HTML Exam Questions and Answers for Effective Preparation

Mastering the fundamentals of web coding is crucial for anyone aiming to demonstrate their expertise in front-end design. As the internet evolves, the demand for proficient developers grows, making it essential to grasp the core principles of markup language. This section is dedicated to helping you prepare for assessments that test your understanding of web structure and syntax.
Understanding key concepts like document structure, element usage, and proper syntax is the foundation of any test. A solid grasp of these elements will help you confidently tackle various challenges, whether they involve building forms, styling text, or structuring web pages efficiently.
By reviewing common tasks, structure-based questions, and their related solutions, you’ll gain valuable insights into what topics to focus on and how to apply your knowledge effectively. With the right preparation, you’ll be ready to excel in practical assessments and advance your web development skills.
HTML Exam Questions and Answers
When preparing for assessments related to web page creation, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the most commonly tested areas. These include essential topics such as structuring a webpage, using elements efficiently, and understanding the purpose of various attributes. Mastery of these concepts will significantly improve your ability to perform well on practical tasks and theoretical evaluations.
Common Topics to Focus On
Some of the most frequently covered areas involve the use of tags like <div>, <span>, and <a>, as well as understanding how these elements interact with each other. Questions often require you to demonstrate your knowledge of creating hyperlinks, formatting text, and embedding multimedia content. Additionally, being able to effectively work with forms and tables is crucial for successfully completing these tasks.
How to Approach Different Tasks
It’s also beneficial to practice hands-on activities like coding simple web pages from scratch, ensuring that you follow best practices in structure and syntax. Common practical challenges may include tasks such as creating responsive layouts or styling elements to match certain specifications. Regular practice will help you develop the skills needed to approach these tasks with confidence and efficiency.
Key Topics for HTML Exams
To successfully navigate evaluations related to web development, it’s essential to focus on the core subjects that are frequently tested. These fundamental concepts lay the groundwork for understanding how web pages are structured, styled, and function across different browsers and devices. A strong grasp of these key areas will enhance your problem-solving abilities during assessments.
Essential Elements and Structure
Understanding the basic structure of a webpage is crucial. This includes knowledge of the main components such as the <header>, <footer>, <article>, and <section> tags, as well as how to correctly nest elements for optimal performance. You’ll also need to demonstrate the ability to create lists, tables, and forms, all of which are fundamental tasks in web development.
Attributes, Links, and Multimedia
Another critical area of focus is the use of attributes within various tags. Understanding how to utilize attributes like href, src, and alt is vital for creating functional hyperlinks, embedding images, and enhancing accessibility. Additionally, working with multimedia elements such as videos and audio files is an important skill to develop for creating rich, interactive webpages.
Understanding HTML Syntax Basics
Mastering the foundational rules of markup language is key to building structured and functional web pages. Knowing how to properly use elements, attributes, and their relationships ensures that your code is readable and works as expected across different browsers. This section covers the essential syntax you need to follow for proper markup and document organization.
Basic Structure of a Web Page
The core of any page includes a series of elements that work together to create the layout and content. A standard structure is as follows:
- <!DOCTYPE> declaration at the top to define the document type
- <html> tag that wraps all the content
- <head> section containing metadata and links to stylesheets
- <body> section which holds the visible content like text and images
Element Syntax and Nesting
Each element follows a specific syntax, which includes an opening tag, possible content, and a closing tag. Correct nesting of elements is critical for maintaining structure and functionality:
- Start tags indicate the beginning of an element (e.g., <p> for paragraphs)
- End tags close the element (e.g., </p>)
- Some elements are self-closing, like <br> for line breaks
Properly nesting tags ensures that content is displayed as intended and avoids errors in layout and functionality.
Common HTML Tags You Should Know
To effectively build web pages, it’s essential to be familiar with a set of core tags that serve as the building blocks for content structure and layout. These tags allow you to define different sections, format text, and link various resources together. Knowing how to use them properly will enhance both the accessibility and functionality of your web projects.
Here are some of the most widely used tags:
- <h1> to <h6> – Headings for defining the hierarchy of content, with <h1> being the highest level and <h6> the lowest.
- <p> – Paragraphs, used to group text into readable blocks.
- <a> – Anchors, used for creating hyperlinks to other pages or external sites.
- <img> – Images, used to embed pictures or graphics into the page.
- <ul> and <ol> – Unordered and ordered lists for grouping items in a list format.
- <li> – List items, used within <ul> or <ol> to define individual elements.
- <div> – Division, used to group content for styling or scripting purposes.
- <span> – Inline container, used to apply styles or manage specific text within a block of content.
- <form> – Forms, used to collect user input, such as text fields, buttons, and checkboxes.
By mastering these essential tags, you will be able to structure your pages effectively and lay a strong foundation for more advanced web development techniques.
HTML Elements and Their Structure
Understanding the building blocks of a webpage is crucial for creating well-structured and functional content. Each component in a webpage is represented by an element, which can be combined and nested to create complex layouts and features. Knowing how to use these elements properly will ensure that your code is clean, efficient, and accessible across different platforms.
Structure of a Web Page
Every webpage is composed of elements that follow a consistent structure. These elements typically consist of an opening tag, content, and a closing tag. For example, a paragraph element is defined by <p> at the beginning and </p> at the end. Properly nesting these elements ensures that the content is displayed correctly and that the page is easily navigable.
Common Element Types
Some of the most common elements include:
- <div> – A container used to group other elements together for styling or layout purposes.
- <a> – An anchor tag, used to create hyperlinks to other pages or resources.
- <form> – A form element, used to collect user input such as text, checkboxes, and buttons.
- <img> – Used to embed images within a page, usually with additional attributes like src and alt.
Mastering the use of these basic elements will provide a solid foundation for more advanced web development tasks, allowing you to create dynamic, interactive websites.
Attributes and Their Usage in HTML
Attributes provide additional information about an element, helping to define its properties or behavior. These modifiers are placed within the opening tag of an element and can control everything from styling and functionality to linking external resources. Understanding how to properly apply attributes is essential for creating fully functional and optimized web pages.
Some attributes are standard across various tags, while others are specific to certain elements. Below are some of the most commonly used attributes:
| Attribute | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| href | Defines the destination of a hyperlink | <a href=”https://example.com”>Visit Website</a> |
| src | Specifies the source of an image or media file | <img src=”image.jpg” alt=”Description”> |
| alt | Provides alternative text for images, improving accessibility | <img src=”logo.png” alt=”Company Logo”> |
| id | Assigns a unique identifier to an element | <div id=”header”>Content</div> |
| class | Assigns a class name to an element for styling or scripting | <div class=”container”>Content</div> |
| style | Defines inline styles for an element | <p style=”color: blue;”>Text</p> |
Using attributes correctly enhances the functionality of your page, ensuring it behaves as expected and is accessible to all users. By applying the appropriate attributes to elements, you can tailor the appearance, behavior, and interactions on your website.
Forms and Input Elements in HTML

Creating forms is essential for gathering user input, whether it’s through text, selections, or file uploads. These elements allow users to interact with a website by submitting data to be processed or stored. Understanding how to properly implement these components ensures a smooth user experience and effective data handling.
Basic Structure of a Form
At the heart of any data submission is the <form> element, which encapsulates all input fields and buttons. A typical form is defined by the following structure:
- <form> – Wraps all form-related elements, including input fields and buttons.
- <input> – Defines an input field where users can enter data.
- <button> – A clickable button to submit the form or trigger an action.
Types of Input Elements
There are several input elements designed for different types of user input:
- <input type=”text”> – A text field for short user inputs.
- <input type=”password”> – Used for password fields to obscure the input.
- <input type=”email”> – A field specifically designed for email addresses, often with built-in validation.
- <textarea> – A larger text area for longer inputs such as messages or comments.
- <input type=”radio”> – A radio button, allowing users to select one option from a set.
- <input type=”checkbox”> – A checkbox, used for multiple selections.
- <select> – A dropdown menu for selecting an option from a list.
By using the appropriate input types, you can create forms that cater to different data collection needs while enhancing user interaction and improving data accuracy.
Creating Links and Navigation Menus
Navigation is a key aspect of any website, enabling users to move between different pages and sections seamlessly. Creating effective links and navigation menus enhances the user experience by making it easy to access relevant content. These elements are essential for structuring a website and guiding visitors through the information available.
Links are typically used to connect different pages within the same site or direct users to external websites. When combined with navigation menus, they provide a clear and organized way for users to explore a site’s content. A well-designed menu can improve site usability and ensure that users find what they need quickly.
For creating navigation, the <a> tag is commonly used to define clickable links. The <nav> element is often used to group these links together, creating a navigation section that can be styled and structured to fit the design of the page.
How to Embed Media in HTML
Embedding media content, such as images, videos, and audio files, is an essential part of creating dynamic and engaging webpages. By incorporating multimedia, you can enhance the overall user experience, making the content more interactive and visually appealing. The ability to embed different types of media allows you to convey information in various formats, reaching a wider audience.
Embedding Images
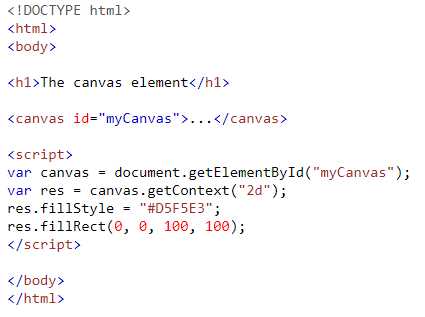
To embed an image, the <img> tag is used, with the src attribute pointing to the image’s location, either locally or on the web. It is also important to provide an alt attribute to describe the image, improving accessibility for visually impaired users.
Embedding Videos
Videos can be embedded using the <video> tag. You can provide different formats for compatibility across browsers and even enable controls such as play, pause, and volume adjustment using the controls attribute.
| Media Type | Tag | Key Attributes |
|---|---|---|
| Image | <img> | src, alt |
| Video | <video> | src, controls, poster |
| Audio | <audio> | src, controls |
By using the correct tags and attributes, you can easily integrate various types of media into your webpage. Whether it’s images, videos, or audio, embedding media adds richness to your content and helps create a more engaging and interactive experience for users.
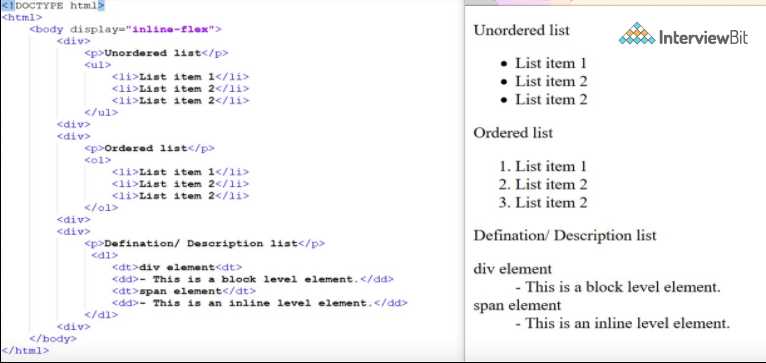
HTML Lists: Ordered and Unordered
Lists are essential elements for organizing content in a structured way. They help present information in a clear and concise manner, making it easier for users to digest. Two common types of lists are ordered and unordered, each serving a different purpose depending on the context of the information being displayed.
Unordered Lists
An unordered list is used when the order of the items does not matter. It is commonly used for lists where the sequence of the elements is not important, such as a list of features or items in a menu. The list items are typically displayed with bullet points.
- First item
- Second item
- Third item
Ordered Lists

Ordered lists are used when the order of the items is significant, such as instructions, steps in a process, or rankings. These lists automatically number the items, indicating a clear sequence or hierarchy.
- Step 1: Open the file
- Step 2: Edit the content
- Step 3: Save the changes
Both unordered and ordered lists are essential tools for organizing content effectively. Using them correctly helps improve readability and enhances the structure of the webpage, providing a better user experience. Whether you need a simple list of items or a step-by-step guide, these elements are versatile and easy to implement.
Working with HTML Tables Effectively
Tables are essential elements for organizing and displaying data in a grid-like structure. They allow content to be presented clearly, with rows and columns that make complex information easier to read and understand. By structuring content within tables, users can quickly identify relationships between different data points, making it an invaluable tool for various types of information presentation.
When working with tables, it’s important to use appropriate tags for defining the structure. The <table> tag creates the table, while <tr> defines each row. The <th> tag is used for header cells, which provide context for the columns, while <td> defines the regular data cells within each row.
To improve readability, tables can be styled with borders, alternating row colors, and proper spacing. Using the <caption> tag can also add a title to the table, giving users a clearer idea of the data being presented. For better accessibility, it’s also helpful to use the <thead>, <tbody>, and <tfoot> tags to group the header, body, and footer sections, respectively.
In summary, tables provide an effective way to present structured data, making it easier for users to digest complex information. By following best practices and organizing the content clearly, you can enhance both the functionality and the user experience of your webpage.
Semantic HTML: Importance and Usage
Using meaningful elements in web development is crucial for improving both the accessibility and readability of content. By choosing the right tags, you can make your pages more understandable to both users and search engines. Semantic markup not only helps clarify the structure and purpose of the content but also enhances the overall user experience and SEO performance.
Semantic elements provide clear meaning about the type of content they contain. For example, using <header>, <footer>, <article>, and <section> elements helps define distinct sections of a webpage, making it easier for users to navigate. These elements also help screen readers interpret the content correctly, which is vital for web accessibility.
Incorporating semantic tags also benefits search engine optimization (SEO). By using appropriate elements like <nav> for navigation links and <main> for primary content, search engines can better understand the structure of the page, leading to more accurate indexing and improved visibility in search results.
In conclusion, semantic markup is a best practice that not only improves accessibility and SEO but also ensures that content is presented logically and effectively. By adopting these principles, web developers can create more robust, user-friendly, and search engine-optimized pages.
HTML Document Structure Explained
The structure of a webpage is vital for organizing content and ensuring proper functionality. A well-structured document allows browsers to interpret and display the content effectively. Understanding the basic components that make up a webpage is essential for both web development and maintaining best practices in content presentation.
Every webpage begins with a <!DOCTYPE> declaration that informs the browser of the document type. This is followed by the <html> element, which serves as the root element of the page. Inside the <html> tag, there are two primary sections: the <head> and <body>.
The <head> section contains metadata such as the title of the webpage, links to external resources like stylesheets, and other information that isn’t directly visible to users. On the other hand, the <body> section holds all the content that is rendered to the page, including text, images, links, and interactive elements.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| <!DOCTYPE> | Defines the document type and version |
| <html> | Root element of the webpage |
| <head> | Contains metadata like title, links to stylesheets, etc. |
| <body> | Holds visible content like text, images, and links |
In summary, the structure of a webpage is a critical aspect of web development. By understanding the roles of each component, developers can ensure their content is well-organized, easily accessible, and properly displayed across different browsers and devices.
Text Formatting with HTML Tags
Properly formatting text is essential for creating readable and well-organized content. By using specific tags, you can alter the appearance of text, making it bold, italic, or underlined, among other things. These simple formatting elements help enhance the user experience by emphasizing key information and ensuring clarity.
For instance, the <strong> tag is commonly used to make text bold, which highlights important parts of the content. Similarly, the <em> tag is used to italicize text, often for emphasis or to indicate a different tone. Additionally, the <u> tag can be used to underline text, making it stand out visually on the page.
Other tags, such as <del> and <ins>, allow you to show text that has been deleted or inserted, respectively, making it useful for editing purposes or tracking changes in content. By combining these formatting tools, developers can create content that is not only visually appealing but also easier to navigate.
HTML Validation Techniques and Tools
Ensuring that a webpage is correctly structured is crucial for compatibility across different browsers and devices. Validation helps identify errors or inconsistencies in the code, ensuring that the document follows established standards. Using proper validation techniques and tools is an essential step in improving website performance, accessibility, and search engine optimization.
Common Techniques for Validation
To validate a webpage, developers need to check various components of the code for correctness. Here are some common techniques:
- Manual Inspection: Carefully reviewing the code for mistakes, missing tags, or improper syntax.
- Automated Tools: Using online or offline tools to automatically check for errors and provide suggestions for improvements.
- Cross-Browser Testing: Testing the code across multiple browsers to ensure compatibility and correct rendering.
Popular Validation Tools
There are several tools available that can help automate the validation process, making it easier to find and fix issues:
- W3C Validator: A widely used tool for validating syntax and structure to ensure compliance with web standards.
- HTMLHint: An open-source tool that checks for syntax errors, style guidelines, and potential issues in the code.
- JSHint: Primarily used for validating JavaScript, but it can also highlight issues in HTML code related to dynamic content.
By utilizing these techniques and tools, developers can improve the quality and reliability of their web content, ensuring that it works properly for all users. Regular validation should be part of the development process to catch issues early and maintain high-quality code.
HTML Accessibility Guidelines
Ensuring that digital content is accessible to all users, regardless of their abilities or disabilities, is an essential aspect of modern web development. Accessibility guidelines help developers create websites that are inclusive, providing equal access to information and functionality for everyone, including individuals with visual, auditory, cognitive, or motor impairments.
Key Accessibility Principles
There are several fundamental principles that should be followed to improve accessibility:
- Perceivable: Information and user interface components must be presented in ways that users can perceive, such as providing text alternatives for non-text content.
- Operable: User interface elements must be operable through various means, including keyboard or other assistive devices.
- Understandable: Content and navigation should be easy to understand, with consistent layout and clear language.
- Robust: Content must be compatible with a wide variety of devices, browsers, and assistive technologies.
Common Techniques for Improving Accessibility
To implement these principles, web developers can use the following techniques:
- Alternative Text for Images: Provide descriptive text for images so that screen readers can convey the meaning to visually impaired users.
- Semantic Markup: Use correct HTML elements for structure, such as
<header>,<nav>,<article>, and<footer>, to help users navigate content. - Keyboard Navigation: Ensure that all interactive elements are accessible and can be navigated using a keyboard alone.
- Color Contrast: Use high contrast between text and background to help users with visual impairments read the content easily.
By following these accessibility guidelines, developers can create websites that provide a better experience for all users, ensuring that no one is left behind due to their specific needs or abilities.
Best Practices for Writing HTML Code
Writing clean, efficient, and maintainable code is essential for building successful web pages. Following best practices helps improve the structure of your content, enhances accessibility, and ensures better performance across different devices and browsers. By adhering to established guidelines, developers can create websites that are easy to manage, scale, and optimize.
Key Guidelines to Follow
Here are some best practices that should be followed to ensure quality and consistency when writing your code:
- Use Semantic Elements: Utilize appropriate tags such as
<header>,<article>,<section>, and<footer>to define the structure of the document. This helps search engines and assistive technologies understand your content better. - Write Clear, Descriptive Code: Ensure that tags and attributes are clear and descriptive. Use meaningful names for classes and IDs to make the code easier to read and understand.
- Maintain Proper Indentation: Consistent indentation improves the readability of the code, making it easier to follow the structure and detect errors quickly.
- Close All Tags: Always close your elements properly to avoid rendering issues or unexpected behavior in different browsers. This applies to self-closing tags as well.
- Use Alt Text for Images: Include
altattributes for images to describe their content. This helps with accessibility and provides context when images fail to load.
Examples of Proper Code Structure
Here’s a simple example demonstrating a properly structured document following best practices:
| Element | Purpose |
|---|---|
<html> |
Defines the start of the document. |
<head> |
Contains metadata such as the title and links to stylesheets. |
<body> |
Holds the main content visible to users. |
<header> |
Defines the top section of the page, typically including navigation and branding. |
<footer> |
Contains footer information like copyright, links, and contact details. |
By following these best practices, your web content will be easier to manage, more accessible, and better optimized for performance.
HTML Resources for Further Learning
To deepen your understanding and improve your skills in web development, there are numerous valuable resources available. These materials provide comprehensive knowledge, practical examples, and expert advice on building web pages. Exploring these resources will help you stay up-to-date with the latest standards and best practices, enabling you to create more advanced and optimized websites.
Recommended Books

Books are a great way to gain structured knowledge, often covering a wide range of topics and providing in-depth explanations.
- “Learning Web Design” by Jennifer Niederst Robbins: A beginner-friendly book that covers the fundamentals of creating websites, from structure to design principles.
- “Web Design with HTML, CSS, JavaScript and jQuery” by Jon Duckett: A visually appealing and highly readable book that breaks down complex concepts into manageable pieces.
- “Responsive Web Design with HTML5 and CSS3” by Ben Frain: A comprehensive guide for creating responsive layouts and improving mobile accessibility.
Online Platforms and Courses
There are many online platforms offering free and paid courses, providing step-by-step guidance and hands-on practice to enhance your skills.
- freeCodeCamp: A free online platform offering interactive lessons, coding challenges, and projects in various web technologies.
- Codecademy: Offers beginner and advanced level courses with interactive coding exercises and quizzes.
- MDN Web Docs: The Mozilla Developer Network provides detailed documentation, tutorials, and guides for all skill levels. It’s an excellent resource for developers looking to learn or refresh their skills.
Interactive Tools and References

Using interactive tools and references can be a fun and effective way to practice coding and stay sharp. Here are some great options:
- CodePen: An online code editor and community where you can experiment with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, and share your projects.
- JSFiddle: Similar to CodePen, JSFiddle allows you to write and test code directly in the browser, making it easy to see changes in real-time.
- W3Schools: A popular resource with tutorials, examples, and exercises to help you learn at your own pace.
By utilizing these resources, you’ll be able to build a strong foundation in web development and continuously expand your knowledge and capabilities.