Civics End of Course Exam Study Guide Answers

Preparing for a government and history-related assessment requires a deep understanding of key principles and structures that define the nation. Whether you’re familiarizing yourself with the foundational documents or grasping the inner workings of political systems, mastering these essential topics is crucial for success. This section is designed to help you navigate through the complexities of U.S. governance and public policy.
You’ll explore critical elements such as the framework of the U.S. government, the roles of its branches, and the significance of landmark decisions that have shaped society. A comprehensive grasp of constitutional rights, the electoral process, and the civic responsibilities of individuals will ensure you’re well-prepared for any related assessment. Understanding these concepts will not only assist in tests but also enhance your overall comprehension of the functioning of the U.S. system.
Civics End of Course Exam Study Guide Answers
To perform well on a U.S. government-related assessment, it’s essential to review key topics and understand the foundational concepts that will be covered. This section provides an overview of the most critical areas to focus on, ensuring that you grasp both the theoretical and practical aspects of governance, laws, and citizen duties. Knowing these concepts thoroughly will not only help you succeed in assessments but also provide a deeper understanding of how the nation operates.
Key Topics to Focus On
- U.S. Constitution: Familiarize yourself with the structure of the Constitution and the Bill of Rights, as well as their impact on laws and individual freedoms.
- Branches of Government: Understand the roles of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches, and how they interact to maintain checks and balances.
- Political Parties and Elections: Study the role of political parties, the election process, and how citizens engage with the electoral system.
- Citizen Rights and Responsibilities: Know the rights guaranteed to individuals under the Constitution and the civic duties expected of U.S. citizens.
- Landmark Court Cases: Learn about significant court decisions that have shaped the interpretation of laws and civil rights in the country.
Effective Test Preparation Strategies
- Review Key Terms and Definitions: Create flashcards for important terms, such as “separation of powers,” “federalism,” and “due process.”
- Practice with Sample Questions: Familiarize yourself with multiple-choice and short-answer questions related to U.S. government principles.
- Focus on High-Yield Topics: Allocate more time to areas that are frequently tested, such as the Constitution, major amendments, and the structure of government.
- Group Study: Discuss key concepts with classmates or study partners to reinforce your understanding and fill in knowledge gaps.
- Simulate the Testing Environment: Practice answering questions under timed conditions to get comfortable with the exam format.
By focusing on these essential topics and applying effective study strategies, you will be well-equipped to perform at your best on any related assessment. A solid understanding of U.S. governance and citizen responsibilities is invaluable, not only for passing the test but also for becoming a well-informed and active participant in society.
Key Concepts for Civics Exam Success
Mastering the fundamental ideas of governance and civic participation is essential for performing well on any related assessment. The core concepts not only help you understand how the government functions but also guide you in answering questions with confidence. A strong grasp of these principles will allow you to demonstrate a clear understanding of political systems, rights, and responsibilities, all of which are crucial for success.
Focus on understanding the major principles behind U.S. governance, the structure of government, and the role of individuals in shaping policy and laws. Key topics such as the Constitution, rights afforded by it, and the balance of powers are integral to your preparation. Additionally, exploring the processes involved in elections, judicial proceedings, and public policies will further solidify your knowledge and improve your performance in the test.
Understanding U.S. Government Structure
The structure of the U.S. government is based on a system designed to ensure a balance of power among various branches and levels. This framework divides authority among different entities, ensuring that no single part of government holds too much power. By understanding how these components interact, you can gain insight into the checks and balances that are essential to maintaining a fair and effective system.
Three Branches of Government
The U.S. government is divided into three branches, each with distinct powers and responsibilities. This separation ensures that each branch can limit the others, preventing any one from becoming too dominant.
| Branch | Responsibilities | Key Powers |
|---|---|---|
| Executive | Enforces laws and administers government | Veto power, appointment of officials, foreign diplomacy |
| Legislative | Creates laws and allocates funding | Passes laws, approves budgets, declares war |
| Judicial | Interprets laws and resolves disputes | Judicial review, ruling on constitutionality of laws |
Federalism and State Power
Another key feature of the U.S. system is the division of power between the national and state governments. This is known as federalism. While the federal government handles national concerns, state governments manage local issues. Understanding the interaction between federal and state authorities is essential to recognizing how decisions are made and implemented in the U.S.
Foundational Principles of Democracy
The principles that form the backbone of a democratic system ensure that all citizens have a voice in the governance of their nation. These fundamental concepts focus on equality, liberty, and justice, aiming to create a system where individuals’ rights are protected, and their participation in political life is both encouraged and valued. Understanding these key principles is essential for navigating the political system and engaging as an informed citizen.
Core Values of Democracy
- Popular Sovereignty: The government’s power comes from the people, who elect their leaders and participate in decision-making.
- Rule of Law: All individuals, including government officials, are subject to the law, ensuring fairness and accountability.
- Equality: Every citizen has the same rights and protections under the law, regardless of status or background.
- Individual Rights: The protection of basic freedoms such as speech, assembly, and religion is a key feature of democratic systems.
Participation and Representation
- Free Elections: Citizens have the right to vote without coercion, ensuring that their choices reflect their preferences.
- Representative Government: Elected officials represent the interests of the people and make decisions on their behalf.
- Active Participation: Democracy encourages citizens to be actively engaged, not just through voting but also by engaging in public discourse and community activities.
By understanding and embracing these foundational principles, individuals can more effectively contribute to the democratic process and ensure that their rights and responsibilities are respected within the system.
Constitution and Bill of Rights Overview
The Constitution serves as the foundational legal document that outlines the framework of the U.S. government and the principles that guide its operations. It defines the roles and powers of the three branches of government while ensuring that individual rights are protected. The Bill of Rights, the first ten amendments to the Constitution, further safeguards the liberties of citizens, making it essential to understanding the country’s commitment to freedom and justice.
Together, these documents not only lay out the structure of the government but also enshrine key protections for individuals. The Constitution provides the system through which laws are made, interpreted, and enforced, while the Bill of Rights explicitly limits the power of government to ensure that personal freedoms such as freedom of speech, religion, and assembly are upheld.
Key Features of the Constitution: It establishes the government’s system of checks and balances, the separation of powers between the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, and outlines the federal structure that divides authority between national and state governments.
Highlights of the Bill of Rights: These amendments guarantee essential freedoms such as freedom of speech, the right to bear arms, protection from unreasonable searches, and the right to a fair trial, among others. They were added to address concerns that the original Constitution did not adequately protect individual rights.
Branches of Government Explained
The structure of the U.S. government is designed to ensure a separation of powers among three distinct branches. Each branch has its own set of responsibilities and powers, and they work together to govern the nation while preventing any one branch from becoming too powerful. This system of checks and balances ensures that decisions are made fairly and that the rights of citizens are protected.
The three branches of government are the Executive, Legislative, and Judicial. The Executive branch is responsible for implementing and enforcing laws, the Legislative branch creates laws, and the Judicial branch interprets them. By distributing powers in this way, the Constitution ensures that no single part of government can dominate the others, fostering a balanced and accountable system.
Important Amendments to Remember
Amendments to the Constitution play a critical role in shaping the rights and freedoms of individuals within the nation. These changes serve to expand or clarify existing laws, often responding to societal changes or addressing issues that arise over time. Understanding the most significant amendments is essential for grasping how the nation’s legal framework has evolved to ensure justice and protect individual liberties.
Several amendments stand out as particularly impactful, as they guarantee fundamental rights such as freedom of speech, the right to vote, and protection from discrimination. These provisions have had lasting effects on American society and continue to guide legal decisions and public policy today.
Role of the Electoral System
The electoral system plays a crucial role in determining how leaders are chosen and how public policy is shaped in a democratic society. This system provides the mechanism through which citizens can express their preferences and participate in the selection of government officials. It ensures that political power is distributed in a way that reflects the will of the people, while maintaining the integrity of the election process.
How Elections Shape Government
At its core, the electoral process enables individuals to have a say in who represents them at local, state, and national levels. Elections are the means by which government officials are selected, and the results influence legislation, public policy, and national priorities. Through voting, citizens actively contribute to the direction in which their society moves.
Key Components of the Electoral System
- Voting Rights: Ensuring that all eligible citizens can participate in the voting process is fundamental to a functioning electoral system.
- Political Parties: Political parties play a key role in organizing candidates and shaping the policy debate during elections.
- Electoral Process: The structure of the elections, including how votes are cast, counted, and how representatives are chosen, is essential for ensuring fairness and transparency.
Electoral Integrity: For the system to remain legitimate, it is vital that elections are conducted with transparency and fairness, and that all voters’ voices are heard equally.
Historical Events Shaping U.S. Policy
Throughout the history of the United States, significant events have played a pivotal role in shaping the nation’s policies and governing principles. These key moments have led to changes in the legal, economic, and social frameworks, influencing both domestic and international affairs. Understanding these historical events provides valuable insights into the development of the current political landscape and the evolution of the country’s priorities.
Key Events Influencing U.S. Policy
- The American Revolution: The fight for independence from Britain established the foundational principles of self-governance and individual rights, which continue to shape the nation’s policy decisions.
- The Civil War: The conflict over slavery and states’ rights resulted in significant shifts in policy, particularly in terms of civil rights, federal authority, and the abolition of slavery.
- The Great Depression: The economic collapse of the 1930s led to the creation of social safety nets, financial regulations, and a more active federal government in managing the economy.
- World War II: The war catalyzed global leadership roles for the U.S., fostering the development of policies related to international relations, military expansion, and economic recovery.
- The Civil Rights Movement: In the 1960s, the push for racial equality and justice led to groundbreaking legislation, including the Civil Rights Act and the Voting Rights Act, reshaping U.S. social policies.
Impact on Modern Policies
These historical events not only influenced the immediate political context but also set the stage for current debates on issues such as civil liberties, economic justice, and global leadership. The policies developed in response to these events continue to influence how the government addresses new challenges and opportunities in the present day.
Rights and Responsibilities of Citizens
In a democratic society, individuals are granted certain freedoms and privileges that allow them to participate fully in the governance of the nation. These rights empower citizens to engage with the government, express their views, and protect their personal freedoms. However, with these rights come certain duties and obligations that ensure the system functions fairly and effectively for all. Understanding the balance between individual rights and societal responsibilities is essential for maintaining a just and orderly society.
Key Rights of Citizens
- Freedom of Speech: The right to express opinions without fear of government censorship or punishment.
- Right to Vote: Citizens have the right to participate in the selection of their leaders through free and fair elections.
- Right to Assemble: The ability to gather peacefully for protests, demonstrations, or meetings to voice collective opinions.
- Freedom of Religion: The right to practice, change, or abstain from any religious belief without government interference.
Key Responsibilities of Citizens
- Obeying Laws: Citizens must follow the laws of the country to maintain order and protect the rights of others.
- Paying Taxes: Contributing to the government’s funding for public services, infrastructure, and defense.
- Serving on Juries: When called upon, citizens must serve as jurors in legal proceedings to ensure justice is served.
- Voting: Participating in elections is not only a right but a civic responsibility to help shape the direction of the nation.
Judicial System and Court Cases
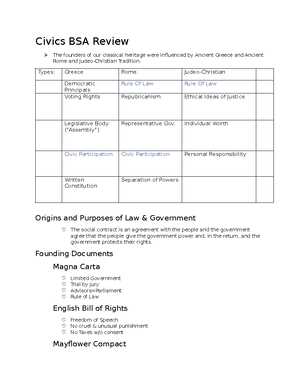

The judicial system plays a fundamental role in interpreting and applying the law, ensuring that justice is served within the framework of the nation’s legal structure. Through court cases, the judiciary resolves disputes, addresses constitutional issues, and ensures that laws are upheld in a fair and consistent manner. The decisions made in these cases can have profound impacts on the rights of individuals and the broader direction of the country’s legal and social policies.
Key Components of the Judicial System

- Courts: The system consists of various levels, from local courts handling minor cases to federal courts that address issues of national importance.
- Judges and Justices: Individuals who preside over legal proceedings and make rulings based on the law and precedents.
- Legal Counsel: Lawyers represent individuals or the government, presenting evidence and arguments to advocate for a particular outcome.
- Jury System: In many cases, a group of citizens is selected to determine the outcome based on the facts presented during the trial.
Landmark Court Cases
- Brown v. Board of Education: This 1954 Supreme Court case declared racial segregation in public schools unconstitutional, significantly advancing civil rights in America.
- Roe v. Wade: A landmark decision in 1973 that recognized a woman’s constitutional right to choose an abortion, fundamentally altering reproductive rights in the U.S.
- Marbury v. Madison: A 1803 case that established the principle of judicial review, allowing courts to review the constitutionality of laws and actions taken by the government.
- Miranda v. Arizona: This case led to the establishment of the “Miranda rights,” requiring law enforcement to inform individuals of their rights during an arrest.
Judicial System and Court Cases
The judicial system plays a fundamental role in interpreting and applying the law, ensuring that justice is served within the framework of the nation’s legal structure. Through court cases, the judiciary resolves disputes, addresses constitutional issues, and ensures that laws are upheld in a fair and consistent manner. The decisions made in these cases can have profound impacts on the rights of individuals and the broader direction of the country’s legal and social policies.
Key Components of the Judicial System
- Courts: The system consists of various levels, from local courts handling minor cases to federal courts that address issues of national importance.
- Judges and Justices: Individuals who preside over legal proceedings and make rulings based on the law and precedents.
- Legal Counsel: Lawyers represent individuals or the government, presenting evidence and arguments to advocate for a particular outcome.
- Jury System: In many cases, a group of citizens is selected to determine the outcome based on the facts presented during the trial.
Landmark Court Cases
- Brown v. Board of Education: This 1954 Supreme Court case declared racial segregation in public schools unconstitutional, significantly advancing civil rights in America.
- Roe v. Wade: A landmark decision in 1973 that recognized a woman’s constitutional right to choose an abortion, fundamentally altering reproductive rights in the U.S.
- Marbury v. Madison: A 1803 case that established the principle of judicial review, allowing courts to review the constitutionality of laws and actions taken by the government.
- Miranda v. Arizona: This case led to the establishment of the “Miranda rights,” requiring law enforcement to inform individuals of their rights during an arrest.
Political Parties and Ideologies
Political parties and ideologies play a pivotal role in shaping the political landscape of a nation. These groups and belief systems help define how governments are formed, how policies are created, and how citizens engage in the democratic process. Political parties represent a collective set of values, ideas, and goals that seek to influence the way a country is governed. Ideologies, on the other hand, offer frameworks for understanding society, economics, and governance, guiding the actions of individuals and parties alike.
Major Political Ideologies
- Liberalism: Advocates for social progress, governmental intervention in the economy, and protection of civil liberties.
- Conservatism: Emphasizes tradition, individual responsibility, and limited government intervention in the economy.
- Socialism: Focuses on reducing inequality through government control or regulation of key industries and wealth redistribution.
- Libertarianism: Prioritizes individual freedoms, minimal government intervention, and free-market economics.
Political Party Breakdown
| Party | Ideology | Core Values |
|---|---|---|
| Democratic Party | Liberal | Social equality, environmental protection, expanded government services |
| Republican Party | Conservative | Limited government, individual freedom, economic growth through free-market policies |
| Green Party | Progressive | Environmental sustainability, social justice, non-violence |
| Libertarian Party | Libertarian | Maximum individual liberty, free-market capitalism, minimal government interference |
Electoral Process and Voting Laws
The process of selecting representatives and leaders in a democratic society is deeply tied to the rules and regulations governing how votes are cast and counted. These procedures ensure that elections are free, fair, and transparent, allowing citizens to express their preferences and shape the future of their government. Understanding the electoral system, as well as the various laws that regulate voter eligibility, participation, and the conduct of elections, is crucial for informed civic engagement.
Key Aspects of the Electoral Process
- Voter Registration: Citizens must register to vote in order to participate in elections. Each jurisdiction has specific requirements regarding registration deadlines, methods, and eligibility.
- Voting Methods: Voting can take place in person, by mail, or electronically, depending on the rules set by local authorities.
- Polling Locations: Designated areas where voters can cast their ballots, which are typically open on election day for a set number of hours.
- Election Results: After ballots are collected and counted, the results are publicly announced, determining the outcome of the election.
Important Voting Laws

- Voting Age: Most countries, including the United States, set a minimum voting age, typically 18 years old, to ensure that only eligible individuals can participate in elections.
- Voter ID Laws: Some jurisdictions require voters to present a valid identification at the polls to verify their identity and prevent fraud.
- Felon Disenfranchisement: In certain regions, individuals convicted of felonies may lose their right to vote, either temporarily or permanently.
- Absentee Voting: Allows eligible voters to vote by mail if they are unable to go to a polling location on election day due to illness, travel, or other reasons.
Influence of Interest Groups

Interest groups play a pivotal role in shaping public policy by advocating for specific issues, policies, or causes that align with their members’ interests. These organizations aim to influence the decisions of lawmakers, government officials, and the public by using various strategies, from lobbying to public campaigns. Their presence in the political landscape is crucial as they serve as a bridge between the government and the citizens, representing various sectors such as business, labor, environmental, or social causes.
Methods of Influence
- Lobbying: One of the primary tools used by interest groups to influence policy is lobbying, where they directly engage with lawmakers and government officials to advocate for their positions.
- Public Campaigns: Many groups engage in media campaigns, organizing petitions, or mobilizing citizens to raise awareness and build public support for their issues.
- Financial Contributions: Interest groups may contribute to political campaigns or political action committees (PACs), hoping to influence candidates’ positions on key issues.
- Litigation: Some groups may use the legal system to influence change, filing lawsuits to challenge laws or regulations they oppose or seeking court rulings that align with their objectives.
Impact on Policy Making
- Policy Shaping: Through continuous advocacy and engagement with policymakers, interest groups can significantly shape the direction of legislation, often leading to new laws or amendments to existing ones.
- Public Awareness: By educating the public on important issues, interest groups can create a more informed electorate, which may influence voting behavior and public opinion on critical topics.
- Representation of Minority Interests: Interest groups can serve as advocates for underrepresented or marginalized communities, ensuring that their needs and concerns are addressed in the policy-making process.
Public Policy and Civic Participation
Public policy is the framework that governs decisions and actions aimed at addressing societal issues, often shaped by the collective input of citizens, organizations, and government institutions. Effective policy-making is closely linked to active civic participation, as individuals and communities play a vital role in influencing the direction of laws, regulations, and governmental actions. The relationship between policy and participation reflects the importance of an engaged and informed citizenry in shaping the democratic process.
Ways Citizens Can Influence Public Policy
- Voting: Voting in elections is one of the most direct forms of civic participation, allowing individuals to have a say in the selection of leaders and the direction of policies that affect their lives.
- Advocacy: Citizens can engage in advocacy by raising awareness, contacting lawmakers, or organizing movements to promote causes they care about, ultimately shaping public discourse and policy outcomes.
- Public Demonstrations: Protests and rallies are powerful tools for individuals to express their views on important issues, often leading to policy changes or increased attention to specific concerns.
- Petitions and Campaigns: Petitioning and organizing campaigns can mobilize public support for or against specific policies, influencing lawmakers to reconsider or revise their stance on particular matters.
The Impact of Civic Engagement on Policy
- Strengthened Democracy: Active participation ensures that policies reflect the needs and desires of the population, enhancing the legitimacy and accountability of government actions.
- Informed Decision-Making: When citizens are involved in the political process, their input helps inform policymakers about the real-world effects of their decisions, leading to more effective and just policies.
- Policy Responsiveness: When citizens are vocal about their needs and concerns, it encourages governments to respond more swiftly and appropriately to emerging issues, ensuring that the policies remain relevant and effective.
Preparing for Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple choice questions are a common format that assesses knowledge on various topics, offering a selection of answers from which the correct one must be chosen. To excel in this format, it is essential to develop strategies that enhance both recall and reasoning. By practicing key techniques, you can increase accuracy and improve your chances of selecting the correct response, even when unsure of the answer.
Effective Strategies for Tackling Multiple Choice Questions
- Read the Question Carefully: Ensure that you fully understand what is being asked before reviewing the options. Pay attention to keywords such as “not,” “always,” or “except,” which can change the meaning of the question.
- Eliminate Wrong Answers: If you are uncertain about the correct answer, start by eliminating choices that are clearly incorrect. This increases your odds of selecting the right one from the remaining options.
- Look for Context Clues: Sometimes, other questions in the test may provide helpful hints that can guide you toward the correct answer for a multiple-choice question.
- Focus on Commonly Tested Themes: Pay attention to patterns in the questions. Frequently tested concepts, terms, and historical events are often revisited in different ways.
Tips to Improve Your Response Accuracy
- Don’t Rush: Take your time to think through each question. Rushing increases the likelihood of making careless mistakes.
- Consider All Options: Read through all answer choices before selecting the one you think is correct. Sometimes, the best choice is not immediately obvious.
- Stay Calm: If you encounter a difficult question, take a deep breath. Panic can impair your ability to think clearly, leading to mistakes. Stay focused on the task at hand.
- Trust Your First Instinct: In many cases, your initial answer choice is correct. If you feel confident in your first response, it’s usually best to stick with it.
Effective Test-Taking Strategies

Success in any assessment requires more than just knowledge; it also demands the right approach and mindset. Developing strong strategies can help you manage time effectively, reduce stress, and increase your chances of performing well. By implementing a series of tactical steps before, during, and after the assessment, you can improve your overall performance and approach challenges with confidence.
Key Strategies for Success
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Pre-Test Preparation | Prepare early by reviewing key concepts and practicing sample questions. Organizing your materials and studying in intervals can help reinforce memory and reduce last-minute cramming. |
| Time Management | Start by scanning the entire assessment to get an overview. Divide your time according to the weight of each section. This helps ensure that you allocate enough time for each part without rushing. |
| Read Questions Carefully | Pay attention to every word in each question, particularly any qualifiers like “always” or “never.” Misinterpreting these can lead to incorrect answers. |
| Answer What You Know First | Go through the assessment and answer the questions you’re most confident about first. This allows you to secure easy points and boosts your confidence for the more challenging ones. |
| Stay Calm and Focused | Maintain a calm mindset throughout the assessment. If a question seems difficult, take a deep breath and move on to the next one. You can always return to challenging questions later. |
Additional Tips to Keep in Mind

- Read Instructions Thoroughly: Don’t skip over the instructions. Understanding the rules and format of the assessment can help you avoid costly mistakes.
- Review Your Work: If time permits, double-check your answers. Look for any errors or questions you may have missed.
- Stay Hydrated and Rested: Make sure to get a good night’s sleep before the test and stay hydrated during the assessment. Mental clarity is essential for success.