Organic Chemistry Exam 3 Answer Key
As you prepare for your upcoming test, it’s essential to have a solid grasp on the fundamental concepts and techniques that will be assessed. Understanding the underlying principles of various reactions, mechanisms, and problem-solving strategies will give you an edge in tackling the more complex tasks. This guide will provide clarity on the most frequently tested topics and offer practical steps to approach the most challenging problems.
Focusing on problem-solving is crucial, as many of the questions require not only memorization but also the ability to think critically and apply knowledge in new contexts. This resource aims to help you identify common areas of difficulty, break them down into manageable parts, and approach them with confidence. With the right techniques, every challenge can be overcome.
Test Solutions Plan
Preparing for a challenging assessment requires more than just memorizing facts; it involves a strategic approach to understanding the material and applying knowledge effectively. This section outlines a structured plan to help you navigate the most complex aspects of the test, providing you with a clear roadmap for success. By breaking down key topics and offering insight into effective problem-solving techniques, you can confidently tackle the questions ahead.
First, it’s important to focus on the most critical areas that are likely to appear in the assessment. This includes a deep dive into essential reactions, mechanisms, and principles that form the foundation of the subject. Mastering these core concepts will enable you to approach each question with confidence and clarity.
Next, developing efficient strategies for managing your time during the test is key. With a mix of multiple-choice and detailed response questions, practicing how to quickly identify the best approach for each can save valuable minutes. Stay organized, prioritize, and tackle each problem systematically.
Finally, reviewing past test questions and their solutions can reveal patterns and common types of problems. By studying these examples, you can sharpen your skills and develop a deeper understanding of the topics that require the most attention.
Overview of Test 3 Key Concepts
Understanding the fundamental principles that will be assessed in the third test is essential for effective preparation. This section provides a broad overview of the core topics and methodologies that are central to the subject. By focusing on the most critical concepts, you can better understand the structure of the assessment and approach it with confidence.
The key concepts covered include reaction mechanisms, structural analysis, and functional group behavior. Mastering these areas allows for a deeper understanding of how different compounds interact and transform under various conditions. Focusing on these main ideas will help you navigate complex problems and apply knowledge effectively throughout the test.
In addition to theoretical knowledge, practical skills such as identifying molecular structures and predicting reaction outcomes are equally important. Strengthening your ability to quickly recognize patterns and make accurate predictions is vital for achieving a high score.
Understanding Key Reactions in Science
Mastering the essential reactions is crucial for success in any advanced scientific test. These reactions form the backbone of many complex processes and are vital for solving problems efficiently. A strong grasp of these transformations will not only improve your theoretical understanding but also enhance your practical problem-solving skills during the assessment.
Key reactions often involve specific mechanisms, intermediates, and conditions that determine the outcome. Being able to predict how molecules will behave under different circumstances is an important skill. Below is a table of some critical reactions that are frequently tested and their characteristics:
| Reaction Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Substitution | A process where one atom or group is replaced by another in a molecule. | CH3Cl + NaOH → CH3OH + NaCl |
| Addition | Occurs when two reactants combine to form a single product. | C2H4 + H2 → C2H6 |
| Elimination | Involves the removal of atoms or groups from a molecule, forming a double bond. | C2H5Br → C2H4 + HBr |
| Oxidation-Reduction | Involves the transfer of electrons between substances, changing their oxidation states. | C2H5OH + O2 → CH3CHO + H2O |
Understanding these reactions will give you a solid foundation for solving more complicated problems and help you recognize patterns that are common in tests.
Step-by-Step Guide to Problem Solving
Approaching complex problems requires a methodical process to ensure clarity and accuracy. By breaking down each challenge into manageable steps, you can systematically address each component and find the best solution. This guide provides a structured approach to solving difficult problems efficiently and with confidence.
Identify and Understand the Problem
The first step is to carefully read the question and identify what is being asked. Pay attention to the key details and make sure you understand the underlying concept. Highlight important information such as reaction types, molecular structures, or conditions that need to be considered.
Break Down the Problem into Steps
Once you understand the question, break it into smaller, logical steps. This could involve identifying reactants and products, choosing the right mechanism, or applying a specific formula. Address each step individually and make sure you follow the correct sequence. By breaking down the problem, you make the task less overwhelming and easier to tackle.
After solving each part, double-check your work to ensure consistency and accuracy. Revisit any areas where you’re uncertain and reanalyze the data or steps to confirm that your solution is correct.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When tackling complex problems, it’s easy to fall into common traps that can lead to errors. Recognizing these mistakes and understanding how to avoid them is key to improving your performance. Below are some of the most frequent issues students encounter and tips on how to sidestep them during the assessment.
- Misinterpreting the Question: Sometimes, questions are phrased in a way that can lead to confusion. Be sure to read each question carefully, paying attention to key terms and instructions.
- Overlooking Reaction Conditions: Many reactions require specific conditions, such as temperature or catalysts. Always double-check that you’re applying the correct conditions for each reaction.
- Skipping Units or Conversions: Forgetting to include units or properly convert measurements can lead to incorrect results. Ensure that all units are consistent and appropriately used throughout the solution process.
- Rushing Through Steps: Hasty work often leads to careless mistakes. Take the time to go through each step methodically, even if you are confident in your knowledge.
- Incorrectly Drawing Structures: Drawing molecular structures inaccurately can lead to incorrect answers. Pay attention to bonding, angles, and stereochemistry when sketching structures.
To avoid these mistakes, practice problem-solving with a focus on detail and precision. Additionally, double-check your work whenever possible to catch any errors early in the process.
Test Strategies for Advanced Science
Successfully navigating a challenging assessment involves more than just knowing the material; it requires effective strategies for managing your time, understanding the question types, and applying knowledge efficiently. This section outlines proven approaches to help you maximize your performance and tackle the test with confidence.
A well-planned strategy can significantly reduce stress and improve your ability to recall important concepts quickly. By focusing on key techniques for time management, question prioritization, and systematic problem-solving, you can ensure that you address each task thoroughly while maintaining focus throughout the test.
| Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Time Management | Allocate a specific amount of time to each section, and stick to it. Don’t linger too long on any one question. | Prevents spending too much time on difficult questions and helps you complete the entire test. |
| Start with Easier Questions | Begin with the questions that seem easiest to you. This boosts confidence and helps secure quick points. | Increases early momentum and saves time for more difficult questions later. |
| Elimination Process | For multiple-choice questions, use the process of elimination to narrow down your options before making a final choice. | Improves the chances of selecting the correct answer, even when unsure. |
| Review Your Work | After completing the test, take time to review your answers. Look for any mistakes or missed details. | Helps catch any errors and provides a final opportunity to ensure all questions are answered accurately. |
By applying these strategies, you can approach the test with a calm and focused mindset, ensuring that you’re not only answering questions correctly but also managing your time effectively throughout the assessment.
Breaking Down Reaction Mechanisms
Understanding the sequence of events that lead to a chemical transformation is crucial for solving many problems. Reaction mechanisms describe how reactants are converted into products, step by step, through various intermediates and transitions. A thorough understanding of these processes not only helps in predicting the outcome of reactions but also allows for a deeper understanding of molecular interactions.
Key Steps in Reaction Mechanisms
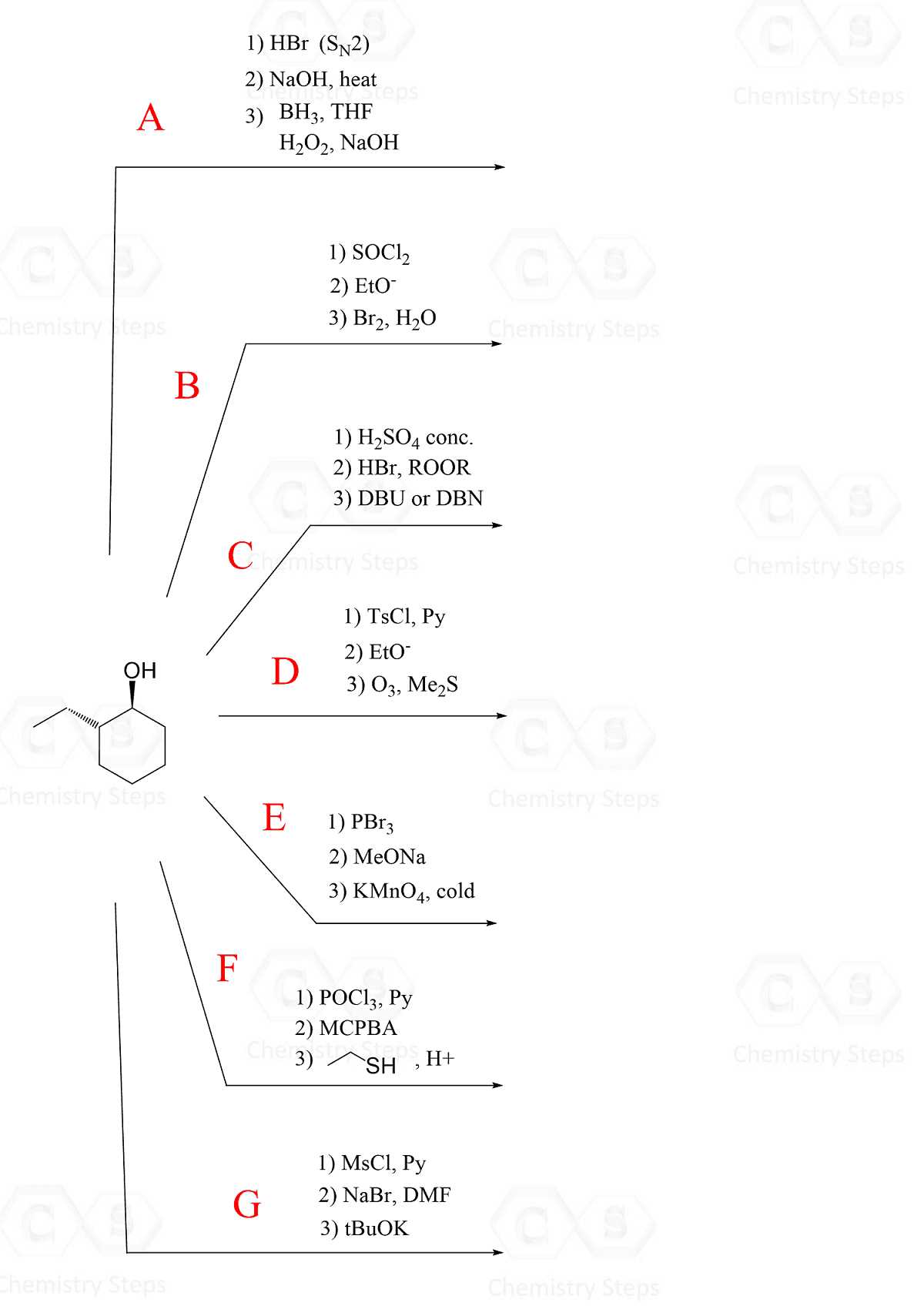
Every reaction proceeds through a series of steps, often involving the breaking and forming of bonds. Identifying these individual steps is crucial for understanding the overall process. In many cases, the reaction follows a specific pathway with characteristic intermediates and transition states that can be tracked and predicted.
Types of Mechanisms
Different reactions follow different mechanisms, which can be broadly categorized into types such as substitution, elimination, and addition. Understanding the type of mechanism helps to predict the conditions under which a reaction will occur and the possible products formed. Each mechanism has its own set of rules and patterns that must be memorized and applied when solving problems.
Essential Formulas for Chemical Reactions
Having a solid understanding of the fundamental equations and relationships in the subject is critical for success in any advanced scientific assessment. These formulas serve as the foundation for solving complex problems, guiding you through calculations and predictions of molecular behavior. Mastering these essential formulas enables you to tackle a wide range of challenges with confidence.
Key formulas often involve calculations for reaction rates, equilibrium constants, and molecular properties. Below are some of the most important relationships to remember:
- Rate Law: Rate = k[A]^n[B]^m – This equation relates the rate of a reaction to the concentrations of reactants.
- Equilibrium Constant (K): K = [products]/[reactants] – Used to describe the ratio of product and reactant concentrations at equilibrium.
- Activation Energy (Ea): k = A e^(-Ea/RT) – Describes how the rate constant varies with temperature and activation energy.
- Hess’s Law: ΔH = ΔH1 + ΔH2 – States that the total enthalpy change of a reaction is the sum of enthalpy changes of intermediate steps.
By keeping these formulas at hand and understanding their applications, you’ll be equipped to solve both theoretical and practical questions in the subject with greater ease and accuracy.
How to Approach Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple choice questions can seem daunting at first, but with the right approach, they can be tackled effectively and efficiently. The key to success lies in how you analyze each option and apply your knowledge to eliminate incorrect answers. By using strategic thinking, you can maximize your chances of selecting the right response, even when you’re uncertain.
Start by reading the question carefully to ensure you understand what is being asked. Focus on identifying key terms and concepts that will guide your decision-making process. Once you understand the question, go through each option methodically and eliminate those that are obviously incorrect.
- Read the Question First: Understand what is being asked before you look at the options. This will help you focus on the relevant information.
- Eliminate Clearly Wrong Answers: Cross out answers that don’t make sense based on your knowledge. This improves your chances if you need to guess.
- Look for Keywords: Pay attention to terms like “always,” “never,” “most likely,” or “least likely,” as they can provide clues about the correct answer.
- Consider All Options: Don’t rush to the first answer that seems correct. Sometimes the best choice is not the most obvious one.
- Use Your Knowledge: Apply what you know about the subject to narrow down the options. If you’re unsure, make an educated guess based on logical reasoning.
By following these steps, you can approach multiple choice questions with more confidence and improve your overall performance on tests.
Understanding Spectroscopy in Assessments
In many advanced scientific assessments, analyzing the results of various techniques used to investigate molecular structures is crucial. Spectroscopic methods allow for the identification and characterization of compounds based on how they interact with light or other forms of energy. Understanding these techniques and their principles is vital for solving a wide range of problems in the subject.
Types of Spectroscopic Techniques

There are several key spectroscopic methods that are commonly encountered. Each technique provides unique information about the structure and properties of molecules, helping to determine their composition and behavior. Below are the most frequently used methods:
- Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy: Measures the absorption of infrared light by a molecule, revealing information about its functional groups.
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy: Provides detailed information about the molecular structure by analyzing the magnetic properties of atomic nuclei.
- Mass Spectrometry (MS): Measures the mass-to-charge ratio of ions, helping to identify the molecular mass and structure of a compound.
- Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-Vis) Spectroscopy: Measures the absorption of ultraviolet or visible light, often used to study electronic transitions in molecules.
Interpreting Spectroscopic Data
When working with spectroscopic data, it’s important to know how to interpret the results in the context of the problem at hand. For example, in IR spectroscopy, the presence of certain absorption peaks can indicate specific functional groups, while NMR spectra can provide information about the arrangement of atoms within a molecule. The key is to match the observed data with known patterns or reference materials to draw accurate conclusions.
By mastering these techniques and understanding how to analyze spectroscopic data, you will be better equipped to solve complex questions and gain deeper insights into molecular structures and their behaviors.
Tips for Tackling Complex Molecules

Dealing with intricate molecular structures can be challenging, especially when multiple functional groups and bonding arrangements are involved. The key to managing complex molecules is breaking them down into smaller, more manageable parts. By understanding the core components and their interactions, you can approach these problems with greater confidence and precision.
Start by identifying the core structure of the molecule. Look for key functional groups, ring systems, or branching patterns that define its framework. Once you have the skeleton, examine the surrounding elements and how they contribute to the molecule’s reactivity and properties.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Identify Functional Groups | Recognize the functional groups that are part of the molecule. This helps in predicting how the molecule will react in different environments. |
| 2. Simplify the Structure | Break the molecule down into simpler components to make understanding the relationships between atoms and bonds easier. |
| 3. Look for Symmetry | Check if the molecule has symmetrical elements, which can simplify the identification of possible reactions or isomers. |
| 4. Understand Stereochemistry | Pay attention to stereochemical aspects like chirality, which affect how the molecule behaves in different chemical contexts. |
| 5. Review Reactions Involving Similar Structures | Refer to known reactions for molecules with similar functional groups or structural elements to predict behavior. |
By applying these strategies, you can effectively break down and understand complex molecules, making it easier to solve problems and gain a deeper understanding of their chemical behavior.
Practice Problems and Their Solutions
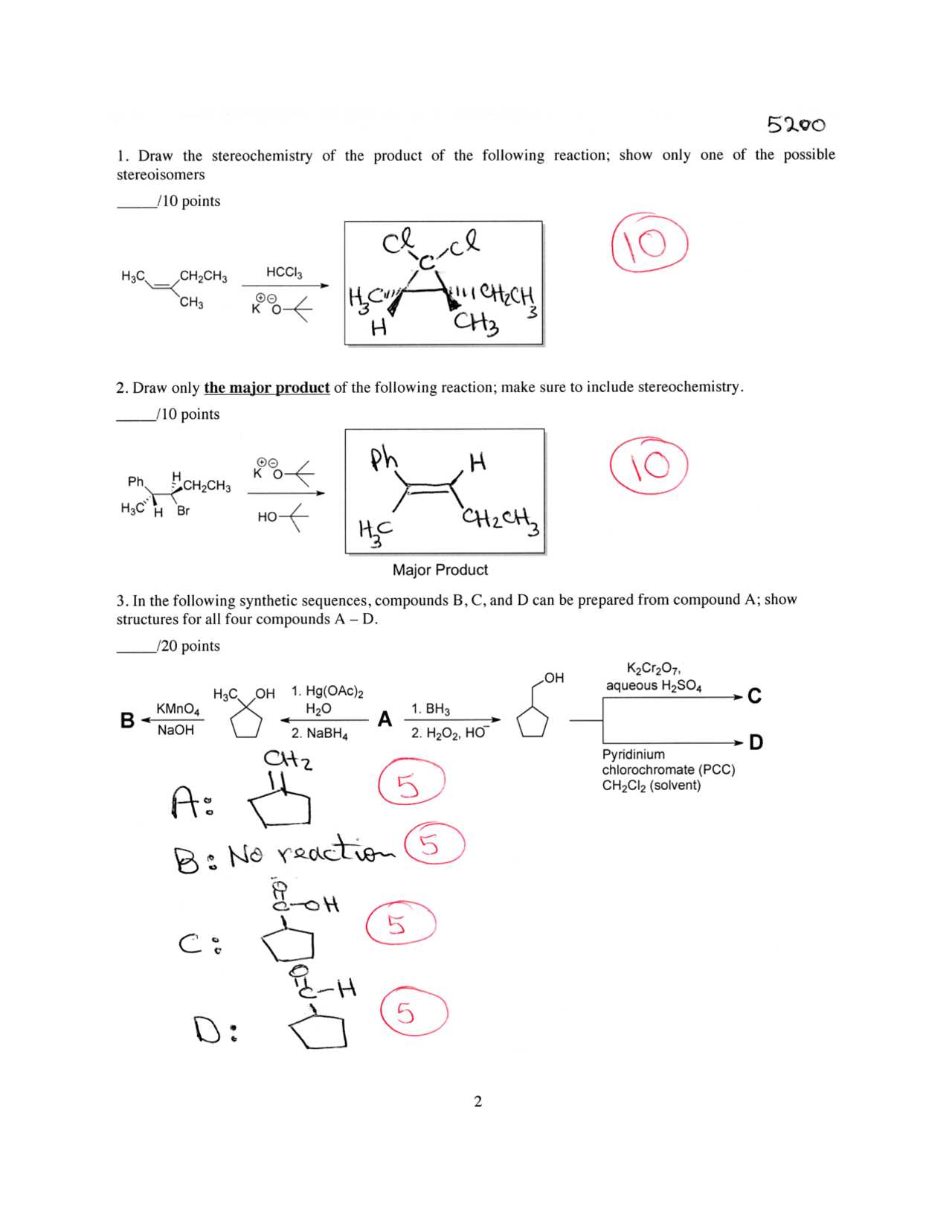
Working through practice problems is an essential method for mastering complex topics. By tackling a range of questions, you can reinforce your understanding and improve your problem-solving abilities. This section provides examples of typical challenges, along with their step-by-step solutions, to help you build confidence and develop effective strategies for tackling similar problems on assessments.
Example 1: Identifying Functional Groups
In this problem, you are asked to identify the key functional groups within a given molecular structure. Follow these steps to break down the structure:
- Examine the molecular framework for recognizable patterns, such as hydroxyl groups, carbonyl groups, or amine groups.
- Identify any specific bonding arrangements, such as double or triple bonds, which indicate the presence of particular functional groups.
- Mark each functional group and ensure that the molecular context is taken into account, such as ring systems or branching chains.
Solution: Upon examining the structure, you will find that the compound contains a hydroxyl group and a carboxylic acid functional group, which are key to understanding its reactivity and potential chemical behavior.
Example 2: Predicting Reaction Products
This problem asks you to predict the product of a reaction between a given molecule and a specific reagent. To solve this, use your knowledge of reaction mechanisms and functional group reactivity.
- Start by analyzing the functional groups in the molecule and determining which are most likely to react with the reagent.
- Next, recall the reaction pathways that involve these groups and how they interact with the reagent under given conditions.
- Consider any possible side reactions or intermediate steps that may occur during the process.
Solution: In this case, the molecule undergoes nucleophilic substitution due to the presence of a halide group, resulting in the formation of a new product with a substituted functional group.
By working through practice problems like these and carefully analyzing their solutions, you can gain a deeper understanding of the material and improve your ability to apply theoretical concepts in practical scenarios.
Importance of Molecular Structures in Exams
Understanding molecular structures is essential for solving a wide range of problems in assessments. The arrangement of atoms within a molecule directly influences its chemical properties, reactivity, and behavior under different conditions. By grasping how atoms are connected and how functional groups interact, you can predict the molecule’s reactivity, stability, and potential transformation during chemical reactions. This foundational knowledge is vital for answering questions related to synthesis, reaction mechanisms, and even spectroscopy interpretation.
Why Molecular Structures Matter
- Predicting Reactions: The structure of a molecule determines how it will behave when exposed to various reagents or environmental conditions. Identifying functional groups and bonding patterns is key to predicting its reactivity.
- Understanding Properties: The physical and chemical properties of a molecule, such as solubility, boiling point, and polarity, are directly related to its structural features.
- Simplifying Problem Solving: By visualizing molecular structures, you can break down complex problems into simpler steps, making it easier to identify possible outcomes or reaction pathways.
Approaching Structure-Based Questions
- Step 1: Start by carefully analyzing the molecular structure provided. Look for key features such as functional groups, bonds, and any symmetrical elements.
- Step 2: Use your knowledge of how different structures react under specific conditions to hypothesize the molecule’s behavior in various scenarios.
- Step 3: Apply the molecular structure to predict potential products, intermediates, or mechanisms involved in a given reaction.
By developing a strong understanding of molecular structures, you can tackle complex problems with greater ease and confidence, ensuring better performance in assessments that test these critical concepts.
How to Manage Time During the Exam
Effective time management is crucial when facing assessments that require both analytical thinking and practical application of concepts. Without a clear strategy, it’s easy to get bogged down in complex problems or misallocate time between sections. By organizing your approach and prioritizing tasks, you can ensure that you tackle all parts of the test efficiently and with confidence.
Steps for Effective Time Management
- Understand the Test Structure: Before you start, quickly scan through the entire test to get a sense of its structure. Note the number of questions and the time allocated for each section.
- Prioritize Questions: Begin with the questions you find easiest to answer. This will help you build momentum and leave more time for difficult problems later on.
- Set Time Limits: Assign a specific amount of time for each section or question. Stick to these limits to avoid spending too long on any one task.
- Don’t Get Stuck: If a question is too time-consuming or difficult, move on to the next one. You can always return to it later with fresh insight.
Tips for Staying on Track

- Use a Watch: Keep track of time throughout the assessment. A simple watch or timer can remind you when to move on to the next question.
- Review Your Work: If time permits, use the last few minutes to quickly review your answers, especially those that seemed uncertain.
- Stay Calm: Stress can lead to rushed decisions or mistakes. Take a deep breath and focus on staying calm and efficient throughout the process.
By planning ahead and managing your time effectively, you’ll be better equipped to complete the test with accuracy, ensuring that you can give each question the attention it deserves.
Reviewing Functional Groups and Reactions
Understanding the role and behavior of functional groups is essential when tackling questions related to molecular transformations. These groups are the building blocks of larger structures and are responsible for most of the chemical properties and reactivity of compounds. By reviewing key functional groups and their typical reactions, you can improve your ability to predict outcomes and identify patterns in various scenarios.
Common Functional Groups
- Alcohols: Compounds containing a hydroxyl group (-OH) that can undergo reactions such as dehydration and oxidation.
- Aldehydes and Ketones: Carbonyl compounds that play a major role in nucleophilic addition reactions.
- Carboxylic Acids: Compounds with a carboxyl group (-COOH) that participate in substitution and esterification reactions.
- Amines: Nitrogen-containing compounds that can act as nucleophiles in substitution and addition reactions.
Important Reaction Mechanisms
- Nucleophilic Substitution: A common reaction where a nucleophile replaces a leaving group in a molecule.
- Electrophilic Addition: A mechanism where an electrophile adds to a nucleophilic site, often seen in alkene reactions.
- Oxidation-Reduction: Redox reactions that involve the transfer of electrons, changing the oxidation states of involved atoms.
- Elimination: A reaction where atoms or groups are removed from a molecule, forming a double or triple bond.
By mastering these functional groups and their corresponding reactions, you’ll be better prepared to navigate complex problems and identify reactivity patterns on your assessments.
Final Preparation Tips for Exam Success

As the assessment day approaches, effective preparation is key to performing well. Understanding the core concepts and practicing the necessary skills will boost your confidence and ensure that you are ready to tackle the toughest questions. Here are some final strategies to maximize your readiness.
Review Core Concepts and Techniques
- Focus on Weak Areas: Identify any topics that you are unsure about and prioritize them during the final days of review.
- Practice Problem Solving: Work through various problems to reinforce your understanding and test your problem-solving speed.
- Understand Key Reactions: Ensure that you are familiar with the main reactions and mechanisms that are commonly tested.
Time Management During Revision
- Create a Schedule: Break your study time into focused blocks with specific goals to avoid cramming at the last minute.
- Practice Under Time Constraints: Simulate exam conditions to build stamina and get used to the time pressure.
- Take Regular Breaks: Allow yourself short breaks between study sessions to refresh and maintain concentration.
Exam Day Preparation
- Rest Well: Ensure you get a full night’s rest before the day of the assessment to be mentally sharp.
- Stay Calm: During the exam, read each question carefully and avoid rushing through any section.
- Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques to remain focused and composed throughout the test.
By following these tips and staying organized, you’ll approach the assessment with clarity and confidence, giving yourself the best chance for success.