CCNA1 Chapter 7 Exam Preparation and Study Guide

In this section, you will dive deep into the essential concepts that lay the foundation for a successful career in networking. Understanding core principles is crucial for anyone looking to advance in the field, as these concepts are key to configuring and managing network devices effectively. The focus here is on strengthening your knowledge of networking basics, including routing, subnetting, and network protocols.
By grasping the fundamental topics covered, you will be well-prepared for practical tasks in real-world scenarios. A strong grasp of these subjects will not only help you understand how devices communicate within a network but also set you up for success in future networking challenges. Confidence in these areas is vital for both exams and hands-on experience.
Through comprehensive study and consistent practice, you can sharpen your skills and prepare to tackle the complexities of network infrastructure. This section will provide you with the tools to better understand key elements that you will encounter, ensuring you are ready for every challenge that lies ahead.
CCNA1 Chapter 7 Exam Overview
In this section, you will focus on the key topics that assess your understanding of networking fundamentals, including device configuration, IP addressing, and routing concepts. These areas are crucial for building a solid foundation in network management and communication. Mastery of these concepts is not only essential for passing the assessments but also for real-world application in network environments.
The content covered in this portion is designed to test your ability to configure, troubleshoot, and secure network devices, as well as to apply your knowledge of IP routing protocols. Understanding how to effectively segment networks, allocate IP addresses, and use routing protocols is central to achieving success in this section. The practical skills gained will be directly applicable to your future work in networking roles.
Preparation for this segment involves reviewing key topics such as subnetting, network topologies, and basic security measures. By becoming familiar with these areas, you will be able to handle the variety of scenarios that may be presented during the assessment, giving you confidence in both theoretical and practical networking challenges.
Key Topics for CCNA1 Chapter 7

This section focuses on essential networking concepts that are crucial for building a robust understanding of network design, configuration, and management. Key areas include IP addressing, routing protocols, and network security basics. These topics are vital for configuring devices and ensuring efficient communication across networked systems.
IP Addressing and Subnetting are fundamental skills covered here. Understanding how to allocate and manage IP addresses within a network is a core aspect of any networking role. You’ll learn how to divide networks into subnets and apply subnet masks to optimize address utilization.
Routing Protocols, including both static and dynamic routing, are also explored in detail. Configuring routers to direct traffic between networks and understanding the functionality of protocols like RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP is key to ensuring smooth and efficient communication in large-scale networks.
Network Security plays a significant role in safeguarding data and preventing unauthorized access. Topics such as basic firewall configurations and access control lists (ACLs) are discussed to help you secure your network and control traffic flow.
Understanding Networking Protocols
Networking protocols are the rules and conventions that allow devices to communicate effectively across a network. These protocols govern how data is transmitted, received, and processed between devices, ensuring that information flows smoothly and securely. A clear understanding of these protocols is essential for troubleshooting, configuring, and maintaining a network.
Common Networking Protocols

Several key protocols form the foundation of networking, each serving a specific function in data communication. Some of the most important protocols include:
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) – A connection-oriented protocol that ensures reliable communication by breaking data into packets and verifying delivery.
- Internet Protocol (IP) – Responsible for addressing and routing data packets to their destination across networks.
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) – Used for transferring web pages over the internet.
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP) – Enables file transfers between devices over a network.
- Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) – Used for sending email messages between servers.
- Post Office Protocol (POP3) – Used for retrieving email from a server.
Role of Protocols in Networking
Each protocol plays a specific role in how data is transmitted and received. For example, TCP ensures that packets are delivered in the correct order, while IP is responsible for routing them through different networks. Together, these protocols enable seamless communication, error checking, and security measures, which are vital for both local and wide-area networks.
Understanding how these protocols work together allows network engineers and administrators to design and manage networks more effectively, ensuring stable and secure communications for users and devices.
Important IP Addressing Concepts
IP addressing is the cornerstone of networking, as it provides a unique identifier for every device connected to a network. It enables devices to communicate and route data across local and wide-area networks. Understanding how IP addresses are assigned and managed is essential for efficient network design and troubleshooting.
Types of IP Addresses
There are different types of IP addresses, each serving a unique function in the network. The most common types include:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Public IP | Used to identify devices over the internet, globally unique and assigned by an ISP. |
| Private IP | Assigned to devices within a local network and not routable on the internet. |
| Loopback Address | Used for testing network functionality within the local machine (127.0.0.1). |
| Link-Local Address | Assigned to devices automatically for communication within a local network segment (169.254.x.x). |
Subnetting and Subnet Masks
Subnetting allows the division of a network into smaller, more manageable subnets. This is achieved by applying a subnet mask, which helps determine the network and host portions of an IP address. Efficient subnetting ensures optimal utilization of IP addresses, reducing waste and improving network performance. Subnetting is crucial when designing networks with many devices or when needing to segment traffic for security reasons.
To calculate the number of subnets or hosts available within a given range, a subnet mask is applied to the IP address. For example, a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 allows for 256 addresses, with 254 usable for devices in the network.
OSI Model and Layer Functions
The OSI model provides a framework for understanding how different network protocols interact and communicate across a network. It is a conceptual tool that divides the complex process of data transmission into manageable layers, each responsible for specific tasks. By understanding the functions of each layer, you can better troubleshoot network issues, design efficient systems, and ensure compatibility between devices.
The model is divided into seven layers, each focusing on a specific aspect of data communication, from physical transmission to application-level functions. These layers work together to ensure data is successfully transferred between devices, whether it’s over a local network or the internet.
Layers of the OSI Model

The OSI model consists of seven distinct layers, each with specific responsibilities:
- Layer 1: Physical Layer – Responsible for the actual transmission of raw data over the physical medium, such as cables or wireless signals.
- Layer 2: Data Link Layer – Handles error detection and correction, and defines how data packets are formatted for transmission on the physical network.
- Layer 3: Network Layer – Responsible for logical addressing, routing, and forwarding data across different networks using protocols like IP.
- Layer 4: Transport Layer – Ensures end-to-end communication and reliability, managing data flow control and error correction through protocols like TCP and UDP.
- Layer 5: Session Layer – Manages sessions or connections between applications, ensuring data is properly synchronized and kept organized during transmission.
- Layer 6: Presentation Layer – Focuses on data translation, encryption, and compression, making data readable and compatible for the receiving system.
- Layer 7: Application Layer – The top layer where end-user applications interact with the network, providing services like email, file transfers, and web browsing.
Each layer of the OSI model provides specific functionality, and issues at any given layer can affect network performance. Understanding the role of each layer allows network engineers to diagnose problems efficiently and understand how different protocols interact to achieve seamless communication.
Routing Basics for Chapter 7
Routing is a key concept in network management, allowing data to be directed from one device to another across different networks. It ensures that packets reach their intended destination by selecting the optimal path based on network topology and routing protocols. Understanding the fundamentals of routing is crucial for configuring and managing network devices, ensuring smooth communication between devices located in separate networks.
Routing Protocols Overview
Routing protocols define how routers exchange information to determine the best paths for data packets. These protocols help routers build and maintain routing tables, which are used to forward packets efficiently. Two main types of routing protocols include:
- Distance Vector Protocols – These protocols use hop count or other metrics to find the best path. Examples include RIP (Routing Information Protocol).
- Link-State Protocols – These protocols provide more accurate information about network topology and are generally more efficient in larger networks. Examples include OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and IS-IS (Intermediate System to Intermediate System).
Static vs. Dynamic Routing
Routing can be either static or dynamic. In static routing, routes are manually configured by network administrators and do not change unless modified by the admin. It’s simpler but less flexible. Dynamic routing, on the other hand, uses routing protocols to automatically adjust to changes in the network, offering greater flexibility and scalability. The choice between static and dynamic routing depends on the network’s size and complexity.
Subnetting Explained in Simple Terms
Subnetting is the process of dividing a larger network into smaller, more manageable sections called subnets. It helps optimize the use of available IP addresses, improves network performance, and enhances security. By creating subnets, network administrators can better organize traffic and reduce congestion, ensuring more efficient communication within each section of the network.
Think of subnetting like dividing a large building into separate rooms. Each room (or subnet) has its own space and is easier to manage, but all rooms still belong to the same building (or network). Each subnet can function independently, with its own devices and services, while still being part of the overall network.
One of the key aspects of subnetting is the subnet mask, which defines the range of addresses available in each subnet. The mask helps routers and devices determine which part of an IP address identifies the network and which part identifies individual devices (hosts) within that network. By adjusting the subnet mask, you can control the size of each subnet and how many devices can be accommodated.
Common Exam Questions in Chapter 7
When preparing for assessments related to networking concepts, it’s essential to focus on the topics and questions that frequently appear. Understanding the most common types of questions can help streamline your study efforts and give you a better grasp of the material. These questions typically revolve around network configuration, troubleshooting, and addressing key concepts in routing, addressing, and subnetting.
Types of Questions You May Encounter
Exam questions often test your knowledge of practical concepts and scenarios. Here are some of the common question types:
- Addressing Questions: You might be asked to identify or assign IP addresses, configure subnet masks, or calculate network ranges. These questions test your understanding of subnetting and IP addressing schemes.
- Routing Table Questions: Questions may involve interpreting or configuring routing tables. You may need to identify routes based on given IP addresses or diagnose routing problems in a network.
- Protocol Understanding: Some questions will focus on how different networking protocols operate. You may be asked to identify the function of a protocol or select the correct one for a particular network scenario.
- Network Design: In these questions, you’ll be asked to design a network using specific criteria such as IP address ranges, routing protocols, and network segmentation.
- Troubleshooting Scenarios: Troubleshooting questions often present a network issue that you must solve by identifying the problem and proposing a solution based on given symptoms.
Strategies for Success
To succeed in these types of questions, practice is key. Familiarizing yourself with subnetting calculations, understanding routing mechanisms, and knowing how to troubleshoot common network issues are essential skills. Using practice tests and scenario-based exercises can also improve your ability to respond quickly and accurately during the assessment.
How to Approach the CCNA Exam
Preparing for a networking certification can feel overwhelming due to the wide range of topics covered. However, with the right approach, you can build confidence and tackle the test effectively. The key to success lies in understanding the core concepts, practicing hands-on skills, and approaching the assessment with a clear strategy. By breaking down your preparation into manageable steps, you can improve both your knowledge and test-taking abilities.
Effective Preparation Tips
To approach the assessment successfully, it’s crucial to structure your study plan. Here are some strategies to help you get started:
- Study the Core Topics: Focus on the foundational topics such as IP addressing, subnetting, routing protocols, and network security. Make sure to understand both the theory and practical applications of each concept.
- Hands-On Practice: Set up your own lab environment or use simulation software to practice configuring routers, switches, and other network devices. This will help reinforce your theoretical knowledge and give you the confidence to handle real-world scenarios.
- Use Practice Tests: Take practice exams regularly to familiarize yourself with the test format and question styles. Review the answers thoroughly, especially the ones you got wrong, to understand the correct solutions.
- Review and Revise: Continuously review key topics and focus on areas where you’re weakest. Revising these areas before the test can boost your chances of scoring higher.
Time Management During the Test
Time management is critical during the test. Being able to pace yourself and allocate enough time for each section will help you stay calm and focused throughout. Here’s how you can manage your time effectively:
| Strategy | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Skim the Entire Test First | Get a sense of the difficulty level and allocate time accordingly. This will help prevent you from getting stuck on difficult questions. |
| Focus on Easy Questions First | Answer the questions you’re confident about first. This will build your momentum and give you more time for tougher ones later. |
| Don’t Spend Too Much Time on One Question | If a question is taking too long, move on and come back to it later. This ensures you answer all the questions in the allotted time. |
By following these strategies, you can increase your chances of success and perform confidently during the assessment. Remember that preparation, practice, and time management are the pillars of a successful test-taking experience.
Practice Tests for CCNA1 Success
Practice tests are an essential tool for mastering networking concepts and preparing for certification assessments. By simulating the conditions of the actual test, these practice questions help you assess your knowledge, identify weak areas, and become familiar with the question format. Regularly taking practice tests boosts your confidence, enhances your time management skills, and allows you to fine-tune your understanding of key networking topics.
Incorporating practice tests into your study routine offers several advantages. They allow you to evaluate your grasp of complex topics like IP addressing, routing protocols, and network troubleshooting. Furthermore, practice tests provide a low-pressure environment in which you can make mistakes and learn from them without the consequences of a real exam.
To maximize the effectiveness of practice tests, it’s important to review your answers after each test, especially the questions you got wrong. Take the time to understand why you made those mistakes and focus on the areas where improvement is needed. This iterative process of testing and review is crucial for building your knowledge base and ensuring that you are fully prepared for the real assessment.
Time Management During the Exam
Effective time management is crucial for success during a certification test. Balancing speed and accuracy can be challenging, especially when faced with a broad range of topics. By planning your approach and maintaining focus throughout the test, you can ensure that you complete all sections without feeling rushed or stressed. The key is to allocate time wisely and avoid getting stuck on difficult questions.
Strategies to Manage Time Effectively

Implementing a few key strategies can significantly improve your time management during the assessment:
- Preview the Entire Test: Start by quickly skimming through the entire set of questions. This will give you an idea of the difficulty level and help you prioritize questions based on your strengths.
- Answer Easy Questions First: Tackle the questions you are most confident about first. This will boost your confidence and ensure you score as many points as possible in less time.
- Set Time Limits: Set a specific amount of time to spend on each question or section. If you find yourself spending too much time on one question, move on and come back to it later.
Dealing with Difficult Questions
Sometimes, you may encounter questions that are particularly challenging. In these cases, don’t let the pressure affect your performance. Here are a few tips to handle tough questions:
- Mark for Review: If you’re stuck, mark the question and move on. This allows you to come back to it later with a fresh perspective, without losing valuable time.
- Eliminate Wrong Answers: If unsure, use the process of elimination to rule out incorrect options. This can increase your chances of selecting the right answer, even when uncertain.
- Stay Calm: Remain calm and focused. Stress can cloud your judgment, so take deep breaths and approach each question with a clear mind.
By practicing good time management techniques and staying focused during the assessment, you can improve your chances of completing the test successfully and achieving your desired results.
Critical Preparation Tips
Effective preparation is key to performing well in any certification assessment. The more thoroughly you prepare, the more confident you will feel during the actual test. Developing a structured study plan, reviewing key topics, and practicing with realistic questions are essential components of a solid preparation strategy. By following a few critical tips, you can optimize your readiness and increase your chances of success.
Essential Steps for Successful Preparation
To ensure you are fully prepared, consider these essential steps:
- Understand the Exam Objectives: Review the main topics and objectives of the test. Make sure you know which areas will be tested, so you can focus your studies accordingly.
- Create a Study Schedule: Develop a study plan that allocates time for each topic based on your strengths and weaknesses. Break your sessions into manageable chunks to avoid burnout.
- Use Quality Study Materials: Invest in trusted textbooks, online courses, or practice guides. Ensure the materials are up-to-date and align with the test content.
Maximizing Your Study Sessions
Once you have a study plan in place, here are some tips to make the most of each session:
- Active Learning: Don’t just passively read through materials–engage with them. Take notes, explain concepts to someone else, or practice applying knowledge through exercises.
- Simulate Test Conditions: Take practice tests under timed conditions. This will help you get used to the pressure of the real test and improve your time management skills.
- Review Mistakes: After completing practice tests or quizzes, carefully review any incorrect answers. Understanding your mistakes is crucial for improvement.
By incorporating these critical tips into your preparation, you’ll be better equipped to tackle the test with confidence and perform at your best.
Understanding VLANs in Chapter 7
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) play a crucial role in modern networking, enabling administrators to logically segment networks for improved security, efficiency, and performance. By creating virtualized networks within a physical network, VLANs allow better control over data flow and network resources. Understanding how VLANs operate and how to configure them is essential for network professionals seeking to optimize and secure their infrastructure.
What is a VLAN?
A VLAN is essentially a broadcast domain created within a switch. Devices within the same VLAN can communicate directly with each other, but devices in different VLANs require a router or layer-3 switch to communicate. VLANs can be used to group users or devices with similar functions, regardless of their physical location within the network. This helps reduce unnecessary broadcast traffic and enhances network management.
Benefits of Using VLANs
Implementing VLANs offers several advantages, including:
- Improved Security: By separating sensitive data and users into different VLANs, you can create more secure network zones.
- Better Network Performance: VLANs reduce broadcast traffic, improving network performance by limiting unnecessary traffic to specific segments.
- Enhanced Network Management: VLANs simplify network management by logically grouping devices based on function or department, making it easier to configure and troubleshoot the network.
Understanding VLANs is critical for managing large-scale networks efficiently, and knowing how to configure and maintain VLANs is a key skill for any networking professional.
Access Control Lists Overview
Access Control Lists (ACLs) are a fundamental aspect of network security that help manage and filter traffic based on specific rules. By defining which users or systems can access certain network resources, ACLs provide a flexible and powerful way to control traffic flow. ACLs can be implemented on routers and switches to secure network boundaries, ensuring that only authorized traffic is allowed to pass through.
Types of Access Control Lists
There are two main types of ACLs, each serving a specific purpose in network security:
- Standard ACLs: These filter traffic based solely on the source IP address. They are typically used to permit or deny traffic from specific networks or hosts.
- Extended ACLs: These provide more granular control, allowing filtering based on source and destination IP addresses, protocols, and port numbers. Extended ACLs are often used to enforce more detailed security policies.
Basic ACL Configuration
ACLs are configured by creating a series of rules, or access control entries (ACEs), that specify which packets should be allowed or denied. The order of these rules is important, as traffic is evaluated in sequence. Here is a basic overview of how to configure ACLs:
| Step | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Create the ACL | Define the ACL and give it a unique name or number. |
| 2 | Define Rules | Specify the conditions for allowing or denying traffic (source IP, destination IP, etc.). |
| 3 | Apply ACL to Interface | Assign the ACL to a specific interface or subinterface on the router or switch. |
ACLs are essential tools for enhancing network security, controlling access, and ensuring that sensitive data is protected from unauthorized users. Understanding how to create and apply ACLs is vital for securing any network environment.
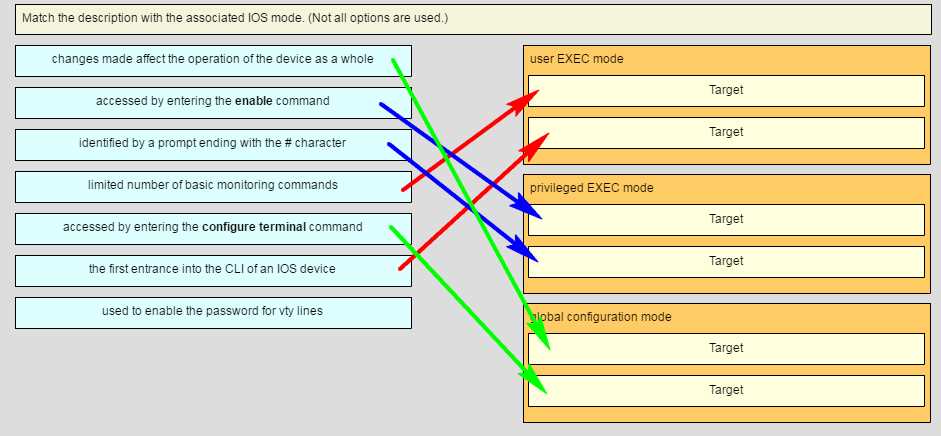
Reviewing Key Cisco Commands
Understanding the essential commands for Cisco devices is crucial for network configuration and troubleshooting. These commands allow network administrators to manage routers, switches, and other Cisco hardware efficiently, ensuring that the network runs smoothly and securely. Familiarity with both basic and advanced commands is vital to perform tasks such as configuring interfaces, setting routing protocols, and monitoring network performance.
Below are some of the key commands that every network professional should know when working with Cisco equipment:
- show ip interface brief: Displays a summary of the router’s or switch’s interfaces, including their IP addresses and status. This command is useful for quickly verifying connectivity.
- enable: Grants access to privileged exec mode, where more advanced commands can be executed.
- configure terminal: Enters global configuration mode, where you can configure the device’s settings.
- show running-config: Displays the current configuration of the device, including settings and applied changes.
- ping: Sends an ICMP echo request to test connectivity between devices on the network.
- show version: Provides detailed information about the Cisco device, including its software version, memory, and hardware specifications.
- interface: Used to configure specific interfaces (e.g., Ethernet, Serial) on the device.
- ip route: Configures static routes, allowing the device to forward traffic between different networks.
- copy running-config startup-config: Saves the current configuration to the startup configuration file, ensuring that settings are retained after a reboot.
These commands form the backbone of day-to-day network administration tasks. Mastery of these commands is not only essential for troubleshooting but also for configuring and optimizing network devices to meet the organization’s needs.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
In network configuration and troubleshooting, even small errors can lead to significant issues. Whether you’re configuring devices, managing IP addresses, or setting routing protocols, avoiding common pitfalls can save time and ensure a smooth experience. Recognizing these mistakes and learning how to prevent them is essential for achieving success in network management.
Here are some of the most frequent mistakes that individuals make and how to avoid them:
- Misconfigured IP Addresses: Assigning incorrect IP addresses or subnet masks can prevent devices from communicating properly. Always double-check your network settings to ensure accuracy.
- Ignoring Interface Status: Forgetting to activate an interface or leaving it in an administratively down state can cause network outages. Use the
no shutdowncommand to ensure interfaces are up and running. - Overlooking Routing Protocols: Failing to configure routing protocols correctly can lead to inefficient routing and packet loss. Ensure proper configuration of routing tables and protocols such as OSPF or EIGRP.
- Inadequate Security Settings: Leaving security settings incomplete or misconfigured can expose your network to vulnerabilities. Set up strong access control lists (ACLs) and secure administrative access with proper passwords.
- Improper VLAN Configuration: Misconfiguring VLANs can lead to broadcast storms or network segmentation issues. Be sure to configure VLANs correctly on both switches and routers, and verify inter-VLAN routing when needed.
- Forgetting to Save Configuration: After making changes to a device, forgetting to save the running configuration can result in the loss of all modifications after a reboot. Use
copy running-config startup-configto save your work. - Ignoring Network Topology: Failing to account for the physical and logical layout of the network can cause inefficiencies. Ensure that devices are appropriately placed in the topology and that links are optimized for performance.
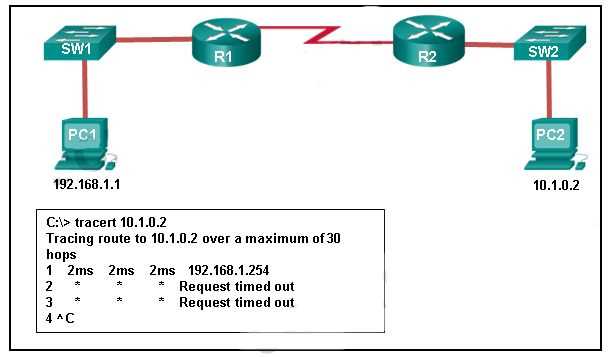
- Not Testing Configurations: Neglecting to test configurations after setup can lead to unresolved issues. Always verify connectivity using tools like
pingandtracerouteto check for errors and ensure proper functionality.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure that your network configurations are effective and your devices are running optimally. Regular practice and attention to detail will help you build a solid foundation in network management.
Study Strategies for Chapter 7
Effective preparation for network-related concepts requires a focused approach to studying key topics, especially when dealing with complex configurations and troubleshooting scenarios. Building a structured study plan will allow you to fully grasp each subject area and apply your knowledge confidently. To succeed, it’s important to focus not only on theory but also on hands-on practice to reinforce your understanding.
Here are several proven strategies that can help you master the material for this section:
- Break Down the Material: Instead of trying to study everything at once, break the topics down into smaller, more manageable sections. Focus on one concept at a time, whether it’s routing basics, IP addressing, or network security. This allows for deeper understanding and better retention.
- Utilize Practice Labs: The best way to solidify your knowledge is by setting up real-world scenarios in a lab environment. Use network simulators or actual devices to practice commands, configurations, and troubleshooting techniques.
- Review Key Commands: Familiarize yourself with essential commands used in network configuration and troubleshooting. Creating flashcards or cheat sheets with the most important commands will help you recall them during study sessions or practice tests.
- Teach Someone Else: Teaching is one of the most effective ways to reinforce what you’ve learned. Try explaining concepts or walking through network setups with a peer or study group. This can help you identify gaps in your own understanding.
- Focus on Problem-Solving: Network exams often present practical problems that require you to diagnose and solve issues. Spend time working on problem-solving exercises and troubleshooting scenarios to build your confidence in applying theoretical knowledge to real-world situations.
- Review Past Mistakes: If you’ve previously encountered difficulties with certain topics, revisit them. Identify the areas where you struggled and focus on them in your studies. Understanding why you made mistakes will help you avoid them in the future.
- Practice Timed Tests: Time management is crucial during the assessment process. Practice solving questions under timed conditions to simulate the real test environment. This helps you improve speed and accuracy while reducing exam-day anxiety.
- Stay Consistent: Consistency is key to mastering technical material. Set aside regular study sessions and make a habit of reviewing and practicing regularly. Avoid cramming and aim for steady, continuous learning to ensure long-term retention.
By applying these strategies, you will be well-prepared to tackle the material effectively, ensuring a solid foundation in the core networking concepts needed for success. Approach your studies with discipline and focus to gain both practical skills and theoretical knowledge.
Resources to Ace the CCNA Exam
To achieve success in mastering network fundamentals and advanced configurations, leveraging the right resources is key. Whether you are studying for theoretical knowledge or hands-on practice, using a mix of study materials, tools, and methods can provide you with the comprehensive understanding needed to perform well. Here’s a list of valuable resources that can guide you through the preparation process and enhance your performance.
Books and Study Guides
Books remain one of the most reliable sources of detailed, structured learning. Well-written study guides break down complex topics into digestible sections, making it easier to understand the core concepts. Consider these highly recommended books:
- “Network+ Guide to Managing and Troubleshooting Networks” by Mike Meyers – An excellent choice for beginners and those looking for a comprehensive overview of networking concepts.
- “CCNA Routing and Switching Complete Study Guide” by Todd Lammle – A detailed resource for anyone preparing for networking certifications, with in-depth coverage of the exam topics.
- “Cisco Networking Academy: CCNA Routing and Switching” by Cisco Press – The official Cisco curriculum, designed to match the requirements of the certification and provide the most up-to-date information.
Online Courses and Video Tutorials
Interactive learning through online platforms is a powerful way to reinforce theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Online courses and video tutorials offer the flexibility to learn at your own pace and provide visual demonstrations of various configurations and network setups. Recommended platforms include:
- Udemy – Offers a range of courses tailored to network professionals. Search for highly-rated CCNA courses from experienced instructors who provide quizzes, real-world examples, and practice labs.
- LinkedIn Learning – Provides video-based courses taught by industry experts. It’s perfect for both beginners and those looking to refresh specific networking topics.
- CBT Nuggets – Known for its in-depth video content and engaging instructors. This platform is ideal for those who need a more interactive learning style.
Practice Tools and Labs
Hands-on experience is essential for mastering networking configurations. Practice labs allow you to simulate real-world networking environments and troubleshoot different network issues. Here are some great tools:
- Packet Tracer – A Cisco-developed network simulation tool that lets you create complex network topologies and practice configuration tasks.
- GNS3 (Graphical Network Simulator-3) – A more advanced simulator that allows you to emulate real Cisco hardware and configure more complex networking scenarios.
- Boson NetSim – A powerful network simulator with pre-configured labs and simulations designed specifically for Cisco certification preparation.
Practice Tests and Flashcards
Testing your knowledge is a crucial part of preparing for the certification. Practice tests simulate the actual test environment and help you gauge your readiness. Flashcards are also effective for memorizing key concepts and commands. Here are some great options:
- ExamCompass – Offers free practice tests and quizzes, giving you a sense of the type and format of questions that may appear on the certification.
- Quizlet – A flashcard-based tool where you can search for or create your own sets to help reinforce important terms and definitions.
- PrepAway – Provides exam practice materials, including questions and answers, to help you prepare for certification exams.
By utilizing these resources effectively, you can increase your chances of passing and understanding the necessary concepts required for a career in networking. Combining theory with hands-on practice and taking advantage of online courses and interactive tools will prepare you to succeed and thrive in the networking field.