Which Question Type Includes One Right Answer
In any form of evaluation, it’s important to design prompts that have a single, undisputed response. These formats are often used in tests to assess knowledge on specific topics, ensuring clarity and accuracy. They are structured to lead to a precise solution, eliminating confusion for both the individual taking the test and the evaluator.
Such formats are widely recognized for their simplicity and effectiveness, making them ideal for measuring understanding. By focusing on straightforward, unambiguous responses, they ensure fairness and consistency in scoring. This approach is commonly applied in standardized exams and learning assessments, where the goal is to test factual recall or a particular skill set.
Clear and concise formats are essential for efficient testing. When evaluating someone’s knowledge, simplicity can often lead to better outcomes, allowing for a more objective and reliable assessment. This structure minimizes the potential for multiple interpretations and provides a level of certainty to both parties involved.
Understanding Different Question Types
Evaluating knowledge or skills can be done through various formats, each serving a different purpose. Some are designed to assess a broad understanding of a subject, while others are more focused, aiming to test specific facts or concepts. These structures can range from those that allow for multiple interpretations to those that have a clear, singular response. Understanding these distinctions is essential for both test designers and participants to ensure that the goals of the evaluation are met.
Objective Formats
Objective formats are commonly used in educational settings and standardized tests. These formats aim for clarity and simplicity, offering predefined options that require the participant to select the most accurate response. The focus is on evaluating recall and comprehension, ensuring that the intended answer is clear and straightforward.
Subjective Formats
In contrast, subjective formats provide more room for interpretation. These often involve open-ended prompts that require detailed responses, allowing the evaluator to assess reasoning, depth of knowledge, and critical thinking. While these formats can be more complex, they offer valuable insights into an individual’s understanding of a topic.
Choosing the right format depends on the goals of the assessment. For assessments that need objective and reliable results, formats that offer a single, indisputable response are often preferred. However, for more complex evaluations, subjective formats can provide a richer understanding of a participant’s capabilities.
Types of Questions in Assessments
In any form of evaluation, the structure of the prompts plays a significant role in determining how effectively knowledge is assessed. Different formats are chosen based on the objectives of the assessment and the level of detail required from the respondent. While some formats require a single precise response, others allow for more expansive or subjective replies. Understanding the various structures helps in selecting the most appropriate method for evaluating a particular skill or knowledge area.
Commonly Used Formats
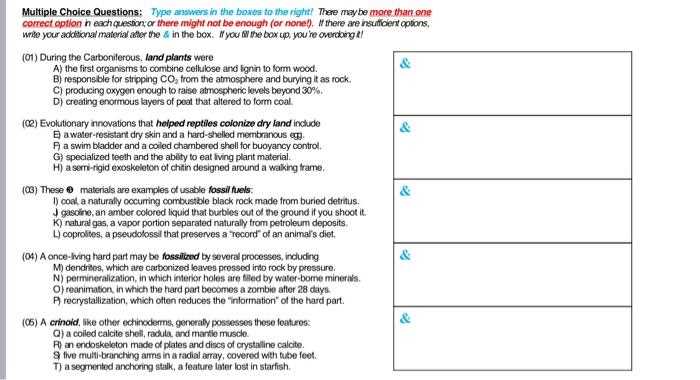
- Multiple Choice: These formats present a set of predefined options, where only one is correct. The participant must identify the correct option from the list.
- True/False: These are binary formats where the participant must choose between two possible outcomes, usually involving a simple factual statement.
- Fill-in-the-Blank: In this format, the respondent is required to provide a missing word or phrase to complete a sentence or statement.
- Matching: This structure pairs items from two lists, requiring the participant to match them based on their relevance or relationship.
Advanced Formats
- Essay: This format allows for in-depth responses, testing the participant’s ability to articulate thoughts and demonstrate comprehension of a topic.
- Short Answer: Similar to essays but requiring concise responses, these formats test the ability to recall specific information.
- Scenario-Based: These involve presenting a situation or case study and asking the participant to apply knowledge to solve a problem or answer a related question.
Choosing the appropriate format is essential for achieving reliable results in assessments. Each structure has its strengths, and the format selected should align with the goals of the evaluation, whether it’s testing factual recall or critical thinking.
What Defines a Question with One Answer
In certain forms of evaluation, it’s crucial to design prompts that lead to a single, unambiguous solution. This ensures clarity and precision in assessing knowledge or skills. The goal is to eliminate any confusion, providing clear guidelines for the participant to follow. These formats are often used when measuring factual recall, where there’s an expected, specific response.
Key Characteristics of This Format
- Clear Instructions: The prompt is straightforward, guiding the participant toward a single response. Ambiguity is avoided, and only one answer can satisfy the criteria.
- Fixed Options: If multiple choices are presented, only one selection is correct. Other options are designed to distract but not provide alternative correct solutions.
- Objective Evaluation: Scoring is based on identifying the precise solution. There is no room for interpretation, and all responses are either correct or incorrect.
Benefits of This Approach
- Simplicity: The format is easy for both the evaluator and the participant. It minimizes complexity, ensuring efficient assessment.
- Reliability: Results are more consistent, as there is no variability in how responses are interpreted.
- Fairness: Every participant is judged on the same criteria, reducing bias and enhancing objectivity.
Using this approach is particularly effective when the goal is to assess factual accuracy or basic understanding, ensuring that each response is clear-cut and universally accepted as correct or incorrect.
Multiple Choice Questions Explained
In assessments, some formats present a set of alternatives, where the participant must select the correct option from a list. These are commonly used in educational settings due to their efficiency and simplicity. The goal is to assess specific knowledge or skills by providing clear choices, among which only one is accurate, ensuring straightforward evaluation.
How This Format Works
Participants are given a prompt followed by a series of options. Among these, only one option is correct, while others serve as distractors. The goal is for the individual to identify the correct choice, using their knowledge or reasoning to make the appropriate selection. The structure of this format ensures quick evaluation and scoring.
Advantages of Multiple Choice
- Efficiency: This structure allows for quick testing of multiple concepts in a short amount of time.
- Standardization: Every participant is presented with the same set of choices, ensuring fairness and consistency in the evaluation.
- Ease of Scoring: Scoring is objective, as only one option is correct, making the grading process fast and accurate.
Effective use of multiple choices in assessments helps to streamline the evaluation process, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of knowledge while minimizing ambiguity in responses.
True or False Question Format
This format presents a statement that the participant must evaluate as either correct or incorrect. It is one of the simplest and most direct approaches to assessing knowledge. By requiring only two possible responses, this method simplifies evaluation and ensures quick, clear results. It is often used in situations where basic comprehension or factual accuracy needs to be tested.
How It Works
In this format, a statement is given, and the participant must decide whether it is true or false. There is no ambiguity, as each statement is designed to be either factual or misleading. This clear-cut approach makes it easy for evaluators to assess understanding, especially in standardized settings.
Advantages of True or False Format
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Simplicity | The structure is straightforward, making it easy to administer and understand for both participants and evaluators. |
| Quick Scoring | Results are easily assessed, with only two possible outcomes per prompt, allowing for fast grading. |
| Fairness | All participants are presented with the same statements, ensuring consistency and fairness in evaluation. |
This format is highly effective for testing basic knowledge, especially when evaluating whether the participant can distinguish between true and false information. Its simplicity makes it a valuable tool in many educational and assessment settings.
Identifying Correct Responses in Assessments
In certain evaluation formats, it’s essential to pinpoint the correct solution from a set of options or within a statement. This process helps to ensure that the assessment measures specific knowledge or skills effectively. The goal is to design tasks that lead to a clear, unambiguous solution, where only one option is valid based on the given criteria.
When crafting such tasks, clarity is paramount. A well-designed prompt will guide the participant towards the correct outcome, whether through recognizing factual information or applying learned concepts. The evaluator, in turn, is able to easily determine whether the individual’s response is accurate, ensuring a fair and efficient grading process.
In these situations, having a defined and indisputable response is crucial for consistency. When there is only one correct choice, both participants and evaluators can be confident in the outcome, reducing any uncertainty in the evaluation process.
Benefits of Questions with One Correct Answer
Evaluations that require selecting a single, definitive response offer several advantages in testing knowledge or skills. These formats are designed to be straightforward, allowing for quick and efficient assessment. Their simplicity ensures that participants can focus on recalling or identifying the correct information without ambiguity.
Key Advantages

- Clarity: There is no room for interpretation or multiple possibilities, making the task simple and easy to understand.
- Speed: Both participants and evaluators can complete and score the assessment quickly, leading to a more efficient process.
- Consistency: Because the correct response is clear-cut, scoring is reliable, ensuring that everyone is judged according to the same criteria.
- Reduced Bias: By eliminating subjective interpretation, this format minimizes the risk of bias in evaluation.
- Objective Grading: Evaluators can score responses instantly, as there is no need for interpretation, reducing grading time.
This structure is especially useful in contexts where the goal is to test foundational knowledge or factual recall. Its straightforward nature ensures that participants are judged based on their ability to identify a specific and unambiguous piece of information, making the evaluation process fair and efficient.
How Multiple Choice Questions Work
This format presents a statement or prompt followed by several possible responses. The task is for the participant to select the most accurate option from the available choices. Only one of the provided answers is correct, while the others are designed to challenge the individual’s understanding or knowledge. This setup allows for efficient assessment of various concepts in a single task.
Structure of Multiple Choices
Typically, multiple options are provided, each representing a potential solution. Among these, only one corresponds to the correct answer, while others are distractors meant to test the participant’s depth of knowledge. The individual must carefully evaluate each choice and select the best match.
Advantages of This Format
- Variety of Topics: Multiple choices enable the inclusion of diverse content in a single assessment, making it easier to test a wide range of knowledge.
- Speed: This format allows for quick responses, benefiting both the participant and the evaluator when time is a factor.
- Objective Scoring: The assessment is straightforward to grade, as there is a clear correct answer, reducing the subjectivity in evaluation.
Multiple choice formats are widely used because they balance efficiency and depth, providing an effective method for testing a broad scope of material in a structured and standardized way.
True or False: A Simple Format
This format presents a statement that participants must evaluate for its correctness. It simplifies the process by offering only two choices: “True” or “False.” This makes it an efficient and straightforward way to assess basic understanding or factual knowledge. The simplicity of this format allows it to be used in various settings, from educational assessments to quick knowledge checks.
Structure and Functionality
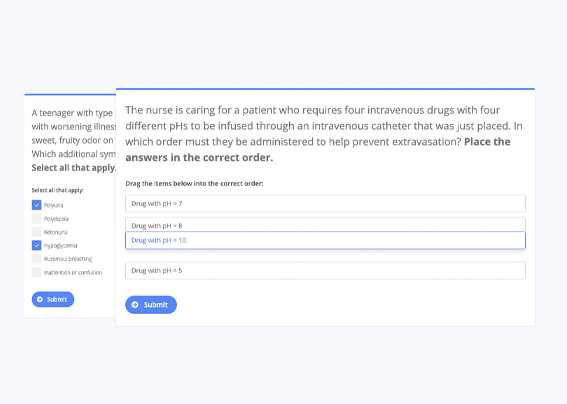
Each item in this format consists of a single assertion. The participant’s task is to determine whether the statement is accurate or not. There is no ambiguity in the response options, as the choices are clearly defined. This setup makes the process of answering quick and easy.
Benefits of the True or False Format
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Simplicity | This format is easy to understand, requiring little explanation or guidance from the evaluator. |
| Speed | With only two possible responses, participants can quickly complete the task, and grading is also faster. |
| Fairness | Each participant is faced with the same set of statements, ensuring a consistent evaluation process. |
This structure is particularly valuable in scenarios where speed and clarity are important. By focusing on clear, unequivocal statements, it tests participants’ ability to assess the accuracy of information quickly and effectively.
Accuracy in Question Design
When creating assessments, precision is crucial. The goal is to craft items that effectively evaluate a specific skill or knowledge area, without introducing confusion or ambiguity. Each task should be clear and unambiguous, ensuring that the individual can demonstrate their understanding accurately. Proper design minimizes the chances of misinterpretation, making the assessment more reliable and fair.
Accurate task creation involves considering the phrasing, context, and clarity of the information presented. A well-designed item focuses on the core concept being tested, avoiding unnecessary complexity that could distract or mislead the participant. The clearer the prompt, the easier it is for the individual to focus on providing the correct response.
In addition to clear wording, the options or solutions provided should be carefully constructed to ensure that there is a distinct, correct choice. This approach prevents confusion and supports a more straightforward evaluation process, leading to more effective assessments.
Why Precision Matters in Quizzes
In any form of evaluation, the accuracy of each item plays a significant role in ensuring that the assessment reflects the true knowledge or skill of the participant. A well-crafted evaluation task not only tests understanding but also provides meaningful feedback. If the prompt or options are unclear or poorly structured, it can lead to confusion, incorrect assessments, and unfair results.
Impact of Precision on Results
When items are precisely worded and structured, the focus is placed solely on the participant’s ability to recall or apply knowledge, without interference from ambiguous language. Precision ensures that only the intended concept is tested, making the process smoother and more objective for both participants and evaluators.
Consequences of Imprecision
| Issue | Effect |
|---|---|
| Ambiguity | Can lead to confusion, where participants may misinterpret the task and provide an incorrect response. |
| Bias | Vague wording can unintentionally favor certain answers, skewing the results and making grading less reliable. |
| Unfair Evaluation | Unclear or misleading tasks can penalize participants who might otherwise demonstrate knowledge accurately. |
Precision is critical in providing a fair and reliable measure of someone’s capabilities. By ensuring clarity and focus, evaluators can create assessments that truly reflect the participant’s understanding, leading to more valid and trustworthy outcomes.
Question Types for Standardized Tests
Standardized assessments rely on various formats to evaluate a range of skills and knowledge. The design of these items is intended to provide an objective measure of a participant’s abilities, ensuring fairness and consistency across different test-takers. Each format serves a specific purpose, targeting different cognitive processes and understanding levels.
Common Formats in Standardized Assessments
Standardized tests often feature a combination of different formats, each chosen for its ability to test specific knowledge areas effectively. Below are some common formats:
- Multiple-Choice: A format offering several options, where only one is correct, testing recall, recognition, and critical thinking.
- True or False: A binary format where participants determine whether a statement is accurate, focusing on basic comprehension.
- Fill-in-the-Blank: Participants are asked to complete a statement with the correct word or phrase, assessing recall and understanding of specific concepts.
- Matching: This format pairs related items, requiring the participant to match a set of choices, evaluating associations and relationships between concepts.
Why These Formats Are Effective
- Objective Scoring: These formats allow for clear, easy-to-grade responses, ensuring consistency and reducing subjective bias.
- Comprehensive Assessment: The variety of formats enables the test to assess different levels of understanding, from basic recall to more complex reasoning.
- Efficient Evaluation: Standardized assessments often feature timed formats, allowing for a broad evaluation of skills within a limited time frame.
These carefully chosen formats make standardized tests a valuable tool for assessing a wide range of knowledge and skills, ensuring fairness and reliability in evaluating participants’ abilities.
Comparing Question Formats for Clarity
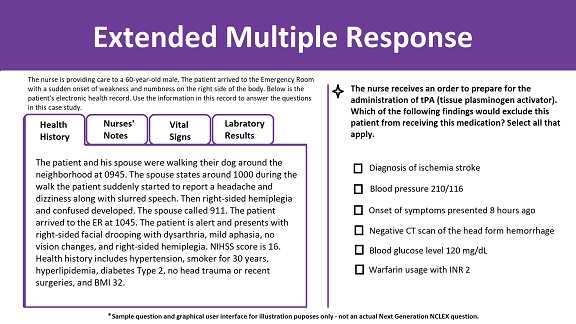
The clarity of any assessment item plays a crucial role in determining whether the participant can effectively understand and respond. A well-constructed prompt ensures that the individual is able to focus on demonstrating their knowledge, rather than deciphering vague or confusing wording. In this section, we compare different formats commonly used to assess comprehension, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses in terms of clarity.
Simple Formats: Easy to Understand
Some formats are inherently more straightforward, providing clear and concise prompts that reduce the chance of misinterpretation. For instance:
- True or False: This binary format is simple, as it requires the participant to assess whether a statement is correct or not. The directness of this format makes it easy to understand and answer quickly.
- Multiple Choice: While slightly more complex, this format clearly presents a question and provides distinct answer choices. Participants only need to choose the correct option, which helps focus their decision-making.
Complex Formats: Potential for Misunderstanding
More intricate formats can sometimes lead to confusion, as they often involve more detailed instructions or require a deeper understanding of relationships between concepts:
- Matching: While effective for testing connections between items, this format can be challenging if the items are not clearly distinguished or if there are too many options.
- Fill-in-the-Blank: Although it is good for assessing recall, it may lead to uncertainty if the prompt is not clearly worded or if multiple correct responses are possible.
Ultimately, the format selected for an assessment should align with the intended learning outcomes while ensuring that the clarity of each prompt is maintained. The simpler the format, the easier it is for the participant to focus on the actual task at hand, without being distracted by confusing language.
Objective vs Subjective Question Formats
When designing assessments, two major formats often come into play: objective and subjective. These approaches differ in how responses are structured and evaluated, affecting the clarity, speed, and depth of the assessment. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each format is crucial for creating effective evaluation tools that meet specific assessment goals.
Objective formats are typically used when the goal is to assess clear, measurable knowledge. These formats are structured in such a way that participants select or identify the correct response from a set of options. The answers are straightforward and unambiguous, making it easier to grade consistently. For example, a participant might choose from a list of options, and only one will match the correct information.
On the other hand, subjective formats allow for more open-ended responses, encouraging participants to express their thoughts in their own words. This type of format is often used when testing deeper understanding, critical thinking, or the ability to explain concepts. Responses are typically longer and require more effort to evaluate, as they often involve interpretation based on the individual’s perspective or reasoning.
Both formats have their place depending on the context of the assessment. Objective formats are ideal for testing specific, factual knowledge that can be easily quantified, while subjective formats are better suited for evaluating comprehension, reasoning, and the ability to articulate complex ideas.
When to Use One Right Answer Questions
Choosing the right format for an assessment is crucial for achieving the desired outcomes. When a clear, definitive response is required, the format where only a single correct option exists is often the best choice. This format is effective for testing basic knowledge and understanding of well-defined facts, concepts, or procedures that have an unambiguous solution.
Such an approach is ideal in situations where the goal is to assess whether individuals have mastered specific content or are able to recall factual information accurately. For example, in exams that focus on technical skills, scientific principles, or historical data, using this format ensures that the evaluation is objective, straightforward, and easy to grade.
Additionally, this format is beneficial when assessing the foundational understanding of a subject before moving on to more complex tasks. It allows instructors to quickly gauge whether learners possess the necessary baseline knowledge to succeed in more advanced assessments that might involve critical thinking or problem-solving.
Overall, questions that demand a single correct response provide a reliable way to assess basic competencies and ensure clarity in the evaluation process.
Common Mistakes in Question Design
Designing effective assessments requires attention to detail, as errors in the format can lead to confusion and inaccurate results. Many common mistakes can occur during the creation process, often stemming from vague wording, poorly structured options, or unclear instructions. These errors can affect both the reliability and validity of the evaluation, leading to frustration for both the evaluator and the participants.
Poorly Crafted Options
One frequent mistake is offering options that are not distinct enough from each other. When choices are too similar, participants may struggle to differentiate between them, reducing the accuracy of their responses. Clear, distinct alternatives are essential to ensure that the evaluation measures what it is intended to, without causing unnecessary confusion.
Ambiguous Wording
Another common issue arises from unclear or overly complex wording. If the phrasing of a prompt is vague or difficult to understand, participants might misinterpret the intent behind the task, resulting in incorrect responses. To avoid this, it is important to use simple, direct language that is easily understood by all individuals, regardless of their background or level of expertise.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures that assessments are both fair and effective, providing accurate insights into participants’ knowledge and abilities.