Cell Unit Exam Answers for Effective Study

Understanding the fundamental principles of living organisms is crucial for excelling in biology assessments. Whether you are preparing for a class quiz or a more comprehensive review, it’s essential to grasp the core ideas that underpin life’s building blocks. By focusing on key topics and processes, students can ensure they’re well-prepared for any challenge that comes their way.
Knowledge of structure, function, and processes plays a pivotal role in mastering biology. From the intricate machinery within each living cell to the complex mechanisms that drive life, there’s a wealth of information to absorb. With the right approach, even the most complex concepts can become clear and manageable.
Success in these evaluations often hinges on effective study strategies and a solid understanding of essential topics. Focusing on the relationships between different components of life and their respective functions can provide a clearer path toward mastering this subject. By reviewing common problem areas and testing yourself with practice questions, you can build confidence and refine your knowledge before tackling your next academic challenge.
Cell Unit Exam Answers

Mastering the core principles of biological systems requires not only understanding the individual components but also how they work together. Whether you’re tackling questions about structure, function, or processes, it’s important to have a deep understanding of how these elements interact. A clear grasp of key topics allows students to confidently approach assessments and demonstrate their knowledge effectively.
Key Topics to Focus On
To excel in this subject, focus on the most critical areas that frequently appear in assessments. The foundational concepts, such as the role of cellular structures and their functions, are essential for understanding more advanced material. Topics like metabolism, reproduction, and genetic material should also be prioritized, as they form the backbone of many questions.
Effective Study Techniques
Developing effective study strategies is key to success. Utilize active recall, spaced repetition, and practice questions to reinforce your understanding. By focusing on challenging topics and reviewing them regularly, you can improve retention and increase your chances of performing well. A structured approach, coupled with a strong understanding of the subject matter, will help you navigate the complexities of biological studies with confidence.
Key Concepts in Cell Biology
Understanding the fundamental principles of living organisms is essential for grasping the complexity of biological systems. At the core of biology lies the study of how living entities function, grow, and interact with their environment. This knowledge provides a foundation for exploring advanced topics in the field, from metabolism to genetic inheritance.
Structure and Function of Biological Components
The key to understanding living organisms lies in comprehending the different structures and their respective roles. Whether it’s the architecture of the building blocks or the specialized functions they perform, each component plays a critical part in maintaining life processes. Familiarizing yourself with these aspects allows for a deeper understanding of how organisms survive and thrive.
Energy Transfer and Genetic Information

Energy flow and the transmission of genetic material are central concepts in biology. The mechanisms that convert energy into usable forms within living organisms, along with the processes that pass genetic information from one generation to the next, are fundamental to understanding life at a molecular level. Mastering these concepts is key to understanding how organisms adapt, evolve, and function in their environment.
Understanding Cell Structure and Functions
To fully comprehend living organisms, it’s crucial to understand the building blocks that make up life. Each entity is composed of various components that perform distinct roles essential for maintaining overall function. These components work together seamlessly, allowing the organism to grow, reproduce, and interact with its environment. Understanding these elements helps clarify the complexities of biological systems and their intricate operations.
Key Structures and Their Roles

Each part of a living structure is designed to carry out specific tasks that contribute to the organism’s survival. From protective layers to energy-producing systems, each component plays a vital role in ensuring that life processes continue. Mastering the functions of these elements is foundational for understanding how the entire organism operates in harmony.
How Structures Support Life Functions
The relationship between structure and function is critical in biology. For example, some structures are involved in energy conversion, while others are dedicated to communication or reproduction. By understanding how each structure supports specific life functions, it becomes easier to comprehend the overall complexity of living organisms and how they adapt to various environmental challenges.
Major Types of Cells in Biology
Living organisms are made up of different types of fundamental building blocks, each with unique structures and functions. These diverse forms are specialized to perform various tasks that sustain life, ranging from energy production to genetic transmission. Understanding these distinct forms helps in comprehending the complexity and adaptability of life in its many forms.
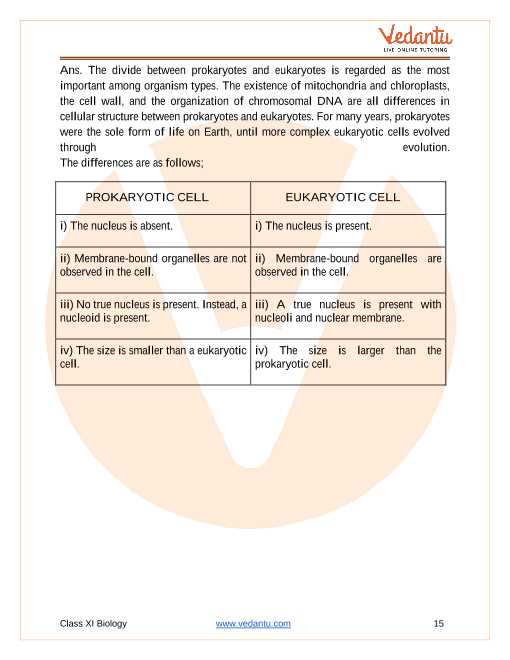
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Variations
The two primary types of biological structures are prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotes are simpler, smaller units that lack a defined nucleus, whereas eukaryotes are more complex and have a membrane-bound nucleus. Both play essential roles in different environments and are crucial for understanding the evolution of life forms.
Specialized Cells in Multicellular Organisms
In more advanced organisms, cells become highly specialized to perform specific functions. From muscle cells that enable movement to nerve cells that transmit signals, these specialized units work together to maintain the health and function of the entire organism. Each type of specialized unit is adapted to its unique role, contributing to the organism’s overall performance and survival.
Important Cellular Organelles and Their Roles
Within every living structure, there are various components that carry out essential functions to maintain life. These specialized parts, known for their unique roles, work together to ensure processes like energy production, protein synthesis, and waste management occur efficiently. Understanding these components is vital for grasping how organisms function at a molecular level.
Key Organelles and Their Functions
Each organelle has a specific task that contributes to the survival and efficiency of the organism. The main structures include:
- Nucleus: Contains genetic material and controls cell activities, acting as the command center.
- Mitochondria: Often called the powerhouse, responsible for generating energy through cellular respiration.
- Ribosomes: Essential for protein synthesis, these small structures read genetic instructions to build proteins.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Divided into rough (with ribosomes) and smooth (without ribosomes), involved in protein and lipid synthesis.
- Golgi Apparatus: Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for transport within or outside the structure.
- Lysosomes: Contain enzymes that break down waste material and cellular debris.
- Chloroplasts (in plants): Responsible for photosynthesis, converting sunlight into chemical energy.
Collaborative Functions of Organelles
The proper functioning of each component is essential for the overall health and performance of the organism. These organelles work in a highly coordinated manner to ensure that life processes such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction are carried out effectively. For example, the nucleus and ribosomes collaborate to produce proteins that are vital for the structure and function of the organism. Similarly, mitochondria provide the necessary energy for cellular activities, allowing other organelles to perform their roles efficiently.
How to Memorize Cell Processes
Learning the complex processes that occur within living organisms can be challenging, but with the right strategies, memorization becomes more manageable. The key to understanding these processes lies in breaking them down into smaller, more digestible parts and using various techniques to reinforce the material. By employing these methods, you can better retain information and recall it when needed.
One effective approach is to visualize the steps involved in each process. Drawing diagrams or creating flowcharts can help you see the sequence of events, making it easier to understand and remember how they unfold. Another strategy is to use mnemonic devices, which associate the steps with memorable phrases or acronyms, making the material easier to recall.
Repetition is also crucial for memorization. Reviewing the material regularly, whether through flashcards, quizzes, or self-testing, reinforces the information and strengthens memory retention. Additionally, teaching the material to someone else can further solidify your understanding and improve recall.
Finally, focusing on the “why” behind each process, rather than just memorizing the steps, can deepen your understanding. Knowing how each event contributes to the overall function of the organism helps you remember not only the sequence but also the purpose behind it. This context can make the material more meaningful and easier to retain in the long term.
Cell Division and Reproduction Explained
Reproduction and growth are fundamental processes that enable organisms to thrive and propagate. These processes ensure that living entities can pass on their genetic material and maintain the continuation of their species. Whether it’s through asexual reproduction, where a single organism creates a clone, or sexual reproduction, which involves genetic exchange, these mechanisms are essential for the diversity and survival of life.
Types of Reproduction

There are two main methods by which organisms reproduce: asexual and sexual. Asexual reproduction involves the creation of offspring from a single parent, leading to genetically identical organisms. In contrast, sexual reproduction requires the fusion of genetic material from two distinct organisms, resulting in genetically diverse offspring.
Stages of Reproduction
The process of creating new organisms involves several stages, whether it’s through simple division or more complex mechanisms. Understanding the stages of division and reproduction is crucial for grasping how life continues and adapts. Below is a comparison of the stages involved in both processes:
| Process | Stages | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Asexual Reproduction | Mitosis: A single cell divides to form two identical cells. | Two genetically identical organisms. |
| Sexual Reproduction | Meiosis: Two parent cells combine their genetic material to create genetically unique offspring. | Genetically diverse offspring with traits from both parents. |
These processes are fundamental to the continuity and diversity of life, ensuring that organisms can reproduce and adapt to changing environments.
Understanding Photosynthesis in Cells

Photosynthesis is a vital process that allows organisms, particularly plants, to convert light energy into chemical energy, providing the necessary fuel for growth and development. This process not only sustains the organism itself but also forms the foundation of the food chain, supporting nearly all life on Earth. Understanding how energy is harnessed from sunlight to produce food and oxygen is essential for grasping the flow of energy through ecosystems.
Key Stages of Photosynthesis
The process of transforming light into energy occurs in multiple steps. These stages ensure that energy is efficiently captured and stored for the organism’s use. The main stages include:
- Light-dependent Reactions: These occur in the presence of sunlight, where light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll, converting it into chemical energy.
- Calvin Cycle: Using the energy produced in the previous stage, carbon dioxide is fixed into organic molecules, producing sugars that serve as energy storage.
The Role of Organelles in Photosynthesis
The process relies on specialized structures within the organism, particularly those involved in energy conversion. The key components include:
- Chloroplasts: Organelles that house the machinery for both stages of photosynthesis, playing a crucial role in capturing sunlight and synthesizing energy-rich molecules.
- Chlorophyll: A pigment found within the chloroplasts, essential for absorbing light energy, particularly from the sun.
Through photosynthesis, organisms can create energy-rich compounds that fuel cellular activities, sustain growth, and produce oxygen–an essential component for life on Earth.
Cellular Respiration and Its Importance
Every living organism requires a continuous supply of energy to perform vital functions, and this energy is generated through complex biochemical processes. One of the most fundamental processes responsible for energy production is cellular respiration. It converts nutrients into usable energy, ensuring that all biological activities, from growth to movement, can be sustained. Understanding this process is key to understanding how organisms survive and thrive on a molecular level.
Cellular respiration involves the breakdown of organic molecules, such as glucose, to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy carrier in cells. This process takes place in several stages, each crucial for maximizing energy production and ensuring efficiency. The importance of this process cannot be overstated, as ATP powers everything from muscle contraction to DNA replication.
Stages of Cellular Respiration
The process can be broken down into three main stages, each contributing to the generation of energy:
- Glycolysis: The first step, occurring in the cytoplasm, where glucose is broken down into pyruvate, releasing a small amount of energy.
- Krebs Cycle: This stage takes place in the mitochondria, where pyruvate is further broken down, releasing more energy in the form of electrons and producing carbon dioxide as a waste product.
- Electron Transport Chain: This final stage also occurs in the mitochondria, where the energy from electrons is used to generate large amounts of ATP, with oxygen playing a key role in accepting the electrons at the end of the chain.
The Significance of Oxygen in Respiration
Oxygen plays a crucial role in the final stages of cellular respiration. It acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, allowing the production of ATP to continue. Without oxygen, this process would halt, and cells would be unable to generate the necessary energy to sustain life. This underscores the interconnectedness of biological processes and the necessity of oxygen for most living organisms.
Genetics and Cells: The Basics
The foundation of inheritance and biological diversity lies in the way genetic material is organized and passed down through generations. This process is intricately linked to the fundamental units of life, which carry the genetic instructions for building and maintaining organisms. Understanding the basics of genetics is essential to grasp how traits are inherited, how organisms grow, and how variation occurs across populations.
Genetics involves the study of genes, the units of heredity that carry the information required for growth, development, and reproduction. These instructions are encoded in DNA, which is found in the nucleus of cells. The transmission of genetic material from one generation to the next is a cornerstone of biology, influencing everything from physical characteristics to susceptibility to diseases.
Structure and Function of Genes
Genes are segments of DNA that provide the blueprint for producing proteins, which perform a vast array of functions within an organism. These proteins are responsible for cellular structure, function, and regulation, making genes a crucial part of life’s processes. The genetic code is read in sets of three nucleotides, known as codons, each specifying an amino acid to be added to a protein chain.
Inheritance and Variation

Genetic material is inherited from parents, with each offspring receiving half of its genetic information from each parent. This combination of genes creates genetic variation, which is essential for adaptation and evolution. The diversity in traits seen among individuals within a species is a direct result of how genes are shuffled and passed on during reproduction.
The Role of DNA in Cells
Within every living organism, the molecular instructions that guide growth, development, and functioning are encoded in a unique sequence. These instructions are stored in a complex molecule that acts as a blueprint for building and maintaining the structure of life. This genetic material is passed on from one generation to the next, ensuring that organisms can reproduce and inherit traits that are critical to survival and adaptation.
The primary function of this genetic material is to store and transmit information necessary for cellular activities. This includes regulating the production of proteins, which are essential for almost every aspect of cellular function. The sequence of nucleotides within the molecule directly determines the traits of an organism, from its physical characteristics to its biochemical processes.
DNA and Protein Synthesis
DNA serves as a template for the creation of proteins, which are the workhorses of the cell. This process occurs through two main stages: transcription and translation. During transcription, a messenger molecule is created based on the DNA sequence, which is then used in translation to assemble amino acids into proteins. These proteins perform critical tasks such as catalyzing biochemical reactions, forming structural components, and regulating various cellular functions.
DNA Replication and Inheritance
In order for organisms to grow and reproduce, DNA must be accurately copied. This process, known as DNA replication, ensures that each new cell receives an exact copy of the genetic material. The precision of this process is vital for maintaining genetic integrity across generations. Errors in replication can lead to mutations, which can be beneficial, harmful, or neutral depending on the nature of the change and its impact on the organism’s survival.
How Cells Communicate with Each Other
In complex organisms, coordination between various biological systems is crucial for maintaining homeostasis and ensuring proper function. The interaction and exchange of information between different components are vital for regulating processes such as growth, immune response, and tissue repair. This communication occurs through intricate signaling mechanisms that allow individual elements to relay messages and coordinate actions.
One of the primary methods of intercellular communication is through signaling molecules. These molecules can bind to specific receptors on the surface of other components, triggering a cascade of responses that influence behavior and function. This process is essential for everything from regulating metabolic pathways to orchestrating the body’s defense mechanisms against pathogens.
Types of Signaling
There are several types of communication pathways, each serving different purposes:
- Autocrine signaling: In this type, a component releases signals that act on itself, influencing its own behavior or function.
- Paracrine signaling: This involves signaling molecules that act on nearby components, affecting a localized group of cells.
- Endocrine signaling: In this form, hormones travel through the bloodstream to target distant components, affecting tissues and organs far from their origin.
The Role of Receptors
For communication to be effective, the receiving components must possess specific receptors capable of recognizing and binding to the signaling molecules. These receptors act like locks, with each signaling molecule acting as a key. When the appropriate key fits into the lock, it triggers a response within the receiving component, allowing for the transmission of information and a coordinated response.
Common Mistakes in Cell Unit Exams

When preparing for assessments related to biological systems and processes, students often encounter certain pitfalls that hinder their performance. These mistakes can range from misunderstanding key concepts to overlooking important details in questions. Recognizing and addressing these common errors can significantly improve understanding and results in any biological evaluation.
One frequent issue is misinterpreting terminology. In biology, specific terms are used with precise meanings, and confusing similar terms can lead to incorrect responses. Another common mistake is neglecting the structure and function relationships, which are critical in understanding how components work together to maintain life. A lack of attention to the context in which certain processes occur can also lead to incorrect answers.
Overlooking Key Concepts

Many students focus too much on memorizing facts without understanding the underlying principles. This often results in confusion when questions are phrased differently than expected. For example, while it’s important to know the names of various components and processes, it is equally important to understand how they interact within a system. Failing to recognize this interconnectivity can lead to errors in questions that require applied knowledge.
Rushed Answers and Misreading Questions
Another common mistake is rushing through the questions. When under pressure, students may misread instructions or overlook key phrases in the questions. This can lead to incomplete or incorrect answers, particularly in sections that require detailed explanations or precise steps. Taking the time to carefully read each question and plan responses can help avoid this issue.
How to Approach Cell Biology Questions
When tackling questions related to biological systems and processes, it is essential to adopt a strategic approach to ensure clarity and accuracy. Success in these types of assessments depends on understanding both the specifics and the broader concepts involved. By breaking down each question and using a structured method to respond, you can significantly improve your performance and avoid common mistakes.
One effective strategy is to begin by carefully reading each question. Take note of keywords or phrases that signal what is being asked, and identify whether the question is asking for a specific detail, a comparison, or an explanation of a process. After understanding the question, take a moment to recall the main concepts related to the topic, and consider how they relate to the question at hand.
Step-by-Step Approach
Breaking down your response into steps is an excellent way to stay organized. A clear and logical sequence allows you to address all parts of the question methodically. Here’s a simple framework to guide your response:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Read the Question Carefully: Ensure you understand what is being asked before beginning your response. |
| 2 | Recall Key Concepts: Reflect on the relevant biological processes, structures, or interactions that relate to the question. |
| 3 | Provide a Clear Explanation: Address each part of the question in a logical order, using specific terminology. |
| 4 | Review Your Answer: Double-check your response for accuracy, clarity, and completeness. |
Time Management and Clarity
Effective time management is essential when answering questions. Make sure to allocate sufficient time to each part of the question, ensuring that you address all components without rushing. Additionally, aim for clarity in your responses. Use simple, concise language to express your understanding, and avoid unnecessary complexity that could confuse the examiner.
Study Tips for Cell Unit Exams
Effective preparation is key to success in any academic assessment. To achieve the best results, it is important to have a structured study plan that allows you to focus on essential concepts while reinforcing your understanding through consistent review. Whether you’re preparing for a test on biological processes, molecular structures, or related topics, these tips will help you organize your study sessions and maximize your retention.
One of the most effective ways to prepare is to break down the material into manageable sections. By organizing your study materials, you can focus on specific topics one at a time, making the overall content less overwhelming. In addition, practicing active recall and using visual aids can improve both comprehension and memory retention.
| Tip | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Organize Your Study Schedule | Divide the material into smaller sections and allocate specific times for each topic. Consistency is key to mastering the content. |
| Use Active Recall | After reviewing a section, close your book and try to recall key points from memory. This technique helps reinforce long-term retention. |
| Create Visual Aids | Diagrams, charts, and mind maps can simplify complex concepts and help you visualize relationships between different topics. |
| Review Past Tests | Reviewing previous assessments helps you familiarize yourself with the types of questions asked and the format of the material. |
| Group Study Sessions | Collaborating with classmates allows you to discuss challenging topics and gain different perspectives on difficult material. |
In addition to these strategies, it’s important to take care of your well-being during the study period. Getting adequate rest, staying hydrated, and taking breaks during long study sessions will help maintain focus and productivity.
Practice Questions for Cell Unit Review
To ensure a solid understanding of the material, it is crucial to test your knowledge regularly. Practicing with sample questions helps reinforce key concepts and identify areas that need further review. Below are some questions designed to help you assess your grasp of the fundamental topics in biology.
Multiple Choice Questions
- What is the primary function of ribosomes in a cell?
- A) Energy production
- B) Protein synthesis
- C) DNA replication
- D) Waste elimination
- Which organelle is responsible for producing energy in the form of ATP?
- A) Mitochondria
- B) Nucleus
- C) Endoplasmic Reticulum
- D) Golgi Apparatus
- What is the process of converting light energy into chemical energy in plants called?
- A) Respiration
- B) Photosynthesis
- C) Fermentation
- D) Osmosis
True or False Questions

- The nucleus contains the cell’s genetic material. (True / False)
- All cells have a cell wall. (True / False)
- Prokaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles. (True / False)
Short Answer Questions
- Explain the role of enzymes in biochemical reactions.
- Describe the process of mitosis and its significance in cell division.
- What is the difference between passive and active transport across cell membranes?
These practice questions are designed to help solidify your understanding of key biological processes. By regularly testing yourself, you can improve both your retention and your ability to apply what you’ve learned in various scenarios. Make sure to review your answers thoroughly and seek clarification on any topics you find challenging.
Strategies for Success in Cell Biology

Mastering the concepts of biology requires a strategic approach that combines effective study habits, a deep understanding of the material, and practical application of knowledge. Whether you are preparing for an assessment or simply aiming to enhance your understanding, implementing a variety of techniques can help you succeed in this subject. Below are key strategies to guide your study process and improve your performance.
Effective Study Techniques
- Active Learning: Engage with the material through activities such as summarizing key points, drawing diagrams, and teaching concepts to others. This method strengthens memory retention and deepens your understanding.
- Consistent Review: Set aside time each day for review. Consistency helps reinforce the material and ensures that you retain knowledge over time.
- Use Visual Aids: Visual tools such as flowcharts, diagrams, and concept maps can help simplify complex ideas and improve recall, especially when studying processes and structures.
- Practice with Questions: Regularly test yourself with practice questions or quizzes. This not only helps identify gaps in knowledge but also boosts your confidence in answering questions during assessments.
- Group Study: Collaborating with peers can help clarify difficult concepts and provide different perspectives. Group discussions often reveal new insights and make studying more interactive.
Focus on Key Concepts

- Prioritize Core Topics: Focus on understanding the most fundamental concepts, such as cellular processes, organelles, and the role of molecules in biology. These are often the foundation for more advanced topics.
- Understand Processes, Not Just Facts: It’s essential to understand how different biological processes are connected. For example, instead of memorizing terms, aim to grasp how they work together within an organism.
- Relate Theory to Real Life: Applying biological concepts to real-world scenarios can make them more relevant and easier to understand. Consider how biological principles are used in medicine, biotechnology, and other fields.
By incorporating these strategies into your study routine, you can not only perform well in assessments but also develop a deeper understanding of the material. Success in biology comes from consistent effort, engagement with the material, and using the right tools to enhance your learning experience.
Exam Preparation: Focus on Key Topics
When preparing for a scientific assessment, it’s essential to focus on the core concepts that are most likely to appear. By identifying and reviewing these fundamental areas, you can ensure that your study time is spent effectively. This approach not only boosts your chances of success but also deepens your understanding of the subject. Below are strategies to help you target the most important topics and enhance your preparation process.
Prioritize High-Impact Topics
- Identify Major Concepts: Review the syllabus or study guide to identify the key topics that are consistently emphasized. These are often the areas that carry the most weight in assessments.
- Focus on Core Processes: Understand the major biological processes and how they interrelate. For example, focusing on energy production, cellular functions, and molecular transport can give you a solid foundation.
- Review Previous Assessments: Analyze past assessments to see which topics were most frequently tested. This can provide insight into the areas that require the most attention.
Effective Strategies for Targeted Study
- Active Recall: After reviewing each topic, test yourself by recalling key points without looking at your notes. This strengthens your memory and ensures you truly understand the material.
- Practice with Flashcards: Use flashcards to review important terms, definitions, and processes. Flashcards are an excellent tool for reinforcing knowledge and improving long-term retention.
- Teach What You Learn: Teaching others is an effective way to solidify your understanding. Explaining complex ideas to a peer or even to yourself forces you to break down the material and grasp the underlying concepts.
- Group Study Sessions: Collaborating with others allows you to compare notes, discuss difficult concepts, and fill in any gaps in your understanding. Group discussions often lead to valuable insights.
By focusing on these key strategies and prioritizing the most important topics, you can streamline your study efforts and maximize your chances of success. Remember, understanding the material thoroughly is more valuable than simply memorizing facts.