Microbiology Lab Practical Exam 2 Preparation Guide

Success in hands-on scientific assessments requires a solid understanding of essential techniques, critical thinking, and the ability to quickly apply theoretical knowledge. In this section, we’ll explore the key areas to focus on as you prepare for the upcoming challenge. From understanding experimental protocols to mastering the use of various tools, each element plays a significant role in achieving top performance.
Understanding the core concepts and practicing them under timed conditions is crucial for effective test-taking. You’ll need to familiarize yourself with various procedures and processes that could appear in the assessment. Moreover, recognizing common mistakes and knowing how to avoid them will give you a distinct advantage when under pressure.
Whether you’re identifying specimens under the microscope or preparing your setup, it’s important to approach each task with confidence and precision. This guide will provide practical advice and tips on how to efficiently tackle different aspects of the test, helping you refine your skills and achieve the best possible results.
Microbiology Lab Practical Exam 2
In this segment, we will delve into the essential elements you need to focus on to excel in the upcoming scientific skills assessment. Mastery of laboratory procedures and a deep understanding of concepts are key to success. This guide provides you with actionable steps to prepare effectively and handle each task with precision.
Understanding the procedural steps involved in various experiments is critical. Knowing what to expect and how to handle different types of samples and equipment will make the entire process smoother. Pay attention to the details in each method, as even minor errors can lead to incorrect results.
During the test, time management will be crucial. Being able to prioritize tasks and work efficiently will allow you to demonstrate your proficiency in handling equipment and applying theoretical knowledge. By familiarizing yourself with common procedures and practicing them in a structured way, you’ll approach each scenario with confidence and accuracy.
Key Concepts for Exam Success
Achieving success in hands-on assessments requires a strong grasp of fundamental principles and techniques. Understanding the core concepts, from experimental setups to data interpretation, will significantly improve your performance. It’s not only about executing procedures correctly but also about demonstrating your ability to apply knowledge under time constraints.
Familiarity with common tools and their specific uses is essential. Knowing how to handle different instruments efficiently and understanding their function in various tests will help you complete tasks with confidence. Additionally, mastering the correct methods for preparation and sample handling ensures accurate results and minimizes errors during the assessment.
Finally, honing your problem-solving skills will allow you to tackle unexpected challenges. Being able to adjust your approach when faced with new or unfamiliar situations is a key aspect of success. The more you practice, the better prepared you will be to handle any scenario that arises.
Essential Lab Techniques to Master
Mastering key techniques is crucial for performing well in any hands-on scientific assessment. Being proficient with fundamental procedures not only ensures accuracy but also allows for greater efficiency during tasks. Whether it’s handling equipment or following a set sequence of steps, practice makes perfect when it comes to these core methods.
One of the most important skills to develop is sterile technique, which prevents contamination and guarantees the reliability of results. Understanding how to properly handle samples, dispose of materials, and sanitize equipment is essential for maintaining a clean and controlled environment. Another critical skill is the use of microscopes for precise observations, as well as the ability to identify and differentiate between various specimens under magnification.
Furthermore, gaining proficiency in accurate measurement is indispensable. Whether you’re pipetting liquids or weighing substances, ensuring correct measurements is key to successful outcomes. Finally, becoming adept at documenting your observations, recording data clearly, and writing concise reports will help you communicate your findings effectively.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in the Lab

Even small errors in the laboratory can lead to inaccurate results or compromised procedures. Being aware of common mistakes and knowing how to prevent them is essential for ensuring the success of your tasks. Understanding where things can go wrong helps you stay vigilant and maintain precision throughout each step.
Handling Equipment and Materials
Improper handling of instruments and materials can lead to contamination or malfunction. Here are some frequent mistakes to watch out for:
- Not properly calibrating instruments before use.
- Forgetting to sterilize equipment between uses.
- Using contaminated tools or containers for sample preparation.
- Inadequate disposal of waste, leading to cross-contamination.
Following Procedures
Failing to follow established protocols can result in incorrect data or missed steps. Avoid these common missteps:
- Skipping or rushing through steps in the procedure.
- Not recording observations promptly and clearly.
- Ignoring safety precautions, which can lead to accidents.
- Not properly labeling samples, leading to confusion or misidentification.
By remaining cautious and adhering to protocols, you can reduce the likelihood of mistakes and increase the reliability of your results. Practicing these techniques and becoming familiar with potential pitfalls will enhance your performance during assessments.
Preparing Your Lab Materials Efficiently

Proper preparation of your materials is a key factor in ensuring a smooth and effective scientific assessment. Being organized and systematic in gathering and arranging everything you need allows you to focus on the task at hand without wasting time searching for tools or materials. Efficiency in preparation not only saves time but also reduces the risk of errors during the procedure.
Start by carefully reviewing the procedure and identifying all the materials required for each step. Make sure you have enough of each item, whether it’s reagents, tools, or containers. It’s essential to have everything within reach and ready to go before you begin the task. This will help you work methodically and avoid unnecessary delays.
Additionally, organizing your workspace is crucial. Keep everything tidy and in its designated place. A clean and structured environment helps you stay focused and prevents mistakes, such as mixing up samples or forgetting to use a specific tool. By taking the time to prepare your materials thoroughly, you set yourself up for success and create a streamlined process for completing the task efficiently.
How to Stay Calm During the Exam
Staying composed under pressure is essential for performing well in any hands-on assessment. Feeling nervous or overwhelmed can hinder your ability to think clearly and execute tasks effectively. By learning techniques to manage stress and maintaining a focused mindset, you can approach each challenge with confidence and precision.
Preparation is Key

Thorough preparation not only helps you understand the material but also reduces anxiety. Here are a few ways to prepare mentally:
- Review key concepts and techniques regularly to build confidence.
- Practice under timed conditions to simulate the actual setting.
- Visualize the steps of each procedure to reduce uncertainty.
Stay Focused and Breathe

During the test, it’s important to stay present and focus on one task at a time. Here are some strategies to help manage stress:
- Take deep breaths to calm your nerves if you feel anxious.
- Keep a steady pace by prioritizing the most straightforward tasks.
- Don’t rush; if you make a mistake, stay calm and correct it methodically.
By following these strategies, you’ll be able to maintain clarity and composure, ensuring you can apply your knowledge and skills effectively throughout the process.
Understanding the Grading Criteria
To perform well in a hands-on assessment, it’s essential to understand how your work will be evaluated. Grading is often based on multiple factors, from the accuracy of your results to your ability to follow procedures efficiently. By knowing the key elements that instructors focus on, you can direct your attention to the areas that matter most and maximize your score.
Typically, the grading system will assess both the quality of your work and your methodical approach. This includes how well you execute each task, how carefully you handle materials, and your ability to demonstrate the correct techniques. Additionally, your ability to troubleshoot and address any issues that arise during the process will be taken into account.
It’s important to also focus on the organization and cleanliness of your workspace, as this can reflect your ability to manage time and maintain precision. Attention to detail, such as labeling samples correctly and following all safety protocols, will also contribute to your overall score.
Test Your Knowledge with Practice Questions
One of the most effective ways to prepare for any hands-on assessment is to test your understanding through practice. By answering questions that simulate real-world scenarios, you can reinforce your knowledge and identify areas that need improvement. This process helps build both your confidence and proficiency, ensuring you’re ready when the time comes to apply what you’ve learned.
Why Practice Matters
Regularly testing yourself not only enhances memory retention but also improves your problem-solving skills. Practice questions give you an opportunity to:
- Familiarize yourself with the types of challenges you may encounter.
- Identify common mistakes and learn how to avoid them.
- Increase your ability to think critically under pressure.
Types of Practice Questions
Here are some types of questions you can use to test your knowledge:
- Multiple-choice questions to test theoretical knowledge and concept application.
- Scenario-based questions that require you to think through a process step by step.
- True or false questions to quickly assess your understanding of specific facts or techniques.
By incorporating these practice questions into your study routine, you can sharpen your skills and ensure you’re well-prepared for the assessment.
Time Management Tips for the Exam
Effective time management is crucial when it comes to performing well under pressure. The ability to allocate your time wisely during an assessment can significantly impact your performance. Proper planning ensures that you complete all tasks on time while maintaining high standards of quality and accuracy.
One of the best strategies is to break the entire process into smaller, more manageable tasks. By doing so, you can focus on each step without feeling overwhelmed. Additionally, allocating a specific amount of time to each task allows you to monitor your progress and adjust if needed. Below is a sample schedule to help you structure your time effectively:
| Task | Time Allocated |
|---|---|
| Preparation and Setup | 10-15 minutes |
| Step-by-step procedure | 30-40 minutes |
| Data recording and analysis | 15-20 minutes |
| Clean-up and review | 10-15 minutes |
By following a clear timeline, you can ensure you have enough time to complete each stage carefully without rushing. Prioritize tasks based on their complexity, and if necessary, adjust the allocated times based on your comfort level and skill with each procedure.
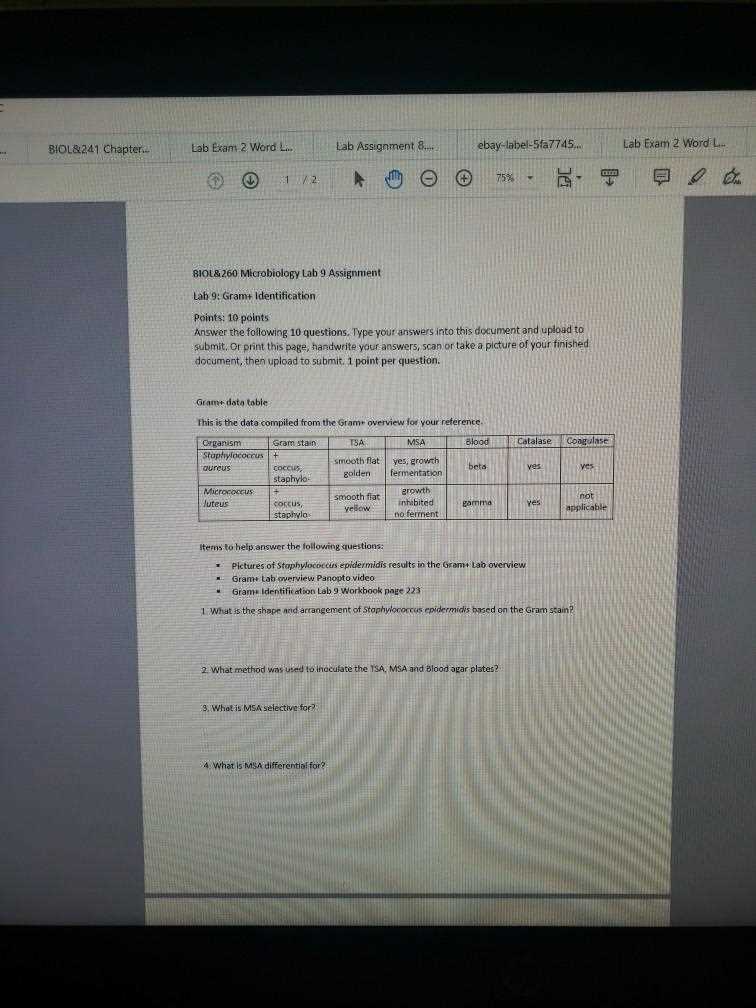
How to Identify Common Microorganisms
Accurately identifying microorganisms is a key skill in any scientific analysis. Different species exhibit unique characteristics that can be detected through various methods, such as examining their shape, size, color, and reactions to specific tests. Being familiar with the common traits of microorganisms helps in distinguishing one from another and applying the correct identification methods.
Key Identification Methods
There are several techniques used to identify microorganisms. These methods often depend on both the physical properties and the biological reactions of the organisms. Here are some common approaches:
- Microscopic Examination: Observing the shape, size, and arrangement of cells under a microscope is often the first step in identification. Bacteria, for example, may appear as rods (bacilli), spheres (cocci), or spirals (spirilla).
- Staining Techniques: Different stains, such as Gram staining, can reveal key features such as the cell wall structure, which helps classify organisms as Gram-positive or Gram-negative.
- Cultural Characteristics: Growing microorganisms on various media can provide valuable clues. Colony shape, color, and texture can indicate the species.
Common Organisms to Recognize
Several microorganisms are commonly encountered and have distinct features that are easy to spot once you are familiar with them:
- Escherichia coli: Often rod-shaped and Gram-negative, this bacterium is frequently used in laboratory studies.
- Staphylococcus aureus: Known for its spherical clusters and Gram-positive staining, it is a common pathogen.
- Aspergillus species: These fungi typically form branching hyphae and produce distinctive spore structures.
By mastering these basic identification techniques, you can confidently recognize microorganisms and understand their role in various biological processes.
Preparing for Microscopic Observations
Before you begin examining specimens under a microscope, it’s important to be well-prepared. Proper preparation ensures that you obtain clear, accurate observations and can identify features with confidence. This includes setting up your equipment, preparing the sample correctly, and knowing what to look for during the observation process.
Steps to Prepare for Microscopic Observations
Here are key steps to ensure effective microscopic analysis:
- Clean your microscope: Make sure all lenses, slides, and other parts are free of dust and stains. Clean the lenses gently with a lens paper to avoid scratches.
- Prepare your samples: Depending on the type of specimen, ensure it is properly mounted on a glass slide with the appropriate medium. This might involve staining or fixing techniques.
- Adjust the lighting: Proper illumination is essential for clear observations. Make sure the light is bright enough without causing glare, adjusting the diaphragm if necessary.
- Focusing: Start with the lowest magnification to locate the specimen and then gradually increase magnification to observe finer details.
Common Tools for Microscopic Preparations
Using the correct tools can make the process smoother. Here’s a table outlining some essential items:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Microscope | Used for magnifying specimens to reveal details that are not visible to the naked eye. |
| Cover Slips | Used to cover the specimen on the slide, ensuring the sample remains in place and protected. |
| Staining Reagents | Enhance the contrast of cellular structures to make specific parts of the specimen more visible. |
| Tweezers | For handling delicate specimens without damaging them. |
By following these steps and using the right tools, you’ll be ready to make accurate and detailed observations under the microscope.
Importance of Proper Sterile Techniques
Maintaining cleanliness and preventing contamination is crucial in any scientific study. The use of proper sterile techniques ensures that the results you obtain are accurate and not influenced by external factors like unwanted microorganisms. Whether working with samples, equipment, or culture media, following strict hygiene protocols is essential for reliable outcomes.
Preventing Cross-Contamination
One of the primary reasons to adhere to sterile techniques is to prevent cross-contamination between samples. Introducing foreign organisms into an experiment can skew results, leading to incorrect conclusions. By using sterilized tools and maintaining a clean workspace, you can minimize the risk of introducing contaminants. Here are some common methods used:
- Autoclaving: Sterilizing equipment by applying high-pressure steam to eliminate harmful organisms.
- Flaming: Sterilizing tools like inoculating loops by passing them through a flame to burn off any microbial life.
- Disinfecting Surfaces: Regularly cleaning surfaces and equipment with disinfectants to prevent the spread of harmful bacteria.
Ensuring Reliable Results
Proper sterilization not only safeguards against contamination but also ensures that the experiment reflects the true behavior of the microorganisms or substances being studied. Without it, results may become unreliable, compromising the integrity of your study. Adopting rigorous sterilization practices should be a standard part of any scientific procedure, ensuring that the study’s findings are both valid and reproducible.
What to Expect on the Practical Exam
The hands-on assessment is designed to evaluate your ability to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios. During this type of test, you will be expected to demonstrate specific techniques, handle different materials, and perform tasks that require precision and attention to detail. It’s essential to be well-prepared, as this is an opportunity to showcase your practical skills in a controlled environment.
Expect to work with various equipment and samples, requiring you to follow established protocols and make accurate observations. The assessment will likely involve several stations or tasks, each focusing on different aspects of your skill set. You may be asked to identify specimens, use specific tools, or perform procedures that require a strong understanding of safety and technique.
During the assessment, time management is critical. Be prepared to work under a time constraint while maintaining accuracy and following best practices. It’s important to stay calm and focused, as completing each task carefully is more important than rushing through them. Make sure you are familiar with all the steps involved in each procedure, as the exam will test both your knowledge and your ability to execute techniques efficiently.
Tips for Working with Lab Equipment
Proper handling of scientific tools is essential for successful experiments and accurate results. Whether you’re working with delicate instruments or robust machinery, understanding how to use each piece of equipment efficiently and safely is key. Following the correct procedures ensures that measurements are precise and helps to avoid contamination or damage to your tools.
Here are some essential tips for working with common equipment:
| Equipment | Tip |
|---|---|
| Microscope | Always start with the lowest magnification and gradually increase to avoid damaging the lens or slides. |
| Incubator | Ensure the temperature is calibrated and consistent. Avoid opening the door too often, as it can affect the internal environment. |
| Centrifuge | Balance the tubes properly to prevent the rotor from becoming unbalanced, which could lead to equipment damage or unsafe conditions. |
| Autoclave | Always allow the autoclave to cool before opening. Never overload the chamber, as it could impact sterilization efficiency. |
| Pipette | Use the appropriate pipette for the volume you need. Ensure the tip is securely attached before dispensing liquids. |
By following these best practices, you can avoid mishandling and ensure that your tools remain in good working condition throughout the experiment. Understanding the proper use of each piece of equipment is an investment in both your safety and the success of your scientific endeavors.
How to Write Reports Quickly
Writing detailed reports is an important skill that allows you to communicate your findings clearly and concisely. However, when under time constraints, it’s essential to streamline the process without sacrificing quality. Understanding how to organize your thoughts and present the necessary information efficiently will help you complete the task quickly while ensuring accuracy.
Here are some tips to write reports faster:
- Plan Ahead: Before you start writing, outline the key sections of your report, such as the objective, methods, results, and conclusions. This will give you a clear structure and prevent you from missing any important details.
- Use Templates: Create or use a standard report template. This allows you to focus on filling in the relevant data rather than formatting each section from scratch.
- Be Concise: Avoid unnecessary details. Stick to the facts, and ensure each sentence serves a purpose. This will make your report more readable and help you write faster.
- Write in Stages: Break the report down into smaller tasks. For example, first draft the methods section, then move on to the results. Writing incrementally helps you maintain momentum.
- Use Bullet Points: For sections that involve lists or step-by-step processes, use bullet points. This will save time and make the information easier to follow.
- Proofread Efficiently: Once you’ve completed your report, do a quick read-through to check for any glaring mistakes or unclear sections. A brief revision is often enough to catch errors without delaying submission.
By adopting these strategies, you can significantly reduce the time it takes to write reports without compromising the quality of your work. Efficient writing is not just about speed but also about organization and clarity.
Improving Your Observation Skills

Developing strong observation skills is crucial for accurately analyzing and interpreting various samples. By honing your ability to notice fine details, you can better understand complex patterns and enhance your overall performance. The more you practice, the sharper your observation skills will become, enabling you to identify key elements that might otherwise be overlooked.
Here are some tips to improve your observational abilities:
- Focus on the Details: Pay attention to small features, shapes, and colors. Often, minor differences can provide important insights. Take the time to examine every aspect of a sample thoroughly.
- Develop a Systematic Approach: Examine the sample methodically, following a consistent process. This ensures that you don’t miss critical elements and helps you stay organized in your observations.
- Use Tools Effectively: Leverage magnification and other observation tools to enhance your view. Whether it’s a microscope or a simple magnifying glass, using the right tools can significantly improve your ability to detect fine details.
- Take Notes: Writing down observations can help you capture fleeting details that might otherwise be forgotten. Jot down anything unusual or noteworthy, even if it seems insignificant at first.
- Practice Regularly: The more you practice observing different samples, the more efficient and accurate you’ll become. Make time for regular observation exercises to refine your technique and sharpen your focus.
- Learn from Experience: Review past observations and outcomes. Understanding what worked and what didn’t will allow you to adjust your approach for future analyses.
By consistently applying these strategies, you can significantly improve your ability to observe with precision, which is essential for making accurate analyses and drawing meaningful conclusions.
Reviewing Key Microbial Cultures

Understanding various microbial cultures is essential for recognizing different types of organisms and their characteristics. Cultures provide a controlled environment for growth, allowing you to examine the morphology, behavior, and other distinguishing features of microorganisms. By familiarizing yourself with key cultures, you’ll be better equipped to identify specific organisms and interpret their role in various processes.
Commonly Encountered Organisms
There are several key types of microorganisms that are frequently encountered and studied. Each type has unique characteristics that make them identifiable in culture. Some of the most important ones include:
- Gram-positive Bacteria: These organisms often exhibit a thick cell wall structure that retains the purple stain in Gram staining. Examples include Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Gram-negative Bacteria: Characterized by a thin cell wall and outer membrane, these organisms do not retain the purple stain and instead appear pink. Common examples include Escherichia coli and Salmonella.
- Fungi: Fungal cultures, such as those from Candida or Aspergillus, are often examined for their growth patterns and spore production.
- Yeasts: These microorganisms often appear as creamy colonies and are commonly studied for their fermentation capabilities.
- Protozoa: Single-celled organisms like Entamoeba histolytica can be identified through their specific motility and shape in culture.
Techniques for Reviewing Cultures
To accurately assess and identify the cultures, there are several important techniques to consider:
- Microscopic Examination: Use a microscope to observe cell shape, size, and arrangement. This step is crucial for differentiating between species.
- Cultural Characteristics: Pay attention to the colony morphology, such as size, shape, and color, which can provide important clues about the organism’s identity.
- Biochemical Tests: These tests can help identify specific metabolic characteristics of microorganisms, such as fermentation patterns or enzyme production.
- Staining Techniques: Staining methods, including Gram staining or acid-fast staining, can help differentiate between different types of microorganisms based on their cell wall structure.
Regular review of key microbial cultures and practicing these techniques will enhance your ability to correctly identify and analyze organisms, leading to more accurate interpretations and a deeper understanding of microbial diversity.