Introduction to Macroeconomics Exam Questions and Answers

Understanding the fundamental principles of economic systems is essential for excelling in any academic assessment focused on large-scale financial structures. By grasping core theories and applying them effectively, students can enhance their problem-solving skills and approach challenging topics with confidence.
Throughout this guide, we will explore common types of problems encountered in such assessments, highlighting essential topics to study. Knowing what to expect and how to structure your responses is crucial to achieving strong results. Whether focusing on government policies, market dynamics, or broader global economic trends, mastering these areas will prepare you for success.
Preparation is key, and with a strategic approach, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle complex concepts with clarity. By using practical examples and reviewing relevant models, you will strengthen your ability to explain and analyze economic phenomena in any test scenario.
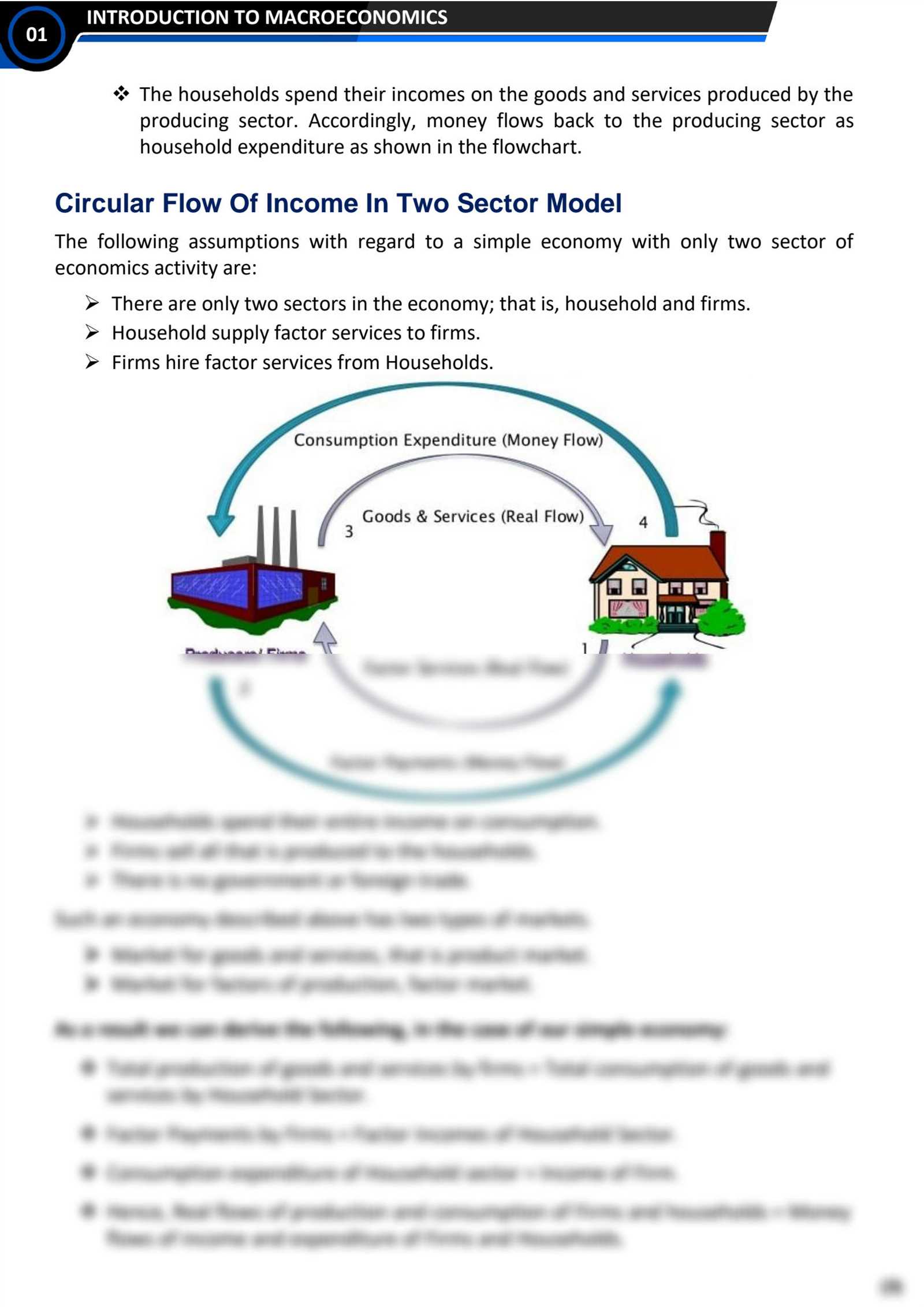
Understanding Key Economic Concepts
To excel in assessments related to large-scale financial systems, it is crucial to grasp the foundational ideas that govern economic structures. These concepts provide the framework for analyzing how economies function, how resources are allocated, and how various forces interact within the market. A solid understanding of these core principles will not only aid in academic evaluations but also improve real-world decision-making abilities.
Core Economic Theories
At the heart of any economic analysis are the primary theories that explain how supply, demand, and production operate. Concepts like market equilibrium help students understand how goods and services are distributed in a competitive environment. By recognizing these theories, you can develop a deeper insight into the behavior of consumers, businesses, and governments in shaping the overall economic landscape.
Key Economic Indicators

In addition to theoretical frameworks, understanding the metrics used to measure economic health is vital. Inflation rates, unemployment levels, and national output are just a few examples of critical indicators that provide insight into the state of an economy. These figures are not only important for tests but also for evaluating policy decisions and forecasting future trends.
Commonly Asked Questions in Exams

In assessments focused on economic principles, certain topics tend to recur more frequently due to their foundational importance. Understanding these recurring themes will help you focus your study efforts and enhance your ability to address key topics effectively. These areas typically cover a broad range of theoretical and practical concepts that are essential for evaluating the structure and functioning of economies.
Key Areas Often Tested
Students can expect a variety of questions addressing different aspects of economic systems. Below are some of the most commonly examined topics:
- Market Structures: Understanding the characteristics of perfect competition, monopolies, and oligopolies.
- Fiscal Policy: Analyzing government spending, taxation, and their effects on national economies.
- Supply and Demand: Explaining shifts in curves and how market prices are determined.
- National Income: Calculating GDP and understanding how income is distributed across an economy.
- Monetary Policy: Investigating the role of central banks and interest rates in stabilizing economic conditions.
Problem-Solving Techniques
In addition to theoretical questions, assessments often present practical problems that require application of learned concepts. These problems may involve:
- Calculating the effects of a price change on supply and demand.
- Evaluating the impact of government fiscal measures on a national economy.
- Predicting economic outcomes based on shifts in key indicators like inflation or unemployment.
Familiarity with these common areas will give you a significant advantage in tackling complex scenarios efficiently.
How to Approach Exam Problems
When tackling challenges in assessments, having a clear strategy is essential for managing your time and applying your knowledge effectively. Approaching problems methodically allows you to break down complex issues into more manageable parts. Whether it’s a theoretical question or a practical calculation, using a systematic approach can significantly improve your performance.
Step-by-Step Problem Solving
The key to solving any problem is understanding what is being asked. Begin by carefully reading the statement and identifying the main components. Here are some steps to follow:
- Read thoroughly: Ensure you understand the requirements of the task before proceeding.
- Identify key concepts: Focus on the core principles that apply to the scenario at hand.
- Break it down: Divide complex problems into smaller, simpler parts.
- Apply formulas: Use relevant formulas or models to calculate or explain the situation.
- Check your work: Always review your calculations and reasoning to ensure accuracy.
Time Management Techniques
Managing your time effectively during an assessment is just as important as solving problems. Allocate enough time for each task, ensuring that you don’t spend too long on any single question. Prioritize questions based on their difficulty and point value, addressing easier ones first to build confidence. Leave the more challenging ones for later, allowing you to approach them with a clear mind.
Types of Macroeconomic Theories
Various economic models aim to explain the broader functioning of economies, focusing on how national and global systems interact. These theories offer different perspectives on critical issues such as inflation, unemployment, and economic growth. By exploring different approaches, you can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying forces that shape economic behavior and policy decisions.
Each theory presents unique assumptions and conclusions about how markets operate and how various economic factors influence one another. Below are some of the most influential schools of thought in this field:
- Classical Theory: Focuses on the idea that markets are self-correcting and that supply and demand naturally lead to full employment.
- Keynesian Theory: Emphasizes the importance of government intervention to manage demand and stabilize the economy, especially during recessions.
- Monetarism: Argues that controlling the money supply is the key to controlling inflation and ensuring economic stability.
- Supply-Side Economics: Focuses on boosting production and reducing taxes to encourage investment, job creation, and economic growth.
- New Classical Theory: Advocates for the efficiency of free markets but incorporates expectations about future economic conditions in decision-making.
Understanding these various perspectives will allow you to approach economic issues from different angles, enhancing your ability to analyze and interpret complex topics in any assessment.
Understanding Supply and Demand Curves
One of the most fundamental concepts in economic analysis is the relationship between supply and demand. These two forces drive the allocation of resources, determining the prices of goods and services in any market. Understanding how these forces interact is crucial for interpreting market behavior and making informed predictions about economic outcomes.
Supply and demand curves represent the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied or demanded at that price. The demand curve typically slopes downward, indicating that as prices fall, consumers are willing to buy more. On the other hand, the supply curve generally slopes upward, showing that as prices increase, producers are more likely to offer higher quantities of the product for sale.
Equilibrium occurs when the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, resulting in a stable market price. Shifts in either the supply or demand curve can cause changes in the equilibrium price and quantity, illustrating the dynamic nature of market economies. Understanding these shifts is essential for analyzing real-world situations, such as price fluctuations during economic changes or policy interventions.
The Role of Government in the Economy
The involvement of the government in the economy is essential for maintaining stability and promoting growth. Through various policies and regulations, governments shape the economic environment by influencing market outcomes, managing public resources, and ensuring the well-being of citizens. Understanding these roles is crucial for analyzing the impact of government actions on national and global economies.
Governments typically engage in several key activities to influence economic performance, including:
- Regulating Markets: Enforcing rules to prevent monopolies, ensure fair competition, and protect consumers.
- Fiscal Policy: Using government spending and taxation to influence economic activity, such as stimulating demand during a recession.
- Monetary Policy: Controlling the money supply and interest rates through central banks to regulate inflation and stabilize the economy.
- Public Goods and Services: Providing essential services, such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure, that benefit society as a whole.
- Income Redistribution: Implementing social welfare programs and tax systems to reduce income inequality and support vulnerable populations.
By intervening in these areas, governments can help maintain economic stability, promote growth, and address disparities within society. However, the degree of intervention and the effectiveness of policies often vary depending on the political, social, and economic context of a particular country.
Exam Tips for Time Management
Efficient time management during assessments is crucial for maximizing your performance. Properly allocating time to each section ensures that you can tackle all tasks with enough focus and avoid rushing through more difficult questions. Developing a strategy for managing time allows you to remain calm and organized, which can lead to better results.
To manage your time effectively, consider the following tips:
- Plan Ahead: Before starting, quickly scan the entire test to get an overview of the content and note any sections you find particularly challenging.
- Prioritize Tasks: Tackle questions you are most confident in first to gain momentum, leaving more complex problems for later.
- Set Time Limits: Assign a specific time for each section or question and stick to it. This prevents you from spending too long on one task at the expense of others.
- Track Time Progress: Regularly check the clock to ensure you are on track and make adjustments if necessary.
- Leave Time for Review: Ensure you have some time left at the end to review your answers and correct any mistakes.
By following these strategies, you will not only ensure that you complete the assessment within the allotted time but also approach each question with a clear and focused mindset.
Analyzing Economic Growth Models

Understanding different models of growth helps explain how economies expand over time and what factors influence this process. These models incorporate various variables such as capital accumulation, technological progress, and labor force changes to provide insights into long-term prosperity. By analyzing these models, you can assess their assumptions, implications, and real-world applications, offering a clearer picture of economic development.
Several key models are used to analyze economic growth, each focusing on different mechanisms and dynamics. Below is a table comparing some of the most well-known models:
| Model | Key Focus | Assumptions | Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solow-Swan Model | Capital accumulation, labor, and technological progress | Exogenous technological progress, diminishing returns to capital | Long-term growth driven by technological advancement and capital deepening |
| Endogenous Growth Model | Role of human capital and innovation | Technological change is influenced by investment in research and development | Policy interventions can influence long-term growth by fostering innovation and education |
| Harrod-Domar Model | Investment and savings ratio | Fixed capital-output ratio, constant savings rate | Emphasizes the need for high investment rates to maintain growth |
Each of these models provides unique insights into the factors driving growth, as well as the challenges economies face in sustaining progress over time. By studying these frameworks, you can better understand the complexities of economic expansion and how policy decisions may impact future development.
Important Macroeconomic Indicators to Know

Key economic indicators provide valuable insights into the overall health and performance of a nation’s economy. These metrics help analysts, policymakers, and businesses track progress, identify trends, and make informed decisions. Understanding the significance of these indicators is essential for interpreting economic conditions and predicting future growth or downturns.
Some of the most important indicators to monitor include:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Measures the total value of all goods and services produced within a country over a specified period, serving as a broad indicator of economic activity.
- Unemployment Rate: Reflects the percentage of the labor force that is jobless and actively seeking work. This indicator is crucial for assessing the health of the labor market.
- Inflation Rate: Tracks the rate at which the general price level of goods and services rises, eroding purchasing power. Central banks closely monitor this indicator to control monetary policy.
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): Measures the average change in prices paid by consumers for a basket of goods and services, providing a direct measure of inflation.
- Interest Rates: Set by central banks, these rates influence borrowing costs, investment decisions, and overall economic activity. Low rates can stimulate growth, while high rates can help control inflation.
- Trade Balance: The difference between a country’s exports and imports, reflecting its position in global trade. A trade surplus occurs when exports exceed imports, while a deficit indicates the opposite.
By monitoring these indicators, you can gain a clearer understanding of the factors shaping economic performance and make better-informed decisions about investments, policies, and strategies for growth.
How to Interpret Fiscal Policy Questions
Understanding how government spending and taxation policies affect the economy is essential for analyzing fiscal policy-related topics. When confronted with queries regarding fiscal strategies, it’s important to focus on the specific objectives of the policy, its potential impacts on national growth, and the broader societal consequences. Clear interpretation requires a grasp of how fiscal measures influence aggregate demand, employment levels, inflation, and income distribution.
To effectively analyze these types of inquiries, consider the following steps:
- Identify the Policy Tools: Determine whether the policy involves government spending, tax adjustments, or both. Understand the difference between expansionary and contractionary approaches.
- Understand Economic Goals: Fiscal policies are often designed with specific goals in mind, such as boosting economic activity, reducing unemployment, or controlling inflation. Recognize these objectives in the context of the question.
- Assess Potential Outcomes: Think about how changes in taxation or government spending could influence economic behavior. For example, a tax cut might increase consumer spending, while increased government spending could stimulate investment and job creation.
- Consider the Timing and Scale: Reflect on whether the policy is a short-term or long-term measure. Short-term measures might focus on immediate economic recovery, while long-term policies aim to stabilize and grow the economy sustainably.
By following these steps, you can better interpret fiscal policy-related inquiries and understand the deeper implications of various strategies in a given economic context.
Monetary Policy and Its Impact

Central banks implement various strategies to influence a nation’s money supply and interest rates, directly affecting the overall economy. These measures are designed to stabilize prices, control inflation, and encourage employment. The outcomes of monetary policies are critical to understanding the short-term and long-term dynamics of an economy, as they shape consumer behavior, business investment, and the broader financial landscape.
Below is a table outlining the primary tools used in monetary policy and their potential effects on the economy:
| Tool | Action | Effect on the Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Open Market Operations | Buying or selling government bonds to adjust the money supply | Increases or decreases the amount of money circulating in the economy, influencing interest rates |
| Discount Rate | Adjusting the interest rate at which commercial banks borrow from the central bank | Lower rates make borrowing cheaper, stimulating spending and investment; higher rates have the opposite effect |
| Reserve Requirements | Changing the amount of reserves banks must hold | Lowering reserve requirements increases the lending capacity of banks, boosting economic activity |
By adjusting these tools, central banks can influence the availability of credit, control inflation, and guide economic growth. Understanding how these policies work and their intended outcomes is essential for interpreting their broader impact on national and global economies.
Key Formulas to Memorize for Exams
Mastering essential equations is crucial for analyzing economic conditions and solving problems efficiently. These formulas serve as the foundation for understanding economic relationships and performing calculations quickly. Familiarity with these key expressions will help you apply theoretical knowledge in practical scenarios, especially when facing time constraints in assessments.
Below are some of the fundamental formulas that you should know:
- GDP (Gross Domestic Product):
GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
Where: C = Consumption, I = Investment, G = Government Spending, X = Exports, M = Imports.
- Unemployment Rate:
Unemployment Rate = (Unemployed / Labor Force) * 100
This formula helps determine the percentage of the workforce that is unemployed and actively seeking work.
- Inflation Rate:
Inflation Rate = ((CPI in Current Year – CPI in Previous Year) / CPI in Previous Year) * 100
The inflation rate measures the percentage change in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) over a specified period.
- Velocity of Money:
V = (P * Y) / M
Where: V = Velocity, P = Price Level, Y = Real Output, M = Money Supply.
- Interest Rate (Fisher Equation):
Nominal Interest Rate = Real Interest Rate + Inflation Rate
This equation links nominal and real interest rates to the inflation rate.
- Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC):
MPC = Change in Consumption / Change in Income
This formula helps measure how much consumption increases with a given increase in income.
By memorizing these formulas and understanding their application, you will be well-prepared to tackle problems and make sense of various economic scenarios with greater ease and precision.
Reviewing Inflation and Unemployment Rates

Inflation and unemployment are two of the most important indicators for assessing the health of an economy. These factors not only reflect the overall economic performance but also influence government policies, business decisions, and individual financial well-being. Understanding how these variables are measured and how they interact with each other is essential for evaluating the broader economic landscape.
Inflation refers to the rate at which prices for goods and services increase, eroding purchasing power over time. A moderate level of inflation is considered normal, but when inflation becomes too high or too low, it can signal economic instability. Economists often use the Consumer Price Index (CPI) to measure inflation by tracking the price changes of a fixed basket of goods and services over time.
Unemployment is a measure of the percentage of the labor force that is actively seeking work but is unable to find employment. A high unemployment rate can indicate economic distress, while a very low rate might suggest an economy operating at full capacity. The unemployment rate is typically calculated by dividing the number of unemployed individuals by the total labor force.
Both inflation and unemployment can influence each other. For example, during periods of high inflation, central banks may raise interest rates to control price increases, which could lead to higher unemployment. On the other hand, low unemployment can sometimes lead to wage inflation, contributing to overall price rises.
By understanding these key indicators, individuals can better anticipate shifts in the economy and make more informed decisions, whether in personal finance, business investments, or policy planning.
Breaking Down International Trade Questions
International trade plays a significant role in shaping global economies, influencing both national growth and global relations. Understanding the key factors and principles behind trade is crucial for analyzing any related queries, especially when evaluating the impacts of trade policies, tariffs, and the balance of payments. These topics often require an in-depth understanding of various economic theories and real-world implications.
Key Concepts in Global Trade

When tackling questions about international trade, it’s essential to have a solid grasp of the fundamental concepts, such as:
- Comparative Advantage: This concept highlights how countries benefit from specializing in the production of goods and services where they have the lowest opportunity cost, leading to greater efficiency in global trade.
- Trade Barriers: Policies such as tariffs, quotas, and subsidies can affect trade flows by increasing costs or limiting market access, often leading to trade disputes.
- Exchange Rates: The value of one currency relative to another can have significant effects on international trade by influencing the cost of imports and exports.
Analyzing Trade Impact
Questions related to the effects of trade often require an understanding of how these concepts work together in practice. For example:
- How do trade barriers impact consumer prices in both importing and exporting nations?
- What are the consequences of currency fluctuations on a country’s trade balance?
- How does comparative advantage lead to mutual gains from trade, even when countries produce the same goods?
By breaking down these components, it becomes easier to analyze how changes in global trade can affect local economies, employment, and overall wealth distribution. These insights not only help in addressing trade-related problems but also assist in crafting policies that promote beneficial international economic relationships.
Studying Macroeconomics with Practice Tests
Engaging with practice assessments is one of the most effective methods for mastering complex economic concepts. These exercises help reinforce knowledge, improve retention, and boost confidence by providing a realistic preview of how theoretical principles are applied in various scenarios. Additionally, simulated problems allow students to identify their strengths and weaknesses, allowing for targeted revision.
Benefits of Practice Assessments
Incorporating practice tests into your study routine offers numerous advantages, such as:
- Improved Conceptual Clarity: Working through diverse problems helps clarify challenging concepts by showing their real-world applications.
- Better Time Management: Practice tests help improve pacing, allowing you to effectively allocate time to each section of a test or assignment.
- Increased Familiarity with Question Formats: Practicing different types of problems prepares you for the structure and language of assessments.
Strategies for Effective Practice
To get the most out of practice exercises, consider the following strategies:
- Simulate Real Conditions: Try to replicate test conditions by timing yourself and working without interruptions.
- Review Incorrect Answers: After completing a practice test, take the time to go over the mistakes and understand the reasoning behind correct responses.
- Mix Topics: Rotate between different topics to ensure a well-rounded understanding of the material and avoid focusing too heavily on one area.
By regularly incorporating practice problems into your study plan, you’ll be better prepared to tackle any challenges that arise during assessments, making the learning process both effective and efficient.
Building Confidence for Your Exam Day
Feeling prepared and confident is key to achieving success on assessment day. The more you familiarize yourself with the material and the testing process, the more you reduce anxiety and increase your chances of performing well. Confidence comes not only from understanding the content but also from having a clear strategy in place for approaching the task at hand.
One of the most important aspects of building confidence is creating a solid study plan. This plan should incorporate a combination of reviewing key concepts, practicing problems, and taking time for relaxation. When you feel organized and well-prepared, it naturally boosts your self-assurance.
Effective Strategies for Confidence
Here are a few strategies to help you build confidence before the big day:
- Consistent Review: Regularly revisit the material, even after you feel you understand it. This reinforcement helps lock in your knowledge and ensures you’re ready for any challenge that might arise.
- Simulate Real Testing Conditions: By mimicking the test environment–timing yourself and working without interruptions–you’ll feel more comfortable on the actual day.
- Manage Stress with Relaxation Techniques: Practicing mindfulness, deep breathing, or short walks can help reduce stress and keep you calm as the test approaches.
Positive Mindset and Focus
Another crucial factor is maintaining a positive mindset. Focus on what you’ve mastered rather than what you still need to learn. Trust in your preparation and avoid negative self-talk, which can undermine your confidence. Remember, confidence is as much about attitude as it is about ability.
On the day of the assessment, take a few moments to review your notes, but also allow yourself to relax. Getting a good night’s sleep before the test is essential to staying sharp and focused. By preparing well and staying calm, you’ll approach the task with confidence and clarity.