Chemistry Semester 1 Exam Review Answers

Preparing for a major assessment in a scientific subject requires a thorough understanding of fundamental principles and problem-solving techniques. The goal is to ensure that you grasp the core ideas and can apply them effectively under test conditions. With a systematic approach, anyone can boost their confidence and performance.
Focused practice and conceptual clarity are essential for mastering this material. By addressing key topics and reinforcing understanding through various methods, such as problem-solving exercises and memorization techniques, you will be well-prepared to tackle any challenges presented during the assessment. It’s all about refining your approach to ensure you can recall and use information efficiently when needed.
Chemistry Semester 1 Exam Review Answers
To succeed in any scientific discipline, it’s crucial to focus on the fundamental concepts and methods that are often tested. Mastering these topics will allow you to apply your knowledge effectively under timed conditions. This section outlines key concepts, problem-solving techniques, and important areas to concentrate on in preparation for your assessment.
Essential Topics to Master
- Understanding atomic structure and the periodic table
- Key types of chemical reactions and their mechanisms
- Stoichiometry and the calculation of molar relationships
- Energy changes in reactions and thermochemistry basics
- Bonding, molecular shapes, and interatomic forces
Study Tips for Success

- Review core principles and make sure you understand the theory behind each concept.
- Practice solving problems to apply your knowledge in real-world scenarios.
- Use flashcards or quizzes to memorize key terms and formulas.
- Focus on areas where you feel least confident and reinforce your understanding.
By following these strategies and focusing on the most important topics, you will be well-equipped to approach your assessment with confidence. Regular practice and a clear understanding of fundamental principles will ensure you’re ready for any challenge.
Key Concepts to Focus On
To achieve a strong grasp of the material and perform well under assessment conditions, it is essential to focus on the core ideas that are commonly tested. A deep understanding of these concepts will enable you to approach problems with confidence and accuracy. Prioritizing the right topics ensures you are well-prepared for any challenge that may arise.
Core Ideas to Master
- The structure of atoms and their properties
- Fundamentals of chemical bonding and molecular interactions
- Principles of balancing reactions and identifying products
- Understanding the periodic table and trends in element behavior
- Calculating quantities in chemical reactions and molar relationships
Important Skills to Develop

- Practice balancing chemical equations and identifying reactants and products.
- Enhance your ability to apply stoichiometric calculations in different scenarios.
- Master the use of formulas for energy changes and thermodynamic calculations.
- Refine your ability to interpret the periodic table and predict element behavior.
By honing these concepts and skills, you will be prepared to tackle various problems and questions with ease, ensuring your readiness for the upcoming test.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When preparing for a major assessment, it’s important to not only focus on mastering key concepts but also to be aware of typical errors that can negatively impact performance. Avoiding these common pitfalls will help you save valuable time and ensure that your answers are as accurate as possible. Below are some of the most frequent mistakes students make and how to prevent them.
| Common Mistake | How to Avoid It |
|---|---|
| Rushing through calculations | Take your time to double-check every step, especially with numerical problems. |
| Not understanding key concepts | Ensure you have a strong foundation in the basics before moving on to advanced topics. |
| Misinterpreting questions | Read each question carefully and underline important information to avoid confusion. |
| Forgetting units | Always include units in your calculations and final answers to avoid losing points. |
| Skipping practice problems | Consistently solve practice questions to become comfortable with the format and types of problems. |
By recognizing and avoiding these common mistakes, you will increase your efficiency and accuracy, ensuring that you approach your assessment with confidence and preparedness.
Understanding Chemical Reactions
At the heart of scientific study in this field is the ability to comprehend how substances interact and transform under various conditions. A strong grasp of these processes allows for predicting outcomes, balancing equations, and applying concepts in real-world scenarios. Understanding the key principles behind reactions is essential for both theoretical knowledge and practical problem-solving.
There are several important factors to consider when studying these processes: the types of reactions, how energy is involved, and how to represent these changes accurately. Mastering these aspects not only improves your ability to solve complex problems but also strengthens your overall understanding of matter and its behavior.
Periodic Table Trends Explained
The arrangement of elements in the table follows a specific pattern that reveals important trends and properties. Understanding these patterns helps predict how elements will behave in different reactions and conditions. Key factors such as atomic size, ionization energy, and electronegativity vary in a predictable way across periods and groups.
These trends are essential for understanding the relationships between elements and their chemical properties. For example, as you move across a period, the atomic radius generally decreases, while ionization energy increases. Similarly, as you move down a group, atomic size increases, and the ability to gain electrons typically decreases. Recognizing these patterns enhances the ability to make informed predictions and solve related problems.
Important Formulas to Remember
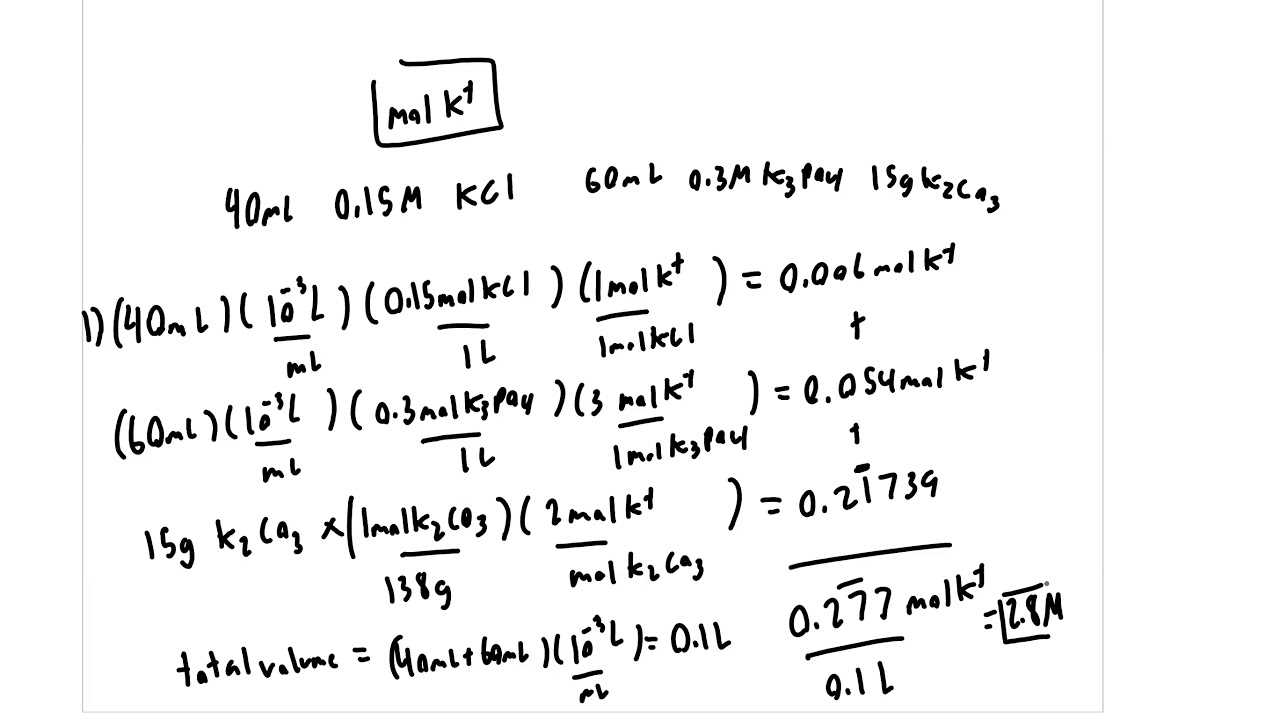
In any scientific field, understanding key mathematical relationships is crucial for solving problems efficiently. Formulas act as shortcuts to apply fundamental principles and make quick calculations. Memorizing the most essential equations will not only improve your problem-solving speed but also ensure accuracy under timed conditions.
Basic Mathematical Relationships
- Mass = Molar Mass × Moles – To calculate the mass of a substance from its moles and molar mass.
- Density = Mass / Volume – Essential for determining how tightly packed the particles in a substance are.
- Pressure × Volume = Constant (Boyle’s Law) – Describes the relationship between pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature.
- Energy = Mass × (Speed of Light)² – This famous equation demonstrates the relationship between mass and energy.
Reaction and Stoichiometry Formulas
- Avogadro’s Number = 6.022 × 10²³ particles per mole – This is the number of particles in one mole of any substance.
- Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) × 100 – Used to measure the efficiency of a chemical reaction.
- Ideal Gas Law: PV = nRT – Relates the pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of an ideal gas.
By committing these essential formulas to memory, you will be better equipped to approach problems with confidence and ease.
Balancing Chemical Equations Simplified

One of the fundamental skills in this field is understanding how to balance reactions. Balancing equations ensures that the law of conservation of mass is respected, meaning the number of atoms on both sides of the equation is equal. This process is essential for determining how substances interact and ensuring accurate calculations in reactions.
Steps for Balancing Reactions
- Write the unbalanced equation with correct formulas for reactants and products.
- Identify the elements involved and compare the number of atoms on both sides.
- Adjust the coefficients (the numbers in front of compounds) to balance the number of atoms for each element.
- Double-check that all elements are balanced and that the smallest whole number coefficients are used.
Tips for Effective Balancing

- Start by balancing elements that appear in only one reactant and one product.
- Balance oxygen and hydrogen atoms last, as they are often found in multiple compounds.
- If necessary, use fractional coefficients and multiply through by the denominator to clear fractions.
With practice, balancing equations becomes a systematic and manageable task, helping to ensure that reactions are properly represented and calculations are accurate.
Significance of Stoichiometry
Understanding the quantitative relationships between reactants and products is crucial for predicting the outcomes of any chemical process. By mastering these calculations, you can determine how much of a substance is needed or produced, which is vital for both theoretical studies and practical applications. Stoichiometry serves as the bridge between molecular theory and real-world measurements, ensuring that reactions are carried out efficiently and accurately.
Key Concepts in Stoichiometry
- The mole ratio: This is the relationship between the amounts of reactants and products in a balanced equation.
- Limiting reactants: Identifying the substance that runs out first in a reaction, which determines the amount of product formed.
- Theoretical yield vs. actual yield: Theoretical yield is the maximum amount of product that can be formed, while actual yield is the amount produced in practice.
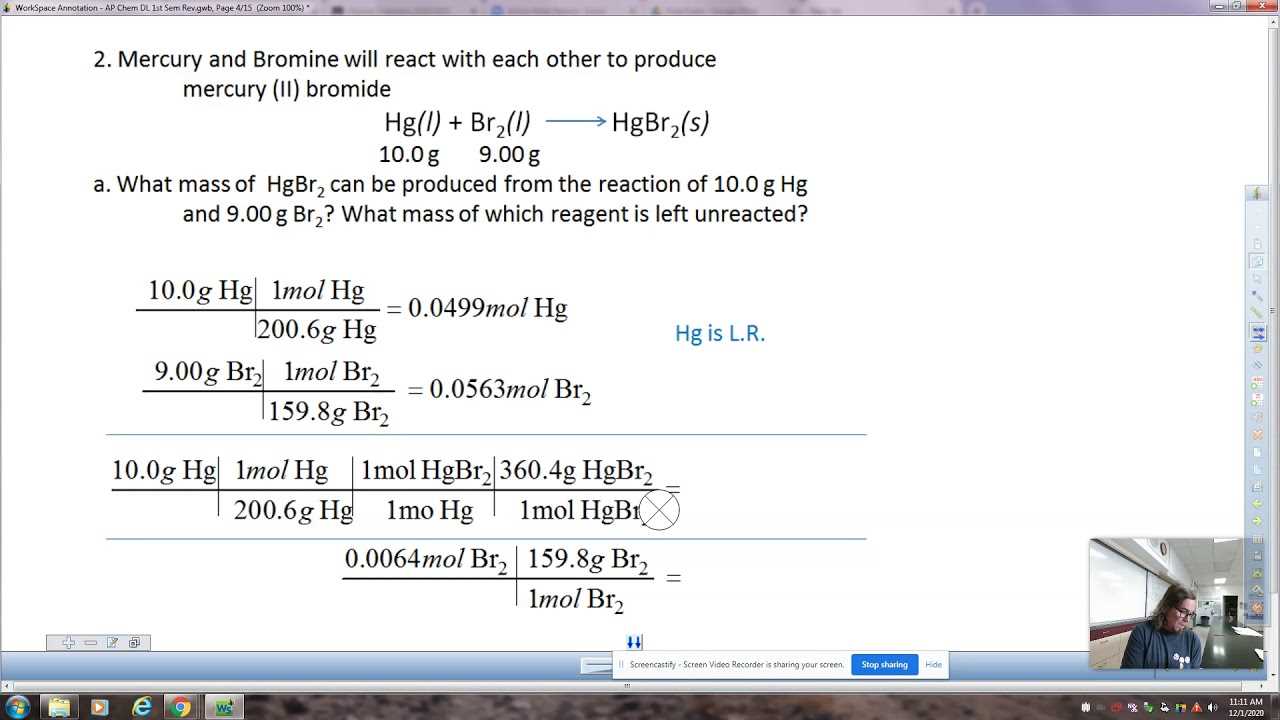
Stoichiometry Calculations
To perform stoichiometric calculations, it’s important to follow a structured approach. Here is an example of the process using the concept of a limiting reactant.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Write the balanced chemical equation. |
| 2 | Identify the given quantities (usually in moles or grams) for the reactants. |
| 3 | Convert given quantities into moles if needed, using molar mass or other conversion factors. |
| 4 | Use the mole ratio to determine how many moles of the product will be produced from the given reactants. |
| 5 | Convert the number of moles of the product into grams or another desired unit. |
By mastering these steps, you can solve problems involving the quantity of reactants and products, ensuring that reactions are efficient and yield the expected results.
How to Tackle Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple choice questions can often feel overwhelming, but with the right strategies, you can approach them confidently and efficiently. These questions are designed to test your understanding and ability to apply key concepts quickly, making it crucial to stay focused and organized. By knowing how to analyze each option and identify the correct answer, you can improve your performance and avoid common pitfalls.
Start by carefully reading the question and all the options. Eliminate any clearly incorrect answers first, as this increases the likelihood of selecting the correct option. Often, there are clues within the question that can guide you toward the right choice. If you’re unsure, try to make an educated guess based on your knowledge of the subject matter, considering any context or details mentioned in the question.
Tips for Success
- Read the question thoroughly – Ensure you understand what is being asked before reviewing the answer choices.
- Eliminate obviously wrong answers – Narrowing down the options can increase your chances of guessing correctly.
- Look for keywords – Words like “always,” “never,” or “most likely” can provide insight into the correct answer.
- Stay calm – If you don’t know the answer right away, take a moment to think critically before choosing an option.
With practice, these strategies will help you navigate multiple choice questions with greater ease, ensuring that you can demonstrate your knowledge effectively under timed conditions.
Reviewing Atomic Structure Basics
Understanding the fundamental components of matter is essential for grasping more complex concepts in science. Atoms are the building blocks of everything around us, and their structure plays a crucial role in determining how substances behave and interact. By revisiting the basics of atomic structure, you can strengthen your foundational knowledge and make it easier to explore more advanced topics.
The structure of an atom consists of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in various energy levels or orbitals. The number of protons in the nucleus defines the element, while the arrangement of electrons determines how atoms bond and react with others. This simple yet profound understanding forms the basis for much of the study in natural sciences.
Key Components of Atomic Structure
- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the nucleus. Their number determines the atomic number of an element.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles also found in the nucleus. They contribute to the atomic mass but do not affect the chemical properties.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in energy levels or orbitals. They play a key role in chemical reactions and bonding.
Understanding Atomic Number and Mass Number
- Atomic Number: The number of protons in the nucleus, unique to each element and determines its position on the periodic table.
- Mass Number: The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. This value helps calculate the atom’s isotopic identity.
By revisiting these key concepts, you can build a solid foundation for understanding the behaviors of elements, the formation of compounds, and the principles behind various chemical processes.
Tips for Memorizing Elements and Compounds
Learning the names, symbols, and formulas of various substances can be a daunting task, but with the right strategies, it becomes much easier. Memorization is not just about rote learning; it’s about making connections and understanding the logic behind the patterns. By applying a few proven techniques, you can retain information more effectively and recall it when needed.
One key approach is to break down the material into smaller, manageable groups. This method, known as chunking, helps prevent overwhelming your memory. Another effective strategy is to use mnemonic devices, which can be especially helpful when memorizing lists of elements or complex compound formulas. Visual aids, such as flashcards or periodic tables, can also reinforce learning by offering a quick and easy way to test your knowledge.
Effective Memorization Techniques
- Chunking: Grouping elements or compounds by similarities, such as their chemical properties or families on the periodic table, can help you remember them more easily.
- Mnemonics: Create memorable phrases or stories that link the names or symbols of elements. For example, “Happy Harry Hates Being Near Cold Stuff” for hydrogen, helium, boron, nitrogen, and carbon.
- Flashcards: Use cards with the name of the element or compound on one side and its symbol or formula on the other. This helps with active recall and improves retention.
Utilizing Visual Tools
- Periodic Table: Familiarize yourself with the table’s layout and the organization of elements based on their atomic number and chemical properties.
- Interactive Apps: Many mobile apps provide interactive quizzes and games to help reinforce your knowledge of elements and compounds in a fun and engaging way.
With consistent practice and the use of these techniques, you can significantly improve your ability to memorize and recall the vast array of substances you encounter in your studies.
Acids and Bases Overview
Understanding the behavior of acids and bases is fundamental to grasping various chemical processes. These substances play a key role in numerous reactions and are characterized by their ability to donate or accept specific particles, which influences their reactivity. Recognizing the properties of acids and bases is essential for predicting how different substances will interact and form compounds under varying conditions.
Acids generally have a sour taste and can donate protons, while bases tend to have a bitter taste and can accept protons. When combined, acids and bases often undergo a neutralization reaction, resulting in the formation of water and a salt. This simple yet crucial interaction is seen in many everyday processes, such as the regulation of pH levels in biological systems or the production of cleaning products.
The strength of an acid or a base depends on its ionization in water. Strong acids and bases fully dissociate into ions, while weaker ones only partially dissociate. This difference in ionization plays a significant role in determining their reactivity and the extent to which they affect the surrounding environment.
Thermochemistry and Energy Concepts
Energy is a fundamental concept in many processes, especially when it comes to transformations between substances. Understanding how energy is absorbed or released during reactions is key to predicting the behavior of different materials. Thermochemistry explores these changes in energy and how they relate to the chemical and physical changes in matter. Whether energy is released as heat or absorbed from the surroundings, this process determines the outcome of many reactions in both laboratory and real-world settings.
Heat is one of the most common forms of energy involved in chemical processes. It flows from high-temperature areas to low-temperature ones, and this transfer can be measured and quantified. The study of how substances absorb, release, or store heat is crucial for understanding reaction dynamics and the development of energy-efficient systems.
Types of Energy Changes
- Exothermic Reactions: These reactions release energy in the form of heat, leading to an increase in the temperature of the surroundings. Combustion is a classic example.
- Endothermic Reactions: In contrast, endothermic reactions absorb energy, causing the temperature of the surroundings to decrease. Photosynthesis is a well-known example.
Key Thermodynamic Concepts
- Enthalpy (ΔH): The total heat content of a system at constant pressure, used to determine if a reaction is exothermic or endothermic.
- Entropy (ΔS): The measure of disorder or randomness in a system. Reactions tend to move towards increased entropy.
- Gibbs Free Energy (ΔG): This value helps predict whether a reaction will occur spontaneously by taking into account both the enthalpy and entropy changes.
Understanding these energy concepts and how they apply to reactions helps in predicting whether certain processes will occur and how efficiently they will operate. These principles are crucial not only in laboratories but also in industrial applications and energy generation systems.
Practice Problems for Concept Mastery
To truly grasp the material, it is important to actively engage with the concepts through practice. Working through problems allows you to apply theoretical knowledge and sharpen your problem-solving skills. This section provides a range of problems designed to test your understanding of core principles, helping to solidify your grasp of the material.
By practicing various types of questions, you can become familiar with different problem-solving techniques, identify areas where further study is needed, and build confidence in your ability to tackle complex problems. The key is consistent practice and reviewing the solutions to understand any mistakes made.
Sample Problems
- Problem 1: Calculate the molar mass of a compound given its molecular formula.
- Problem 2: Determine the type of reaction occurring when two compounds are mixed.
- Problem 3: Predict the products of a specific type of chemical reaction.
- Problem 4: Given the concentrations of reactants, calculate the equilibrium constant for a reaction.
Problem-Solving Tips
- Understand the concept: Always begin by reviewing the theory behind each topic before attempting the problems.
- Break it down: Divide complex problems into smaller, manageable steps to make them easier to solve.
- Check your work: After solving, double-check calculations and assumptions to avoid simple errors.
By regularly practicing these types of problems, you will build a deeper understanding and strengthen your skills, ultimately preparing you for future challenges. Practice is the key to mastering any concept, and it enhances your ability to recall information when needed most.
Understanding Moles and Avogadro’s Number
One of the fundamental concepts in science is the idea of quantifying the amount of substance. This is where the concept of moles comes into play. A mole is a standard unit used to measure the amount of a substance, linking the microscopic world of atoms and molecules to the macroscopic world we can measure. To understand how atoms and molecules interact in large quantities, scientists use a constant called Avogadro’s Number, which provides a way to convert between atomic scale and everyday quantities.
Avogadro’s Number represents the number of particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.) in one mole of a substance. This number is approximately 6.022 x 10²³, a figure so large it allows scientists to work with manageable amounts of material, rather than dealing with individual atoms or molecules.
How to Use Moles in Calculations
- Converting between grams and moles: The mass of a substance in grams can be converted to moles using its molar mass (grams per mole).
- Counting particles: Using Avogadro’s number, we can calculate how many individual particles are present in a given amount of substance.
- Stoichiometry: Moles are essential in stoichiometric calculations, allowing us to relate reactants to products in chemical reactions.
Example Calculation
Suppose you have 2 moles of a substance, and you want to know how many molecules are present. You would multiply the number of moles by Avogadro’s number:
2 moles × 6.022 x 10²³ molecules/mole = 1.2044 × 10²⁴ molecules
Understanding the mole concept and Avogadro’s number is crucial for solving problems related to quantities of substances. With these concepts, you can move beyond simply knowing the weight of materials and start connecting microscopic details to larger-scale chemical processes.
Strategies for Time Management During Exams
Effective time management is essential for success during high-stakes assessments. Having a plan in place can help ensure that you allocate enough time for each section and avoid rushing through important questions. By employing specific strategies, you can maximize your productivity, minimize stress, and improve your chances of performing well under pressure.
One of the key aspects of time management is the ability to prioritize tasks based on difficulty and point value. Dividing your time wisely between questions of varying complexity will allow you to complete each section efficiently, without spending too much time on any one part. It’s also crucial to remain aware of the clock and avoid getting bogged down by questions that seem too challenging at first.
Key Time Management Strategies
- Read Instructions Carefully: Before jumping into any question, make sure you fully understand what is being asked. Misinterpreting a question can waste precious time.
- Allocate Time Per Section: Decide how much time you’ll spend on each section beforehand. Break down your time into manageable chunks, so you don’t feel rushed as you approach each question.
- Answer Easy Questions First: Start with questions you feel confident about. This helps build momentum and ensures that you secure points before tackling harder ones.
- Leave Difficult Questions for Later: If you encounter a difficult question, don’t dwell on it for too long. Move on and come back to it later when you have more time or a fresh perspective.
- Keep Track of Time: Regularly check the time to ensure you’re staying on track. A clock or timer can be useful to remind you of how much time remains.
How to Avoid Time Management Pitfalls
- Avoid Perfectionism: Don’t waste time obsessing over minor details. Aim for clarity and accuracy without getting caught up in perfection.
- Don’t Panic: Staying calm and composed will help you think more clearly. If you find yourself overwhelmed, take a deep breath and refocus.
- Review When Possible: If time allows, go back and review your answers. Check for simple mistakes or missed questions.
By implementing these strategies, you can enhance your efficiency and effectiveness, giving you the best chance to perform well. Planning ahead, staying organized, and managing your time wisely are critical skills that not only improve exam performance but also contribute to reducing anxiety and ensuring a more positive testing experience.
How to Review Effectively Before the Exam
Preparation is the cornerstone of success in any assessment. A well-structured approach to revisiting material before the big day can make all the difference in achieving high performance. By organizing your study sessions and using active learning techniques, you can maximize your retention and understanding of the key concepts. It’s not just about reading through notes but actively engaging with the material in ways that help reinforce your knowledge.
Effective preparation involves more than simply revisiting notes or textbooks. It’s about creating a strategy that ensures you cover all critical areas without feeling overwhelmed. By prioritizing what needs the most attention, focusing on areas of difficulty, and practicing regularly, you can confidently approach any challenge that arises during the assessment.
Essential Techniques for Effective Review
- Active Recall: Test yourself on the material you’ve studied. Instead of passively reading your notes, try to retrieve the information from memory. This strengthens your ability to recall important details during the assessment.
- Spaced Repetition: Space out your review sessions over days or weeks. Repeating the material periodically allows your brain to retain information more effectively, improving long-term retention.
- Teach What You Learn: One of the best ways to solidify knowledge is to explain it to someone else. Try teaching a peer or even explaining concepts aloud to yourself as if you were the instructor.
- Practice Problems: Solve practice questions or sample problems to familiarize yourself with the format and types of questions you may encounter. Practicing under time constraints can help you improve speed and accuracy.
Tips for Maximizing Review Sessions

- Stay Organized: Break down the material into manageable chunks and set clear goals for each review session. Use study guides, outlines, or flashcards to help guide your review process.
- Focus on Weak Areas: Identify the concepts or topics you struggle with the most and dedicate more time to reviewing them. Prioritize understanding rather than simply memorizing facts.
- Take Regular Breaks: Avoid burnout by incorporating short breaks into your study sessions. Following the Pomodoro technique–studying for 25 minutes and taking a 5-minute break–can help maintain focus and energy.
By applying these strategies, you can transform your study sessions into powerful opportunities to enhance your knowledge and readiness. With consistent effort, clear goals, and an active approach to revising, you will be prepared to tackle any challenge that comes your way.