Food Protection Course Questions and Answers

Ensuring the safety of what we consume requires knowledge of essential practices that prevent contamination and illness. With the right guidelines, anyone involved in handling consumables can minimize risks and ensure hygiene standards are met. This section provides valuable insights to help workers and learners understand core principles for maintaining safe environments.
From handling raw ingredients to maintaining clean surfaces, there are numerous practices that contribute to overall cleanliness and health. Gaining clarity on these topics not only prepares individuals for certification exams but also equips them with the skills to apply safety measures effectively in their daily work. Whether you’re new to the field or looking to refresh your knowledge, these key points are crucial for success in any setting where consumables are prepared and served.
Essential Safety Training Tips

Proper training is the foundation of maintaining a hygienic and secure environment in any setting that involves the preparation or handling of consumables. Whether you’re starting your learning journey or revisiting important guidelines, understanding the key elements of safety protocols is crucial for preventing contamination and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Here are some essential tips to guide you in mastering safety practices:
- Know the Basics – Familiarize yourself with the core principles of cleanliness, safe handling, and proper sanitation techniques.
- Stay Informed – Regularly update your knowledge on evolving safety regulations, local laws, and best practices.
- Focus on Hygiene – Prioritize personal hygiene by wearing protective gear, washing hands frequently, and maintaining cleanliness in all work areas.
- Use Temperature Controls – Always monitor temperatures when storing, cooking, or serving items to avoid bacterial growth and contamination.
- Implement Cross-Contamination Prevention – Separate raw materials from ready-to-eat items and disinfect surfaces between tasks.
- Maintain Clean Equipment – Ensure that all tools, utensils, and surfaces are cleaned and sanitized regularly to prevent harmful germs from spreading.
By following these fundamental guidelines, you can help create a safer environment for everyone involved in the process. These tips not only enhance safety but also build confidence in your ability to prevent risks in any situation.
Understanding Safety Basics
Achieving a high standard of hygiene and minimizing hazards requires a deep understanding of essential safety measures. This knowledge covers several key areas that are crucial to preventing contamination and ensuring the health of individuals who consume prepared items. The fundamentals of maintaining a safe environment play an integral role in every stage, from handling raw ingredients to serving the final product.
Core Principles for Maintaining Hygiene

To maintain a safe environment, it is necessary to focus on cleanliness and prevent harmful microorganisms from spreading. This involves proper handwashing techniques, wearing appropriate protective clothing, and ensuring that surfaces and equipment are regularly cleaned and sanitized. By adhering to these basic practices, contamination risks can be significantly reduced.
Safe Handling Practices
Proper handling methods are essential for preventing cross-contamination between raw and cooked items. By separating different types of ingredients and using designated tools for each task, the chances of harmful bacteria spreading are minimized. Additionally, it’s vital to store items at the right temperature to prevent spoilage and the growth of pathogens.
Common Questions About Handling Practices
When it comes to preparing consumables, there are several key concerns that frequently arise. These inquiries often relate to maintaining cleanliness, proper storage, and ensuring safe handling to prevent any potential hazards. Addressing these concerns helps individuals develop a clearer understanding of best practices and how to implement them effectively in their daily routines.
How to Ensure Proper Hygiene?

Maintaining hygiene is essential for preventing contamination. This includes washing hands thoroughly, using gloves when necessary, and sanitizing all surfaces and utensils after use. Additionally, it’s important to regularly clean workstations and store consumables in designated areas to avoid cross-contact.
What Are the Best Storage Methods?
Proper storage techniques are critical for maintaining safety and preventing spoilage. Temperature control is one of the most important factors to consider, as different items have different requirements for refrigeration or freezing. Below is a summary of the best storage practices:
| Item Type | Storage Temperature | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Meats | 32°F to 40°F (0°C to 4°C) | Store separately to avoid cross-contamination |
| Prepared Dishes | 40°F or lower (4°C) | Cool before storing and use within a few days |
| Vegetables and Fruits | Varies (typically room temperature) | Keep in clean, dry areas away from raw meats |
Top Hygiene Practices for Safe Consumption
Maintaining high standards of cleanliness is vital to avoid contamination and ensure the safety of prepared items. Proper hygiene practices not only protect consumers but also help workers create a sanitary environment where potential risks are minimized. By incorporating these key habits, everyone involved in the process can contribute to a safer, healthier experience for all.
Hand Hygiene and Personal Cleanliness
Washing hands frequently is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of harmful bacteria. Always wash your hands thoroughly before handling any items, after touching raw ingredients, and after using the restroom. Additionally, wearing clean gloves when necessary and covering hair with a clean cap or hairnet can further reduce the chances of contamination.
Sanitizing Equipment and Surfaces
It’s essential to sanitize all surfaces and utensils regularly. Cutting boards, knives, and counters should be disinfected after each use, particularly when transitioning between different ingredients. This helps prevent cross-contamination, which can occur when harmful microbes spread from one surface to another. Using designated equipment for raw versus ready-to-eat items is another effective practice.
Foodborne Illness Prevention Methods
Preventing illness caused by harmful microorganisms requires adopting specific measures throughout the preparation, storage, and serving processes. By understanding key risk factors and implementing practical strategies, it’s possible to significantly reduce the likelihood of contamination and ensure the safety of those consuming meals. Below are some effective methods to minimize health risks.
- Proper Temperature Control – Always store perishable items at the correct temperatures to prevent bacterial growth. Cold items should be kept below 40°F (4°C), and hot items should be maintained above 140°F (60°C).
- Thorough Cooking – Ensure that all items, especially meats, are cooked to the appropriate internal temperature to kill harmful pathogens.
- Hand Hygiene – Wash hands frequently, especially after handling raw ingredients, using the restroom, or touching potentially contaminated surfaces.
- Separation of Raw and Ready-to-Eat Items – Always use separate utensils, cutting boards, and storage containers for raw ingredients and ready-to-eat products to avoid cross-contamination.
- Cleaning and Sanitizing – Regularly clean and sanitize all surfaces, equipment, and utensils to eliminate harmful germs and bacteria.
- Safe Thawing – Thaw items in the refrigerator or using a microwave, never at room temperature, to avoid allowing pathogens to multiply.
How to Prevent Cross-Contamination

Cross-contamination is a leading cause of illness and occurs when harmful microorganisms spread from one item to another, often through direct contact or improper handling. Preventing this issue requires careful attention to detail and the implementation of several key strategies. By adopting simple practices, it’s possible to create a safer environment and minimize health risks.
- Separate Raw and Cooked Items – Always use separate cutting boards, utensils, and containers for raw ingredients and items that are ready to eat. This prevents harmful bacteria from raw materials transferring to other products.
- Clean Utensils and Surfaces Regularly – Wash knives, cutting boards, and countertops between tasks to remove any residue that could carry bacteria from one item to another.
- Use Proper Storage Containers – Store raw ingredients, especially meats, in leak-proof containers to prevent juices from contaminating other items in the fridge or storage areas.
- Wear Gloves When Necessary – When handling raw or potentially hazardous ingredients, it’s important to wear clean gloves to prevent direct contact. Remember to change gloves frequently and wash hands between tasks.
- Regularly Disinfect Equipment – Ensure all kitchen tools, including tongs, spoons, and brushes, are sanitized regularly to prevent harmful microorganisms from spreading.
Personal Protective Equipment in Food Safety

In any environment where consumables are prepared, the use of personal protective gear plays a crucial role in maintaining cleanliness and preventing contamination. Protective equipment ensures that workers remain safe while handling various materials and minimizes the risk of transferring harmful microorganisms to products. Understanding the proper use and maintenance of these items is essential for creating a safe environment.
Below is a list of common protective items used in such settings:
| Protective Equipment | Purpose | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| Gloves | Prevent direct contact with harmful substances and reduce cross-contamination. | When handling raw materials, cleaning, or working with ready-to-eat items. |
| Hairnets/Head Covers | Prevent hair from contaminating products and surfaces. | When preparing or serving items that require hygiene standards. |
| Aprons | Protect clothing and prevent bacteria from being transferred from clothing to products. | When working with raw ingredients or cleaning. |
| Face Masks | Prevent airborne contaminants from entering the work area or food. | When in direct contact with materials that can be aerosolized. |
| Boots/Shoes | Protect feet and prevent contamination from spreading across surfaces. | When working in environments with potential for spills or dirty surfaces. |
Using the right gear at the right time not only ensures personal safety but also contributes to the overall hygiene and well-being of the environment. Regular inspection and replacement of equipment are also essential to maintain effectiveness and compliance with safety standards.
Temperature Control in Food Safety
Managing temperature is one of the most effective ways to prevent harmful bacteria and pathogens from multiplying. Proper temperature control ensures that materials are kept at safe levels throughout preparation, storage, and service. This helps avoid contamination, spoilage, and ensures that all items remain safe for consumption. Understanding and following temperature guidelines is essential for maintaining hygiene and safety standards.
Safe Temperature Ranges
Different types of consumables require different temperature settings for optimal safety. The key to reducing the risk of illness lies in adhering to these temperature ranges:
- Refrigeration – Keep perishable items below 40°F (4°C) to slow bacterial growth.
- Freezing – Store frozen items at 0°F (-18°C) or lower to prevent bacterial development.
- Hot Holding – Maintain hot foods at 140°F (60°C) or higher to ensure they remain safe for consumption.
Methods for Proper Temperature Control
Several techniques can help ensure temperature control is properly maintained:
- Use Thermometers – Regularly check the temperature of refrigerators, freezers, and holding equipment to confirm they are within the safe range.
- Monitor Internal Temperatures – Always check the internal temperature of cooked items with a food-safe thermometer to ensure they have reached the necessary level.
- Proper Thawing – Thaw items in the refrigerator or microwave, not at room temperature, to avoid the growth of bacteria.
- Use Hot Holding Equipment – Keep prepared items at proper temperatures using warming trays or heated display cases during service.
By maintaining strict temperature control, the risk of contamination is significantly reduced, helping to ensure safe practices in any environment where consumables are prepared or served.
Safe Storage and Preservation Techniques
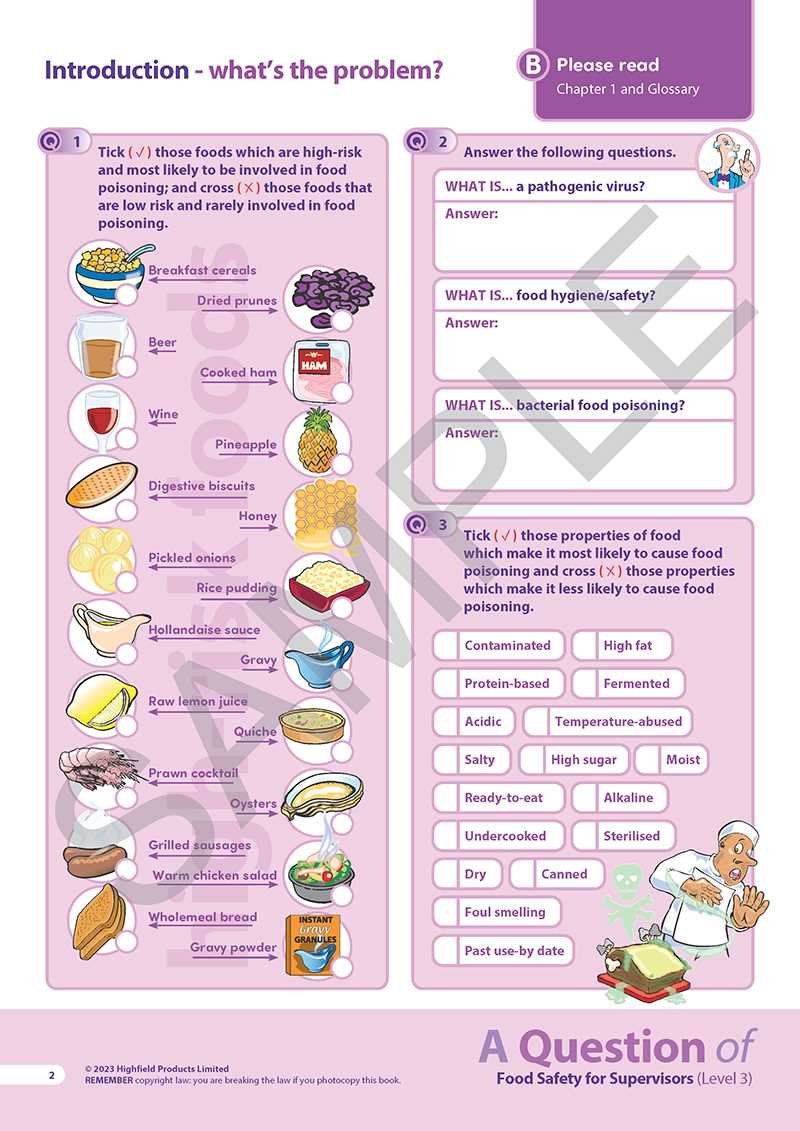
Ensuring that items remain safe for consumption over time requires proper storage and preservation practices. By maintaining appropriate conditions and following specific guidelines, it is possible to extend the shelf life of materials, prevent spoilage, and reduce the risk of contamination. Proper handling from the moment of receipt to the time of use is essential to maintaining quality and safety.
Key Storage Practices
Implementing correct storage methods plays a vital role in maintaining the safety of items. The following practices should always be followed:
- Temperature Control – Store perishable items in refrigerators or freezers, ensuring that temperatures are regularly monitored and maintained.
- Labeling – Clearly label containers with the date of receipt and expiration to ensure items are used in the correct order and within safe timeframes.
- Separation of Raw and Ready-to-Eat Items – Store raw items separately from cooked or ready-to-eat items to prevent cross-contamination.
- Proper Packaging – Use appropriate, airtight containers for storing goods, which helps to maintain freshness and prevent contamination from external sources.
Preservation Methods
In addition to proper storage, several techniques can be used to preserve items for longer periods:
- Canning – Sealing materials in jars or cans helps protect them from bacterial contamination and spoilage by creating a vacuum seal.
- Drying – Removing moisture from items can prevent the growth of microorganisms, which thrive in moist environments.
- Pickling – Preserving through acidic solutions, such as vinegar, can prevent the growth of harmful bacteria.
- Freezing – Freezing is one of the most effective methods for long-term storage, preserving items by slowing down bacterial growth and preventing spoilage.
By adhering to these practices and techniques, the risk of spoilage and contamination can be minimized, ensuring that all materials remain safe for consumption and maintain their quality over time.
Critical Points in Food Safety Regulations

To ensure that consumables remain safe for human consumption, it is crucial to adhere to established standards and regulations. These guidelines are designed to minimize the risks of contamination and illness by controlling various factors during handling, storage, and preparation. Following these regulations not only protects consumers but also promotes a safe environment for everyone involved in the production process.
Below is a table summarizing some of the critical points to be aware of in safety regulations:
| Regulation Area | Key Focus | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Ensuring that items are kept at safe temperatures throughout storage and preparation. | Prevents bacterial growth and spoilage. |
| Hygiene Practices | Requiring proper hand washing, sanitizing surfaces, and using clean equipment. | Reduces the risk of cross-contamination and infection. |
| Cross-Contamination | Separation of raw and cooked materials, along with the use of dedicated utensils and equipment. | Prevents harmful microorganisms from transferring between items. |
| Labeling and Date Marking | Clear labeling of expiration dates and storage instructions. | Helps ensure proper rotation and usage of materials. |
| Employee Training | Training staff on proper safety procedures and awareness of risks. | Ensures a knowledgeable workforce committed to maintaining high standards. |
Understanding and following these key aspects of safety regulations is essential for any operation that handles consumables. Compliance with these guidelines not only reduces health risks but also builds consumer trust and meets legal requirements for safety.
Best Practices for Food Preparation Areas
Creating a clean and safe environment for the handling and processing of items is critical to preventing contamination and ensuring quality. Properly maintaining preparation areas ensures that everything from raw materials to finished products is handled correctly, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses and preserving the integrity of the items being prepared.
Key Practices for Maintaining Cleanliness
To maintain a hygienic preparation area, the following practices should always be implemented:
- Regular Cleaning – Ensure that all surfaces, tools, and equipment are cleaned thoroughly before, during, and after use to remove any residues and prevent contamination.
- Sanitization – Use appropriate sanitizers to disinfect surfaces after cleaning to eliminate any harmful microorganisms that may be present.
- Proper Waste Management – Regularly remove waste, including food scraps and packaging, from preparation areas to avoid attracting pests and contaminating materials.
- Ventilation – Maintain proper airflow in the area to reduce moisture and prevent the buildup of mold or bacteria on surfaces.
Organizing and Preventing Cross-Contamination
Effective organization and preventing the spread of contaminants are essential steps in any preparation area:
- Color-Coded Equipment – Use separate tools and utensils for different tasks (e.g., chopping, mixing) and color-code them to prevent cross-contamination between raw and cooked items.
- Separation of Raw and Ready-to-Eat Items – Always store raw materials separately from cooked or ready-to-eat items to minimize the risk of transferring harmful bacteria.
- Proper Storage – Ensure that all ingredients and prepared items are stored at the correct temperature and in appropriate containers to preserve quality and safety.
- Staff Training – Educate all personnel on best practices for hygiene and handling to ensure a consistent approach to maintaining a safe environment.
By following these best practices, preparation areas can remain safe and efficient, minimizing the risks of contamination and ensuring that all materials are handled with care and respect for quality.
Understanding Food Safety Audits
Regular evaluations are essential to ensuring that safety standards are being upheld within any establishment that handles consumables. These assessments are carried out to identify potential risks, verify compliance with regulations, and improve processes related to cleanliness, storage, and handling. By regularly reviewing practices and procedures, organizations can maintain a high level of safety and reduce the likelihood of contamination or health issues.
Audits typically involve a thorough examination of operational practices, documentation, staff behavior, and the physical environment. The goal is to assess the effectiveness of existing protocols, identify areas for improvement, and ensure that all safety standards are being met consistently. During these evaluations, auditors will look for compliance with industry guidelines and legal requirements, as well as provide recommendations for corrective actions when needed.
These audits not only focus on hygiene and sanitation but also consider staff training, equipment maintenance, and the proper use of resources. Successful audits help to create a safer environment for both employees and consumers, ensuring that safety remains a top priority throughout the entire operation.
Effective Cleaning and Sanitizing Methods
Maintaining a hygienic environment is essential for ensuring safety and preventing contamination. Proper cleaning and disinfecting procedures not only help eliminate dirt and visible residues but also remove harmful microorganisms that could pose health risks. Implementing effective cleaning practices is crucial in all environments where products are handled, ensuring that all surfaces and tools remain safe and sanitary.
Key Steps in Effective Cleaning
The cleaning process involves removing dirt, grease, and debris from surfaces and equipment. The following steps are critical:
- Pre-Rinsing – Begin by rinsing surfaces or tools with water to loosen and remove any loose dirt or particles.
- Detergent Application – Use appropriate cleaning agents to break down grease, oils, and other residues that water alone cannot remove.
- Scrubbing – Thoroughly scrub all surfaces using brushes or sponges to dislodge dirt and debris from difficult-to-reach areas.
- Rinsing – Rinse with clean water to remove the detergent and any remaining contaminants.
Effective Sanitizing Practices
After cleaning, sanitizing is necessary to eliminate harmful bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. Key methods include:
- Use of Disinfectants – Apply approved sanitizers that are effective against a wide range of pathogens. Follow manufacturer instructions regarding concentration and contact time.
- Proper Storage of Cleaning Agents – Store cleaning supplies in a dry, cool place, and ensure they are clearly labeled and used according to the recommended guidelines.
- Routine Checks – Regularly check cleaning tools and disinfectants for effectiveness, ensuring they are not expired or damaged.
By following these cleaning and sanitizing methods, organizations can create a safer environment for employees and customers, minimizing the risk of contamination and promoting overall health and hygiene standards.
Key Certification Requirements for Food Workers
In many industries, it is essential for workers to be properly trained and certified to ensure that proper safety and hygiene practices are followed. Certification serves as proof that individuals have acquired the necessary skills and knowledge to work responsibly in environments where consumables are handled. This certification process typically includes both theoretical learning and practical assessments to verify competence in essential safety procedures.
To meet certification standards, workers must demonstrate understanding in key areas, including hygiene, temperature control, cross-contamination prevention, and safe handling techniques. Training programs often include both classroom-based learning and hands-on experiences, ensuring that workers are fully prepared for the challenges they may face in their daily tasks.
Additionally, workers must pass exams that assess their knowledge of relevant regulations and best practices. Achieving certification ensures that they are not only compliant with legal standards but also equipped to maintain a high standard of health and safety. It is important to regularly renew certifications and participate in refresher courses to stay up to date with the latest industry standards and safety guidelines.
Key certification requirements include:
- Completion of Approved Training Programs – Participation in accredited educational programs that cover all necessary topics.
- Demonstration of Practical Skills – Ability to apply learned concepts in real-world scenarios to ensure safety practices are maintained.
- Passing Written Exams – Successful completion of exams that test knowledge of relevant safety protocols, sanitation practices, and regulations.
- Ongoing Education and Renewal – Commitment to continuous learning and recertification to stay current with evolving standards and requirements.
By meeting these key certification requirements, workers are not only ensuring their own safety but also contributing to the overall health of the community they serve. The certification process is an investment in maintaining a safe, hygienic, and professional working environment.
Handling Allergens in Food Protection
When working in environments where consumables are prepared, it is crucial to manage allergens carefully to prevent harm to individuals with sensitivities. Proper handling, labeling, and storage practices are essential to minimize the risk of cross-contamination. Understanding how allergens can affect consumers and taking proactive measures is a fundamental part of maintaining a safe environment.
Allergens can cause severe reactions, ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions. For this reason, workers must be trained to recognize common allergens, understand how they can contaminate other products, and take appropriate steps to control exposure. Effective allergen management includes thorough cleaning procedures, careful ingredient sourcing, and transparent labeling of all items being served.
Key Allergen Handling Strategies
- Segregation – Keeping allergen-containing ingredients separate from others to prevent accidental cross-contact.
- Thorough Cleaning – Ensuring surfaces, utensils, and equipment are properly cleaned after handling allergens to avoid contamination.
- Labeling – Clearly marking products that contain allergens to alert staff and consumers to potential risks.
- Staff Training – Providing ongoing education to workers on allergen risks, safe handling practices, and emergency response protocols.
Minimizing Risk of Cross-Contamination
Cross-contact is one of the leading causes of allergen-related incidents. To minimize these risks, it is critical to implement dedicated storage, preparation, and cooking practices. Tools and surfaces that come into contact with allergens should be thoroughly sanitized before being used for allergen-free products. In addition, clear protocols must be in place for handling allergic reactions, including immediate access to medical support when needed.
Best practices for allergen control:
- Clear identification of allergens – All ingredients and finished products should be accurately identified and labeled to ensure clarity for everyone handling them.
- Prevention through proper hygiene – Workers should follow strict hand-washing and sanitizing procedures to reduce the risk of allergen transfer.
By following these best practices, establishments can significantly reduce the risks associated with allergens, creating a safer environment for all individuals, regardless of their sensitivities.
How to Maintain a Food Safety Plan
Developing a comprehensive strategy for ensuring health standards is essential for any organization handling consumables. However, a plan alone isn’t enough; it requires regular upkeep to ensure that risks are mitigated and procedures remain effective. The maintenance of such a strategy involves continuous evaluation, staff training, and updates to meet the evolving guidelines and requirements.
Effective management of a health and safety strategy involves ongoing assessment and adjustment. This ensures the procedures are in line with current regulations and industry best practices. Regular checks help identify potential risks, allow for adjustments, and ensure that corrective actions are taken promptly.
Steps for Maintaining an Effective Safety Plan
- Regular Review – Consistently evaluate the existing procedures to ensure they align with updated regulations and standards.
- Employee Training – Conduct regular training sessions to ensure that all team members are aware of the latest practices and protocols.
- Audit and Inspections – Schedule periodic internal audits and inspections to assess compliance and identify areas for improvement.
- Incident Tracking – Keep detailed records of any safety-related incidents to analyze patterns and prevent future occurrences.
Implementing Continuous Improvement
Maintaining an effective strategy is not a one-time task. It requires an approach of continuous improvement, where lessons learned from past mistakes are integrated into future plans. Establishing a feedback loop through employee input, inspections, and audits is vital for identifying gaps and making necessary adjustments.
Key practices for ongoing improvement:
- Feedback integration – Use insights from staff and audits to refine and improve the plan.
- Adaptability – Be prepared to modify procedures in response to new risks, regulatory changes, or emerging industry standards.
By following these steps and maintaining vigilance, a safety plan can be kept effective, ensuring that risks are minimized, and the environment remains compliant with health standards.