Data Visualization Exam Questions and Answers
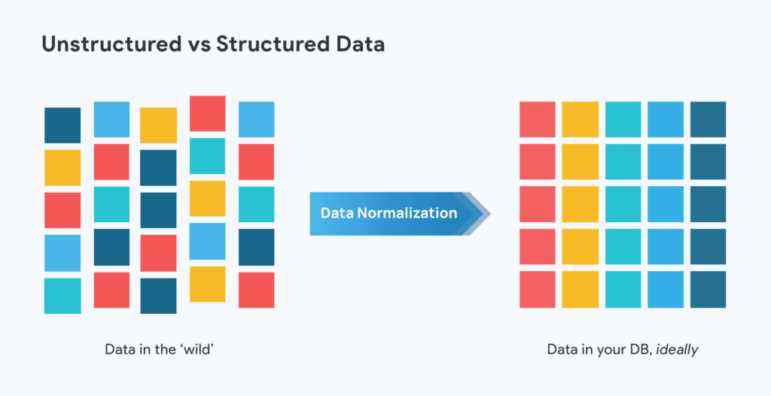
Understanding how to present complex information clearly is essential for anyone aiming to excel in assessments focused on interpreting and showcasing insights through visuals. The ability to convey patterns, relationships, and key findings in an accessible way is often tested through various tasks that require both analytical thinking and creative representation skills.
In this guide, we will explore the key topics you need to focus on to prepare effectively for challenges in this area. From recognizing common formats to mastering tools that help in structuring data effectively, this resource will cover everything you need to know for success. Whether you’re tackling theoretical aspects or applying concepts to real-world scenarios, building confidence in these areas will be crucial for achieving top results.
Data Representation Challenges and Solutions
Preparing for assessments in this field often involves a thorough understanding of how to effectively present numerical or categorical information through various graphical techniques. Success relies not only on the ability to design clear visuals but also on demonstrating an in-depth comprehension of the concepts that underpin them. The questions typically assess your knowledge of different tools, interpretation methods, and how to apply these to real-world data scenarios.
Key Areas to Master
Focus on mastering concepts like chart types, trends, and the relationships between data points. Understanding when and why to choose a specific representation method is critical, as well as being able to accurately interpret the information provided. You may also be asked to describe the best practices for presenting certain types of insights, such as when to use a line graph versus a bar chart.
Strategic Preparation Tips
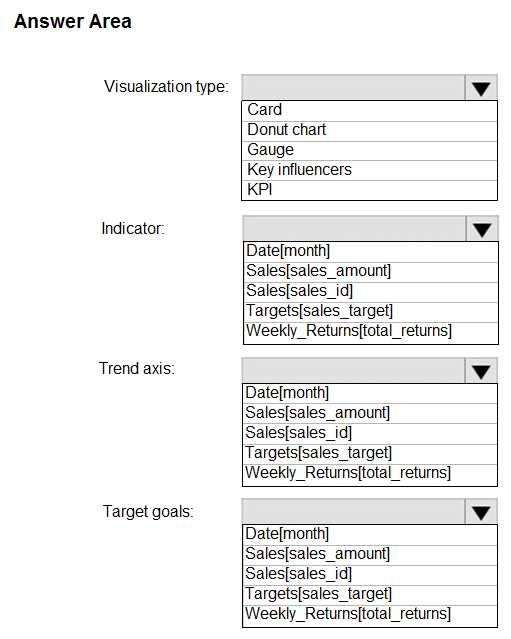
Effective preparation involves both theoretical knowledge and practical experience. It is essential to practice interpreting visuals and working with different tools to ensure you can respond confidently to any challenge. Reviewing past assessment materials and practicing under timed conditions can also help you become more comfortable with the format and structure of the tasks. Make sure to focus on both the practical application of techniques as well as understanding their theoretical foundations.
Key Concepts in Data Representation
Understanding the essential elements of effectively conveying information through graphical means is fundamental to excelling in assessments related to this field. It is important to not only grasp the different types of charts and graphs, but also to know how to interpret and present data in ways that highlight key trends, comparisons, and patterns. Mastering these core ideas will ensure that you can approach any related challenge with confidence and precision.
- Chart Selection: Knowing when to use specific chart types such as bar graphs, line charts, or scatter plots depending on the data’s nature and purpose.
- Scale and Proportions: Understanding how to accurately represent numerical relationships and differences through proper scaling techniques.
- Trend Identification: Being able to recognize trends in data and choose appropriate ways to emphasize these patterns in visual formats.
- Color Theory: Using color to differentiate data sets effectively, enhancing clarity without overwhelming the viewer.
- Labeling and Annotations: Properly annotating graphs and charts to ensure that key insights are immediately apparent to the viewer.
Each of these concepts plays a critical role in transforming raw information into an engaging and comprehensible visual format. Understanding how to combine these principles effectively will make it easier to tackle any related task in assessments or practical applications.
Common Topics to Focus On
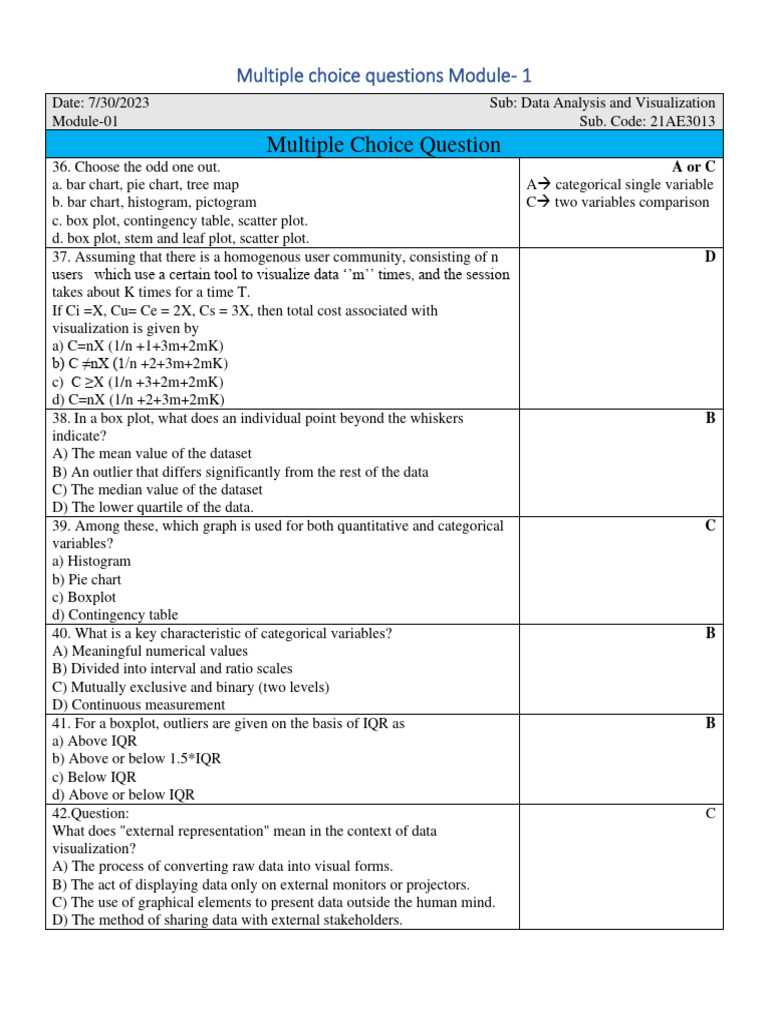
When preparing for assessments in this field, it’s important to focus on the core topics that are frequently tested. These areas often cover a range of fundamental concepts, including how to interpret various types of visual data representations, how to choose the right methods for displaying trends, and how to work with different tools for analysis. Having a clear understanding of these topics can significantly enhance your ability to tackle related tasks with confidence.
Chart Interpretation and Selection
One key area to focus on is understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different chart types. You may be required to identify which type of visual representation best suits a particular dataset or scenario. Be prepared to recognize when to use bar graphs, line charts, histograms, or scatter plots, and understand how each can highlight specific aspects of the data.
Analyzing Trends and Relationships
Another important topic is the ability to identify trends and relationships within data. You should be familiar with concepts such as correlation, distribution, and outliers, and be able to interpret these trends from visual representations. Focus on understanding how these patterns can reveal meaningful insights, and how to communicate those insights effectively through graphs and charts.
Understanding Data Types and Structures
Grasping the different categories and arrangements of information is essential for effectively interpreting and representing insights. Each type of information has unique characteristics, and knowing how to handle these variations will allow you to choose the best approach for analysis and display. The ability to differentiate between numerical, categorical, and temporal elements is a critical skill when working with complex sets of information.
Types of Information
- Numerical: Quantitative values, such as sales figures, temperatures, or any data that can be measured and expressed numerically.
- Categorical: Grouped or classified information, such as product categories, regions, or other non-numeric labels.
- Temporal: Data that changes over time, such as dates, hours, or periods, often used to analyze trends and patterns.
- Ordinal: Information that has a clear ordering or ranking, such as survey responses from “strongly agree” to “strongly disagree.”
Common Data Arrangements
- Tables: Organize information in rows and columns, making it easier to reference and manipulate for analysis.
- Arrays: Structured formats used to store data points in a sequence, ideal for processing multiple values at once.
- Hierarchical Structures: Organize data in a nested format, which is useful for representing relationships between elements.
Understanding these basic structures will help you interpret information more accurately and select the most appropriate tools and methods for your analysis tasks. Recognizing the characteristics of each type ensures a more efficient and effective approach to presenting findings.
Essential Tools for Data Analysis
Having the right set of tools is crucial for efficiently processing and interpreting numerical and categorical information. These tools enable users to analyze complex datasets, uncover hidden patterns, and generate meaningful insights. Mastery of these resources will allow you to approach challenges with confidence and precision, ensuring that you can present your findings in a clear and effective manner.
Popular Software and Platforms
- Excel: A widely used tool for handling structured data and performing basic analysis, including pivot tables, graphs, and statistical functions.
- R: A programming language tailored for statistical computing and complex visual representation, favored for its powerful analysis capabilities.
- Python: A versatile language with libraries like Pandas and Matplotlib, which are ideal for both data manipulation and generating advanced graphs.
- Tableau: A leading tool for visual representation, known for its ability to transform data into interactive and shareable dashboards.
Key Analytical Techniques
- Regression Analysis: A method for examining relationships between variables and predicting future trends based on historical data.
- Clustering: Grouping similar data points together, useful for identifying patterns and segmenting datasets.
- Hypothesis Testing: A statistical technique for validating assumptions and making inferences about a larger population based on sample data.
By leveraging these tools and techniques, you’ll be better equipped to tackle complex analysis tasks and effectively present your findings. Whether you’re working with large datasets or focusing on specific trends, these resources offer the power and flexibility needed for success.
Visual Representation of Data Insights
Effectively showcasing insights through graphical formats plays a critical role in understanding complex information. The ability to present key patterns, trends, and relationships visually helps audiences quickly grasp critical points without delving into raw numbers. The right approach not only clarifies findings but also makes the information more accessible and actionable.
- Charts: Used to represent numerical information in a clear, concise manner. Different chart types like bar, line, and pie charts are used to illustrate various patterns and comparisons.
- Heat Maps: Visual tools that display data in a matrix format, using color to represent values, making it easy to identify areas of interest or variation.
- Histograms: Provide a way to visualize the distribution of data by displaying the frequency of different ranges of values in a dataset.
- Scatter Plots: Ideal for showing correlations or relationships between two variables, helping to identify trends, clusters, or outliers.
Each graphical tool serves a distinct purpose and allows for the presentation of specific types of insights. Choosing the right representation is crucial in highlighting the most important elements of the information, ensuring that viewers can draw meaningful conclusions at a glance.
Practical Applications in Data Representation
The ability to present complex information through clear, understandable visuals is crucial in many industries. Practical applications of this skill are seen in areas ranging from business analytics to scientific research. Whether you are summarizing trends, comparing variables, or tracking performance over time, visual representation enables insights to be communicated efficiently and effectively.
- Business Intelligence: Companies use visual tools to track performance metrics, monitor market trends, and make informed decisions based on real-time data. Dashboards and charts help executives quickly assess key performance indicators.
- Healthcare: Medical professionals use graphs to track patient statistics, such as heart rate, blood pressure, or treatment progress. These visuals aid in understanding patient conditions and making timely interventions.
- Finance: Financial analysts rely on graphs to predict market trends, track stock performance, and visualize economic indicators, enabling better investment decisions.
- Scientific Research: Researchers use plots and graphs to present experimental results, test hypotheses, and compare findings across different conditions or populations.
Across all these fields, the ability to effectively convey information through visual means has a direct impact on decision-making and understanding. Practicing these techniques ensures the ability to communicate complex insights in a simple and impactful way.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid During Assessments
When tackling assessments in this field, it’s easy to fall into certain traps that can affect performance. Being aware of these common mistakes and learning how to avoid them can make a significant difference in achieving success. Whether it’s rushing through tasks or overlooking important details, staying focused and organized is key to navigating the challenges effectively.
One common pitfall is neglecting to carefully analyze the given problem before diving into the solution. It’s important to take time to understand the requirements and limitations, as well as to plan your approach before applying any techniques. Another issue is overcomplicating answers or using overly complex methods when simpler solutions may be more effective. This often leads to confusion and errors in interpretation.
Additionally, failing to double-check the work can result in avoidable mistakes. It’s essential to review calculations, visual formats, and interpretations to ensure accuracy. Lastly, not managing time properly can prevent you from completing all tasks or dedicating enough attention to each section. Effective time management ensures that each part of the task is thoroughly addressed without rushing.
How to Interpret Graphs and Charts
Understanding how to read and extract meaning from graphical representations is essential for analyzing any set of numerical or categorical information. By carefully examining the structure and components of charts, one can quickly identify trends, relationships, and anomalies. Interpreting these visuals accurately allows you to draw meaningful conclusions and make informed decisions based on the presented information.
Key Elements to Consider
- Title: The title often indicates the primary focus or context of the graph, providing insight into what is being represented.
- Axes: The x-axis typically represents time or categories, while the y-axis displays the corresponding values. Understanding the scale and labels is crucial for interpreting the data correctly.
- Legends and Labels: Legends help identify different variables or groups in the chart. Labels provide further clarification on what each point or section of the graph represents.
- Trends: Look for patterns or trends, such as upward or downward movement, to understand how variables relate over time or across categories.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Misinterpreting Scale: Always ensure you understand the scale on each axis. A change in scale can drastically alter the way information is perceived.
- Overlooking Outliers: Pay attention to any points that deviate significantly from the rest of the data. These may indicate anomalies or important findings.
- Ignoring Context: Without proper context, a chart might mislead or be misinterpreted. Always consider the background information and any assumptions made in creating the graph.
By mastering these fundamental techniques, you’ll improve your ability to interpret graphs and charts, leading to more accurate conclusions and better decision-making.
Important Statistical Methods to Know
Understanding statistical techniques is crucial for analyzing patterns, making predictions, and drawing conclusions from a variety of numerical information. These methods allow you to quantify relationships, identify trends, and assess the significance of results. Familiarity with the most commonly used statistical tools enhances your ability to interpret information accurately and effectively.
| Method | Purpose | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | Calculates the average of a set of values. | Used to find the central tendency of a dataset. |
| Median | Identifies the middle value in an ordered dataset. | Useful when dealing with skewed distributions or outliers. |
| Mode | Finds the most frequent value in a dataset. | Commonly used to determine the most popular or common occurrence. |
| Standard Deviation | Measures the amount of variation or dispersion in a dataset. | Helps in understanding how spread out the values are from the mean. |
| Correlation | Quantifies the relationship between two variables. | Used to assess the strength and direction of relationships. |
Mastering these statistical methods provides a solid foundation for interpreting numerical patterns, conducting rigorous analyses, and making informed decisions based on your findings.
Preparing for Multiple Choice Questions
When approaching assessments with multiple-choice formats, it is essential to develop strategies that help you navigate through options efficiently. These types of questions often test your knowledge of specific details, so preparation should focus on understanding key concepts and recognizing patterns in the way questions are framed. Being able to eliminate incorrect choices and identify the most accurate answer will improve your performance.
Effective Study Techniques
- Understand Core Concepts: Focus on grasping the fundamental principles and their applications. This ensures that you can quickly identify the correct response, even if the phrasing of the question is unfamiliar.
- Practice with Mock Tests: Working through sample assessments simulates the real environment and helps identify common question types. Regular practice sharpens your decision-making skills under time constraints.
- Review Past Mistakes: After practicing, review incorrect answers to understand why they were wrong. This helps reinforce the correct concepts and avoid similar mistakes in the future.
Strategic Approaches During the Test
- Read Each Option Carefully: Even though one choice may seem correct, ensure that you thoroughly analyze each possibility. Often, there is one option that is subtly more precise than others.
- Eliminate Clearly Incorrect Answers: Narrowing down choices by eliminating obviously wrong options increases your chances of selecting the correct answer even when unsure.
- Stay Calm and Manage Your Time: If you find yourself stuck, move on to the next question and return to the difficult ones later. Time management ensures you can address all questions.
By combining solid study habits with strategic techniques during the test, you can maximize your chances of success and perform confidently in multiple-choice assessments.
?
How to Approach Open-Ended Questions

When faced with questions that require detailed, thoughtful responses, it’s essential to structure your approach carefully. These types of inquiries assess your ability to apply knowledge rather than just recall facts. To excel, you need to present clear, well-organized arguments and demonstrate an in-depth understanding of the subject matter.
Effective Strategies for Answering
- Understand the Core Topic: Before crafting your response, make sure you fully comprehend the concept being asked. This helps you stay focused and relevant in your answer.
- Break Down the Question: Identify key components of the inquiry. Address each part separately to ensure that all aspects are covered thoroughly.
- Provide Real-World Examples: Whenever possible, include practical examples or case studies to reinforce your points. This shows not only theoretical knowledge but also the ability to apply concepts in real-life scenarios.
Structuring Your Response
- Introduction: Start with a brief overview of your understanding of the topic. State the main points you will cover in your response.
- Body: Develop each point in a clear, logical order. Use bullet points or short paragraphs to separate ideas and make the response easier to follow.
- Conclusion: Summarize the key takeaways from your answer, reinforcing the main concepts. Offer insight into how they relate to broader topics or future developments.
By following these strategies, you can ensure that your response is well-structured, insightful, and comprehensive, demonstrating both your knowledge and analytical skills.
Time Management During the Exam

Efficiently allocating time during an assessment is crucial for ensuring that you can complete all tasks to the best of your ability. A well-managed schedule allows you to focus on each section without feeling rushed, while also providing the flexibility to review your work before submission. Understanding how to pace yourself can significantly improve your performance.
Strategic Planning for Time Allocation
- Assess the Total Time Available: Begin by understanding how much time you have in total and how many tasks you need to complete. This allows you to allocate an appropriate amount of time to each section.
- Prioritize Tasks: Start with the sections you find easiest, or those that carry more weight in terms of points. This boosts your confidence and ensures you secure the guaranteed marks.
- Set Time Limits: For each task, set a time limit based on its complexity. Stick to these limits to avoid spending too long on any one part and ensure you have time for everything.
Maximizing Focus and Efficiency
- Stay Calm and Focused: Time pressure can cause stress, but staying calm helps you think clearly. Regularly remind yourself to take deep breaths and stay on task.
- Monitor the Clock: Regularly check the time to ensure you are on track. This helps prevent surprises at the end of the assessment.
- Leave Time for Review: Allocate some time at the end to review your work. A quick check can help you catch any mistakes or unclear responses.
By applying these time management techniques, you will improve your efficiency and reduce stress during the assessment, allowing you to perform at your best.
Reviewing Past Exam Papers
Analyzing previous assessments is an essential technique for improving performance in future tasks. By reviewing past materials, you can identify recurring themes, understand the typical format of tasks, and uncover common areas of focus. This process also helps to familiarize yourself with the types of challenges you may encounter, allowing you to prepare more effectively.
Identifying Key Patterns and Topics
When reviewing past assessments, it’s important to focus on understanding which topics were most frequently addressed. This allows you to prioritize studying the areas that are more likely to appear again. Additionally, analyzing the structure of past assessments can give you insights into how to approach each section and manage your time effectively.
Benefits of Reviewing Previous Materials
- Boosts Confidence: Familiarity with the format and content of past materials can reduce anxiety and increase confidence during the actual task.
- Improves Understanding: Going through past content helps reinforce your understanding of key concepts and principles.
- Refines Time Management: By practicing under similar conditions, you can gauge how long each section typically takes and adjust your approach accordingly.
Table: Commonly Appearing Topics in Previous Assessments
| Topic | Frequency of Appearance | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Graph Interpretation | High | Identifying trends, understanding scales |
| Statistical Methods | Medium | Mean, median, standard deviation |
| Data Representation Techniques | High | Bar charts, pie charts, histograms |
| Conceptual Understanding | Low | Theoretical explanations and definitions |
By incorporating past assessments into your study routine, you can enhance your preparedness and approach upcoming tasks with greater efficiency.
Real-World Data Visualization Examples
Real-life applications of graphical representation of information are abundant across industries. These practical examples help bridge the gap between theory and practice, illustrating how abstract concepts can be brought to life in an accessible format. Understanding these examples enhances comprehension and shows the true potential of presenting complex information visually.
Business Insights through Graphical Displays
Many companies rely on charts and graphs to make strategic decisions. For example, financial dashboards often feature performance metrics that are essential for decision-making. These visuals simplify large datasets, helping executives and managers quickly identify trends, potential problems, or opportunities without needing to sift through raw numbers.
Healthcare Analysis in Visual Form
The healthcare sector uses infographics and interactive charts to track patient outcomes, treatment effectiveness, and disease trends. By visualizing patient statistics, hospitals and medical organizations can enhance the efficiency of treatments and improve patient care. Real-time data can be presented on interactive maps, showing the spread of diseases or monitoring patient conditions.
Environmental Impact Tracking
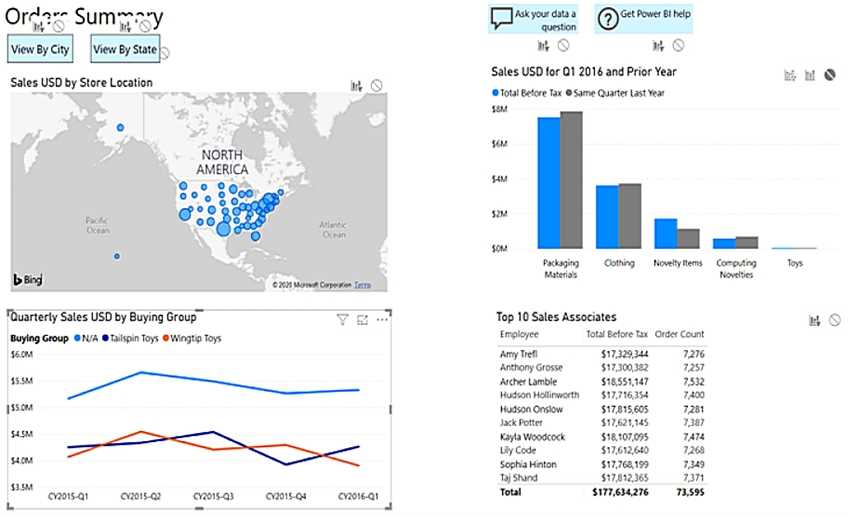
Environmental agencies also rely on graphical tools to assess climate change, air quality, or deforestation rates. Interactive maps and line charts are used to represent changes in environmental conditions over time, making it easier to grasp complex issues and support policy decisions based on visual evidence.
Tips for Answering Case Studies
Approaching case studies effectively requires a structured approach to analyze the scenario, identify key points, and present a clear, well-supported solution. These exercises often test your ability to apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations, so it’s crucial to break down the problem systematically. Below are some practical suggestions to help you navigate case study questions with confidence.
Understand the Problem Thoroughly
Before diving into the solution, ensure you fully comprehend the case at hand. Take time to read the material carefully and identify the main issues, objectives, and any constraints mentioned. Here’s how to approach it:
- Highlight key points in the scenario.
- Note any specific challenges or opportunities described.
- Pay attention to any underlying assumptions that could affect your analysis.
Develop a Logical Approach
Once you’ve understood the problem, outline your approach for tackling the solution. A logical and organized answer will be more effective and easier to follow. Consider these steps:
- Break down the issue into manageable parts.
- Use relevant models, frameworks, or methods to guide your analysis.
- Ensure your solution aligns with the objectives stated in the case.
Provide Clear, Supported Recommendations
Finally, your answer should focus on providing a clear solution, supported by reasoning and evidence from the case. Use visuals, examples, or calculations if necessary to strengthen your argument. Avoid general statements–be specific about your recommendations and how they address the problem effectively.