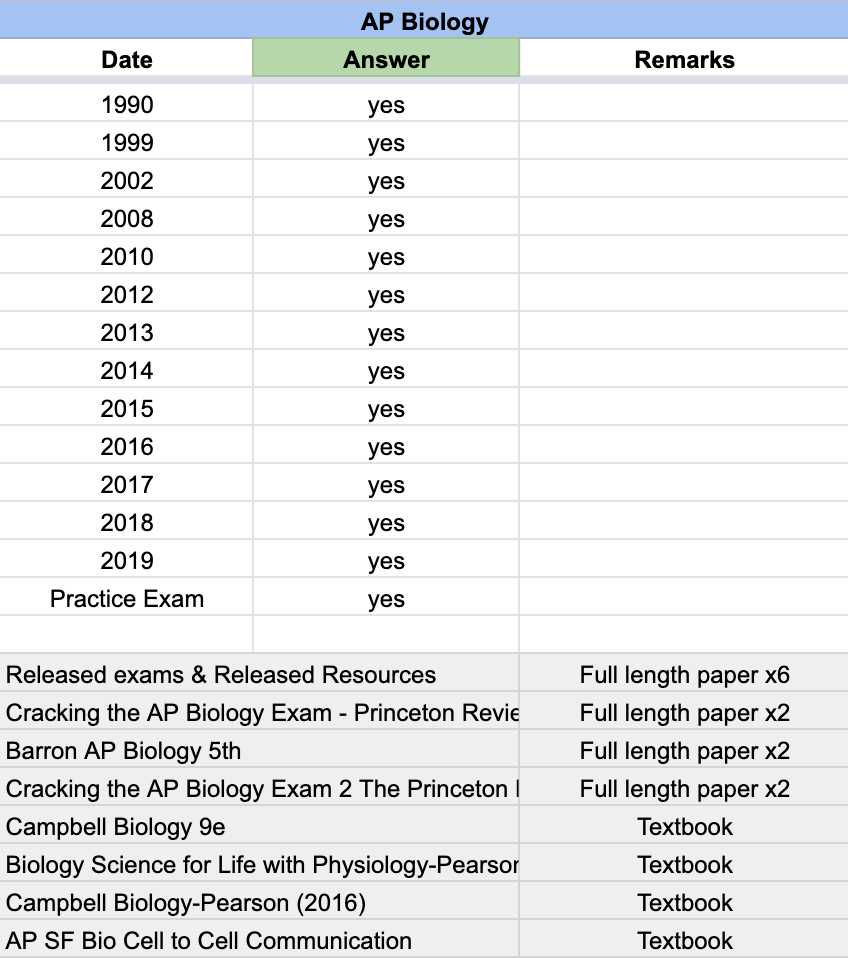
AP Biology Exam Questions and Answers Guide

Preparing for an advanced assessment requires a deep understanding of various scientific concepts. This process involves mastering a broad range of topics, each requiring focused study and practice. To succeed, it’s essential to develop a strategy that highlights key areas, strengthens weak points, and builds confidence in tackling complex material.
Familiarity with core principles is the foundation of effective preparation. By reviewing important theories, principles, and methods, students can better grasp the connections between different topics. Through consistent practice and revisiting challenging sections, one can gain a comprehensive understanding and improve their overall performance.
Mastering critical techniques plays a crucial role in successfully answering challenging prompts. This not only includes theoretical knowledge but also understanding how to apply it under pressure. With the right approach, anyone can enhance their ability to answer questions accurately and efficiently, ensuring success when it matters most.
AP Test Review: Essential Practice

Achieving success in advanced assessments requires careful preparation, particularly when it comes to mastering key concepts. Understanding the structure of prompts and being able to respond accurately is vital. Focusing on core areas, applying learned principles, and practicing different types of tasks will boost confidence and performance.
Key Areas to Focus On

- Cell Structure and Functions
- Genetic Principles
- Evolutionary Concepts
- Ecological Systems
- Energy Flow and Biochemical Reactions
Effective Study Strategies
- Review practice materials regularly to reinforce knowledge.
- Focus on both theoretical concepts and their real-world applications.
- Take timed practice tests to simulate the actual environment.
- Utilize study guides and peer discussions to clarify doubts.
- Break down complex topics into simpler, more manageable sections.
By focusing on these areas and practicing consistently, you can significantly improve your ability to answer complex tasks. Effective time management and strategic review will ensure better results when it’s time to take the test.
Essential Topics for the AP Test
To succeed in any challenging assessment, it’s important to focus on the most critical concepts. A deep understanding of core scientific principles will help you confidently approach various tasks. Mastering these key topics ensures that you are well-prepared for the variety of prompts that might appear.
Key Concepts to Master
- Cell Structure and Function
- Genetic Inheritance and Molecular Mechanisms
- Evolutionary Theories and Processes
- Ecological Interactions and Environmental Systems
- Biochemical Pathways and Energy Transfer
Important Themes to Explore
- Membrane Transport and Cell Communication
- Genomic Technologies and Their Applications
- Patterns of Evolution in Different Species
- Population Dynamics and Ecosystem Health
- Enzyme Activity and Regulation in Metabolism
These essential topics serve as the foundation for most tasks. Understanding the relationships between these areas allows for a holistic grasp of the subject matter, which is key to performing well when it’s time to tackle more complex questions.
Key Concepts in Cell Biology
Understanding the fundamentals of cellular structures and their functions is critical for mastering complex scientific topics. This includes knowing how cells maintain their integrity, interact with their environment, and perform essential processes. A strong grasp of these concepts forms the foundation for many advanced subjects and tasks.
At the core of cellular knowledge is the understanding of various organelles, their specific roles, and how they contribute to the cell’s overall function. Additionally, comprehending the mechanisms of cellular communication, energy production, and reproduction is essential for deeper insights into biological systems.
Some of the most important areas to focus on include:
- Structure and function of cell membranes
- Energy conversion processes such as respiration and photosynthesis
- Cell cycle, mitosis, and meiosis
- Signal transduction pathways
- Protein synthesis and genetic regulation
By mastering these fundamental principles, you will be better equipped to understand how organisms function on a cellular level and apply that knowledge to more complex scenarios.
Understanding Genetics and Inheritance
The study of heredity explores how traits are passed from one generation to the next. This field focuses on the mechanisms that determine genetic variation and how organisms inherit specific characteristics. A solid understanding of these concepts is key to understanding how organisms evolve and adapt over time.
Central to this area is the idea of genetic material being transferred through generations, with dominant and recessive traits determining the physical outcomes in offspring. Moreover, exploring how mutations and genetic recombination lead to diversity is essential for grasping how traits are inherited and expressed.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Genotype | The genetic makeup of an organism. |
| Phenotype | The observable traits or characteristics of an organism. |
| Alleles | Different forms of a gene that exist at a specific locus on a chromosome. |
| Homozygous | An organism with two identical alleles for a trait. |
| Heterozygous | An organism with two different alleles for a trait. |
By understanding the basic principles of how traits are inherited, you can gain insight into more advanced genetic topics, such as genetic disorders, gene editing, and the role of genetic variation in populations.
Examining Evolution and Natural Selection
Understanding how species change over time is a cornerstone of evolutionary theory. The process through which organisms adapt to their environments involves complex mechanisms that drive change across generations. These mechanisms explain the diversity of life and the traits that make organisms suited to their environments.
At the heart of these processes lies the concept of adaptation, where traits that enhance survival become more common in a population. This gradual change is shaped by natural forces, such as competition, predation, and environmental shifts, leading to the emergence of new species over time.
Key Principles of Evolution
- Variation within populations leads to differences in traits.
- Natural selection acts on the genetic variation in populations.
- Over time, beneficial traits become more prevalent.
- Speciation occurs when populations are isolated and evolve independently.
Factors Driving Evolutionary Change
- Mutation introduces new genetic variation.
- Gene flow occurs when individuals migrate between populations.
- Genetic drift causes random changes in gene frequencies.
- Natural selection favors advantageous traits in a specific environment.
By analyzing these principles, one gains a deeper understanding of how life on Earth has evolved over millions of years, with species constantly adapting to changing conditions in their environments.
Principles of Ecology for AP Test
Understanding the interactions between organisms and their environments is key to grasping the complexities of ecological systems. These interactions form the foundation for studying how species live, reproduce, and evolve within their ecosystems. Ecology explains the relationships between living organisms and their surroundings, as well as how energy and nutrients flow through these systems.
The balance of ecosystems depends on the intricate web of interactions that occur between producers, consumers, decomposers, and their environment. Exploring these relationships provides insights into how populations grow, how species interact, and how environmental changes impact biodiversity.
Core Concepts in Ecology

- Energy flow through ecosystems, including food chains and webs.
- Nutrient cycling and its importance in maintaining ecosystem stability.
- Population dynamics, including factors that influence population size.
- Species interactions, such as predation, competition, and mutualism.
Environmental Factors Impacting Ecosystems
- Abiotic factors such as climate, temperature, and water availability.
- Biotic factors including the presence of other organisms and species diversity.
- Human impact on ecosystems, including habitat destruction and pollution.
These principles help explain the behavior of populations and communities, shedding light on how ecological systems function and how they may be affected by both natural and human-induced changes.
Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Insights
The processes that allow organisms to convert energy from one form to another are central to life. These vital mechanisms enable cells to produce the energy needed for growth, reproduction, and maintenance. Both energy-producing and energy-storing processes work in tandem to support life on Earth, with one producing the fuel necessary for the other to function.
In this section, we explore how cells capture energy from food and sunlight. Cellular respiration is responsible for converting stored energy into usable forms, while photosynthesis harnesses solar energy to create food for plants and other producers. Together, these processes form the cornerstone of energy flow within ecosystems.
Key Steps in Cellular Respiration
- Glycolysis: Breakdown of glucose into pyruvate, releasing energy.
- Citric Acid Cycle: Conversion of pyruvate into electron carriers and ATP.
- Electron Transport Chain: Transfer of electrons to produce ATP in mitochondria.
Critical Stages of Photosynthesis
- Light-dependent reactions: Capture of sunlight to produce energy-rich molecules.
- Calvin Cycle: Conversion of carbon dioxide into glucose using energy from light reactions.
Both processes are tightly regulated, ensuring that energy production and consumption meet the cell’s needs. Understanding the steps involved helps clarify how energy is transferred and stored across different organisms in a variety of environments.
Structure and Function of Biological Molecules
The structure of molecules determines their function in living organisms, as the unique arrangement of atoms allows them to interact in specific ways. Understanding how these molecules are built and how they work within cells is essential for grasping the complexity of life. These molecules are involved in a wide range of processes, from energy storage to information transmission.
Among the most critical biological molecules are proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates. Each of these has a distinct structure that enables them to perform vital roles in cellular functions. By examining their shapes and interactions, one can better understand how they contribute to the overall functionality of the organism.
Key Biological Molecules
- Proteins: Composed of amino acids, they function as enzymes, structural components, and signaling molecules.
- Carbohydrates: Serve as energy sources and structural components in cells.
- Lipids: Provide energy storage, insulation, and are key components of cellular membranes.
- Nucleic Acids: Carry genetic information and are involved in protein synthesis.
Molecular Interactions and Functions
- The role of enzymes in catalyzing biochemical reactions.
- How energy is stored and released through chemical bonds in molecules.
- The importance of molecular recognition in cellular communication.
Each class of molecule plays a specific role in maintaining cellular processes, and understanding these roles helps clarify how organisms function on a molecular level. The interplay between these molecules is what drives the intricate systems of life.
Understanding the Nervous and Endocrine Systems
The ability of organisms to respond to internal and external stimuli is essential for survival. Two key systems coordinate these responses: the nervous system, which provides rapid communication through electrical impulses, and the endocrine system, which uses chemical signals to regulate longer-term functions. Together, these systems ensure that the body reacts appropriately to various changes in the environment and maintains internal balance.
While the nervous system delivers quick, short-term signals to specific target cells, the endocrine system releases hormones that travel through the bloodstream to regulate processes like growth, metabolism, and reproduction. Both systems are intricately connected, with some organs serving dual roles in both signaling pathways.
Key Components of the Nervous System
- The brain: Central control center for processing information and coordinating responses.
- The spinal cord: Transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
- Neurons: Specialized cells that transmit electrical impulses.
- Synapses: Junctions where signals are passed between neurons.
Essential Functions of the Endocrine System

- Hormone production and release by glands such as the pituitary and thyroid.
- Regulation of growth, metabolism, and stress responses through various hormones.
- Homeostasis maintenance through feedback mechanisms to stabilize bodily functions.
The interplay between these two systems ensures that the body can respond to immediate threats and maintain long-term health and stability. Both work together to coordinate a wide range of physiological processes that are crucial for survival and adaptation.
How to Approach AP Biology Practice Tests
Effective preparation involves more than just reviewing material; it also requires practicing under conditions similar to the real situation. Using practice tests is a great way to familiarize yourself with the format, improve time management, and assess your understanding. The key is to approach them strategically to maximize their benefits.
Rather than just taking practice tests casually, treat them as a tool for identifying areas of weakness and reinforcing strengths. By reviewing your performance in detail, you can adjust your study plan and focus on the areas that need the most improvement. This focused approach will help you build confidence and refine your skills before the actual assessment.
Preparing for the Practice Test

- Review key concepts and focus on weak areas before taking the test.
- Set up a quiet, distraction-free environment to simulate testing conditions.
- Keep track of time during the test to practice pacing yourself.
Post-Test Review and Reflection
- Go through each question carefully and analyze why you chose a particular answer.
- Understand any mistakes you made and use them as opportunities for improvement.
- Take note of recurring topics to ensure they are well understood before retaking practice tests.
By incorporating practice tests into your preparation routine, you can enhance your test-taking skills, build your knowledge base, and enter the assessment with a greater sense of readiness and assurance.
Important Laboratory Techniques and Applications
Practical skills in the lab are essential for understanding complex concepts and conducting experiments that provide valuable insights into living systems. The techniques used in scientific investigations are designed to extract, measure, and analyze information that helps answer questions about biological processes. These methods are not only fundamental for research but are also crucial for understanding the mechanisms behind various biological phenomena.
Mastering laboratory techniques allows researchers to explore everything from cellular structures to genetic material, providing the foundation for discoveries that drive modern science. Whether it’s isolating DNA, studying enzymes, or conducting tests for metabolic activity, each method has its own unique application in the study of living organisms.
Common Techniques in the Laboratory
- Microscopy: Using microscopes to visualize cells and their components at high magnification.
- Chromatography: Separating complex mixtures for further analysis.
- Gel Electrophoresis: Analyzing DNA, RNA, or proteins based on their size and charge.
- Spectrophotometry: Measuring light absorption to quantify concentrations of substances.
Applications of Laboratory Methods

- Genetic research: Isolating and analyzing genetic material to understand inheritance patterns.
- Medical diagnostics: Testing samples to detect diseases or abnormalities at the molecular level.
- Pharmaceutical development: Using lab techniques to test the effectiveness of new drugs and therapies.
Each laboratory method is integral to advancing knowledge in the field and plays a vital role in both theoretical and applied science. By understanding and utilizing these techniques, researchers can develop more precise hypotheses and produce reliable results that further our understanding of biological systems.
Strategies for Mastering AP Biology Essays
Writing effective essays requires more than just a solid understanding of key concepts; it involves organizing thoughts clearly, presenting ideas logically, and supporting arguments with evidence. To excel in written assessments, it’s important to approach essay prompts with a structured strategy that showcases both knowledge and critical thinking skills. Developing these skills will help you craft comprehensive, well-supported responses under time constraints.
By practicing specific strategies, you can improve your ability to respond to essay prompts in a clear and concise manner. Understanding the structure of a successful essay, planning your response, and reviewing your work can make a significant difference in how your ideas are communicated and how effectively they address the topic at hand.
Key Elements of a Strong Essay
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Clear Thesis | State your main argument or point clearly in the opening sentence of your essay. |
| Logical Structure | Organize your ideas into a coherent flow with distinct paragraphs, each focused on a single point. |
| Evidence and Examples | Support your arguments with specific details, examples, and data from your studies or relevant sources. |
| Conclusion | Summarize your main points and reinforce how they answer the prompt, leaving a lasting impression. |
Effective Writing Tips
- Read the prompt carefully and underline key phrases to understand what is being asked.
- Draft a quick outline before writing to organize your thoughts and ensure you address all aspects of the prompt.
- Use precise language and avoid unnecessary jargon or overly complex sentences.
- Review your essay after writing to check for clarity, coherence, and any errors in grammar or logic.
By following these strategies, you can approach written tasks with confidence and increase your ability to produce well-structured, comprehensive essays that effectively demonstrate your understanding of key topics.
Time Management Tips for AP Biology Exam
Effective time management is crucial when preparing for a comprehensive assessment. By using your time wisely, you can maximize your performance and reduce stress during the process. Proper planning and execution help ensure that all tasks are completed on time while maintaining focus on key concepts and strategies.
Whether you’re in the middle of studying or taking the test itself, knowing how to allocate your time effectively is essential. Having a clear strategy for each section of the process, from preparation to answering the questions, can make a significant difference in your ability to succeed.
Planning Your Study Schedule
- Set realistic goals: Break your study sessions into manageable chunks and set achievable goals for each session.
- Prioritize topics: Focus on areas that need the most improvement or areas that are heavily weighted in the test.
- Include regular breaks: Short breaks can help maintain focus and improve retention during long study sessions.
- Track your progress: Keep a schedule to monitor your progress and ensure you’re staying on track with your goals.
During the Test
- Read instructions carefully: Make sure to understand what is being asked before beginning to answer any questions.
- Allocate time for each section: Be mindful of the time allotted for each part and pace yourself accordingly to avoid rushing at the end.
- Stay calm and focused: Don’t let difficult questions cause panic. If you’re stuck, move on and come back to it later.
- Review your answers: Use the remaining time to review your responses and make adjustments if necessary.
By following these time management techniques, you can approach both the preparation process and the test day itself with confidence, allowing you to perform at your best.
Common Mistakes in AP Biology Exams

Many students encounter challenges when attempting a comprehensive assessment, often due to overlooked details or rushed decisions. Avoiding common missteps can significantly improve performance and lead to better results. Recognizing these errors in advance can help you stay focused and prepared, ensuring that you approach each section with confidence.
Understanding the most frequent mistakes allows you to prepare more effectively, refine your approach, and ultimately enhance your ability to tackle challenging questions. By recognizing these pitfalls, you can streamline your approach and optimize your time management, giving yourself the best chance for success.
- Misreading instructions: Skipping over the details of the instructions can result in answering incorrectly or misunderstanding the task at hand.
- Skipping difficult questions: Moving past tough questions without attempting to answer them often leads to missed opportunities to earn points. It’s better to try an answer and come back if necessary.
- Not reviewing answers: Failing to review completed sections may result in overlooked mistakes that could have been corrected with a second look.
- Time mismanagement: Poorly allocating time across sections can lead to rushing through the latter parts of the test. Prioritizing time is essential for completing all tasks effectively.
- Overcomplicating answers: Trying to provide overly detailed or complex explanations can sometimes make the answer unclear. Keep it simple and direct, focusing on the key points.
- Not following the question format: Some sections may require specific formats for responses, such as bullet points or concise paragraphs. Ignoring these instructions can hurt your score.
By being aware of these frequent mistakes, you can develop strategies to minimize their impact and enhance your performance on the test. Taking your time, staying focused, and reading carefully will help you navigate through each section smoothly.
How to Use Flashcards for Exam Prep
Flashcards are an effective tool for reinforcing key concepts and reviewing material in a concise, interactive format. This method allows you to actively recall important information, identify areas that need improvement, and ensure that essential topics are thoroughly understood. By incorporating flashcards into your study routine, you can boost retention and improve your performance.
Creating and utilizing flashcards strategically can maximize your preparation efforts. Here are a few ways to get the most out of this study tool:
- Break down complex topics: Divide large concepts into smaller, manageable parts. This helps you focus on specific details and prevents feeling overwhelmed.
- Focus on key terms: Write a term or concept on one side, with a brief definition or explanation on the other. Review these cards regularly to ensure mastery.
- Use active recall: Don’t just passively flip through cards. Try to recall the information before checking the answer to reinforce memory.
- Incorporate visual aids: For complex processes or structures, include diagrams or images on the cards to visualize the concept.
- Group related cards: Organize your flashcards by topic to study them in groups. This helps you focus on specific areas at a time.
- Use spaced repetition: Review cards at increasing intervals to strengthen long-term retention. This technique is highly effective in retaining information.
- Practice with a partner: Quiz each other using flashcards. This can provide additional insights and help you test your understanding in a more interactive way.
By using flashcards consistently and strategically, you can improve your ability to recall vital information quickly and accurately, giving you an edge when facing the test.
Preparing for Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple-choice assessments often test a wide range of knowledge, requiring a mix of recall, analysis, and decision-making skills. To effectively prepare for this type of evaluation, it’s crucial to develop strategies that allow you to approach each item with confidence and accuracy. Understanding how to approach these assessments can help you perform better by eliminating incorrect options and narrowing down the choices.
Here are some strategies to consider when preparing for multiple-choice assessments:
- Understand the format: Familiarize yourself with the structure of the items. Recognize common patterns in how the questions are phrased, such as using terms like “except” or “not.”
- Focus on key concepts: Make sure you have a solid understanding of the foundational topics. Reviewing key definitions, processes, and theories can make it easier to identify the correct option.
- Read each option carefully: Don’t rush through the available choices. Pay attention to subtle differences between them to avoid making errors based on small details.
- Eliminate obviously incorrect options: If you are unsure, start by eliminating choices that are clearly wrong. This increases your chances of selecting the right answer from the remaining options.
- Use context clues: Often, the surrounding items can provide valuable hints or contextual information that help you answer a particular question correctly.
- Watch for tricky wording: Be cautious of questions that try to mislead or confuse with complex wording or negatively phrased statements. Take time to analyze each question carefully before selecting your response.
- Practice with mock tests: Simulating the real test experience by practicing with multiple-choice items can help improve your speed, accuracy, and overall confidence.
By following these strategies, you can enhance your preparation and increase your ability to answer multiple-choice items with precision and insight.
Tips for Writing AP Free-Response Answers
When tasked with providing detailed written responses, it’s essential to effectively communicate your understanding while addressing every part of the prompt. These types of items require clear, concise, and structured explanations. Your responses must demonstrate both depth and accuracy to secure maximum points. Knowing how to approach these written tasks can significantly improve your performance and confidence.
Here are several tips to consider when writing free-response responses:
- Read the prompt carefully: Before beginning your response, make sure you fully understand what is being asked. Identify all components of the prompt to ensure you address every part in your answer.
- Plan your response: Take a few moments to organize your thoughts before you start writing. Creating a brief outline of the key points you want to include can help you stay on track and ensure that your answer is logical and coherent.
- Use specific terminology: While it’s important to be clear, it’s equally vital to use precise terminology relevant to the subject. This demonstrates your familiarity with the material and improves the clarity of your response.
- Provide examples: Whenever possible, use concrete examples to support your points. Real-world examples or specific case studies can make your response more persuasive and show a deeper level of understanding.
- Be concise yet thorough: Avoid over-explaining or providing irrelevant information. Focus on answering the prompt directly and succinctly while still providing all necessary details. Balance is key.
- Check your grammar and structure: A well-organized response not only looks more professional but also enhances readability. Use paragraphs effectively, and ensure that your response flows logically from one point to the next.
The following table provides an example structure to help guide your writing:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Introduction | Provide a brief overview of the topic or issue. Introduce the main points you will cover in your response. |
| 2. Explanation | Elaborate on the key concepts, definitions, or processes involved. Be clear and specific in your descriptions. |
| 3. Examples | Include relevant examples or case studies that demonstrate your understanding of the topic. |
| 4. Conclusion | Summarize your key points and offer a final insight or takeaway related to the topic. |
By following these guidelines, you can write more effective, well-rounded responses that clearly showcase your understanding of the material.
Review Resources for AP Students
When preparing for challenging assessments, having access to high-quality study materials is crucial. Whether you’re looking for detailed content explanations, practice exercises, or strategy tips, the right resources can help reinforce your knowledge and improve your performance. Below, you’ll find several useful tools that can guide you in your preparation.
Books and Textbooks
Textbooks are a foundational resource for revisiting key concepts. Several comprehensive guides cater specifically to test preparation, offering concise reviews, in-depth explanations, and practice exercises. Consider the following:
- Review Guides: Specialized guides provide a thorough overview of essential topics and often include practice questions and answers.
- Study Workbooks: These workbooks help reinforce key concepts through exercises, diagrams, and scenario-based questions.
- Concept-Specific Textbooks: If you need to revisit specific subjects, textbooks that cover specialized areas can be extremely beneficial for a deeper understanding.
Online Resources
With the advancement of technology, the internet has become an invaluable tool for students. There are several online platforms that offer interactive study materials:
- Video Tutorials: Websites like YouTube or educational platforms provide in-depth video lectures on complex topics. These videos can help visualize abstract concepts and offer step-by-step explanations.
- Interactive Quizzes: Online quizzes test your knowledge and provide immediate feedback, helping you identify areas that need improvement.
- Study Groups: Online forums or social media groups allow students to discuss difficult concepts and share resources, giving a collaborative edge to your preparation.
By utilizing a mix of these materials, you can enhance your understanding of key subjects and build confidence in your knowledge. Tailor your study approach to the resources that best suit your learning style for maximum success.