Wall Street Prep DCF Modeling Exam Answers Guide

In the world of financial analysis, mastering valuation techniques is essential for anyone looking to excel in investment banking, private equity, or corporate finance. One of the most critical skills to acquire is the ability to build and interpret complex financial models, particularly those used to determine the intrinsic value of companies based on projected cash flows and other financial metrics. This section aims to provide insight into key strategies and approaches that will help you navigate through a rigorous assessment process.
Understanding how to apply these methodologies correctly can be challenging without a solid foundation in both theory and practical application. With proper preparation, you can improve your ability to tackle financial calculations, interpret results accurately, and make informed decisions. Here, we explore how to break down complicated scenarios, avoid common errors, and use available resources to build your skills and confidence for real-world financial analysis tasks.
Financial Valuation Assessment Solutions
When preparing for an assessment that involves valuing a company based on its financial performance, it’s important to approach the task with a structured mindset. These tests typically require you to demonstrate a deep understanding of valuation techniques, making accurate assumptions, and performing rigorous calculations. In this section, we will cover key strategies and considerations to help you approach such challenges with confidence, ensuring you can showcase your skills in a thorough and precise manner.
Key Steps to Success
To succeed in this type of financial evaluation, it’s crucial to understand the methodology behind calculating the worth of a business. The first step is to gather accurate financial data and ensure that all assumptions made during the process align with realistic market conditions. From there, building out the model, adjusting for variables like growth rates, discount factors, and terminal values, becomes an essential part of the process. Reviewing and refining your work will allow you to present your findings with clarity and precision.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
Many individuals struggle with certain aspects of financial analysis, especially when it comes to making assumptions or interpreting results. One common mistake is not thoroughly testing the sensitivity of the model, which could lead to inaccurate conclusions. Another pitfall is failing to clearly document the reasoning behind key assumptions, leaving your analysis open to questions. To avoid these issues, it’s vital to take time at each stage of the process to verify data, check for consistency, and double-check all calculations before finalizing your analysis.
Understanding the Financial Valuation Assessment
In this type of assessment, candidates are required to demonstrate their proficiency in applying financial analysis techniques to evaluate the value of a business. The task typically involves calculating the intrinsic value of a company based on projected cash flows and a series of key financial assumptions. It’s essential to understand not just the technical aspects of building the model, but also the underlying principles that drive these calculations.
To excel in this evaluation, it’s crucial to focus on several key areas:
- Accurate data collection: Ensuring the financial information used is reliable and up-to-date.
- Assumption setting: Establishing realistic growth rates, discount factors, and other variables.
- Model construction: Building a clear and structured financial model that allows for precise forecasting.
- Sensitivity analysis: Testing how changes in key assumptions affect the model’s output.
- Final interpretation: Understanding and explaining the results with clarity and logical reasoning.
The assessment often requires candidates to answer questions and make decisions based on the outputs of their financial models. Being able to clearly communicate the reasoning behind each assumption, calculation, and result is just as important as executing the model itself.
In addition, some assessments may involve case studies or scenarios where candidates must adapt their approach to reflect changes in market conditions or financial information. This flexibility will demonstrate the ability to think critically and adapt to new challenges, a key skill in financial analysis.
Key Concepts in Financial Valuation
In any financial valuation process, understanding the foundational concepts is essential to building accurate and meaningful models. These key principles help structure the analysis, guide decision-making, and ensure that the calculations reflect realistic financial scenarios. Whether assessing a company’s potential or projecting future performance, a strong grasp of these concepts will enable more reliable conclusions and better outcomes.
Time Value of Money
One of the core principles in any valuation process is the time value of money. This concept asserts that a dollar today is worth more than the same dollar in the future due to its potential earning capacity. Discounting future cash flows to present value is a critical step, as it allows analysts to account for the opportunity cost of capital. Understanding how to apply appropriate discount rates to future earnings is fundamental to generating accurate valuations.
Forecasting and Assumptions
Accurate forecasting is crucial in any financial analysis. It involves projecting a company’s future earnings based on historical data, market conditions, and realistic assumptions. These assumptions may include growth rates, profitability margins, and capital expenditures, among others. Clear and well-justified assumptions are vital, as they directly impact the reliability of the final valuation. It’s important to ensure that these assumptions are grounded in reality and adjusted based on current and expected future trends.
Steps to Solve Financial Valuation Models
Solving a financial valuation requires a methodical approach to ensure that all factors are properly considered and accurately represented. From gathering relevant data to applying assumptions and interpreting results, each step plays a critical role in determining the final valuation. Understanding the sequential process is key to developing a reliable model that can effectively assess a company’s worth.
Step 1: Gather and Analyze Financial Data
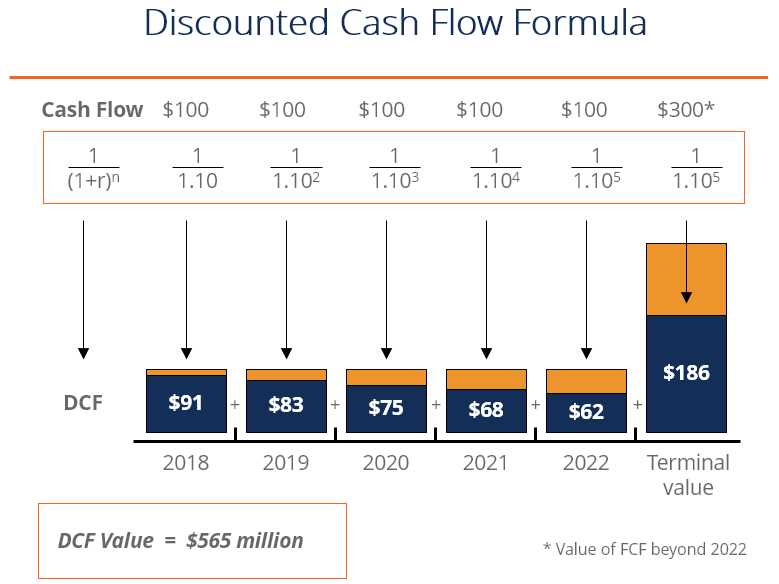
The first step in constructing a financial valuation is collecting the necessary financial information. This includes historical financial statements such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Additionally, industry-specific data and market trends should be taken into account. Once the data is gathered, it must be carefully analyzed to identify trends, assess profitability, and understand the company’s financial health. This analysis forms the basis for future projections and assumptions.
Step 2: Project Future Performance
Next, you will need to forecast the company’s future performance. This involves estimating future revenues, expenses, and cash flows based on historical data, industry trends, and growth expectations. It’s important to make realistic assumptions about growth rates, operating costs, and capital investments. These projections are essential for building the financial model and will guide the calculation of the company’s intrinsic value. This stage often requires sensitivity analysis to test how different assumptions affect the overall outcome.
Common Mistakes in Financial Valuation Assessments
When working through a financial analysis assessment, even small mistakes can lead to inaccurate results and missed opportunities. Understanding common pitfalls can help you avoid errors that often occur during the process. By recognizing these issues early on, you can improve the accuracy and reliability of your valuation models. Below are some typical mistakes that candidates make during these assessments and how to avoid them.
| Mistake | Description |
|---|---|
| Incorrect Assumptions | Using overly optimistic or unrealistic assumptions about growth rates, profit margins, or market conditions can lead to misleading results. It’s crucial to base assumptions on historical performance and market trends. |
| Not Accounting for Sensitivity | Failing to run sensitivity tests on key assumptions can result in overlooking how changes in variables affect the model’s output. Always test different scenarios to see how robust your valuation is to changes in assumptions. |
| Overlooking Terminal Value | The terminal value often accounts for a large portion of the total valuation. Underestimating or miscalculating it can distort the results. Make sure to apply a reasonable long-term growth rate and discount factor to this component. |
| Data Errors | Even small data errors can throw off the entire analysis. Double-check all inputs and calculations to ensure accuracy, especially when transferring data between different financial statements and models. |
| Ignoring Risk Factors | Risk factors such as market volatility, economic downturns, or changes in industry trends can significantly affect a company’s valuation. Failing to incorporate risk into your discount rates or projections can result in an overly optimistic model. |
Tips for Time Management in Assessments
Effective time management is crucial when completing any type of financial analysis assessment. The ability to allocate time wisely ensures that you can address all sections of the task, produce accurate results, and avoid rushing through critical steps. Proper planning allows you to maintain focus and deliver high-quality work, even when under pressure. Here are several strategies to help you manage your time more effectively during such assessments.
Prioritize Key Sections
Start by identifying the most complex or time-consuming sections of the task. Focus your efforts on these areas first, allowing ample time to carefully work through the more challenging parts of the analysis. Once these sections are completed, you’ll have a clearer view of the remaining work and can allocate your time accordingly.
Set Mini-Deadlines
Break the task into smaller, manageable sections and assign a specific time limit to each one. For example, allocate 30 minutes to complete the financial projections, then move on to calculating the discount rate. This strategy helps keep you on track and prevents you from spending too much time on any one part of the process. Stick to these time limits as much as possible to maintain momentum.
Use Templates and Tools
If available, use pre-built templates or financial tools that can automate parts of the process, such as calculating discounted cash flows or running sensitivity analyses. This can save you valuable time while ensuring accuracy in your calculations. Familiarize yourself with these tools before the assessment so you can use them efficiently when needed.
Leave Time for Review
Lastly, always leave time at the end to review your work. It’s easy to miss small errors or inconsistencies when you’re focused on completing tasks quickly. Having a few extra minutes to check your calculations and assumptions can help you spot mistakes and refine your final results before submission.
How to Approach Discount Rates
Choosing the appropriate discount rate is a critical step in any financial analysis, as it directly affects the present value of future cash flows. The rate represents the opportunity cost of capital and accounts for the risk associated with investing in a particular project or company. Understanding how to properly determine and apply this rate ensures that the valuation reflects both market conditions and the risk profile of the business.
Understand the Components of the Discount Rate
The discount rate typically consists of two main components: the risk-free rate and the risk premium. The risk-free rate is often derived from government bond yields, as these are considered to carry minimal risk. The risk premium reflects the additional return required by investors to compensate for the uncertainty associated with a particular investment. This premium can vary depending on the company’s risk factors, industry, and broader market conditions.
Risk-Free Rate Selection
When selecting the risk-free rate, it’s important to choose a rate that reflects the currency and maturity of the investment horizon. For instance, if you are valuing a company over a long-term period, consider using long-term government bond yields, as they best reflect the time value of money for a similar timeframe. The risk-free rate should be updated periodically to account for changes in economic conditions and interest rates.
Adjust for Company-Specific Risk
After establishing the risk-free rate, adjust it for the specific risks of the company being analyzed. This is where the risk premium comes into play. Companies in volatile industries or those with uncertain growth prospects may require a higher premium to reflect these risks. Factors such as company size, debt levels, market volatility, and geographic exposure should be considered when determining the appropriate premium.
Using the Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC)
The Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) is a commonly used method to determine the overall discount rate for a company. It takes into account the costs of both equity and debt financing, weighted by their respective proportions in the company’s capital structure. When using WACC, it’s essential to ensure that the appropriate market values for debt and equity are used, and that the cost of debt reflects the company’s borrowing rate after taxes.
Re-evaluate Regularly
The discount rate is not static; it should be periodically reviewed and adjusted as market conditions, interest rates, and company-specific risks evolve. A failure to update the discount rate in response to changes in these factors can lead to inaccurate valuations and potentially misguided investment decisions. Ensure that you revisit this key assumption regularly to maintain the accuracy of your financial models.
Importance of Cash Flow Projections

Cash flow projections are essential for assessing the financial health and future performance of a business. They provide valuable insights into how well a company generates cash, how it manages its expenses, and whether it can meet its financial obligations over time. Accurate forecasts allow stakeholders to make informed decisions about investment opportunities, budgeting, and strategic planning.
Forecasting Financial Stability
Cash flow projections serve as a key indicator of a company’s ability to maintain financial stability. By projecting future cash inflows and outflows, businesses can identify periods of potential liquidity issues and take proactive measures to ensure they can meet obligations such as debt payments, operating expenses, and capital expenditures. This foresight helps to avoid financial distress and supports long-term sustainability.
Supporting Investment Decisions
For investors, understanding a company’s future cash flows is crucial when determining its valuation. Projected cash flows provide a clearer picture of the company’s growth prospects and potential returns on investment. Accurate projections help investors assess the risk involved in an investment and make better decisions about allocating capital.
Facilitating Business Planning
Having reliable cash flow projections enables companies to plan for the future effectively. This includes making decisions about expansion, financing, and resource allocation. Projections also provide a framework for setting realistic performance goals and tracking progress over time. With detailed cash flow forecasts, businesses are better equipped to adjust their strategies in response to changes in market conditions or internal operations.
Guiding Debt Management
Cash flow projections are also critical for managing debt. They help businesses assess whether they will be able to meet debt obligations in the future. Lenders often rely on these projections to determine a company’s creditworthiness and its ability to repay loans. By ensuring that projected cash flows are sufficient to cover interest and principal payments, businesses can maintain positive relationships with creditors and avoid defaulting on loans.
Dealing with Terminal Value Calculations
Calculating the terminal value is a crucial step in determining the overall value of a business, especially when projecting cash flows far into the future. This calculation estimates the company’s value beyond the projection period and captures its long-term growth potential. The terminal value is an essential component of any valuation model, as it typically represents a significant portion of the total value derived from future cash flows.
The most common approaches to calculating terminal value are the perpetuity growth method and the exit multiple method. Each method has its own strengths and applications, depending on the specific circumstances of the company and the industry in which it operates.
Perpetuity Growth Method
The perpetuity growth method assumes that free cash flows will grow at a constant rate indefinitely. This approach is often used when a company is expected to grow at a stable rate beyond the forecast period. The formula for calculating terminal value using this method is:
Terminal Value = Final Year Cash Flow × (1 + Growth Rate) / (Discount Rate – Growth Rate)
This method is widely used for stable businesses with predictable cash flows, such as mature companies in established industries. The key challenge with this approach is selecting an appropriate long-term growth rate, which should be conservative and reflect the expected inflation rate or long-term economic growth rate.
Exit Multiple Method
The exit multiple method involves applying an industry comparable multiple to the company’s final year projected metric, such as EBITDA or EBIT. This multiple is typically derived from comparable company analysis or historical transaction data. The terminal value is then calculated as:
Terminal Value = Final Year Metric × Exit Multiple
This method is particularly useful for industries where companies are often bought and sold, as it reflects the market value for similar businesses. However, the key challenge is selecting an appropriate multiple, as it can vary significantly depending on market conditions, industry trends, and the company’s growth potential.
Considerations and Adjustments
Both methods for calculating terminal value require careful consideration of several factors, including the company’s risk profile, the stability of cash flows, and the prevailing economic environment. Sensitivity analysis is often used to test how changes in key assumptions–such as the growth rate or exit multiple–can impact the final terminal value calculation. Additionally, it is important to adjust the terminal value for any non-operating assets or liabilities that may affect the overall valuation.
Analyzing Sensitivity and Scenarios
When conducting financial analysis, it’s essential to test how sensitive a company’s value is to various assumptions and variables. Sensitivity analysis allows analysts to evaluate the impact of changing key factors on a business’s valuation, helping to identify potential risks and uncertainties. Additionally, scenario analysis can provide insights into how different market conditions or business strategies might affect outcomes.
Both approaches are essential tools in assessing the robustness of a financial model and ensuring that the results are not overly dependent on a single assumption. By examining different assumptions under various conditions, analysts can form a more comprehensive view of the potential outcomes and make more informed decisions.
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis involves varying one key input at a time to determine how sensitive the valuation is to changes in that input. Common inputs that are analyzed include:
- Discount rate
- Growth rate assumptions
- Operating margins
- Capital expenditure levels
By adjusting these variables within a reasonable range, analysts can observe how different values for each assumption impact the company’s overall valuation. The goal is to assess the range of possible values and identify any areas of potential concern. For example, if a small change in the growth rate results in a significant fluctuation in value, this indicates high sensitivity and a need for further consideration of that assumption.
Scenario Analysis
Scenario analysis takes a broader approach by considering multiple variables at once. It creates different “what-if” scenarios based on potential changes in market conditions, company strategy, or economic factors. Scenarios can range from optimistic to pessimistic, and they help to explore how a combination of factors could affect the business.
- Base Case Scenario: Assumes that current trends will continue, with no significant changes in key drivers.
- Best Case Scenario: Assumes favorable conditions, such as higher-than-expected growth rates or reduced costs.
- Worst Case Scenario: Considers negative outcomes, such as economic downturns, increased competition, or regulatory changes.
By evaluating these different scenarios, analysts can better understand the potential range of outcomes and how external factors, beyond just the financial assumptions, could influence the results. This helps to assess the likelihood of various outcomes and prepare for potential risks.
How to Interpret Results Effectively
Interpreting the results of a financial analysis requires more than just reviewing numbers; it involves understanding the context, recognizing potential limitations, and drawing meaningful insights from the data. Effective interpretation allows decision-makers to identify key trends, assess risks, and make informed decisions. While the numbers in a valuation model or financial projection provide valuable information, it’s crucial to understand what those numbers represent and how they relate to the broader business environment.
Here are some important considerations to keep in mind when interpreting financial results:
Understand the Assumptions Behind the Numbers
Every financial model or analysis is based on certain assumptions about the business, market conditions, and external factors. These assumptions can significantly affect the results, so it’s essential to understand them thoroughly. Key assumptions include:
- Revenue growth rates
- Operating cost projections
- Discount rates
- Terminal value assumptions
Understanding the basis of these assumptions will help you assess whether the results are realistic and whether they align with current market conditions or historical performance.
Evaluate the Sensitivity of the Results
Results should never be interpreted in isolation. A key part of analysis is evaluating how sensitive the outcomes are to changes in key inputs. Sensitivity analysis can show how different assumptions impact the valuation or projections, helping you understand the potential range of outcomes.
- If small changes in assumptions lead to significant variations in results, this indicates high sensitivity and potential uncertainty.
- If results remain relatively stable despite changes in assumptions, it suggests a more robust model with less inherent risk.
Compare to Industry Benchmarks
Comparing the results to industry benchmarks or comparable companies is an essential part of interpretation. This allows you to gauge how the company or project stacks up against others in the same sector. Key metrics to compare might include:
- Profit margins
- Valuation multiples
- Growth rates
- Return on investment (ROI)
If the results differ significantly from industry norms, it could indicate unique risks or opportunities that require further analysis.
Assess the Impact of External Factors
Financial results are not generated in a vacuum. External factors such as economic conditions, regulatory changes, and market trends can all influence the outcome. When interpreting results, it’s important to consider how these factors might affect the company’s performance in the future. For example:
- How might changes in interest rates affect profitability?
- What impact could new government regulations have on the business?
- How might shifts in consumer demand or competition alter the growth prospects?
By understanding these external influences, you can gain a more accurate perspective on the results and make better-informed decisions.
Focus on the Key Drivers
While financial models may produce a wide range of results, it’s important to focus on the key drivers that have the most significant impact on outcomes. These drivers could include:
- Revenue growth
- Cost control
- Capital investment requirements
- Market share
By understanding which factors are most influential, you can better assess the company’s potential for growth or risk and identify areas that require more attention or improvement.
Practical Applications of DCF Models
Financial valuation techniques are crucial tools for decision-making, especially when assessing the long-term value of a company or investment. These models allow analysts to estimate the present value of future cash flows, making them highly applicable across various real-world scenarios. Understanding the practical uses of these models can significantly improve investment strategies, corporate financial planning, and business decisions.
Here are some of the common ways in which these valuation models are applied in practice:
Business Valuations
One of the most common uses of financial valuation models is in determining the value of a business. Whether for mergers, acquisitions, or divestitures, understanding the true value of a company is essential. This process typically involves:
- Estimating future cash flows
- Selecting an appropriate discount rate
- Determining the terminal value
Through these steps, analysts can establish a range of values that reflect the company’s potential under different assumptions, providing decision-makers with essential information for structuring deals.
Investment Decision-Making
Investors frequently rely on valuation models to assess the attractiveness of investment opportunities. Whether considering stocks, bonds, or real estate, understanding the intrinsic value of an asset is critical to making informed decisions. By using these models, investors can compare the current market price to their estimated value, helping them determine if an asset is undervalued or overvalued. This allows for more strategic investment decisions, such as:
- Identifying undervalued assets
- Assessing the potential for future growth
- Analyzing risk-return profiles
Corporate Financial Planning
For companies, these models are valuable tools in financial planning and forecasting. By projecting future cash flows, a company can determine its funding requirements, assess project feasibility, and allocate resources efficiently. Some specific uses in corporate finance include:
- Evaluating new projects or capital expenditures
- Assessing the impact of changes in market conditions on financial performance
- Determining appropriate capital structure
Table: Example of Cash Flow Projections for a Business
| Year | Projected Cash Flow | Discount Rate | Discounted Cash Flow |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | $5,000,000 | 8% | $4,629,630 |
| 2025 | $5,500,000 | 8% | $4,718,519 |
| 2026 | $6,000,000 | 8% | $4,762,907 |
| 2027 | $6,500,000 | 8% | $4,763,372 |
This table demonstrates how projected future cash flows can be adjusted for the time value of money, providing a more accurate picture of the company’s future financial health.
Strategic Business Decisions
These financial models are also used in strategic planning and corporate decision-making. Companies can use them to assess the impact of various strategic initiatives, such as:
- Expanding into new markets
- Launching new products or services
- Evaluating potential partnerships or joint ventures
By understanding the financial implications of these decisions, companies can make choices that maximize shareholder value while minimizing risks.
Resources for DCF Exam Preparation
Preparing for financial assessments requires access to the right tools and materials to fully understand the underlying principles and methods. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced professional, having the right resources at your disposal can make a significant difference in mastering complex calculations and analysis. From textbooks to online courses, there are several resources available that can guide you through the concepts and ensure a thorough understanding of financial valuation techniques.
Books and Study Guides
Books remain one of the most reliable resources for understanding theoretical concepts and applying them in practical scenarios. Many texts provide clear explanations of the core principles and detailed examples that are essential for mastering advanced financial techniques. Some of the most useful books include:
- Investment Valuation by Aswath Damodaran – This book is widely regarded as an authoritative source on valuation, offering in-depth coverage of various valuation methods.
- Valuation: Measuring and Managing the Value of Companies by McKinsey & Company – A practical guide for understanding valuation methods, this book is especially valuable for professionals involved in corporate finance.
- The Valuation Handbook by James R. Hitchner – This handbook offers practical advice on conducting valuations and includes numerous real-life examples.
Online Learning Platforms
In addition to traditional books, online platforms provide an interactive approach to learning, with video lessons, quizzes, and discussion forums. These platforms allow you to learn at your own pace, providing flexibility for busy schedules. Popular online resources for mastering financial valuation techniques include:
- Coursera – Offers courses from leading universities, covering topics related to business finance, valuation, and corporate strategy.
- Udemy – Provides courses tailored for beginners and professionals, featuring video tutorials and practical exercises to solidify your understanding.
- LinkedIn Learning – Includes short, targeted lessons on financial analysis, including tutorials on valuation techniques and interpretation of financial statements.
By combining books, online courses, and practical exercises, you can build a strong foundation for any financial assessment or analysis task. These resources ensure that you are well-equipped to tackle complex valuation problems with confidence and precision.
Mastering Excel for DCF Calculations
Proficiency in Excel is crucial when working with complex financial analyses, especially when performing valuations and forecasting future cash flows. Excel allows for the efficient organization of large datasets, performing calculations quickly, and automating repetitive tasks. Whether you’re preparing for a financial evaluation or working through various scenarios, understanding key Excel functions can significantly enhance your productivity and accuracy.
For those looking to refine their Excel skills, focusing on the following areas is essential:
- Functions and Formulas: Familiarize yourself with essential Excel functions such as NPV (Net Present Value), IRR (Internal Rate of Return), and PMT (Payment). These formulas are fundamental when calculating and analyzing financial data in real-time.
- Data Organization: Learn how to structure your data effectively, using tables, pivot tables, and filters. Proper data organization allows for easier analysis and faster decision-making.
- Model Design: Build clean and transparent models by using consistent formatting and color-coding. This will make it easier to identify inputs, assumptions, and outputs when reviewing your work.
- Charts and Graphs: Excel’s built-in charting tools are invaluable for visualizing trends, projections, and comparisons. Mastering the art of creating dynamic charts allows you to present financial data more effectively.
By becoming proficient in these essential Excel tools and functions, you will significantly improve your ability to create detailed financial models, perform in-depth analyses, and interpret the results with confidence. Ultimately, mastering Excel not only saves time but also ensures that your calculations are as precise and reliable as possible.
Real-Life Case Studies in DCF

Understanding how to apply theoretical financial techniques to real-world situations is key to mastering valuation and forecasting. Case studies offer invaluable insights into how analysts use various financial models to assess company value, make investment decisions, and predict future performance. By examining these real-life scenarios, you can gain a deeper understanding of how to navigate complex financial landscapes and make more informed decisions in practice.
Case Study 1: Technology Startup Valuation
One common application of financial models is in the valuation of early-stage companies. For a technology startup, projecting future cash flows is a challenge due to uncertainties about revenue generation and market conditions. However, analysts rely on conservative growth estimates, adjusting their calculations as new information becomes available. The key takeaway from this case is the importance of flexibility in projections and the need to constantly refine assumptions as the company evolves.
- Focus: Estimating future revenues and expenses
- Key Assumption: Revenue growth rate and market penetration
- Lesson Learned: Constantly adjust assumptions based on market trends
Case Study 2: Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A)
Another area where financial models are frequently used is in mergers and acquisitions. When a company is considering the purchase of another, it needs to evaluate the target company’s value and potential synergies. Through detailed financial projections, an acquirer can determine whether the price is justified based on expected future cash flows. The case study emphasizes the importance of understanding synergy effects, integration costs, and the proper adjustment of discount rates.
- Focus: Evaluating target company’s potential and risks
- Key Assumption: Future cost savings and growth from synergies
- Lesson Learned: Properly assess integration costs and synergies
These case studies illustrate how financial models are not just theoretical tools but essential instruments for real-world decision-making. They highlight the need for a deep understanding of assumptions, flexibility in projections, and the ability to adapt to changing conditions. By examining these examples, you can improve your ability to apply financial analysis in any business context.
Commonly Asked Questions in Financial Valuation Assessments
During financial assessments, particularly those that focus on company valuation, candidates often face questions that test their understanding of key concepts, the application of techniques, and their ability to solve complex problems. These questions typically explore fundamental principles, methods for projecting future performance, and approaches to estimating value under different conditions. Familiarity with the types of questions commonly asked in such evaluations can greatly enhance one’s preparation and ensure a deeper grasp of the material.
Below are some of the frequently encountered queries in financial valuation assessments:
- How do you determine the appropriate discount rate?
This question tests the ability to select the correct rate that reflects the time value of money and the risks associated with the business or project being analyzed. - What is the importance of free cash flow in valuation?
Candidates are asked to explain why free cash flow is critical in valuation and how it differs from other financial metrics like net income or EBITDA. - How do you handle terminal value in your calculations?
A common challenge involves calculating the terminal value, which requires understanding the assumptions behind perpetual growth rates and the method used to estimate value beyond the forecast period. - How do you incorporate sensitivity analysis into your valuation?
Sensitivity analysis is essential for understanding the impact of different assumptions, such as growth rates or discount rates, on the final valuation. This question evaluates how well a candidate can assess potential risks and uncertainties. - What are the limitations of using valuation models in uncertain markets?
Assessments often include questions that encourage candidates to discuss the limitations of their methods, particularly during times of economic volatility or when dealing with companies that have unpredictable cash flows.
These questions require more than just technical knowledge–they demand an ability to think critically about financial assumptions and their real-world implications. By understanding the most common topics covered in financial assessments, you can approach them with greater confidence and efficiency, demonstrating your ability to apply theory to practice.
Improving Accuracy in Financial Models
Creating accurate financial models is essential for informed decision-making in business and investment contexts. Inaccurate assumptions or errors in calculations can lead to misleading results, affecting strategic choices, valuations, and forecasts. To enhance the reliability of financial models, it’s important to adopt practices that ensure precision and consistency across all stages of the model-building process. These practices range from carefully selecting inputs to performing thorough checks at every step.
Key Practices to Enhance Accuracy
- Thorough Data Verification: Ensure that all data inputs are accurate, current, and sourced from reliable platforms. Cross-checking historical data and assumptions about future performance can help minimize errors.
- Clear Assumptions: Document and clarify all assumptions made during the modeling process. This includes projections about revenue growth, discount rates, and terminal value assumptions. Having clear, justified assumptions reduces the risk of overlooking key factors.
- Use of Consistent Formulas: Avoid using inconsistent formulas across different sheets or sections of the model. This ensures that the logic remains sound and results are comparable across different scenarios.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Conduct sensitivity analysis to understand how changes in key inputs (such as growth rates or costs) affect the output. This can help identify which variables have the greatest impact on your model’s accuracy.
Review and Testing
- Regular Audits: Perform periodic audits of the model to identify any discrepancies or logical errors. Having another person review the model can help catch mistakes that may have been overlooked.
- Stress Testing: Test the model under extreme conditions or scenarios to ensure it holds up under various assumptions. This helps identify weaknesses in the structure of the model or its underlying assumptions.
- Cross-Check with Industry Benchmarks: Compare your model’s results with industry averages or comparable companies to ensure that your conclusions align with broader market trends.
By incorporating these practices, financial models can achieve higher levels of accuracy, leading to more reliable insights for decision-making. The accuracy of a financial model is only as strong as its weakest link, so meticulous attention to detail and ongoing validation is key to its success.