Spanish 2 Semester 1 Exam Review Guide
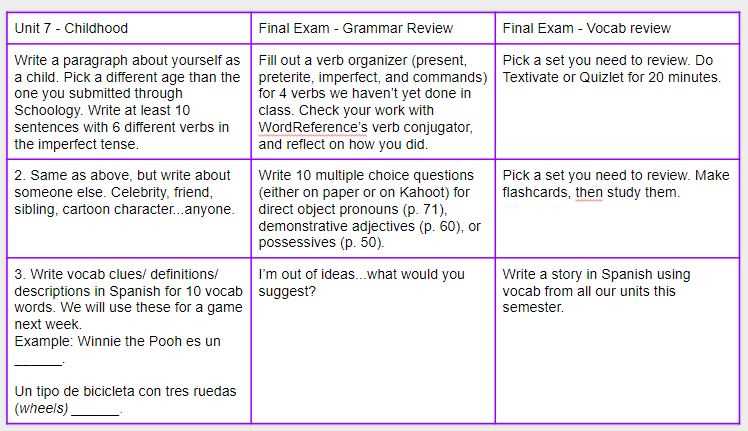
Success in language learning requires a solid understanding of key concepts, from grammar rules to vocabulary usage. Mastering these elements is crucial for advancing and achieving fluency. Whether you’re preparing for a test or simply reinforcing your knowledge, focusing on the right areas can make a significant difference in your performance.
In this section, we will delve into important topics and strategies to help you solidify your foundation. You’ll be able to sharpen your grasp on various structures, improve your comprehension skills, and boost your confidence. With dedicated preparation, even the most challenging aspects can become manageable.
By breaking down the material into manageable sections, we aim to guide you through the essential concepts. Whether you need to practice verb conjugations or review common sentence patterns, this guide will provide the tools necessary to approach your studies with confidence and clarity.
Spanish 2 Semester 1 Exam Review
In this section, we will focus on strengthening your language skills through a comprehensive exploration of key concepts and techniques. Understanding core elements such as grammar structures, verb conjugations, and essential vocabulary will lay a strong foundation for mastering the language.
To help reinforce your learning, we will break down the content into clear, digestible topics. Each area is designed to target specific aspects of the language, enabling you to approach each challenge with confidence. Whether you need to revisit verb forms or fine-tune sentence construction, this guide will assist you in preparing effectively.
With careful practice and a focused approach, you can enhance both your understanding and application of the language. By revisiting key concepts and identifying areas for improvement, you will feel more prepared for any assessment or real-world use of the language.
Key Grammar Concepts to Focus On
Mastering grammar is essential for building a strong foundation in any language. Focused attention on key structures will help you gain better control over sentence construction and improve your overall fluency. Below are some crucial elements to prioritize in your preparation.
Verb Conjugations
Understanding verb forms and their proper use is one of the most important aspects. Pay close attention to these areas:
- Regular vs. irregular verb forms
- Conjugation in different tenses: present, past, and future
- Subjunctive mood usage in specific contexts
Adjective Agreement and Placement
Proper adjective agreement with nouns is essential for accurate sentence structure. Be sure to review:
- Agreement in gender (masculine vs. feminine) and number (singular vs. plural)
- Placement of adjectives before or after the noun
- Exceptions to standard adjective agreement rules
By focusing on these fundamental grammar points, you’ll be able to construct more accurate and expressive sentences, ensuring greater clarity in communication.
Common Verb Conjugation Rules
Verb conjugation is a cornerstone of language mastery, as it allows you to communicate actions across different times and subjects. Understanding how to properly alter verbs for tense, mood, and subject is essential for forming accurate and meaningful sentences. Below, we explore some of the most commonly used conjugation patterns that will help you express ideas clearly and correctly.
| Verb Ending | Conjugation Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
| -ar | Regular | hablar (to speak) – hablo (I speak) |
| -er | Regular | comer (to eat) – como (I eat) |
| -ir | Regular | vivir (to live) – vivo (I live) |
| -ar | Irregular | tener (to have) – tengo (I have) |
| -er/-ir | Stem-changing | querer (to want) – quiero (I want) |
These common verb endings cover a wide range of actions, and understanding their variations is crucial for fluency. Regular verbs follow consistent patterns, while irregular and stem-changing verbs require more attention to their specific changes. Mastering these rules will significantly improve your command of the language.
Vocabulary You Need to Know
Building a strong vocabulary is essential for effective communication. Having a solid grasp of commonly used words allows you to express yourself clearly and understand others in various contexts. Focusing on key themes and frequently used terms will improve your ability to engage in conversations and comprehend texts.
Commonly Used Verbs
Verbs are the backbone of any sentence. Mastering a set of important action words will allow you to describe a wide range of activities and situations.
| Verb | Meaning |
|---|---|
| comer | to eat |
| hablar | to speak |
| vivir | to live |
| tener | to have |
| ir | to go |
Essential Nouns and Adjectives
Understanding common nouns and adjectives will help you describe objects, people, and situations accurately. Focus on terms related to everyday life.
| Word | Meaning |
|---|---|
| casa | house |
| amigo | friend |
| grande | big |
| feliz | happy |
| nuevo | new |
By focusing on these core vocabulary words, you can quickly expand your ability to communicate and understand key topics. Regular practice with these terms will help you feel more confident in both written and spoken communication.
Understanding Sentence Structure in Spanish
Mastering the arrangement of words in a sentence is crucial for clear communication. Sentence structure dictates how different elements, such as subjects, verbs, and objects, interact within a statement or question. Understanding the order in which these components appear will allow you to form grammatically correct and coherent sentences.
In most cases, the typical structure follows a straightforward subject-verb-object order, but variations exist depending on the sentence type and context. Additionally, certain sentence elements, such as adjectives and adverbs, must be placed in specific locations to maintain proper meaning and fluency.
For instance, in affirmative sentences, the subject usually comes first, followed by the verb and then the object. In negative sentences, the word “no” is placed before the verb. Questions, on the other hand, require subject-verb inversion or specific question words at the beginning of the sentence. Understanding these key rules will improve both comprehension and expression.
Reviewing Past Tense Forms
Understanding how to express actions that have already happened is essential for storytelling, describing events, and explaining past experiences. The ability to correctly conjugate verbs in the past is a fundamental skill, as it allows you to convey when and how something occurred. Different forms of the past tense exist, each serving a specific function in conveying the nature of the action.
The two most common past tenses are the preterite and the imperfect. The preterite is used for actions that are viewed as completed or specific events, while the imperfect describes ongoing actions or habitual behaviors in the past. Mastery of these forms will help you express yourself clearly and accurately when discussing events that have already taken place.
Regular verbs follow consistent conjugation patterns, while irregular verbs may require special attention. Familiarizing yourself with both regular and irregular conjugations will ensure you are prepared to handle a wide variety of past tense situations.
Mastering Future Tense Usage
Being able to talk about what will happen in the future is essential for expressing plans, predictions, and intentions. The future tense is used to convey actions or events that have yet to occur. Understanding when and how to use this tense will allow you to make statements about what you believe or expect to happen.
In many languages, the future tense is formed by conjugating verbs in a specific way. Regular verbs follow a set pattern, while some verbs are irregular and require memorization of their unique forms. The future tense is often used not only to describe planned actions but also to make predictions based on current knowledge.
For example, the future tense can be used to talk about personal goals, like “I will travel next summer,” or to describe things people believe will happen, like “It will rain tomorrow.” By mastering this tense, you can expand your ability to discuss upcoming events with confidence.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Spanish
When learning a new language, it’s easy to make certain errors that can affect communication. Understanding the most common mistakes and knowing how to avoid them can greatly improve your fluency. Below are some of the most frequent pitfalls and tips on how to steer clear of them.
- Incorrect verb conjugations – One of the most frequent mistakes is using the wrong verb form for a specific subject or tense. Pay close attention to regular and irregular verb conjugations.
- Misplacing adjectives – In some cases, adjectives must follow the noun, while in others they precede it. Be sure to know the rules of adjective placement for clarity.
- Confusing gender and number – Many learners forget to match nouns and adjectives in gender (masculine/feminine) and number (singular/plural). Always check for agreement between these elements.
- Using incorrect prepositions – Prepositions can vary between languages, so be careful not to translate directly from your native language. Some prepositions have different meanings depending on the context.
- Overusing direct translations – Avoid directly translating phrases or idioms from your native language, as they may not make sense or have the same meaning in the target language.
By staying mindful of these common mistakes and practicing the correct usage, you can enhance both your speaking and writing skills. With careful attention, you can avoid these errors and communicate more effectively.
Pronunciation Tips for Spanish Learners
Mastering proper pronunciation is essential for clear communication. Correctly pronouncing words not only helps you be understood but also boosts your confidence in speaking. Some sounds in this language may be different from those in English, so focusing on key pronunciation rules can significantly improve your speaking skills.
Focus on Vowel Sounds
Vowel sounds in this language are more consistent than in English. There are five vowels–a, e, i, o, and u–and each one has a distinct sound. Pay attention to these vowels and practice their clear, crisp pronunciation.
- a – sounds like the “a” in “father”
- e – sounds like the “e” in “bed”
- i – sounds like the “ee” in “see”
- o – sounds like the “o” in “pot”
- u – sounds like the “oo” in “food”
Consonant Clarity
Some consonants can be tricky, especially for learners. Certain letters like r, j, and v have different pronunciations compared to English. Practice these sounds slowly and consistently to improve your pronunciation.
- r – rolled or trilled in many words, especially at the beginning of a word or between vowels.
- j – sounds like the “h” in “hello,” but more guttural.
- v – often pronounced like a soft b, especially in many regional accents.
By regularly practicing these sounds and paying attention to the rhythm and flow of the language, you’ll soon notice improvements in your clarity and fluency. Make a habit of listening to native speakers and mimicking their pronunciation to further enhance your speaking skills.
Important Adjective Agreement Rules
In many languages, adjectives must match the nouns they describe in both gender and number. This means that the form of an adjective changes depending on whether the noun is masculine or feminine, singular or plural. Understanding these agreement rules is crucial for constructing accurate and natural-sounding sentences.
For most adjectives, the rule is simple: if the noun is masculine, the adjective will typically end in -o, and if the noun is feminine, the adjective will end in -a. However, there are exceptions, such as adjectives that end in -e, which do not change for gender. Pluralization involves adding -s or -es depending on the ending of the adjective.
- Masculine singular: amigo alto (tall friend)
- Feminine singular: amiga alta (tall friend)
- Masculine plural: amigos altos (tall friends)
- Feminine plural: amigas altas (tall friends)
Some adjectives, particularly those ending in -e or a consonant, do not change for gender, only for number. It’s important to recognize these exceptions and practice them to avoid mistakes. Additionally, certain adjectives may change meaning depending on whether they are used in their masculine or feminine forms.
By mastering these agreement rules, you can construct sentences that are both grammatically correct and fluent, helping you express yourself more naturally and confidently.
Questions and Negations in Spanish
Asking questions and making negations are essential skills in any language. In order to effectively communicate your needs and opinions, it’s important to understand the proper structures and rules for forming questions and negative statements. These constructions often follow specific patterns and can change depending on the context.
To form questions, there are a few key components to remember. First, the word order may shift, and second, question words (such as qué, dónde, cuándo, etc.) are used to gather specific information. Additionally, the use of rising intonation can indicate a yes/no question without needing a question word.
Forming Questions
- Yes/No questions – Simply invert the subject and the verb. Example: ¿Estás listo? (Are you ready?)
- Information questions – Use question words like qué (what), dónde (where), cómo (how), etc. Example: ¿Dónde vives? (Where do you live?)
- Raising intonation – In spoken language, you can often form a question simply by raising the pitch at the end of a statement. Example: Tú vas al cine? (You are going to the movies?)
Negating Statements
When making negative statements, the most common method is to place the word no before the verb. However, there are several other words that can be added to intensify or clarify the negation. For example, nunca (never), nadie (no one), and nada (nothing) can be used for emphasis or to add detail.
- Basic negation – No quiero ir (I don’t want to go)
- Double negation – In some cases, negations are doubled for emphasis. Example: No tengo nada (I don’t have anything)
- Negation with other words – Example: Nadie vino a la fiesta (No one came to the party)
By practicing these structures, you’ll be able to form clear and correct questions and negative sentences, enhancing your ability to engage in conversations and express yourself effectively.
Using Prepositions Correctly
Prepositions are vital components of language that establish relationships between different elements within a sentence. They can indicate direction, location, time, and various other connections. Mastering the use of prepositions is key to forming accurate and fluent sentences, as improper usage can lead to confusion or miscommunication.
While some prepositions may seem straightforward, many require specific usage patterns. Additionally, different languages often pair prepositions with verbs, adjectives, and nouns in ways that do not always align with the patterns in other languages. Therefore, it’s important to understand the correct pairing and context for each preposition.
Common Prepositions and Their Uses
- Para – Used to indicate purpose or destination. Example: Voy para la tienda (I am going to the store).
- Con – Indicates association or accompaniment. Example: Estoy con mis amigos (I am with my friends).
- De – Shows possession or origin. Example: Es de mi hermana (It is my sister’s).
- En – Refers to location or time. Example: Estoy en la casa (I am at the house).
Prepositions with Verbs
In many cases, specific verbs require particular prepositions to complete their meaning. Here are a few examples:
- Soñar con – To dream of. Example: Sueño con viajar a Europa (I dream of traveling to Europe).
- Enamorarse de – To fall in love with. Example: Me enamoré de ella (I fell in love with her).
- Pensar en – To think about. Example: Pensamos en el futuro (We think about the future).
By becoming familiar with prepositional phrases and their specific contexts, you will greatly enhance your ability to communicate clearly and accurately. Practice and exposure to various sentence structures will help reinforce correct usage.
Practice with Regular and Irregular Verbs
Verbs are essential to sentence construction, and understanding how to properly conjugate them is crucial for expressing actions and states of being. While many verbs follow predictable patterns, others deviate from these rules and require special attention. Being able to identify and correctly use both regular and irregular verbs is key to mastering sentence formation and achieving fluency.
Regular verbs follow consistent conjugation patterns across different tenses, which makes them easier to learn and predict. In contrast, irregular verbs do not adhere to standard conjugation rules, which can be more challenging. However, with practice, these irregular forms become easier to recognize and use correctly.
Regular Verb Conjugation
Regular verbs typically follow a fixed set of endings depending on the verb type. For example:
- -ar verbs: hablar (to speak) → hablo, hablas, habla, hablamos, habláis, hablan
- -er verbs: comer (to eat) → como, comes, come, comemos, coméis, comen
- -ir verbs: vivir (to live) → vivo, vives, vive, vivimos, vivís, viven
Once you learn the basic endings, conjugating regular verbs in different tenses becomes more intuitive. The key is practice and repetition.
Irregular Verbs and Their Forms
Irregular verbs, on the other hand, do not follow the standard conjugation patterns. Some common examples include:
- Ser (to be) → soy, eres, es, somos, sois, son
- Ir (to go) → voy, vas, va, vamos, vais, van
- Estar (to be) → estoy, estás, está, estamos, estáis, están
- Tener (to have) → tengo, tienes, tiene, tenemos, tenéis, tienen
These irregular verbs often require memorization, as they don’t follow the predictable rules of regular verbs. A helpful tip is to practice common irregular verbs frequently and focus on their unique conjugation forms.
By dedicating time to both regular and irregular verb forms, you’ll gain confidence in using them correctly across different tenses, which is essential for fluency and effective communication.
Essential Phrases for Everyday Conversation
Effective communication is key to building confidence and connecting with others. Having a solid grasp of essential phrases helps you navigate daily interactions with ease, whether you’re ordering food, asking for directions, or making small talk. These commonly used expressions serve as the foundation for conversations and are critical for engaging in various situations.
While vocabulary and grammar are important, it’s the practical use of phrases that often defines successful communication. Mastering a few key expressions allows you to respond quickly and naturally in different contexts, whether formal or informal.
Common Phrases for Different Situations
Below are some of the most useful expressions for daily conversations:
| Situation | Phrase | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Greeting | ¿Cómo estás? | How are you? |
| Asking for Help | ¿Puedes ayudarme? | Can you help me? |
| Expressing Gratitude | Gracias | Thank you |
| Making Requests | Por favor | Please |
| Apologizing | Lo siento | I’m sorry |
| Asking for Information | ¿Dónde está…? | Where is…? |
| Parting | Hasta luego | See you later |
Building Confidence with Key Phrases
Practicing these common phrases will help you feel more confident and prepared in various situations. Remember, it’s not just about knowing the words; it’s about using them in context and with the right tone. Once you are comfortable with these basic expressions, you can start building on them to expand your conversational skills.
With time and practice, these phrases will become second nature, and you’ll be able to engage in everyday conversations smoothly and effectively.
Reading Comprehension Strategies
Understanding written content is a critical skill, especially when learning a new language. Developing effective strategies for reading comprehension not only enhances your ability to grasp the meaning of texts but also builds your overall language proficiency. Whether you’re dealing with short passages or longer narratives, these strategies will help you process information more efficiently and accurately.
One of the most important techniques is to focus on context clues, which can often help you deduce the meaning of unfamiliar words. Additionally, paying attention to sentence structure and key phrases will give you a clearer understanding of the overall message. Regular practice with diverse reading materials can help reinforce these skills and increase your confidence in reading.
Effective Techniques for Improved Understanding

Here are some strategies to improve your reading comprehension:
- Preview the Text: Before diving into the reading, skim the text to get an overview. Look for headings, keywords, and any images or captions that might provide context.
- Highlight Key Information: As you read, underline or highlight important details that support the main idea. This will help you focus on essential content and understand the text better.
- Take Notes: Jot down summaries of each paragraph or section. This will help reinforce what you’ve learned and keep track of important points.
- Practice Summarizing: After reading, try summarizing the text in your own words. This will help you check your understanding and identify any gaps in comprehension.
- Revisit Difficult Sections: If something is unclear, don’t hesitate to read it again. Often, multiple readings can provide new insights and make the content easier to understand.
Building Confidence through Consistent Practice

Like any skill, reading comprehension improves with practice. Consistently engaging with texts that challenge your current level will help you grow and refine your abilities. Over time, you’ll notice an improvement in both your understanding and your ability to retain information.
By using these strategies and dedicating time to regular reading, you’ll become more comfortable with complex materials and be better equipped to tackle different types of texts. Remember, persistence and practice are key to mastering comprehension skills.
How to Prepare for Oral Exams
Oral assessments require more than just memorizing facts; they test your ability to express yourself clearly and confidently. The key to success lies in preparation and practice. Whether you’re facing a conversation with an examiner or responding to specific prompts, being comfortable with the material and the structure of the conversation will help you perform your best.
The first step in preparation is to review the topics and vocabulary you may be expected to use. Having a strong grasp of relevant terms and structures will make it easier to form your thoughts during the conversation. Practicing aloud, even if it’s by yourself, can help you get used to speaking fluidly and with confidence.
Key Strategies for Success
Here are some effective techniques to help you succeed in oral assessments:
- Practice Speaking Regularly: Consistent practice is essential for improving fluency. Try to speak as much as possible, whether it’s with a language partner, tutor, or even in front of a mirror.
- Use Flashcards for Vocabulary: Create flashcards with important terms, phrases, and questions. Reviewing them regularly will reinforce your memory and prepare you for potential questions during the assessment.
- Record Yourself: Recording your responses and listening to them will help identify areas where you may need improvement, such as pronunciation, speed, or clarity.
- Familiarize Yourself with Common Questions: Practice answering common interview-style questions. This will help you feel more confident when you’re asked similar questions during the real assessment.
- Focus on Pronunciation: Pay attention to your pronunciation and intonation. Clear pronunciation is just as important as knowing the correct words and phrases.
Staying Calm During the Assessment

During the assessment, stay calm and take your time to think before you speak. It’s okay to pause and gather your thoughts; speaking too quickly may cause you to make mistakes or forget important details. If you don’t understand a question, don’t hesitate to ask the examiner to repeat or clarify. A calm and confident demeanor will help convey your knowledge more effectively.
Remember, preparation is key, but so is staying relaxed. With practice and confidence, you can approach any oral assessment with ease and succeed in showcasing your abilities.
Effective Study Methods for Spanish
Mastering a new language requires a combination of strategies that reinforce learning through consistent practice and engagement. The most successful methods are those that integrate listening, speaking, reading, and writing, ensuring that all aspects of language acquisition are covered. Whether you’re aiming to improve vocabulary, grammar, or conversational skills, using a variety of study techniques will help you retain information and boost confidence.
It’s essential to tailor your approach to suit your personal learning style. Some students find success through repetition and memorization, while others benefit from more interactive and immersive methods. Below are some of the most effective study practices that can help accelerate progress.
Top Study Techniques
- Active Recall: Focus on retrieving information from memory rather than passively reviewing notes. This technique improves retention and strengthens neural connections.
- Spaced Repetition: Break up your study sessions over longer periods of time. Reviewing material at increasing intervals helps transfer information from short-term to long-term memory.
- Flashcards: Use digital or physical flashcards to memorize vocabulary, phrases, or grammar rules. Flashcard apps like Anki or Quizlet allow for personalized practice and easy tracking of progress.
- Language Immersion: Surround yourself with the language by listening to music, watching videos, or engaging with media in the target language. This helps you internalize pronunciation, sentence structure, and vocabulary.
- Practice Speaking: Speaking regularly, even if it’s with a study partner or tutor, is crucial for improving fluency. Focus on pronunciation and building confidence in expressing yourself.
- Writing Exercises: Write essays, journal entries, or short stories using the language. This enhances grammar, vocabulary, and sentence structure, while also improving your ability to think in the language.
Maximizing Your Study Sessions

To make the most of your study time, set clear goals for each session. Start with a review of previously learned material, then focus on new content or practice areas where you feel less confident. Be mindful of fatigue–studying for longer than 45 minutes at a stretch without a break can lead to diminishing returns. Take short breaks to recharge, and try to keep study sessions focused and productive.
In addition to individual study, collaborating with classmates or joining study groups can provide opportunities for mutual support and learning. Language exchange platforms or group chats are also great for engaging with native speakers and enhancing conversational skills.
Remember, consistency is key. The more regularly you engage with the material, the more natural it will become. Keep track of your progress, celebrate small victories, and maintain a positive, proactive attitude throughout your learning journey.