Basic Life Support Exam C Answer Key
Preparing for a certification test in emergency medical procedures is crucial for healthcare professionals. This process involves mastering key skills required to respond effectively during critical situations. Knowing the correct methods for providing immediate care can save lives and ensure safety in various emergency scenarios.
In this section, we will explore the different aspects of the assessment, focusing on the techniques and concepts that are critical for passing the test. From chest compressions to airway management, understanding the essential actions required in life-threatening conditions will help ensure readiness and competence. The review of materials and test patterns is designed to enhance your knowledge and build confidence.
By reviewing the correct protocols, you will gain a clearer understanding of what to expect during the certification process. The guidelines provided here will help you grasp essential procedures and increase your chances of success. Whether you’re new to the field or looking to refresh your knowledge, this guide will support your preparation effectively.
Basic Life Support Exam C Answer Key
When preparing for the certification assessment, it’s essential to understand the correct techniques and procedures that ensure effective emergency response. This section outlines the critical concepts, actions, and strategies that are tested. Reviewing these details helps you align with the required standards for performing life-saving interventions and passing the evaluation.
Critical Skills for Success
Success in this evaluation depends on mastering essential procedures that address various emergency situations. Here are the key areas that are typically covered:
- Chest compressions and their correct depth and speed
- Proper use of an automated external defibrillator (AED)
- Recognizing and managing airway obstructions
- Effective mouth-to-mouth ventilation
- Handling cardiac arrest scenarios
Steps to Review and Verify
To ensure readiness, focus on these vital aspects:
- Understand the sequence of actions in critical situations
- Ensure competency in CPR and AED use
- Review the correct protocols for different age groups
- Familiarize yourself with the timing and pressure for compressions
- Double-check your understanding of the safety measures involved
Overview of Basic Life Support Exam C
This section provides an overview of the certification assessment designed to evaluate the proficiency of healthcare professionals in emergency response techniques. The focus is on assessing essential procedures that are critical in saving lives during medical emergencies. Successful completion of this test demonstrates a candidate’s ability to effectively handle critical situations and apply key actions promptly and accurately.
The certification process is structured to cover a range of skills necessary for immediate intervention, including the proper use of devices like automated defibrillators and performing manual resuscitation. This evaluation ensures that healthcare providers are well-prepared to react to various medical emergencies, from cardiac arrest to airway obstructions.
Preparation for the test requires a thorough understanding of the critical actions required to stabilize patients until professional medical care can be provided. A solid grasp of timing, pressure, and technique is essential for success in this assessment.
Importance of BLS Certification for Healthcare Workers
For healthcare professionals, mastering emergency procedures is not just a requirement but a responsibility. Proper certification in critical care techniques ensures that providers are equipped to handle life-threatening situations with confidence and accuracy. These skills are essential in offering immediate assistance until advanced care can be administered, potentially saving lives in the process.
Obtaining certification demonstrates a healthcare worker’s commitment to patient safety and professional competency. Here are some key reasons why this certification is crucial:
- Enhances Patient Outcomes: Quick and effective intervention during emergencies increases survival rates.
- Boosts Confidence: Certified professionals are more likely to remain calm and focused during high-pressure situations.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: Many healthcare settings require proof of certification to meet regulatory and institutional guidelines.
- Prepares for Various Emergencies: Certification ensures readiness for different scenarios, from cardiac arrest to choking incidents.
Healthcare workers with this certification are better positioned to handle critical situations, ultimately improving patient care and ensuring that the best possible outcomes are achieved during emergencies.
How to Prepare for the BLS Exam
Preparing for the certification assessment in emergency medical procedures requires focused study and hands-on practice. Understanding the core skills and techniques, coupled with reviewing protocols, is essential for success. Proper preparation will help you feel confident and ready to perform life-saving actions in real-world scenarios.
Key Areas to Focus On
Familiarize yourself with the essential areas of the test. These include understanding the sequence of interventions, performing resuscitation, and using emergency equipment like defibrillators. Below is a summary of key concepts to concentrate on:
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Chest Compressions | Learn the proper depth, speed, and rhythm for effective compressions. |
| Airway Management | Understand techniques for opening airways and providing ventilation. |
| Defibrillator Use | Know when and how to use an automated external defibrillator (AED) appropriately. |
| Cardiac Arrest Protocols | Review the correct sequence of steps for responding to cardiac emergencies. |
Practical Steps for Preparation

In addition to theoretical knowledge, practice is key. Perform hands-on exercises in simulated emergency settings to build muscle memory and improve reaction times. It’s also important to review instructional materials, attend training sessions, and take practice quizzes to test your knowledge under timed conditions.
Key Concepts Tested in the BLS Exam
In this certification assessment, candidates are evaluated on their knowledge and application of essential procedures needed to respond effectively in medical emergencies. The concepts tested cover critical areas, from performing manual resuscitation to using automated equipment. Mastery of these key skills ensures that professionals can act confidently and competently when faced with life-threatening situations.
Core Skills for Evaluation
The test focuses on several critical skills that are vital for providing immediate care in emergency situations. Below are the main areas of focus:
- Chest Compressions: Proper technique and understanding of the correct depth, rate, and rhythm for effective compressions.
- Ventilation Techniques: Proper methods for providing oxygen to patients, including mouth-to-mouth and using breathing devices.
- Defibrillation: Correct use of automated external defibrillators (AED) during a cardiac arrest event.
- Airway Management: Ensuring the airway is clear and open for proper ventilation.
- Recognition of Emergencies: Identifying symptoms of severe medical conditions like choking, heart attack, and stroke.
Understanding the Response Protocols
Familiarity with the proper sequence of actions during an emergency is critical. Candidates must demonstrate knowledge of what to do first, second, and third in life-threatening situations. This includes the order of performing CPR, using AEDs, and ensuring the safety of the patient and those around them.
Understanding CPR in Basic Life Support
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is one of the most crucial interventions for individuals experiencing cardiac arrest. This technique involves a combination of chest compressions and artificial ventilation, aimed at maintaining circulation and oxygenation until professional help arrives. Mastering CPR ensures that healthcare providers can deliver immediate and effective care during emergencies, potentially saving lives.
CPR focuses on two primary goals: restoring blood flow and providing oxygen to vital organs. The procedure is performed by compressing the chest to circulate blood and using mouth-to-mouth ventilation or other devices to ensure the patient receives enough oxygen. The timing, depth, and speed of the compressions are critical to the success of the intervention.
Key Points to Remember:
- Compression Rate: Chest compressions should be delivered at a rate of 100 to 120 per minute.
- Compression Depth: Compressions must be deep enough, typically about 2 inches, to generate adequate blood flow.
- Airway Management: Ensuring the airway is open and clear is essential for effective ventilation.
- Rescue Breaths: If trained, delivering two breaths after every 30 compressions helps maintain oxygen levels in the bloodstream.
Proper training in CPR is critical for healthcare workers, as it ensures they can deliver high-quality care when faced with life-threatening situations. Practicing these skills regularly is necessary to respond efficiently and confidently during emergencies.
Life-Saving Techniques in BLS Exam
During emergency situations, knowing how to apply life-saving techniques is critical for healthcare providers. These techniques are designed to stabilize patients, manage immediate threats to life, and ensure the patient receives appropriate care until advanced medical help is available. Mastering these procedures is a vital component of emergency medical training and certification.
In the context of this assessment, several key techniques are tested to evaluate a healthcare worker’s readiness to respond efficiently and effectively. These methods are often the difference between life and death, and proper execution is essential. Below are some of the critical life-saving procedures covered:
- Chest Compressions: Performing high-quality compressions to circulate blood and maintain organ function.
- Defibrillation: Using an automated external defibrillator (AED) to restore a normal heart rhythm during a cardiac arrest.
- Airway Management: Ensuring the airway is clear and unobstructed to facilitate breathing.
- Rescue Breathing: Providing oxygen through mouth-to-mouth or mechanical means to maintain oxygenation.
- Choking Relief: Performing the Heimlich maneuver to remove obstructions from the airway in choking victims.
Proficiency in these life-saving techniques is essential not only for passing the assessment but also for ensuring the best possible outcomes in real-world emergencies. Regular practice and review are necessary to retain the skills needed to respond to critical situations with confidence and accuracy.
Exam Format and Structure Explained
Understanding the structure and format of a certification assessment is essential for candidates looking to succeed. This particular evaluation tests your knowledge and skills related to critical emergency procedures. Familiarizing yourself with how the test is organized and what to expect can help reduce anxiety and improve performance during the assessment.
Components of the Assessment
The assessment consists of two main sections: theoretical questions and practical skills evaluation. Each part is designed to measure your understanding of emergency protocols and your ability to perform these tasks under pressure.
- Theoretical Section: Multiple-choice or true/false questions that assess your knowledge of medical protocols, emergency procedures, and safety guidelines.
- Practical Section: A hands-on evaluation where you demonstrate your ability to perform critical interventions like chest compressions, airway management, and defibrillation.
Time and Scoring
The time allotted for the entire assessment varies, but typically, the theoretical portion has a specific time limit, while the practical section is performance-based. Scoring is usually done on a pass/fail basis, with the focus on demonstrating competency in essential life-saving techniques rather than achieving perfect scores in every category.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During the Exam
During the assessment, there are several common errors that candidates tend to make, which can negatively impact their performance. Being aware of these pitfalls and understanding how to avoid them is crucial for ensuring success. Preparation and attention to detail can help you stay focused and improve your chances of passing the certification.
- Skipping Important Steps: Missing crucial steps in emergency procedures, such as forgetting to check for a pulse before starting compressions, can lead to poor outcomes. Always follow the correct sequence of actions.
- Improper Compression Technique: Inadequate depth or rate of chest compressions is a frequent mistake. Make sure to perform compressions at the right depth (about 2 inches) and at a rate of 100-120 per minute.
- Not Ensuring Airway Patency: Neglecting to properly open the airway or ensure it remains clear can prevent effective ventilation. Always check for any blockages and clear the airway before starting ventilation.
- Rushing Through the Process: Many candidates rush through the procedures due to nervousness or lack of practice. Take your time to perform each task with precision and care.
- Failure to Use Equipment Correctly: Not using the automated external defibrillator (AED) or other devices properly is another common mistake. Familiarize yourself with the equipment and how to use it effectively in a real emergency.
- Ignoring Team Communication: In scenarios involving multiple responders, clear communication is key. Failing to coordinate with others can delay actions and reduce effectiveness. Always communicate clearly and calmly with your team members.
By practicing these techniques and focusing on avoiding these common errors, you can improve your performance and increase your confidence during the assessment.
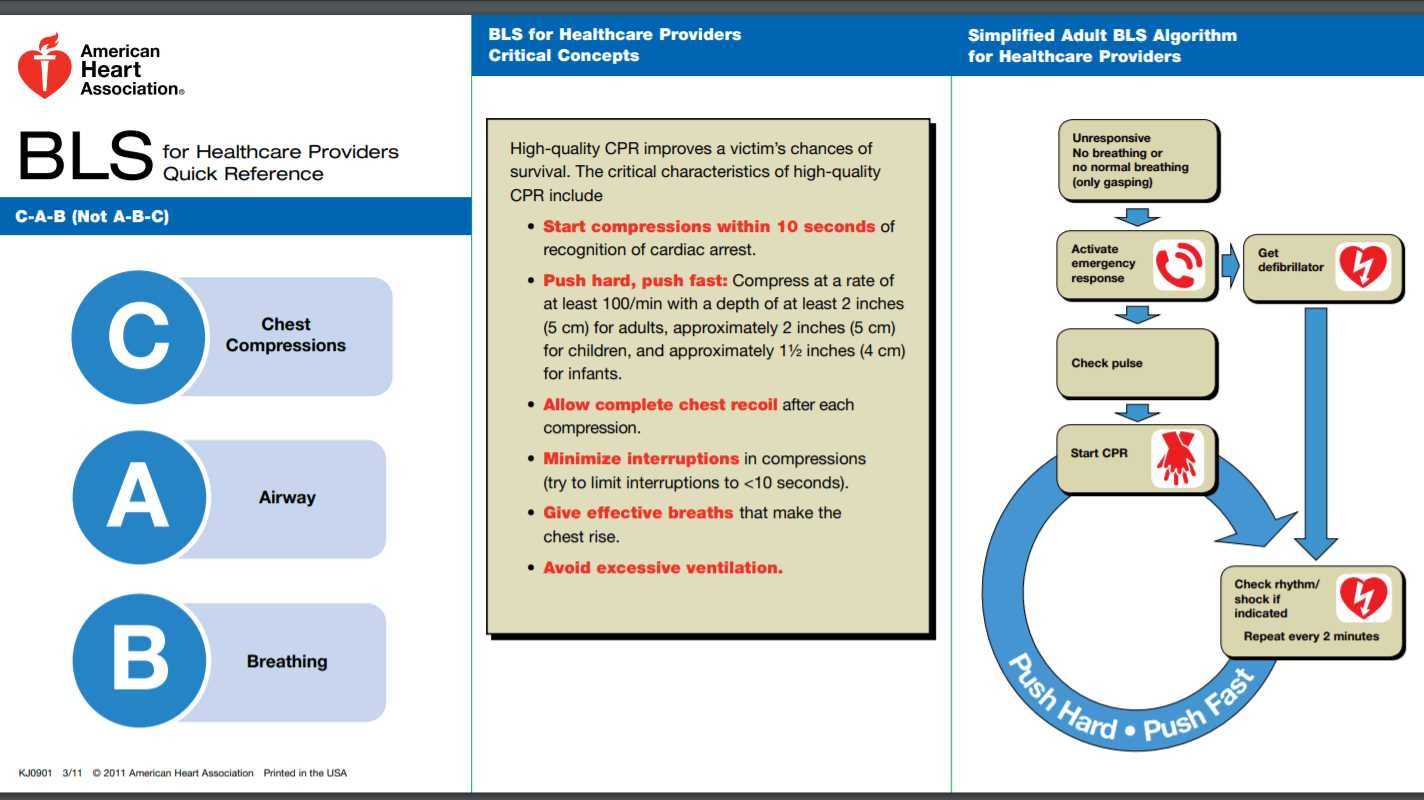
Steps for Effective Chest Compression
Chest compressions are one of the most vital components in providing care during a cardiac emergency. Performing high-quality compressions can significantly improve the chances of survival by maintaining blood circulation to vital organs, especially the brain and heart. Understanding the correct technique and steps to perform effective compressions is essential for anyone involved in emergency response.
Correct Technique for Chest Compressions
When administering chest compressions, it is crucial to follow a precise method to ensure that blood circulates effectively throughout the body. The following steps outline the correct technique:
- Positioning Your Hands: Place the heel of one hand on the center of the chest, just below the sternum. Place your other hand on top of the first, interlocking your fingers.
- Proper Body Position: Ensure that your shoulders are directly over your hands, with your elbows fully extended. This position helps you apply the necessary force while maintaining efficiency.
- Compression Depth: Compress the chest to a depth of at least 2 inches (5 cm) for adults. This depth ensures adequate blood flow to vital organs.
- Compression Rate: Perform compressions at a rate of 100 to 120 per minute, aiming to provide a consistent rhythm without pausing for too long between compressions.
- Allow Full Recoil: After each compression, let the chest fully rise before performing the next compression. This allows the heart to refill with blood, ensuring effective circulation.
- Avoid Over-compressing: Do not push too deep as this could cause injury to the patient or reduce the effectiveness of your compressions. Maintain the proper depth and rhythm throughout.
Additional Considerations
It is essential to monitor your technique throughout the process. If you become fatigued or cannot maintain proper depth and rate, consider switching with another trained rescuer. Effective chest compressions are physically demanding, but they are crucial in keeping the patient alive until advanced medical help arrives.
How to Handle a Cardiac Arrest Situation
Cardiac arrest is a life-threatening emergency that requires immediate action. The inability of the heart to pump blood effectively means that vital organs, especially the brain, are deprived of oxygen. In such situations, quick intervention can make the difference between life and death. Understanding how to respond calmly and effectively is crucial for anyone facing this type of emergency.
The first priority is to recognize the signs of cardiac arrest, which include sudden collapse, lack of pulse, and unresponsiveness. Once this is confirmed, it’s essential to act fast by following a series of critical steps to help increase the chances of survival until professional medical assistance arrives.
Step-by-Step Approach
Follow these steps to manage a cardiac arrest situation:
- Ensure Safety: Before approaching the individual, make sure the environment is safe for both you and the victim. Look for any hazards such as traffic, fire, or electrical risks.
- Check for Responsiveness: Gently tap the person and shout to see if they respond. If they are unresponsive, immediately call for help or instruct someone else to do so.
- Start Chest Compressions: If the person is unresponsive and not breathing, begin chest compressions immediately. Position your hands in the center of the chest and press down firmly, ensuring a depth of at least 2 inches.
- Use an AED: If available, quickly apply an automated external defibrillator (AED). Follow the voice prompts and allow the device to assess the heart’s rhythm. If a shock is advised, administer it promptly.
- Continue CPR: Keep performing chest compressions and ventilation (if trained) until emergency medical services (EMS) arrive or the person shows signs of recovery, such as breathing or movement.
Staying calm and focused is key during a cardiac arrest emergency. By following these steps correctly, you can provide life-saving support that increases the chances of survival until professional help takes over.
Guidelines for Using an AED
An automated external defibrillator (AED) is a vital tool in emergencies where the heart stops beating effectively, such as during sudden cardiac arrest. The device can analyze the heart’s rhythm and, if necessary, deliver a shock to restore normal function. Knowing how to operate an AED can greatly increase the chances of survival for someone experiencing a cardiac emergency.
While AEDs are designed to be user-friendly, it is important to understand the basic steps for its correct use. The following guidelines outline how to safely and effectively use an AED in an emergency situation.
Step-by-Step Instructions for Using an AED
Follow these instructions when using an AED:
- Assess the Situation: Confirm that the person is unresponsive and not breathing. If there is no pulse, call emergency services immediately and begin CPR.
- Turn on the AED: Once you have the AED, turn it on by pressing the power button. The device will provide step-by-step prompts on what to do next.
- Attach the Pads: Place the adhesive electrode pads on the patient’s bare chest as indicated on the device. One pad should go on the upper right side of the chest, just below the collarbone, and the other on the lower left side, just below the ribcage.
- Let the AED Analyze the Heart Rhythm: Ensure no one is touching the patient while the AED analyzes the heart’s rhythm. The device will notify you if a shock is required.
- Deliver the Shock: If the AED advises a shock, make sure everyone is clear of the person, then press the shock button. The device will deliver a shock to the chest to attempt to restart the heart.
- Continue CPR: After the shock is delivered, or if no shock is advised, continue with CPR (chest compressions and rescue breaths) as directed by the AED until emergency help arrives or the patient shows signs of recovery.
Using an AED is an essential skill that can save lives. By following these clear steps, even someone with minimal training can provide critical care in a time-sensitive situation and help improve the survival rate in cardiac emergencies.
Importance of Airway Management in BLS
Ensuring an open airway is one of the most critical steps in emergency situations where a person is unable to breathe effectively. Without proper airway management, even the best efforts at resuscitation can fail, as the body’s organs, especially the brain, require a constant supply of oxygen. During emergencies, it is essential to prioritize airway management to prevent suffocation and support overall recovery.
The airway refers to the passage that allows air to reach the lungs. In situations such as choking, drowning, or cardiac arrest, the airway can become blocked or compromised. In such cases, medical professionals or responders need to take immediate action to clear the airway and restore normal breathing.
Key Airway Management Techniques
Several methods can be used to maintain or clear the airway effectively:
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Head-Tilt, Chin-Lift | This maneuver helps open the airway by tilting the head back and lifting the chin. It is the first step in clearing an obstructed airway in a victim who is unconscious. |
| Jaw-Thrust | This method is used when a spinal injury is suspected. It involves thrusting the jaw forward to open the airway while minimizing movement of the neck and spine. |
| Airway Suctioning | Used when there is an obstruction such as vomit, blood, or secretions in the airway. A suction device can help clear the airway and restore proper airflow. |
| Insertion of an Oropharyngeal Airway (OPA) | This device is inserted into the mouth to maintain an open airway, especially in unconscious individuals, by preventing the tongue from blocking the airway. |
Proper airway management is a skill that can save lives in emergency situations. By ensuring the airway remains clear and open, responders can facilitate better oxygenation, enhance the effectiveness of chest compressions, and increase the chances of successful resuscitation. Immediate attention to the airway can make a significant difference in the outcome of a medical emergency.
Legal Considerations in Performing BLS
When providing emergency care to an individual, it is important to be aware of the legal implications that may arise. Rescuers must understand the boundaries of their actions and the protections offered by the law to ensure that they are acting in the best interest of the patient, while also protecting themselves from potential legal consequences. The law provides certain rights and obligations for those administering emergency care, and being informed can help avoid complications.
In many jurisdictions, individuals who offer assistance during an emergency situation are protected by “Good Samaritan” laws. These laws are designed to encourage people to help others in distress without the fear of legal repercussions. However, these protections usually apply when the responder acts within the scope of their training and does not engage in gross negligence or misconduct.
Good Samaritan Laws
Good Samaritan laws are put in place to protect well-intentioned individuals who step in to provide aid in an emergency. Key points include:
- The law typically covers healthcare professionals and trained individuals, such as those certified in first aid or emergency care.
- Protection is only extended when care is provided voluntarily and without compensation.
- The responder must act in a reasonable and prudent manner, within the scope of their training.
- Protection does not extend to actions that cause harm due to gross negligence or intentional misconduct.
Informed Consent

Obtaining consent from the victim, if they are conscious, is another important legal consideration. In cases where a person is incapacitated, the law assumes implied consent, meaning that the individual would likely agree to receive help if they were able to. However, if the person is conscious and able to communicate, they must consent before any intervention is performed. Failing to obtain consent in such situations may lead to legal ramifications, including accusations of battery or negligence.
Understanding the legal framework within which emergency care is provided ensures that responders can offer help without fear of legal retribution. It also reinforces the importance of acting within the limits of one’s training and expertise while prioritizing the safety and well-being of the individual in need of assistance.
Reviewing the BLS Exam Answer Key
Reviewing your performance on a certification test is an essential part of mastering the skills and knowledge required for effective emergency response. Going over the results of the test allows individuals to identify areas where they may need improvement and reinforces their understanding of critical concepts. This process helps ensure that responders are fully prepared to provide high-quality assistance in emergency situations.
When reviewing the results, it is important to focus on understanding the rationale behind each correct and incorrect answer. This approach not only clarifies why certain actions are necessary but also deepens comprehension of the underlying principles that guide effective emergency care. Through careful examination, learners can refine their abilities and gain greater confidence in their skills.
Common Areas for Review
Some common areas where test-takers may seek clarification include:
- Proper techniques for administering chest compressions and ventilation.
- Recognizing the signs of cardiac arrest and determining when to initiate CPR.
- Knowing when and how to use an automated external defibrillator (AED).
- Understanding the steps for opening and maintaining an airway in unconscious individuals.
- Legal and ethical considerations when providing emergency assistance.
Review Table: Key Concepts and Correct Procedures

| Topic | Correct Procedure | Common Mistakes |
|---|---|---|
| Chest Compressions | Maintain a compression depth of at least 2 inches and a rate of 100-120 per minute. | Not providing deep enough compressions or improper hand placement. |
| Ventilation | Give two full breaths after every 30 compressions. | Incorrectly sealing the airway or providing inadequate breaths. |
| AED Use | Turn on the device, attach pads to the chest, and follow voice prompts. | Not checking the victim’s pulse before using the AED or using it incorrectly on a child. |
| Airway Management | Use the head-tilt, chin-lift maneuver to open the airway. | Forgetting to clear the airway before providing breaths. |
By carefully reviewing these key concepts, test-takers can ensure they are fully prepared to respond effectively during an emergency. Understanding the rationale behind each procedure helps reinforce learning and prepares individuals to act with confidence in high-pressure situations.
Tips for Achieving a High Score on BLS Exam
Preparing for any certification test can be challenging, but with the right strategies, you can increase your chances of success. The key to excelling on a certification test focused on emergency response lies in both understanding the material thoroughly and practicing essential skills regularly. By focusing on important concepts and mastering the necessary techniques, you can approach the assessment with confidence and achieve a high score.
Here are some practical tips to help you prepare effectively:
Effective Study Techniques
- Understand Key Concepts: Familiarize yourself with the most critical elements, such as chest compressions, ventilation, and the use of defibrillators. Understanding the rationale behind these procedures will ensure that you apply them correctly in real-life scenarios.
- Practice Hands-On Skills: Make sure to practice performing key actions, such as delivering chest compressions and using an AED. Regular hands-on practice helps reinforce your knowledge and improves muscle memory.
- Take Practice Tests: Use practice tests to simulate the actual test environment. This will help you get comfortable with the format and identify areas where you may need additional review.
- Review Incorrect Answers: When taking practice quizzes, spend time reviewing incorrect answers. Understanding why certain answers are wrong will help you avoid similar mistakes during the actual assessment.
Preparation Before the Test
- Get Plenty of Rest: Ensure you are well-rested before the test. Fatigue can impair your ability to focus and recall key information during the assessment.
- Stay Calm and Focused: During the test, maintain a calm and focused mindset. Take deep breaths if you feel stressed and remember that the test is designed to assess your readiness to perform well under pressure.
- Know the Test Format: Familiarize yourself with the structure of the assessment. Understanding how questions are framed and what types of scenarios you may encounter will help you feel more prepared and less anxious.
During the Test
- Read Questions Carefully: Pay attention to the wording of each question and ensure that you understand what is being asked before selecting your answer.
- Use Process of Elimination: If you’re unsure about a question, use the process of elimination to rule out incorrect answers. This can increase your chances of selecting the right response.
- Stay Positive: Approach each question with a positive mindset. If you’re uncertain, stay calm and move on to the next question if necessary, coming back to it later.
By following these strategies, you can maximize your chances of achieving a high score and feel confident in your ability to provide effective care in emergency situations. Remember that consistent practice and a solid understanding of key concepts are essential for success.