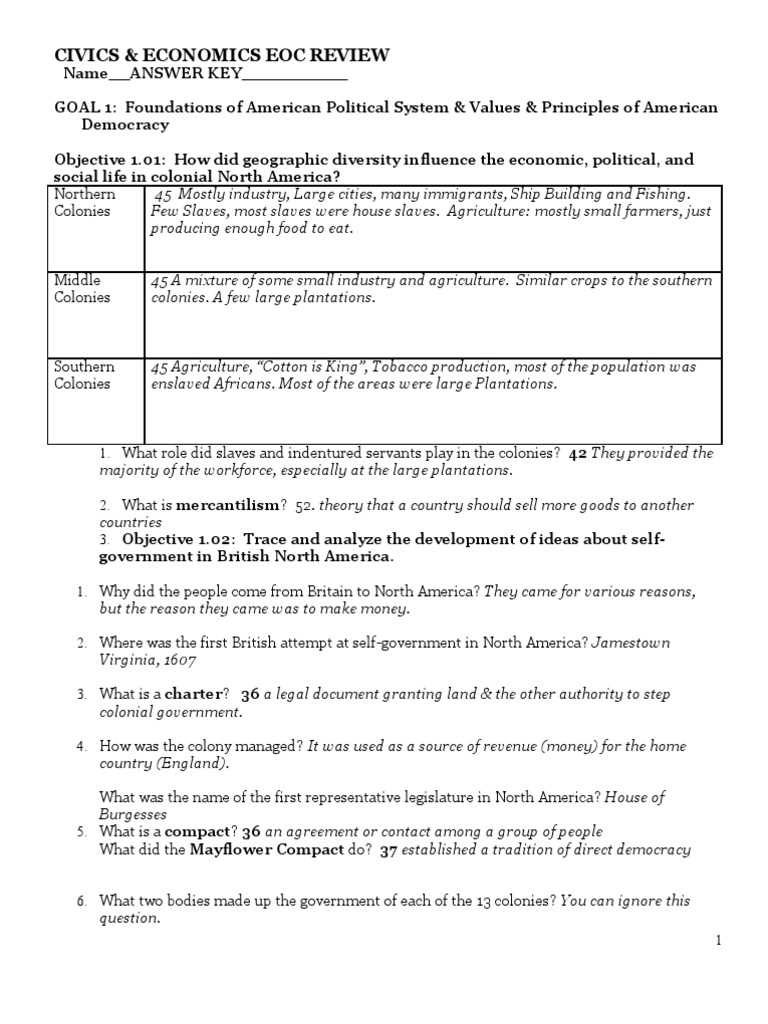
Civics EOC Review Sheet with Answers

Preparing for the upcoming test on U.S. government and history can be a daunting task, but breaking down the material into manageable sections is the key to success. Whether you’re revisiting foundational documents or reviewing the roles of government branches, a strategic approach will help you retain crucial information. This guide is designed to provide a structured overview of the topics you’ll encounter, offering a clear path to mastering the content.
Each section of the material plays a vital role in understanding the political system that shapes the nation. From the Constitution’s framework to the intricacies of judicial rulings, it’s essential to grasp how these elements interact and influence modern governance. Focusing on the core principles and key historical events will sharpen your ability to apply this knowledge when answering questions.
Understanding the structure of the government and the rights of citizens is central to this preparation. Emphasis should be placed on significant legal documents, landmark decisions, and the principles that have evolved over time. By focusing on these core topics, you’ll be well-equipped to face any challenge that the exam presents.
Civics EOC Review Sheet with Answers

Preparing for a comprehensive exam on U.S. history and government requires a clear understanding of key concepts and historical events. Focusing on critical topics, such as the Constitution, government structures, and citizens’ rights, is essential for achieving success. In this section, we’ll break down important areas of study, providing explanations and practice questions to solidify your knowledge.
To perform well on the test, it’s important to recognize the central principles that underpin the American political system. Key documents such as the Constitution, Bill of Rights, and other influential texts offer insights into the framework that guides governance. Understanding how these elements influence current laws and practices will prepare you to answer any related questions confidently.
The roles of different government branches are another fundamental aspect to grasp. Each branch, whether legislative, executive, or judicial, has distinct responsibilities and powers that affect how decisions are made. Familiarity with the function of each will help you better understand their interactions and the checks and balances that maintain a fair system.
Important historical events also play a significant role in shaping the modern government. Events such as major Supreme Court rulings, key amendments to the Constitution, and landmark legislation are essential to understanding how the U.S. political system has evolved. Mastering these topics will enhance your ability to provide accurate responses during the exam.
Key Topics for Civics EOC Exam

Understanding the main concepts that shape the U.S. political system is crucial for excelling in the upcoming exam. The material covers foundational principles, key historical events, and the structure of government. By focusing on these critical areas, you’ll be prepared to tackle questions related to governance, citizens’ rights, and the legal framework that defines the nation.
Important topics include the Constitution and its amendments, the roles and responsibilities of government branches, and the evolution of American law. Additionally, it’s vital to familiarize yourself with major Supreme Court cases and landmark legislation that have shaped the country’s legal landscape. Grasping these core ideas will provide a solid foundation for understanding how the U.S. system operates.
In addition to legal documents and governmental structures, understanding the electoral process, political parties, and their influence on policy decisions is essential. These areas will help you interpret how citizens’ participation affects governance and how laws are created and enforced. Thoroughly studying these topics will ensure that you’re ready for the most important sections of the test.
Understanding the U.S. Constitution
The Constitution serves as the foundational framework for the United States government. It establishes the core principles of governance, outlining the powers of the federal government while protecting individual freedoms. Understanding this document is essential for grasping how the American political system operates and how laws are created and interpreted.
Key elements of the Constitution include the division of powers, the system of checks and balances, and the Bill of Rights. These components ensure that no single branch of government becomes too powerful and that citizens’ rights are safeguarded. Each article of the Constitution addresses specific aspects of governance, including the structure of the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
| Article | Focus Area |
|---|---|
| Article I | Establishes the Legislative Branch (Congress) |
| Article II | Establishes the Executive Branch (President) |
| Article III | Establishes the Judicial Branch (Courts) |
| Article IV | State Relations and Federal Authority |
| Article V | Amendment Process |
| Article VI | Supremacy Clause and Oaths of Office |
| Article VII | Ratification of the Constitution |
By studying the Constitution, one gains insight into the principles that guide American democracy, including the separation of powers and the protection of civil liberties. This knowledge is essential for understanding how the government functions and how the rights of individuals are maintained within the system.
The Structure of U.S. Government

The U.S. government is designed with a system that ensures a balance of power among different branches, preventing any single entity from becoming too dominant. This framework of governance is essential for maintaining democratic principles and protecting the rights of citizens. The government is divided into three main branches, each with specific powers and responsibilities.
- Legislative Branch: Responsible for creating laws, this branch is made up of Congress, which is divided into two chambers: the House of Representatives and the Senate.
- Executive Branch: Led by the President, this branch enforces laws and manages the day-to-day operations of the government. It includes the President’s Cabinet, various federal agencies, and the military.
- Judicial Branch: Composed of courts, including the Supreme Court, this branch interprets laws and ensures that they align with the Constitution. It also has the power of judicial review to assess the constitutionality of laws.
In addition to these three branches, the system of checks and balances ensures that no single branch becomes too powerful. For example, while Congress can create laws, the President has the power to veto them. Similarly, the judiciary can declare laws unconstitutional, limiting the power of both the legislative and executive branches.
- The President can veto laws passed by Congress, but Congress can override the veto with a two-thirds majority.
- The Supreme Court can rule executive actions or laws passed by Congress unconstitutional.
- Congress can impeach and remove the President or federal judges who have abused their power.
This balance of powers is crucial for maintaining the stability and fairness of the political system, ensuring that each branch functions effectively while being held accountable to the others. Understanding the structure of the government is key to appreciating how the country is governed and how decisions are made at the federal level.
Rights and Responsibilities of Citizens
Being a citizen in a democratic society comes with both privileges and duties. Citizens are granted certain freedoms that allow them to participate in the political and social life of the country. At the same time, they are expected to fulfill obligations that support the well-being and stability of the nation. Understanding these rights and responsibilities is essential for active and informed participation in the community.
The rights of citizens are fundamental and are protected by law, ensuring personal freedoms and the opportunity to participate in governance. These include the freedom of speech, the right to vote, and the right to a fair trial. Additionally, citizens have the right to express their opinions, practice their religion, and pursue their chosen careers without discrimination.
On the other hand, there are responsibilities that every citizen must uphold. These include obeying laws, paying taxes, and serving on a jury when called. Active participation in elections and staying informed about government actions are also important ways for citizens to contribute to society. By fulfilling these duties, citizens help maintain the democratic system and ensure its continued effectiveness.
The Legislative Branch Explained

The legislative branch plays a crucial role in shaping laws and policies that govern the nation. Comprising two chambers, it is tasked with creating, debating, and passing laws that address a wide range of issues. This body ensures that the needs and concerns of citizens are represented through elected officials who make decisions on their behalf.
Structure of the Legislative Branch
The legislative branch is bicameral, meaning it consists of two separate chambers: the Senate and the House of Representatives. Each chamber has distinct responsibilities and powers, but both work together to pass legislation and oversee the actions of the executive branch.
- The Senate: The upper chamber, with 100 members, each representing a state. Senators serve six-year terms and focus on broader national issues, such as foreign relations and judicial appointments.
- The House of Representatives: The lower chamber, with 435 members, each representing a congressional district. Representatives serve two-year terms and are more closely aligned with the public’s immediate concerns.
Key Responsibilities of the Legislative Branch

Members of the legislative branch are responsible for a variety of tasks that directly impact the functioning of the country. These duties include lawmaking, oversight, and approving government spending. In addition, they play a role in checking the power of the executive branch through hearings and investigations.
- Creating Laws: Legislators draft, debate, and vote on bills that can become laws after passing both chambers and being signed by the president.
- Approving the Budget: Congress is responsible for approving the federal budget, determining how government funds will be allocated.
- Overseeing the Executive: Through hearings, investigations, and audits, the legislative branch ensures that the executive branch is acting within the law and budgetary constraints.
- Impeachment Powers: The House can initiate impeachment proceedings, while the Senate holds trials to remove public officials from office if necessary.
The legislative branch is essential for maintaining a balance of power within the government. Its actions directly affect the lives of citizens by shaping policies that impact healthcare, education, taxes, and other critical areas of public life.
The Role of the Executive Branch
The executive branch is responsible for implementing and enforcing the laws that are passed by the legislative body. Headed by the President, this branch plays a vital role in managing the daily operations of the government and ensuring that policies are carried out effectively. Its responsibilities span a wide range, from national defense to economic management and diplomacy.
At its core, the executive branch is tasked with ensuring that the nation runs smoothly, fulfilling its duties both domestically and internationally. The President, as the head of state, has the authority to make key decisions that affect national security, international relations, and the overall direction of the country’s policies. In addition, this branch includes numerous federal agencies and departments that manage specific areas like healthcare, transportation, and education.
Key Responsibilities of the Executive Branch:
- Enforcing Laws: The President and federal agencies are responsible for ensuring that laws passed by Congress are executed properly and efficiently.
- Commander-in-Chief: The President oversees the nation’s armed forces, making key military decisions and managing national security matters.
- Foreign Relations: The executive branch represents the country in foreign affairs, negotiating treaties and building diplomatic relations with other nations.
- Appointing Officials: The President appoints individuals to key positions in the government, including members of the Cabinet, federal judges, and ambassadors.
- Managing the Budget: The executive branch plays a role in drafting the federal budget, proposing how government funds will be allocated across various programs.
The executive branch is integral in shaping the nation’s laws and policies. Its actions and decisions have a lasting impact on the country’s direction, making it one of the most powerful elements of the U.S. government.
The Judicial Branch and Its Functions
The judicial branch is essential for interpreting and applying the laws of the nation. It ensures that justice is served by evaluating legal cases, settling disputes, and determining the constitutionality of laws. This branch plays a critical role in maintaining a fair and just society, acting as a check on the powers of both the legislative and executive branches.
At the heart of the judicial system is the Supreme Court, which serves as the highest court in the land. Below the Supreme Court are lower federal courts, including Courts of Appeals and District Courts, each with specific functions related to handling legal matters. These courts interpret laws, resolve conflicts, and protect individuals’ rights by ensuring laws are fairly enforced.
Key Functions of the Judicial Branch:
- Interpreting Laws: Judges and justices review laws to determine their meaning and how they should be applied in various cases. This helps to clarify ambiguities in legislation.
- Ensuring Constitutionality: The judicial branch has the power of judicial review, meaning it can declare laws and executive actions unconstitutional if they violate the principles of the Constitution.
- Resolving Disputes: Courts are responsible for resolving legal disputes between individuals, organizations, or between individuals and the government.
- Protecting Rights: The judicial system safeguards the rights and freedoms of individuals, ensuring that laws do not infringe upon personal liberties.
- Setting Precedents: Through its rulings, the judicial branch sets legal precedents, which guide future decisions in similar cases.
By fulfilling these functions, the judicial branch helps maintain the rule of law and ensure that the rights of citizens are protected, making it an indispensable part of the nation’s governance.
Important Supreme Court Cases
The decisions made by the Supreme Court shape the legal landscape of the country and have far-reaching effects on society. These landmark cases often set precedents that influence the interpretation of the Constitution and the laws of the nation. By examining these cases, we can understand how the judiciary plays a critical role in defining the rights of individuals and the powers of government institutions.
Over the years, the Supreme Court has heard numerous cases that have had a significant impact on issues such as civil rights, the balance of powers, and personal freedoms. These rulings often reflect the evolving values of society while maintaining a commitment to the principles laid out in the Constitution.
Notable Supreme Court Cases:
- Brown v. Board of Education (1954): This case overturned the “separate but equal” doctrine, declaring racial segregation in public schools unconstitutional and advancing the cause of civil rights.
- Roe v. Wade (1973): A landmark decision that legalized abortion, ruling that the right to privacy extends to a woman’s decision to terminate a pregnancy.
- Miranda v. Arizona (1966): This case established the requirement for law enforcement to inform suspects of their rights, such as the right to remain silent, during arrests and interrogations.
- Marbury v. Madison (1803): A foundational case that established the principle of judicial review, giving the Court the authority to declare laws unconstitutional.
- Plessy v. Ferguson (1896): Though later overturned, this case upheld racial segregation in public facilities, establishing the “separate but equal” doctrine for nearly 60 years.
Each of these decisions has contributed to the shaping of American law and society, demonstrating the Supreme Court’s role in interpreting the Constitution and ensuring that justice is applied equally across the nation.
Electoral Process and Voting System

The process by which citizens select their representatives and leaders is fundamental to a democratic society. Elections provide the opportunity for individuals to express their preferences, ensuring that public officials are accountable to the people. This system allows for the peaceful transfer of power and maintains the integrity of governance. It involves several stages, from registration and campaigning to voting and the counting of ballots.
At the heart of this process is the act of voting, which is both a right and a responsibility. The voting system is designed to reflect the will of the majority, while also protecting individual rights and ensuring fair representation. Understanding how the electoral system works is crucial for informed participation in the democratic process.
Key Components of the Electoral Process

- Voter Registration: Citizens must register to vote, ensuring they meet all legal requirements, such as age and citizenship, to participate in elections.
- Campaigning: Candidates and political parties engage in campaigns to persuade voters, using media, debates, and public events to spread their message.
- Voting: On election day, voters cast their ballots either in person or through absentee voting, depending on local laws and procedures.
- Counting and Certification: After the polls close, votes are counted, and the results are certified by election officials to ensure accuracy and fairness.
Types of Voting Systems
- Plurality Voting: In this system, the candidate with the most votes wins, even if they do not secure an absolute majority.
- Majority Voting: This system requires a candidate to win more than half of the votes to be declared the winner.
- Proportional Representation: This method allocates seats in proportion to the number of votes received by each party or candidate.
The electoral process and voting systems are designed to ensure that every citizen has the opportunity to participate in the decision-making process, fostering a system of government that is reflective of the people’s will. By understanding the intricacies of this process, citizens can engage more effectively in shaping the future of their country.
Political Parties and Their Impact

Political organizations play a vital role in shaping the political landscape, influencing government policies, and mobilizing voters. These groups bring together individuals with shared ideologies and values, advocating for their vision of how society should function. They are essential to democratic processes, providing voters with choices and helping to structure the political debate. The influence of political parties extends from local elections to national governance, and they are key in shaping laws, policies, and public opinion.
Political parties help organize the government, create platforms that represent various interests, and foster political participation. By contesting elections, they offer voters a clear distinction between competing visions of government and society. Their impact is felt not only in electoral outcomes but also in the decisions that affect everyday life.
Major Functions of Political Parties:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Candidate Selection | Political parties select candidates to represent them in elections at all levels of government, ensuring a slate of individuals who align with their goals. |
| Policy Formation | They develop platforms that outline their positions on key issues, which guide the actions of elected officials and influence legislation. |
| Electoral Support | Political parties provide resources, funding, and organizational support to help their candidates win elections. |
| Political Socialization | They engage in educating and informing the public about political processes, issues, and the importance of participation. |
Throughout history, political parties have been essential in organizing and driving political movements. Their impact on governance, policy formation, and societal change cannot be overstated. Through their efforts, they foster dialogue, represent diverse viewpoints, and contribute to the stability of democratic institutions.
Federalism and States’ Rights
The division of power between national and regional authorities is a cornerstone of governance in many countries. This structure creates a system where different levels of government have distinct areas of responsibility, balancing the central authority’s power with that of individual states or provinces. The relationship between federal and state governments has been a central theme in the development of political systems, impacting everything from lawmaking to civil rights protections.
At its core, this system allows for flexibility and local autonomy, enabling state governments to address issues that are specific to their populations while still adhering to broader national principles. However, this division can also lead to conflicts over the extent of state versus federal authority. Understanding the balance between these two levels of government is crucial to comprehending how policies and laws are shaped in such systems.
Key Features of Federalism:
- Dual Sovereignty: Both state and national governments have their own areas of power, and neither can fully dominate the other.
- Shared Powers: Some responsibilities, such as taxation or law enforcement, are shared by both levels of government.
- Reserved Powers: States retain certain powers that the federal government cannot infringe upon, as outlined in the constitution.
- Supremacy Clause: When state and federal laws conflict, the federal law typically takes precedence, ensuring national unity.
This system allows for a dynamic and adaptable approach to governance, offering the benefits of local control while ensuring a cohesive national framework. Yet, the balance of power between state and federal authorities continues to evolve, shaped by political, legal, and social changes over time.
Understanding Political Ideologies
Political ideologies are sets of beliefs and values that shape the way individuals view the role of government, society, and economics. These frameworks influence how people interpret political issues, advocate for policies, and align with particular political movements or parties. Ideologies provide individuals with a lens through which they understand and engage in the political world.
While ideologies can vary greatly from one individual or group to another, they often share core principles about the nature of power, freedom, and equality. Understanding these ideologies helps to explain the diverse political perspectives that exist within a society and provides insight into the motivations behind different political actions and decisions.
Common Political Ideologies:
- Liberalism: Advocates for individual rights, equality, and government intervention in the economy to address social inequalities.
- Conservatism: Emphasizes traditional values, limited government intervention, and a focus on maintaining societal stability.
- Socialism: Advocates for collective ownership of resources and wealth distribution to achieve greater social equality.
- Libertarianism: Stresses individual freedom and minimal government interference in both personal and economic matters.
- Fascism: A far-right ideology that promotes authoritarian control, nationalism, and the suppression of political opposition.
The Role of Political Ideologies in Society:
- Shaping Policy: Political ideologies influence the types of policies that individuals and political parties support.
- Guiding Voter Choices: Voters often align themselves with ideologies that match their values and beliefs about how society should be governed.
- Driving Political Movements: Ideologies inspire social and political movements aimed at bringing about change in government or society.
By understanding the various political ideologies, individuals can better navigate the complexities of political discourse and make informed decisions about the direction they want their country or society to take. Whether through voting, activism, or public discourse, ideologies continue to shape political landscapes around the world.
Historical Documents You Should Know
Throughout history, certain written works have played a pivotal role in shaping the laws, values, and structures of societies. These documents have not only influenced political systems but have also helped define the rights and responsibilities of citizens. Understanding these key texts is essential for grasping the development of modern governance and the ongoing evolution of democratic principles.
Important Historical Documents:
- The Magna Carta (1215): A foundational document in the history of constitutional law, limiting the power of the monarchy and establishing certain legal rights for citizens.
- The Declaration of Independence (1776): The United States’ declaration to separate from British rule, asserting the inherent rights of individuals to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.
- The U.S. Constitution (1787): The supreme law of the United States, outlining the structure of government, the separation of powers, and the rights of individuals.
- The Bill of Rights (1791): The first ten amendments to the U.S. Constitution, guaranteeing fundamental freedoms such as freedom of speech, religion, and the right to a fair trial.
- The Federalist Papers (1787-1788): A series of essays written to support the ratification of the U.S. Constitution, explaining the need for a strong central government and the principles of federalism.
- The Emancipation Proclamation (1863): An executive order by President Abraham Lincoln that declared the freedom of slaves in Confederate states during the American Civil War.
- The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948): A United Nations document proclaiming the fundamental rights and freedoms to which all people are entitled, irrespective of nationality or background.
Why These Documents Matter:
- Legal Foundation: Many of these documents serve as the basis for modern legal systems, influencing laws, court rulings, and governmental policies.
- Human Rights: These texts have helped shape the global understanding of human rights and individual freedoms.
- Government Structure: They provide insight into the principles of governance, the balance of power, and the relationship between citizens and the state.
By studying these essential documents, individuals gain a deeper understanding of the historical events that have shaped the world today and how the concepts of freedom, justice, and governance have evolved over time.
Key Amendments to the Constitution
The Constitution of the United States has been amended several times since its inception to address changing societal needs, protect individual freedoms, and ensure the government’s ability to function effectively. These modifications have shaped the legal landscape and have played a crucial role in defining the rights and responsibilities of citizens. Some amendments are particularly significant due to their far-reaching impact on the nation’s history, politics, and justice system.
Important Amendments:
- First Amendment: Guarantees essential freedoms including freedom of speech, religion, press, assembly, and petition, forming the backbone of individual rights in the U.S.
- Second Amendment: Protects the right of individuals to keep and bear arms, a provision that remains a cornerstone of the debate surrounding gun control and personal security.
- Fifth Amendment: Ensures protections against self-incrimination, double jeopardy, and guarantees due process, safeguarding individuals in the legal system.
- Sixth Amendment: Provides the right to a fair and speedy trial, an impartial jury, and the right to confront witnesses in criminal prosecutions.
- Thirteenth Amendment: Abolishes slavery and involuntary servitude, a landmark change in American history following the Civil War.
- Fourteenth Amendment: Guarantees equal protection under the law and due process for all citizens, extending protections to former slaves and influencing civil rights movements.
- Fifteenth Amendment: Prohibits denying the right to vote based on race, color, or previous condition of servitude, a critical step in expanding suffrage rights.
- Nineteenth Amendment: Grants women the right to vote, marking a monumental achievement in the fight for gender equality.
- Twenty-Sixth Amendment: Lowers the voting age to 18, reflecting the social and political changes of the 1960s and recognizing young adults as full participants in the democratic process.
The Impact of Amendments:
- Protection of Rights: Amendments like the First, Fifth, and Fourteenth have been instrumental in ensuring the protection of individual liberties and promoting justice.
- Expanding Suffrage: Key amendments have expanded voting rights, moving the country toward greater inclusion and representation for all citizens.
- Adapting to Change: The Constitution’s ability to be amended has allowed it to evolve with societal shifts, addressing emerging issues such as civil rights, voting access, and gender equality.
Each of these amendments has had a profound influence on American society and governance, contributing to the ongoing development of the nation’s democratic principles and the protection of its citizens’ rights.
Exam Preparation Tips for Success
Preparing for an important exam in government and history requires a well-rounded approach to studying. Focusing on key topics, understanding the structure of the exam, and practicing active recall can significantly boost your chances of success. By using effective study techniques and resources, you can build confidence and improve your performance on the test.
Effective Study Techniques:
- Understand Core Concepts: Start by reviewing the foundational principles such as the structure of government, individual rights, and the historical context of key documents. Make sure you have a solid grasp of how different systems function.
- Create a Study Schedule: Break down your study time into manageable blocks, focusing on one topic at a time. This method will help you retain information more effectively and avoid last-minute cramming.
- Use Practice Questions: Practicing with sample questions or past exam papers will help familiarize you with the types of questions that may appear on the test. It also provides a good opportunity to test your knowledge and identify areas that need improvement.
- Summarize Key Points: Condense lengthy material into concise notes or flashcards. This allows you to review the most important information quickly and reinforces your memory.
- Teach Others: One of the most effective ways to solidify your understanding is by teaching the material to someone else. Explaining concepts aloud forces you to recall and process the information in a meaningful way.
Additional Tips:
- Stay Organized: Keep all your study materials, notes, and resources neatly organized. Use binders, folders, or digital tools to track your progress and stay on top of the topics you’ve covered.
- Practice Time Management: During your study sessions, set time limits for each topic to avoid spending too much time on any one section. This will help ensure that you cover all the material before the exam.
- Stay Healthy: Never underestimate the importance of physical and mental health during exam preparation. Make sure to get enough rest, eat nutritious meals, and take breaks to keep your mind sharp.
Stay Calm and Confident: The key to excelling in any exam is a positive mindset. Stay confident in your preparation, trust your knowledge, and approach the test with a calm attitude. You’ve put in the effort, and now it’s time to demonstrate what you know!
Common Mistakes to Avoid on the Exam
When preparing for a major exam, it’s important to be aware of the common pitfalls that can hinder your performance. Understanding these frequent errors allows you to avoid them, ensuring that you approach the test strategically and confidently. By recognizing these mistakes ahead of time, you can maximize your score and reduce unnecessary stress.
Rushing Through Questions: Many students make the mistake of rushing through questions, especially under time pressure. This can lead to careless errors, such as misreading questions or failing to notice key details. Take your time to carefully read each question and think through your response before answering.
Overlooking Instructions: It’s easy to overlook specific instructions or guidelines, especially if you’re feeling anxious. Be sure to carefully read all instructions, whether they’re on the exam itself or on individual questions. This includes knowing if you should select multiple answers or provide an explanation for your choice.
Neglecting to Review Your Work: Many students don’t take the time to review their answers once they’ve completed the exam. If time allows, always go back to double-check your responses. Look for mistakes in calculations, grammar, or logical consistency that could impact your overall score.
Not Managing Time Effectively: Poor time management is a common issue during exams. Failing to allocate enough time for each section or question can result in incomplete answers. Create a strategy for how much time to spend on each part of the exam and stick to it, ensuring you address all sections.
Ignoring the Question Format: It’s easy to misinterpret the format of questions. For example, multiple-choice questions might require you to select more than one answer, while true/false questions may have a slight twist. Be mindful of the question format and follow the instructions carefully.
Second-Guessing Yourself: Second-guessing your answers too often can lead to confusion and errors. Trust in your preparation and instincts, and avoid constantly changing your answers unless you’re sure of a mistake. Often, your first choice is the right one.
Leaving Questions Blank: Leaving questions unanswered because you’re unsure of the answer can significantly affect your score. If you don’t know the answer, try to eliminate any obviously incorrect options and make an educated guess. Don’t leave any questions blank unless absolutely necessary.
Failing to Stay Calm: Anxiety can impair your ability to focus and think clearly. Stay calm throughout the exam and take deep breaths when you start feeling overwhelmed. A calm mind will help you make better decisions and complete the test more effectively.
By being mindful of these common mistakes, you can approach your exam with confidence and ensure that you make the most of your knowledge and preparation. Stay focused, stay organized, and avoid these pitfalls for a more successful outcome.