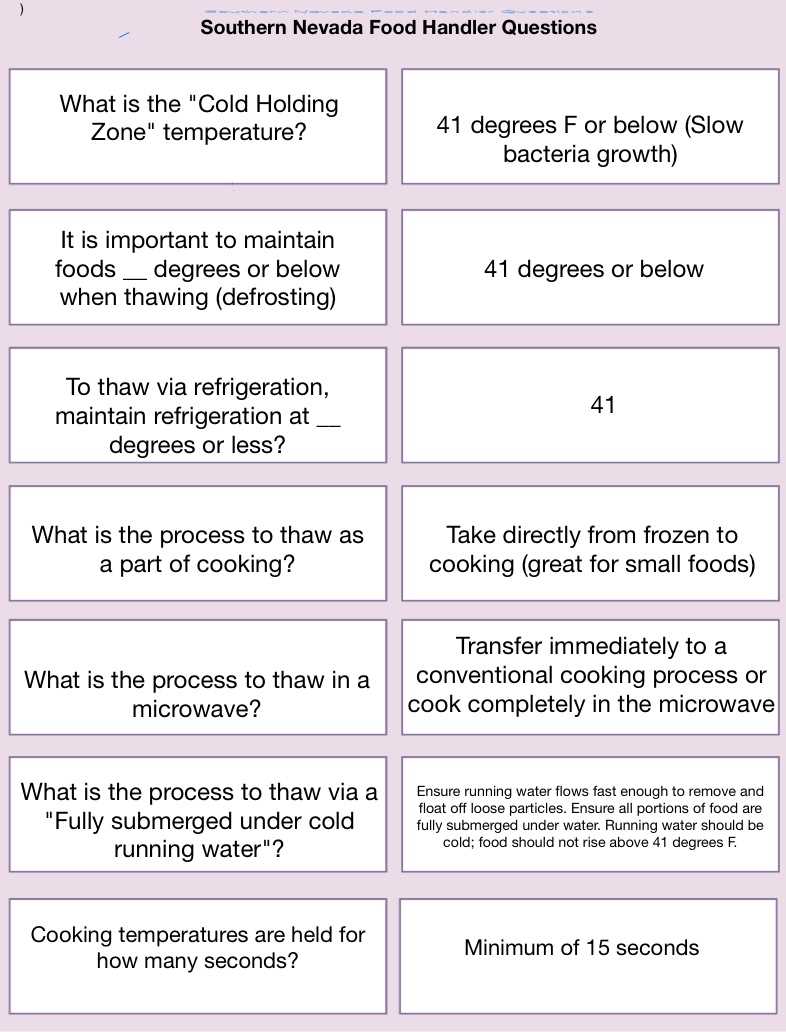
Safe Temperature Ranges for Storage
To prevent harmful bacteria from multiplying, certain temperature ranges must be maintained. The following guidelines help keep ingredients safe:
- Refrigerate perishable items at or below 40°F (4°C) to slow bacterial growth.
- Hot items should be stored at a temperature above 140°F (60°C) to keep pathogens from developing.
- Frozen items should be kept at 0°F (-18°C) or lower to prevent spoilage and preserve freshness.
Cooking and Serving Temperatures
When preparing meals, cooking to the correct internal temperature is critical to kill harmful organisms. The following are the recommended cooking temperatures for various types of ingredients:
- Poultry should be cooked to at least 165°F (74°C).
- Ground meats should reach 160°F (71°C) to ensure safety.
- Seafood should be cooked to 145°F (63°C) for safe consumption.
By closely monitoring temperatures during cooking, storage, and serving, you can greatly reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses and ensure that meals remain safe to consume.
What to Do After a Cross-Contamination Incident
Cross-contamination can occur when harmful microorganisms are transferred from one surface or ingredient to another, posing a serious health risk. Immediate action is crucial to prevent the spread of contaminants and minimize potential harm. Understanding the proper steps to take after an incident can help contain the issue and maintain a safe environment.
The first priority is to identify the source of contamination and isolate the affected area. Once the problem is identified, thorough cleaning and sanitization should take place. All surfaces, utensils, and equipment that may have come into contact with contaminants must be properly disinfected to prevent further spread.
Steps to Take Immediately
- Isolate contaminated items: Remove any affected ingredients or surfaces from the workspace to prevent further exposure.
- Clean and sanitize: Use appropriate cleaning agents to wash surfaces, followed by a disinfectant to ensure the removal of harmful pathogens.
- Dispose of contaminated items: If an ingredient is visibly contaminated or no longer safe, discard it to avoid any risks to health.
Preventing Future Incidents
To avoid recurrence, review the procedures and practices that led to the incident. Ensure all staff members are properly trained on safety protocols and reinforce the importance of maintaining hygiene standards at all times. Additionally, regularly inspect equipment and storage areas to ensure they are being used appropriately and cleaned effectively.
Best Practices for Cleaning and Sanitizing
Maintaining cleanliness in a workspace is crucial to prevent the spread of harmful pathogens and ensure a safe environment. Proper cleaning and sanitizing techniques help eliminate contaminants from surfaces, equipment, and utensils, reducing the risk of illness. A well-established routine for cleaning and sanitizing is essential for any facility that handles consumables.
Effective Cleaning Procedures
Cleaning is the first step in the process, as it removes dirt, grease, and debris. Without proper cleaning, sanitizing agents may not be as effective in eliminating harmful organisms. The following steps should be followed to ensure thorough cleaning:
- Use warm water and soap or detergent to wash surfaces, utensils, and equipment.
- Scrub all areas, paying attention to corners, edges, and hard-to-reach places where dirt can accumulate.
- Rinse with clean water to remove any soap or detergent residue.
Sanitizing After Cleaning

Once the cleaning process is complete, sanitizing is essential to kill any remaining pathogens. Sanitizing agents, such as disinfectants or chemical sanitizers, should be used according to manufacturer instructions for maximum effectiveness. Follow these guidelines for proper sanitizing:
- Apply a sanitizing solution to all cleaned surfaces, utensils, and equipment.
- Allow the sanitizer to sit for the recommended time to ensure it works effectively.
- Rinse with clean water if necessary, especially for food contact surfaces.
By adhering to these best practices for cleaning and sanitizing, you can significantly reduce the risk of contamination and maintain a safe environment for preparation and storage.
Training Requirements for Food Handlers
Proper training is essential for individuals working in environments where consumables are handled, prepared, or served. The goal is to ensure that employees understand safety standards and are equipped to reduce the risk of contamination. Training programs are designed to educate workers about hygiene practices, temperature control, and safe handling techniques to protect public health.
Key Topics Covered in Training
The following table outlines the critical areas that are typically covered during training sessions for individuals in relevant roles:
| Training Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Personal Hygiene | Understanding the importance of cleanliness, handwashing, and proper grooming to prevent contamination. |
| Cross-Contamination | Methods to avoid the transfer of harmful microorganisms between different surfaces, equipment, and ingredients. |
| Temperature Control | Recognizing safe temperature ranges for storage, cooking, and serving to prevent the growth of harmful bacteria. |
| Cleaning and Sanitization | Effective methods for cleaning surfaces, equipment, and utensils to reduce the risk of pathogens. |
| Allergen Awareness | Identifying and preventing cross-contact with common allergens to protect individuals with sensitivities. |
Certification and Recertification
In many regions, it is a legal requirement for workers in relevant sectors to complete certification programs. These programs often involve written tests and practical assessments to confirm that employees have acquired the necessary knowledge and skills. Regular recertification is also important to ensure that employees stay up to date with evolving safety standards and regulations.
Understanding Food Safety Regulations
Comprehending the rules and standards that govern the handling, preparation, and storage of consumables is critical to ensuring public health. Regulations are designed to mitigate the risk of contamination, prevent foodborne illnesses, and maintain the quality and safety of products. Adhering to these guidelines helps create a safer environment for both employees and consumers.
Key Areas of Regulation
The following points outline the major areas covered by safety regulations that must be followed in food-related environments:
- Hygiene Standards: Rules regarding personal cleanliness, handwashing, and the proper handling of raw materials to avoid contamination.
- Temperature Control: Guidelines for maintaining the appropriate temperatures during cooking, cooling, and storage to inhibit bacterial growth.
- Cross-Contamination Prevention: Measures to avoid the transfer of harmful microorganisms from one surface or item to another.
- Sanitation Practices: Instructions for the proper cleaning and sanitizing of equipment, surfaces, and utensils.
- Labeling Requirements: Specifications on how products should be labeled with information such as allergens, expiration dates, and proper storage instructions.
Compliance and Enforcement

Regulations are enforced by governmental agencies that regularly inspect businesses to ensure compliance with safety standards. Non-compliance can result in fines, temporary closures, or other legal actions. It is essential for anyone working in related sectors to stay informed about these laws and implement them rigorously to avoid health risks and legal consequences.
How to Handle Allergens in Food
Ensuring the safety of individuals with sensitivities to certain ingredients is a crucial aspect of working in environments where edible products are prepared or served. Properly managing allergens involves understanding which substances pose a risk and implementing practices to prevent accidental exposure. These precautions are vital to safeguard the health of consumers and comply with regulations.
Preventing Allergen Cross-Contact
To minimize the risk of cross-contact, it is essential to follow these key practices:
- Separate Storage: Store allergenic ingredients separately from other products to avoid contamination.
- Designated Equipment: Use dedicated utensils, cutting boards, and containers for ingredients that contain allergens.
- Thorough Cleaning: Clean surfaces, tools, and equipment thoroughly between tasks to remove any traces of allergens.
- Labeling: Ensure all products are properly labeled with allergen information, making it easier for consumers to identify risks.
Training and Awareness
Employees must receive proper training on identifying allergens, understanding their risks, and how to handle them. Regular refresher courses help reinforce these practices and ensure that everyone in the workplace is aware of their role in preventing allergic reactions. Creating a culture of awareness is key to maintaining a safe environment for all customers.
When to Report Safety Concerns
Identifying and reporting safety issues is critical to maintaining a safe environment. Employees must be vigilant and aware of potential hazards that could jeopardize public health. Promptly reporting these issues ensures that corrective actions can be taken quickly to prevent any risks from escalating.
Situations to Report

There are several situations in which it is essential to report concerns immediately:
| Concern | Reason for Reporting |
|---|---|
| Contamination of products | To prevent harmful substances from spreading and causing illness. |
| Improper temperature control | To avoid bacterial growth that can lead to foodborne illnesses. |
| Unsanitary conditions | To prevent the spread of germs or pathogens that could affect consumers. |
| Expired products | To ensure that spoiled or outdated items are not used or sold. |
| Lack of proper labeling | To protect customers, especially those with allergies or dietary restrictions. |
How to Report
Once a concern is identified, it is important to report it to the appropriate supervisor or authority. Clear communication is key, and employees should ensure that the issue is documented and resolved quickly. In some cases, regulatory bodies may need to be notified depending on the severity of the problem. Being proactive helps maintain high standards of safety and trust within the establishment.
The Role of Gloves in Food Handling
Wearing gloves in environments where items are prepared or served plays a significant part in reducing the risk of contamination. When used properly, gloves can act as a protective barrier between contaminants and consumables. However, improper use can lead to unintended risks, so it’s important to follow best practices for their use and disposal.
When to Use Gloves
Gloves are necessary in several situations to maintain hygiene and prevent cross-contamination. Below is a list of scenarios where wearing gloves is important:
| Situation | Reason for Wearing Gloves |
|---|---|
| Handling ready-to-eat items | To prevent direct contact with potentially harmful bacteria from hands. |
| Handling raw ingredients | To avoid transferring pathogens from raw items to cooked ones. |
| Preparing meals for individuals with allergies | To avoid cross-contact with allergens and protect sensitive consumers. |
| Cleaning and sanitizing | To protect hands from harsh chemicals and contaminants. |
Best Practices for Using Gloves
To ensure gloves provide adequate protection, it’s essential to follow proper guidelines:
- Change gloves frequently: Always replace gloves when switching tasks or after handling raw items.
- Do not touch face or phone: Avoid contact with your face, especially eyes and mouth, while wearing gloves.
- Use gloves as a supplement: Gloves should not replace regular hand washing. Always wash hands before wearing new gloves.
- Proper disposal: Dispose of gloves immediately after use in a designated waste container to avoid contamination.
By adhering to these practices, gloves can significantly enhance hygiene and safety in environments where consumables are prepared or served.
Food Handling Best Practices for Catering
In catering, ensuring that all items are prepared, transported, and served safely is essential to prevent contamination and guarantee the well-being of those consuming the meal. A set of best practices must be followed to avoid risks associated with improper handling, storage, and service.
Essential Practices During Preparation
During the preparation phase, it’s critical to maintain high hygiene standards to ensure safety. Key practices include:
- Keep raw and ready-to-eat items separate: Prevent cross-contamination by using separate equipment and storage areas for raw ingredients and those ready to serve.
- Maintain proper temperature: Keep cold items below 40°F (4°C) and hot items above 140°F (60°C) to inhibit bacterial growth.
- Wash hands frequently: Ensure that everyone involved in food prep washes hands thoroughly before and after handling ingredients, especially after using the restroom or handling waste.
- Use clean utensils: Always sanitize knives, cutting boards, and other utensils before use to prevent transferring bacteria from one item to another.
Safe Transportation and Service
Transporting food from the kitchen to the event location requires careful attention to prevent temperature abuse and contamination. Best practices include:
- Keep items at safe temperatures: Use insulated containers or food warmers to maintain proper temperatures during transport, ensuring that cold foods remain cold and hot foods stay hot.
- Transport in sealed containers: All food should be covered securely during transport to prevent exposure to contaminants and cross-contact with allergens.
- Avoid reusing disposable gloves: Once used for tasks such as handling raw items, disposable gloves should not be reused to touch clean items or prepared dishes.
- Serve quickly: When food reaches the event location, serve it as soon as possible to prevent any delays that could compromise food safety.
By following these best practices, caterers can provide safe, high-quality meals while reducing the risks associated with improper handling and ensuring a positive experience for their clients.
Dealing with Expiration and Waste
Managing expired products and minimizing waste is crucial for maintaining both quality and safety in any establishment. Proper handling of items past their prime can reduce health risks and contribute to a more sustainable environment. Implementing efficient strategies to control spoilage, while also focusing on waste reduction, can lead to a better overall operation.
Understanding Expiration Dates
Expiration dates are guidelines that indicate the optimal period for the freshness and safety of items. It is essential to recognize the difference between “use by” and “best before” dates. Key practices include:
- Regularly check items: Inspect items for signs of spoilage, even if the expiration date hasn’t passed. This includes checking for off smells, discoloration, or unusual textures.
- First in, first out (FIFO): Always use older items first to ensure that nothing is left to expire unnecessarily. Labeling products with the date of purchase can help keep track.
- Monitor storage conditions: Proper storage is crucial to extending the shelf life of products. Keep items in appropriate temperature ranges and avoid overloading storage spaces, which could cause items to deteriorate faster.
Minimizing Waste in the Workplace
Reducing waste not only improves sustainability but can also lower operational costs. Below are some effective strategies:
- Portion control: Accurately measure portions to avoid overproduction, which leads to leftover waste. Training staff on proper portioning can make a big difference.
- Composting: For organic waste, consider composting as a way to repurpose food scraps into valuable soil for gardens or landscaping.
- Repurpose leftovers: Rather than discarding leftovers, look for ways to creatively use them in future meals or in employee meals to reduce waste.
- Donation programs: Consider partnering with local charities to donate unused, but still safe, items before they reach the expiration date.
By paying attention to expiration management and implementing waste reduction methods, establishments can create a more efficient and responsible approach to handling perishable goods.