A&P 2 Lab Exam 1 Study Guide and Tips
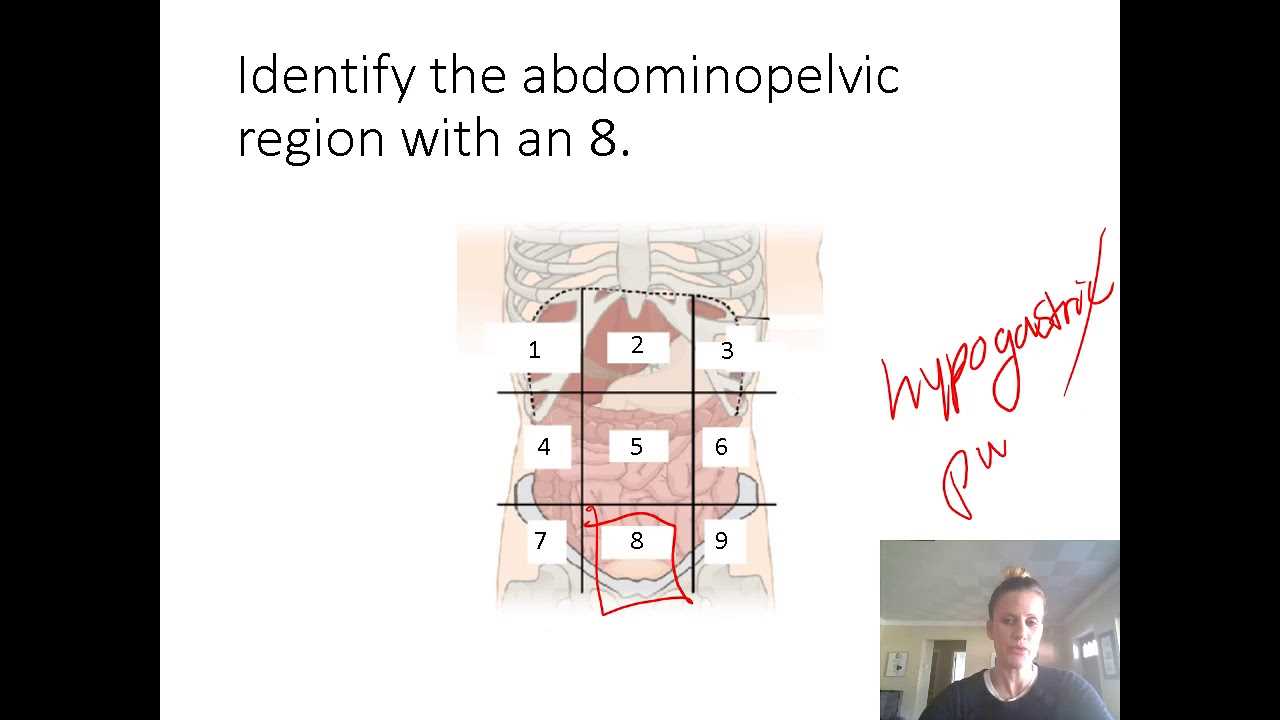
Preparing for the first major assessment in your anatomy and physiology course requires focus, dedication, and a clear understanding of key concepts. This type of evaluation challenges your ability to apply theoretical knowledge in hands-on situations, ensuring you grasp both the structure and function of the human body. Success in this assessment can significantly impact your overall performance in the subject, making efficient preparation essential.
To excel, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the specific techniques, tools, and systems that will be tested. A structured approach to reviewing materials and practicing procedures will help solidify your knowledge and boost your confidence. By focusing on critical areas, practicing with relevant tools, and avoiding common pitfalls, you’ll be well-prepared to tackle the practical assessment with confidence and precision.
Essential Concepts for A&P 2 Lab Exam
When preparing for the first practical assessment in your anatomy and physiology course, understanding core principles is key. These principles encompass both the structure and function of the human body, with a focus on how systems interact. Mastering these concepts will not only help in demonstrating your knowledge but will also enable you to perform effectively in practical scenarios.
Key Systems and Their Functions
Familiarity with major systems in the human body is crucial. For this assessment, a solid grasp of the following systems will be necessary:
| System | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular | Heart anatomy, blood flow, and circulation |
| Muscular | Types of muscles, muscle contraction, and movement |
| Nervous | Neurons, brain structure, reflexes, and sensory systems |
| Respiratory | Lung structure, gas exchange, and breathing mechanics |
Important Techniques and Tools
In addition to theoretical knowledge, mastering practical techniques and using the right equipment efficiently is essential. You should be able to identify and use tools for examining and measuring body parts, as well as demonstrate proficiency in procedures such as dissections and specimen identification. Familiarity with microscopes and slides is also important, especially for understanding cellular structures and tissue organization.
Understanding Human Anatomy in Labs
Mastering human anatomy is essential for anyone studying the structure and function of the body. In practical settings, it’s vital to understand not only the names and locations of organs, but also their relationships and functions within systems. A deep knowledge of the body’s framework allows students to perform procedures effectively and analyze structures with precision.
Key Body Systems and Their Structure
Familiarity with the major body systems and their components is crucial. Understanding how each system is organized and its role in maintaining overall health provides a foundation for further learning. The following systems are essential for study:
| System | Components |
|---|---|
| Skeletal | Bones, joints, ligaments, cartilage |
| Muscular | Skeletal muscles, tendons |
| Circulatory | Heart, blood vessels, blood |
| Respiratory | Lungs, trachea, diaphragm |
Dissection and Hands-on Exploration
Hands-on exploration is an important aspect of studying human anatomy. Through dissections and the examination of preserved specimens, students gain a better understanding of the body’s internal organization. This practical experience helps to solidify theoretical knowledge and allows for a more tactile approach to learning anatomical structures.
Key Physiology Topics to Focus On
Understanding the physiological processes of the human body is fundamental for success in practical assessments. These processes govern how the body functions at both the cellular and systemic levels. By mastering key physiological concepts, students can better connect theoretical knowledge with real-world applications and demonstrate a comprehensive understanding during practical evaluations.
Homeostasis and Regulatory Mechanisms
One of the most critical concepts to grasp is the body’s ability to maintain stability through various regulatory systems. The concept of homeostasis involves how the body keeps internal conditions like temperature, pH, and blood pressure within optimal ranges. Understanding the feedback mechanisms that control these variables, such as negative and positive feedback, is essential for recognizing how the body responds to internal and external changes.
Circulatory and Respiratory Functions
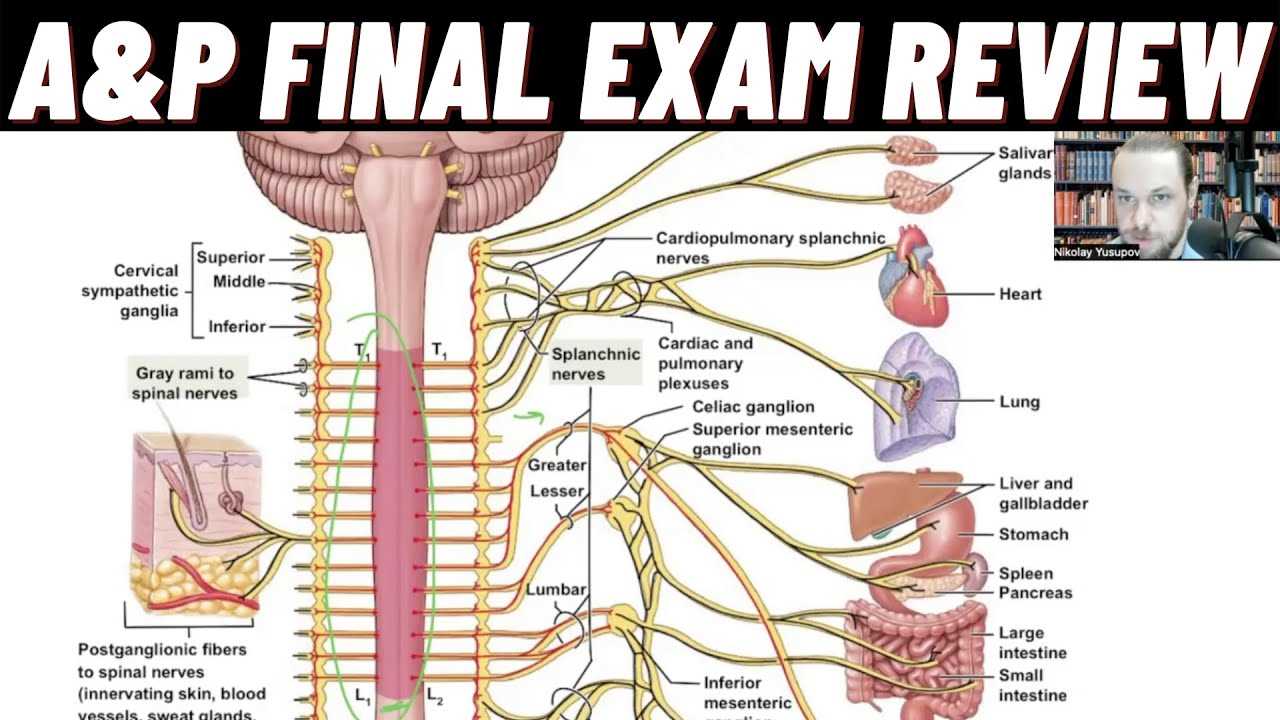
The circulatory and respiratory systems are vital for delivering oxygen to tissues and removing waste products. Focus on how the heart pumps blood, the movement of gases across membranes in the lungs, and how blood flow is regulated to meet the body’s demands. Key topics include cardiac output, blood pressure regulation, and gas exchange mechanisms in the lungs. Understanding these physiological processes will be important for interpreting bodily functions during practical scenarios.
Practical Tips for Lab Exam Success
To perform well in hands-on assessments, preparation must go beyond theoretical knowledge. It’s essential to develop a clear understanding of both the concepts and practical skills that will be tested. Proper preparation ensures you’re ready to apply your knowledge confidently and effectively under exam conditions.
Effective Study Strategies
- Review Key Concepts Regularly: Continuously go over essential topics to reinforce your understanding.
- Practice with Specimens: Familiarize yourself with common tools and specimens that may appear during the assessment.
- Simulate the Test Environment: Practice procedures under time constraints to build confidence and improve time management.
- Form Study Groups: Collaborate with classmates to review material and test each other’s knowledge.
During the Assessment
- Stay Organized: Carefully organize your workspace and tools to minimize distractions and ensure efficiency.
- Follow Instructions: Pay attention to every detail of the task and double-check steps to avoid mistakes.
- Stay Calm Under Pressure: Keep a level head and stay focused on the task at hand, even if you encounter challenges.
- Review Your Work: Before submitting, take a few moments to review your answers and actions to ensure everything is accurate.
How to Study Efficiently for A&P 2
Effective studying is essential for mastering the complexities of human anatomy and physiology. To succeed, it’s important to adopt strategies that enhance retention, comprehension, and practical application. By organizing your study sessions and focusing on high-yield topics, you can maximize your learning while minimizing stress and wasted time.
Organize Your Study Sessions
Breaking down your study time into manageable sessions is a key step in efficient preparation. Set clear goals for each study session, and avoid cramming. Focus on one topic or system at a time, ensuring you understand it fully before moving on. Use active recall and spaced repetition techniques to reinforce your knowledge over time.
Use Multiple Study Resources
Don’t rely solely on textbooks. Supplement your learning with a variety of resources, such as online videos, interactive diagrams, and practice quizzes. Visual aids, like 3D models or anatomy apps, are particularly useful for understanding complex structures. Additionally, working with classmates or forming study groups can help reinforce material through discussion and collaborative problem-solving.
Common Lab Techniques and Procedures
Proficiency in essential techniques and procedures is vital for performing well in practical assessments. These skills allow students to gather, analyze, and interpret data accurately while working with specimens and equipment. Mastering these methods ensures that you can apply your knowledge effectively in a hands-on environment.
Essential Techniques to Master
- Dissection: Carefully following protocols to study the internal structure of specimens, allowing for hands-on exploration of anatomy.
- Microscopic Examination: Using microscopes to examine cells, tissues, and organ structures at a detailed level.
- Measuring and Recording Data: Accurately measuring physiological parameters like blood pressure, temperature, and heart rate.
- Staining Techniques: Applying dyes to tissues to enhance visibility and identify specific structures under the microscope.
Important Procedures to Follow
- Proper Handling of Specimens: Always handle specimens with care, ensuring correct preservation and preparation for observation.
- Following Safety Protocols: Adhering to safety guidelines, including wearing protective gear and handling chemicals and sharp objects properly.
- Maintaining Equipment: Ensuring microscopes, dissection tools, and other equipment are in good condition for accurate results.
- Documenting Findings: Keeping detailed notes of observations and measurements to accurately report results and conclusions.
Best Resources for A&P 2 Lab Exam

Having the right resources at your disposal can make all the difference when preparing for a practical assessment in anatomy and physiology. A variety of tools, from textbooks and online platforms to interactive applications, can help reinforce your understanding and provide valuable hands-on practice. Utilizing these resources effectively will allow you to study more efficiently and improve your performance during the evaluation.
Top Study Materials
- Textbooks: Standard textbooks such as “Human Anatomy & Physiology” by Elaine N. Marieb offer comprehensive information on structures and functions of the body.
- Interactive Websites: Websites like Khan Academy and Visible Body provide interactive diagrams and videos that illustrate complex concepts in an engaging way.
- Practice Quizzes and Flashcards: Online platforms such as Quizlet offer sets of flashcards and quizzes to test your knowledge on key topics and terminology.
Apps and Tools for Hands-On Practice
- Anatomy Apps: Applications like Complete Anatomy or 3D4Medical allow you to explore 3D models of the human body, enhancing your understanding of spatial relationships between structures.
- Virtual Dissection Tools: Programs like BioDigital Human allow you to perform virtual dissections, simulating real-life procedures and helping you familiarize yourself with anatomy.
- Microscopy Tools: For microscopic analysis, apps like Labster provide virtual labs to help you practice examining cells and tissues without a physical microscope.
Preparing for Lab Practical Assessments
Preparation for hands-on evaluations requires both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Unlike traditional tests, these assessments challenge your ability to apply concepts in real-world scenarios. Effective preparation involves familiarizing yourself with procedures, mastering key concepts, and practicing with relevant tools and specimens to enhance both speed and accuracy during the assessment.
Key Areas to Focus On
To excel in practical evaluations, it’s essential to concentrate on the core areas that will be tested. The following table outlines some of the most important topics and skills you should focus on:
| Topic | Key Skills |
|---|---|
| Human Anatomy | Identifying body structures, organs, and their functions |
| Microscopic Techniques | Using a microscope to examine cells and tissues |
| Measurement Techniques | Accurately recording physiological data (e.g., blood pressure, heart rate) |
| Dissection Procedures | Properly handling and dissecting specimens |
Practical Tips for Success
- Practice Regularly: Consistent hands-on practice with specimens and equipment will help reinforce your skills.
- Study with a Partner: Collaborating with a study partner can help you test each other’s knowledge and skills.
- Stay Organized: Ensure all materials and tools are ready before the assessment to avoid wasting time during the test.
- Understand the Process: Familiarize yourself with the sequence of tasks to minimize errors and ensure efficiency.
Understanding Microscopy in A&P Labs
Microscopy is an essential skill for studying the intricate structures of the human body at a cellular level. By using microscopes, students can explore tissues, cells, and other microscopic components that are vital to understanding biological functions. Mastering this technique allows for a deeper understanding of anatomy and physiology that cannot be achieved through observation alone.
Effective use of the microscope involves more than just focusing on the specimen. It requires knowledge of how to prepare samples, adjust the magnification, and interpret findings accurately. Familiarity with different types of microscopes, such as light microscopes and electron microscopes, is also crucial for working with various samples in a practical setting.
Microscope Preparation and Setup
Before using the microscope, ensure that the equipment is clean and functioning properly. Preparing samples correctly is also key to obtaining clear, usable images. The following steps outline the basic preparation process:
- Clean the lenses: Wipe the ocular and objective lenses with a lens paper to avoid distortions.
- Prepare the sample: Mount the sample on a glass slide and apply a cover slip to avoid contamination.
- Adjust the light source: Ensure adequate lighting for clear visualization of the sample.
- Start with low magnification: Begin with a low-power objective to locate the sample, then switch to higher magnifications as needed.
Interpreting Microscope Images
Accurate interpretation of microscope images requires familiarity with common cell structures and their functions. As you observe a specimen, focus on identifying key features such as cell membranes, nuclei, and organelles. Being able to distinguish between different tissue types or identifying abnormalities in a cell’s structure is crucial for understanding underlying physiological processes.
Critical Systems to Study for Exam
When preparing for practical evaluations, it is crucial to focus on the key physiological systems that govern the body’s functions. A deep understanding of these systems allows you to connect theoretical knowledge with practical applications, making it easier to identify structures and processes during assessments. Mastery of these systems ensures you can recognize their components, functions, and interactions, which is vital for success.
Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system is essential for transporting oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. It includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood. Understanding the anatomy of the heart, how blood flows through the circulatory system, and the mechanisms behind blood pressure regulation is fundamental. You should focus on:
- Heart Anatomy: Study the chambers, valves, and major vessels connected to the heart.
- Circulatory Pathways: Understand how blood flows through systemic and pulmonary circuits.
- Electrophysiology: Know how electrical impulses regulate heartbeats and how to interpret an electrocardiogram (ECG).
Respiratory System
The respiratory system enables the exchange of gases, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, between the body and the environment. The key structures to focus on include the lungs, trachea, bronchi, and alveoli. Understanding how oxygen is transferred to the bloodstream and how carbon dioxide is removed is essential. Key topics to study include:
- Lung Anatomy: Identify the major regions of the lungs and their functions in gas exchange.
- Breathing Mechanics: Understand the process of inhalation and exhalation and the role of diaphragm and intercostal muscles.
- Gas Exchange: Study how oxygen diffuses into the bloodstream and how carbon dioxide is expelled.
Nervous System
The nervous system controls and coordinates the body’s responses to internal and external stimuli. It includes the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. It is important to understand how sensory input is processed and how motor functions are executed. Focus on:
- Brain Structure and Function: Study the regions of the brain and their roles in cognition, motor control, and autonomic functions.
- Neurons: Understand the structure of neurons and how they transmit electrical signals across synapses.
- Reflexes and Pathways: Study reflex arcs and neural pathways responsible for automatic responses.
How to Master Dissection Techniques
Dissection is an essential skill for studying the structures and functions of the human body. It allows students to gain a hands-on understanding of anatomy by carefully examining and identifying various tissues, organs, and systems. Mastering dissection techniques not only enhances knowledge but also improves the precision needed for future studies and assessments.
To succeed in dissections, it’s crucial to be familiar with the proper tools, techniques, and safety procedures. The ability to handle specimens with care while maintaining accuracy in your cuts and observations will help you gain a deeper understanding of anatomical structures.
Essential Tools for Dissection
Having the right tools is fundamental to performing a successful dissection. Below is a list of essential tools that should be part of your dissection kit:
- Scalpel: A sharp scalpel allows for precise cuts through tissue.
- Scissors: Scissors are useful for cutting larger sections of tissue and organs.
- Forceps: Forceps help manipulate tissues and hold structures in place without damaging them.
- Probe: A probe assists in separating and identifying small or hidden structures.
- Dissection Tray: A tray provides a stable and sterile surface for dissection activities.
Steps for a Successful Dissection
Follow these steps to ensure a careful and organized dissection:
- Preparation: Begin by thoroughly reading any dissection guidelines or instructions to understand the objectives of the procedure.
- Positioning the Specimen: Secure the specimen properly in the dissection tray, ensuring that it is stable and accessible.
- Making the First Cut: Start with small, controlled cuts. Always make cuts along the natural lines of the tissue to avoid unnecessary damage.
- Systematic Exploration: Work methodically, moving from one area to another, examining each structure carefully.
- Documentation: Take notes and document your observations. Label structures clearly, and take time to reflect on their function and relationship to surrounding tissues.
By practicing these techniques and becoming familiar with your tools, you can improve your dissection skills and gain a more thorough understanding of anatomy and physiology.
Important Lab Equipment and Tools
In any scientific setting, having the right equipment and tools is crucial for performing accurate experiments and procedures. These instruments not only ensure safety and precision but also help in gaining deeper insights into the subject matter. Familiarity with the essential tools will allow students to navigate the complexities of their practical sessions more confidently.
From cutting-edge instruments to basic tools, understanding the function and proper usage of each item in your toolkit is key. Knowing how to handle and maintain these tools also contributes to successful outcomes in any practical setting.
Common Instruments Used in Experiments
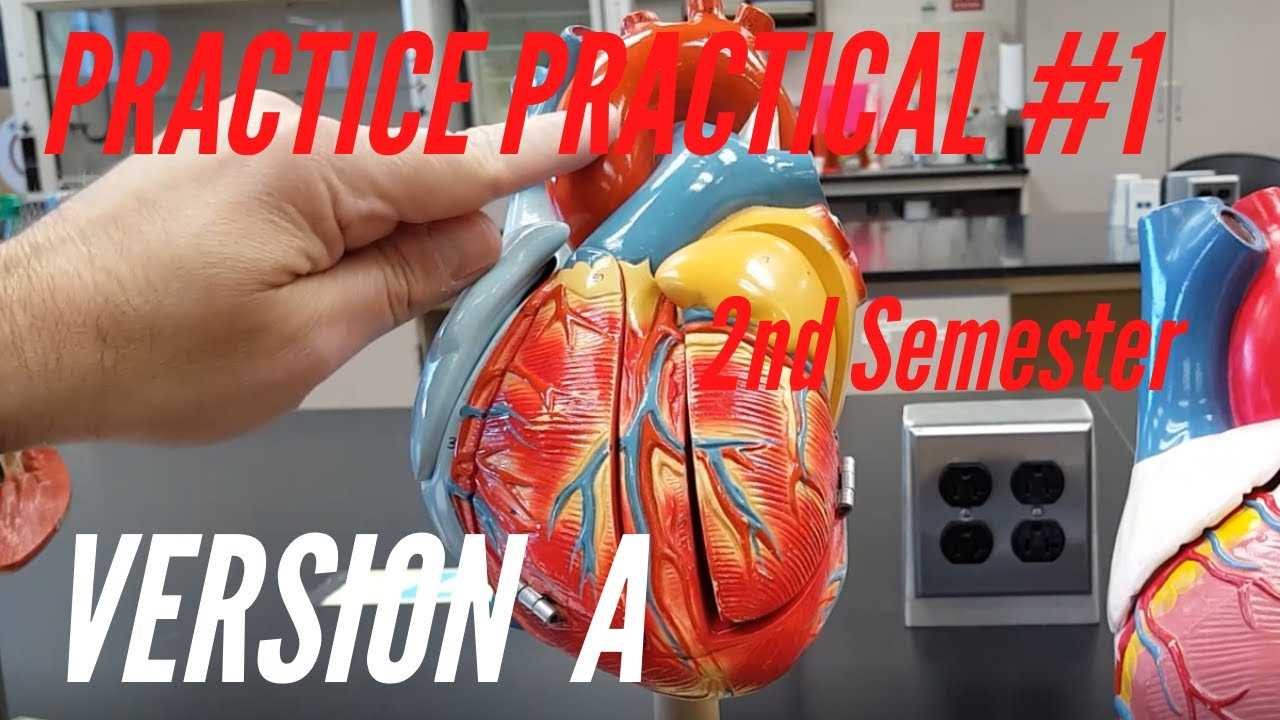
Here are some of the most common instruments you’ll encounter during your studies:
- Microscope: Essential for examining small structures, such as cells and tissues, that are not visible to the naked eye.
- Dissection Tools: A set of tools including scalpels, scissors, and forceps, designed for careful examination and manipulation of specimens.
- Incubators: These are used to maintain a controlled environment, especially when growing cultures or maintaining tissue samples at a specific temperature.
- pH Meters: Instruments used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, critical for experiments involving chemical reactions.
- Test Tubes and Petri Dishes: Used for holding small samples or cultures, providing a surface for various experiments.
Essential Tools for Precision and Accuracy
In addition to basic instruments, precision tools help ensure accurate results and measurements during practical activities:
- Balances: These are used for measuring the mass of substances, critical in experiments requiring exact amounts of materials.
- Thermometers: Accurate temperature measurement is vital for experiments that depend on specific temperature conditions.
- Graduated Cylinders and Pipettes: These tools are essential for measuring and transferring liquids with high precision.
- Stereomicroscopes: These provide a three-dimensional view, making them perfect for larger specimens or objects that require magnification without altering their structure.
Knowing when and how to use these tools effectively is essential for performing tasks accurately and efficiently, ultimately contributing to your success in scientific investigations.
Time Management Strategies for Labs
Effective time management is crucial in any hands-on scientific environment, where tasks often have strict timelines and multiple steps that need to be completed with precision. Mastering how to allocate time wisely ensures that each task is completed thoroughly, without unnecessary rush or stress. By following strategic approaches, you can optimize your productivity and ensure all objectives are met on time.
Balancing theoretical knowledge with practical application often means juggling several experiments, tasks, and analyses within a short period. Developing strong organizational skills and planning ahead will help streamline the entire process and minimize errors caused by time pressure.
Key Time Management Tips
Here are some useful strategies for maximizing your efficiency in hands-on environments:
- Prepare in Advance: Before beginning any procedure, review the instructions, gather all necessary materials, and set up your workspace. This reduces time spent looking for items during the task.
- Set Clear Priorities: Identify the most important steps in your work and tackle them first. This ensures that critical tasks are completed even if time runs short.
- Use a Timer: For tasks that require precise timing, such as incubation periods or reaction times, use a timer to stay on track and avoid losing focus.
- Work in Teams: Collaborating with others can divide the workload and allow for more tasks to be completed in less time. Assigning specific responsibilities ensures everyone works efficiently.
- Stay Organized: Keep your tools, materials, and notes well-organized. A clutter-free workspace can save time and help you avoid mistakes that would require additional corrections.
Managing Multiple Tasks
Handling more than one task at a time requires careful attention and planning. Here are some approaches to manage multiple tasks effectively:
- Break Down Complex Tasks: Divide large or complicated tasks into smaller, more manageable sections. Completing each part step-by-step ensures nothing is overlooked.
- Allocate Time Slots: Dedicate specific time blocks to each task. This prevents multitasking and allows you to focus on one thing at a time, improving accuracy and efficiency.
- Limit Distractions: During critical tasks, limit distractions and stay focused on the immediate job. Turn off unnecessary notifications or interruptions to maintain concentration.
By implementing these strategies, you’ll be able to manage your time effectively, ensuring a smoother, more successful experience during any hands-on project or practical session.
Typical Mistakes to Avoid in Labs
In any hands-on scientific setting, it’s easy to make mistakes due to the complexity of the tasks and the pressure of time constraints. Some errors can be avoided by adopting careful practices and staying mindful of the common pitfalls. Recognizing these mistakes early on can significantly improve your performance and results.
Being aware of the common errors in practical tasks can prevent unnecessary setbacks and ensure that your work is both accurate and efficient. Here are a few of the most frequent mistakes to watch out for:
| Common Mistake | How to Avoid It |
|---|---|
| Neglecting to read instructions thoroughly | Always take time to read all instructions and guidelines before starting. Clarify any doubts before proceeding. |
| Improper handling of equipment | Familiarize yourself with all tools and instruments before use. Follow proper handling techniques to avoid damage or inaccurate results. |
| Skipping preparation steps | Set up your workspace and gather all materials before starting. This will help avoid unnecessary delays or mistakes during the process. |
| Not following safety protocols | Always follow safety guidelines to ensure your well-being and the safety of those around you. Wearing the correct protective gear is essential. |
| Mislabeling samples or materials | Label all samples and containers clearly and accurately to prevent mix-ups. Double-check labels before proceeding with tests. |
| Rushing through tasks | Take your time to complete each step methodically. Rushing often leads to mistakes that could have been easily avoided with more attention. |
By being conscious of these common mistakes, you can improve your efficiency and accuracy in scientific tasks. Proper preparation, attention to detail, and following best practices will ensure a more successful and productive experience.
Reviewing Lab Safety Protocols
Maintaining safety during scientific tasks is crucial to ensure the well-being of individuals and the integrity of the work being done. Proper safety procedures not only protect you but also the environment and those around you. Understanding and adhering to safety protocols is a fundamental aspect of any practical experience involving equipment, chemicals, or biological materials.
Adherence to safety protocols helps prevent accidents, reduces the risk of exposure to harmful substances, and ensures that all procedures are carried out in a controlled and secure manner. The key to a safe environment is being prepared and staying vigilant at all times. Here are the essential protocols you should always review before beginning any practical task:
- Wear appropriate protective gear: Ensure you are wearing gloves, goggles, lab coats, or any other necessary equipment based on the task at hand. This is your first line of defense against potential hazards.
- Know emergency procedures: Familiarize yourself with the location of emergency exits, first aid kits, and fire extinguishers. Knowing how to react in case of an emergency is vital for quick response and minimizing damage.
- Understand material handling: Always be aware of the materials you are working with, especially chemicals or specimens that require special care. Follow the correct handling and disposal methods to avoid contamination or injury.
- Keep the workspace organized: A clean and organized workspace minimizes the risk of accidents. Ensure tools, materials, and substances are stored correctly and safely.
- Follow guidelines for equipment usage: Every tool and piece of equipment has specific instructions for use. Always review and follow the guidelines to prevent misuse or damage.
Reviewing and adhering to these safety protocols before starting any task will ensure a secure and efficient environment, reducing the likelihood of accidents and improving the overall quality of your work.
How to Interpret Lab Results Accurately
Accurate interpretation of results is essential for drawing valid conclusions in any scientific analysis. Whether you’re assessing physiological data, analyzing specimens, or interpreting measurements, understanding the meaning behind the numbers is key to making informed decisions. A thorough approach to result analysis can help identify patterns, confirm hypotheses, and avoid errors that could lead to incorrect conclusions.
To interpret results accurately, several strategies must be followed:
- Understand the context: Each set of results should be examined in relation to the specific experiment or procedure it was derived from. Factors such as the method used, the conditions under which data were gathered, and the purpose of the test all play a role in determining how to read the results.
- Check for consistency: Cross-reference data points to ensure that they are consistent with one another. Look for outliers or discrepancies that may require further investigation or could indicate errors in measurement or procedure.
- Use control data: Comparing experimental results to control groups or baseline measurements can help assess whether changes are significant and provide insight into the accuracy of the data.
- Consult reference ranges: Understanding the normal or expected range for particular results is critical. If data falls outside these ranges, it may indicate an anomaly that requires closer examination.
- Consider the limitations: Be aware of any limitations or potential sources of error in the data collection process. Factors like sample size, timing of measurements, or environmental conditions can influence results and should be taken into account when interpreting the findings.
- Use statistical tools: Statistical analysis can help validate results and identify trends or correlations. Familiarize yourself with common statistical methods like averages, standard deviations, and confidence intervals to better interpret data.
By following these principles, you can ensure a more accurate understanding of your results, leading to better insights and more reliable conclusions.