Spongebob Scientific Method Answer Key Explained

When conducting an experiment, there are certain steps to follow in order to reach a logical conclusion. These steps provide a framework for testing ideas, gathering data, and drawing meaningful results. Whether in a classroom setting or in everyday situations, this process helps individuals explore questions and find solutions based on evidence and reasoning.
The process begins with an idea that needs testing. This idea, often in the form of a prediction, serves as the foundation for an investigation. Once the idea is established, experiments are designed to test its validity, followed by careful observation and analysis. The final stage involves examining the data collected to determine whether the initial hypothesis was correct or needs adjustment.
Understanding how to approach this process can significantly improve critical thinking skills. It teaches individuals to approach problems systematically, focusing on facts and evidence rather than assumptions. This method is not only essential in academic studies but also useful in making informed decisions in everyday life.
Understanding the Experimentation Process with Spongebob
In the world of discovery and exploration, there are structured ways to investigate ideas and find answers to questions. By following a clear sequence of steps, it’s possible to test concepts, collect information, and come to conclusions based on evidence rather than assumptions. This approach helps individuals think critically and solve problems effectively in various contexts, whether it’s for fun or learning.
Through entertaining scenarios and hands-on challenges, the characters of the show engage in experiments that demonstrate how to explore new possibilities. By observing their journey, viewers learn how to pose questions, test hypotheses, gather data, and draw conclusions. Each stage in the process is crucial, helping to refine thinking and understand the cause-and-effect relationships that shape the outcomes.
By applying this approach to everyday situations, anyone can develop a deeper understanding of how things work. The process is not limited to academic settings but extends to personal discovery, allowing individuals to make more informed decisions and form stronger reasoning skills.
What is the Process of Investigation?
The process of investigation involves a series of steps designed to explore ideas, test predictions, and arrive at conclusions based on evidence. It begins with identifying a question or problem, followed by forming an educated guess, conducting experiments, and analyzing the results. This organized approach ensures that findings are based on facts and not assumptions, providing a reliable way to learn about the world around us.
At its core, this process encourages curiosity, experimentation, and systematic analysis. Each phase builds upon the previous one, helping to clarify ideas and guide the exploration of new concepts. The goal is to find logical answers that can be consistently repeated and verified by others.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Observation | Identify a question or problem that needs exploring. |
| 2. Hypothesis | Form an educated guess or prediction about the outcome. |
| 3. Experiment | Test the hypothesis through controlled experiments. |
| 4. Data Collection | Gather and record results from the experiments. |
| 5. Conclusion | Analyze the data to determine whether the hypothesis was correct. |
By following these steps, individuals are able to approach problems in a structured and effective manner, ensuring that their conclusions are based on solid evidence and logical reasoning.
Key Steps in the Experiment
When conducting an experiment, several important steps guide the process to ensure that the results are meaningful and reliable. These steps help organize the exploration, allowing for clear objectives and thorough investigation. Each phase plays a critical role in forming valid conclusions that are based on data rather than assumptions or guesses.
The process typically starts with identifying a question or problem that needs to be solved, followed by creating a prediction or hypothesis about the outcome. Afterward, experiments are designed to test that prediction, and data is collected to assess the results. Finally, the data is analyzed to determine whether the hypothesis is supported or if adjustments are needed.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Identify the Problem | Recognize an issue or question that requires investigation. |
| 2. Form a Hypothesis | Make an educated guess about what will happen based on prior knowledge. |
| 3. Plan the Experiment | Design a test that will help verify the hypothesis in a controlled setting. |
| 4. Collect Data | Observe and record results from the experiment to gather valuable information. |
| 5. Analyze the Results | Review the data to determine if the hypothesis was accurate or needs revising. |
By following these organized steps, any experiment becomes a clear, logical process, allowing for reliable conclusions that can be tested and repeated to verify their accuracy.
How Hypothesis Testing is Applied
Hypothesis testing is a crucial step in validating ideas and ensuring that conclusions are based on evidence. By proposing a possible explanation and testing it through experiments, it’s possible to determine whether the initial assumption holds true. This approach allows for the objective evaluation of a hypothesis and provides insight into how to refine or adjust the idea based on the findings.
In an experimental setting, the key to successful hypothesis testing lies in designing tests that are focused and measurable. By clearly identifying variables and controlling outside factors, one can observe whether the outcome aligns with the prediction. The process involves several stages, from formulating a hypothesis to analyzing the data to draw logical conclusions.
Steps in Hypothesis Testing
- Formulating a Hypothesis: Start by making an educated guess based on available information.
- Designing the Experiment: Set up an experiment to test the hypothesis with measurable outcomes.
- Running the Test: Carry out the experiment while controlling variables that might affect the results.
- Observing the Results: Record data from the experiment to analyze and compare against the hypothesis.
- Drawing Conclusions: Determine if the results support or contradict the initial hypothesis.
Practical Considerations
When testing a hypothesis, it is essential to remain open to new information and be prepared to modify the hypothesis if needed. The goal is not just to prove an idea right but to explore and learn through systematic testing. This flexibility ensures that the process remains rigorous and valuable in drawing accurate conclusions.
Analyzing Observations in the Experiment
Once an experiment is complete, the next crucial step is to carefully examine the data and observations gathered. This analysis helps determine whether the results support the initial hypothesis or whether adjustments are needed. By focusing on the details and looking for patterns or inconsistencies, researchers can draw meaningful conclusions that contribute to a deeper understanding of the experiment’s subject.
The process of analyzing observations involves comparing the expected outcomes to what was actually observed. This comparison helps identify any discrepancies, allowing for further exploration of why certain results occurred. It is important to be thorough in documenting all findings, even those that might seem insignificant, as they can lead to important insights.
Key Points to Consider During Analysis
- Consistency: Look for patterns in the data to see if results are repeatable under similar conditions.
- Unexpected Results: Identify any outcomes that deviate from what was predicted and explore possible reasons.
- Variables: Consider how changes in different factors may have affected the results.
- Data Accuracy: Ensure that the data collected is accurate and free from errors.
Making Sense of the Findings
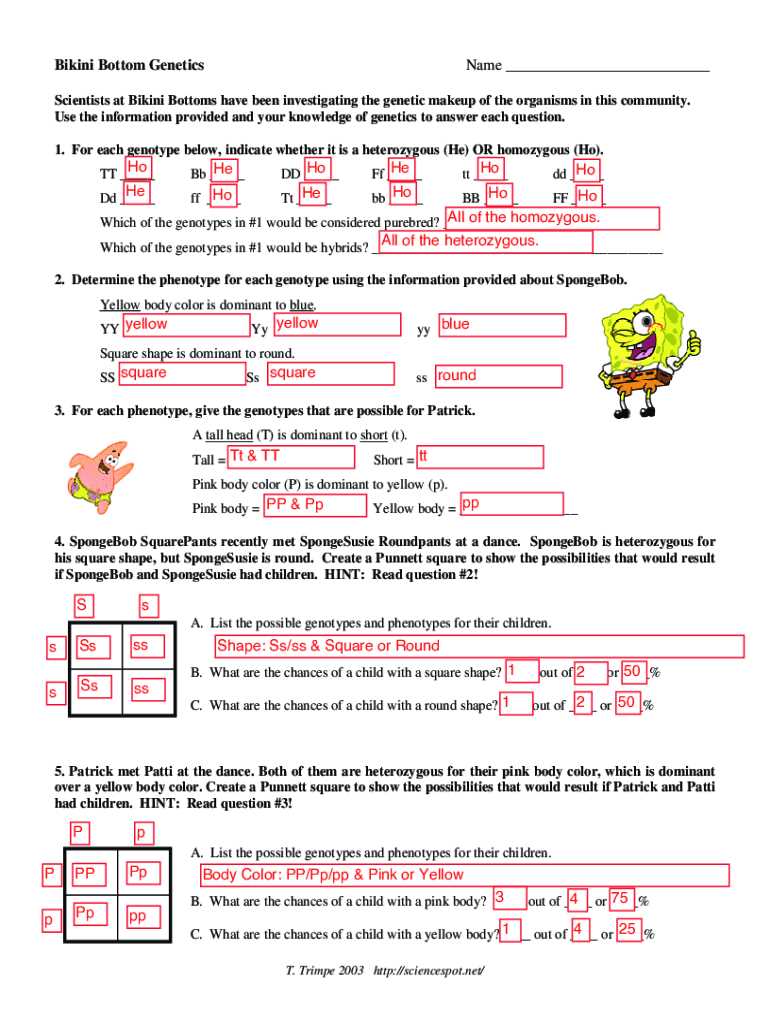
After analyzing the data, the next step is to interpret the findings and draw conclusions. This involves determining whether the hypothesis was supported or if it needs to be revised. The analysis not only answers the original question but also opens the door for new inquiries, helping to refine understanding and guide future experiments.
Experimentation Techniques Used by Spongebob
When it comes to testing ideas and solving problems, a variety of techniques can be employed to gather information and draw conclusions. The key to successful experimentation lies in designing tests that are structured and manageable, ensuring that the results are both reliable and informative. By following a consistent approach, individuals can observe cause-and-effect relationships and understand how different factors influence the outcome.
In the context of his many adventures, the character engages in a range of experiments, often involving creative solutions and unexpected challenges. The key techniques used in these experiments involve carefully controlling variables, setting clear objectives, and documenting the process and results in an organized manner. These techniques are essential for producing meaningful data and drawing accurate conclusions.
Core Experimentation Techniques
- Controlled Variables: Ensuring that certain factors remain constant while only one variable is changed during testing.
- Clear Hypothesis: Establishing a clear prediction or assumption about what will happen during the experiment.
- Repeatability: Conducting the experiment multiple times to ensure that results are consistent and reliable.
- Data Collection: Gathering and recording detailed observations throughout the experiment to analyze later.
Practical Applications of Experimentation
The real value of these techniques is seen when the data is analyzed and used to improve understanding. By applying these principles to everyday situations, it becomes easier to approach problems methodically, ensuring that conclusions are based on facts rather than assumptions. Experimentation provides a way to explore new possibilities and find solutions that might not have been immediately obvious.
How to Create Your Own Experiment
Designing your own experiment can be an exciting and rewarding way to explore new ideas and test predictions. By following a structured approach, you can ensure that the results are accurate and meaningful. The key is to develop a clear plan that allows you to test your hypothesis while controlling for factors that could influence the outcome.
The process begins with identifying a question or problem that you want to explore. Once you have your question, the next step is to form a hypothesis–an educated guess about what you expect to happen. After that, you can create a detailed plan for testing your idea, making sure to collect data carefully and observe your results. The more organized you are, the clearer your findings will be.
Steps to Create an Experiment
- Identify the Problem: Choose a question or issue that is both interesting and testable.
- Formulate a Hypothesis: Make a prediction about what you expect to happen based on prior knowledge or observations.
- Design the Test: Plan the procedure carefully, deciding on the variables to test and how to control them.
- Collect Data: Carry out the experiment, recording the data accurately and consistently.
- Analyze the Results: Examine the data to determine if the hypothesis was supported or if further testing is needed.
Tips for Successful Experiments
Be prepared for unexpected results: Experiments don’t always go as planned, and that’s okay. Be open to learning from any surprises you encounter.
Repeat the process: Conducting multiple tests can help confirm your findings and ensure that your results are reliable.
Stay organized: Keep detailed notes and record everything, from the steps you took to the observations you made, to help analyze the data later.
Examples of Successful Experiments
Experimentation often leads to surprising and rewarding outcomes, especially when the process is approached with creativity and attention to detail. Through various trials, different experiments can yield successful results that not only prove a hypothesis but also lead to new discoveries. The key to success lies in understanding the variables involved and ensuring the right conditions are in place for the experiment to succeed.
Several examples highlight how even in unusual or challenging scenarios, experimenting with the right approach can bring about unexpected successes. Whether solving problems in daily life or exploring new ideas, these experiments serve as valuable lessons in learning how to test assumptions and adapt to changing circumstances.
Experiment 1: The Jellyfish Catching Challenge
In one experiment, an attempt was made to catch jellyfish using various tools and techniques. By controlling for environmental factors such as water depth, current speed, and equipment type, the experiment successfully identified the most effective method. The results were surprising, as the previously assumed methods were not as successful as expected. This experiment demonstrated the importance of testing different variables to find the optimal solution.
Experiment 2: The Krabby Patty Recipe Test
Another experiment involved testing different ingredients to improve the flavor of a famous recipe. By systematically changing one ingredient at a time while keeping others constant, the experiment found that a small change in seasoning led to a significant improvement in taste. This experiment showcased how even minor adjustments in a controlled environment can lead to major improvements in the end result.
The Importance of Variables in Experiments
In any experiment, understanding and controlling the various factors that can influence the results is crucial. These factors, known as variables, play a significant role in determining the outcome of the test. By carefully managing these elements, researchers can ensure that the conclusions drawn are accurate and reliable. Whether they are being manipulated or kept constant, variables must be identified and considered at every stage of the experiment.
There are different types of variables that need to be accounted for, and each has its own impact on the experiment. Some variables can be controlled to isolate their effect, while others may change naturally during the testing process. The challenge lies in understanding how these factors interact and how their influence can be measured or minimized to achieve the most valid results.
Types of Variables
- Independent Variables: These are the factors that are deliberately changed or manipulated to observe their effect on other variables.
- Dependent Variables: These are the outcomes that are measured or observed to see how they change in response to the independent variable.
- Controlled Variables: These are the factors that are kept constant throughout the experiment to ensure that the results are not influenced by outside changes.
Why Variables Matter
By carefully controlling variables, it becomes easier to identify cause-and-effect relationships and draw meaningful conclusions. This helps to avoid misleading results that could occur if important factors are overlooked or left unregulated. Additionally, understanding variables allows for greater flexibility in experimental design, as it enables researchers to adjust their approach based on initial findings and refine their hypotheses over time.
Common Mistakes in Experiments
Conducting experiments can be a rewarding yet challenging task. Even the most well-planned tests can go awry if certain mistakes are made. These errors can lead to inaccurate results, wasted resources, or missed opportunities for learning. Recognizing and avoiding common pitfalls is key to ensuring that the experiment produces reliable data and meaningful conclusions.
One of the most frequent mistakes is not properly controlling all the factors that can influence the outcome. In some cases, overlooked variables may introduce bias or confound the results. Another common error is jumping to conclusions based on limited data, without fully considering other possible explanations or conducting repeated trials to confirm the findings.
Common Errors to Avoid
- Not Controlling Variables: Failing to account for all factors that might affect the outcome can skew results and make it difficult to draw valid conclusions.
- Insufficient Data: Drawing conclusions based on too few data points can lead to misleading results, as variability may not be fully accounted for.
- Confirmation Bias: Selectively gathering or interpreting data to support a pre-existing belief rather than testing the hypothesis objectively.
- Not Repeating the Experiment: Relying on a single trial can be risky. Repeating the experiment ensures that the findings are consistent and not just a result of chance.
How to Avoid These Mistakes
Plan ahead: Ensure you have a clear hypothesis, control variables, and a detailed procedure in place before starting.
Collect enough data: Always aim to gather a sufficient amount of data to account for variability and ensure reliability.
Remain objective: Avoid bias by carefully analyzing all the data, even if it contradicts your initial hypothesis.
Testing Your Hypothesis: Approach and Strategy
Once a hypothesis is formed, testing it becomes the critical next step. The goal is to gather evidence through experimentation to either support or refute the original assumption. A well-structured test involves carefully observing the effects of different variables, ensuring that the results are measurable and meaningful. By adopting a systematic approach, it’s possible to evaluate the validity of the hypothesis and learn from the outcomes.
Testing a hypothesis requires careful planning and an open mind. Even when the expected results seem obvious, it’s important to be objective and allow the data to speak for itself. Whether the hypothesis is supported or disproven, each outcome provides valuable insights that contribute to the overall understanding of the experiment. The key is to stay flexible and adapt the testing process as new information emerges.
Steps to Effectively Test a Hypothesis

- Design a Clear Experiment: Ensure that the experiment is designed to isolate the key variable and provide data that can confirm or challenge the hypothesis.
- Collect Accurate Data: Gather data in a consistent and reliable way to ensure that the results are valid and can be analyzed meaningfully.
- Control External Variables: Make sure that all other potential factors that could influence the outcome are kept constant to avoid skewed results.
- Analyze the Results: After collecting the data, analyze it carefully to see whether it supports or contradicts the hypothesis.
Adapting the Approach Based on Results
Stay open to unexpected outcomes: If the results do not match the expected hypothesis, it’s important to review the data objectively. This may lead to a reevaluation of the original assumption or an exploration of new questions that arise from the findings.
Iterate if necessary: A single test is rarely enough. Conduct multiple trials, adjust your approach as needed, and refine your hypothesis based on the data collected.
Interpreting Data from Experiments

Once data is collected from an experiment, the next crucial step is interpreting it. The process of analyzing the results helps to determine whether the initial hypothesis is supported or refuted. Interpreting the data involves looking for patterns, trends, and relationships between variables that can provide insight into the underlying questions being tested. Proper interpretation allows researchers to draw meaningful conclusions and make informed decisions based on the evidence at hand.
Data analysis is not just about confirming expectations; it also involves considering unexpected results and determining their significance. A critical aspect of interpreting experimental data is being objective and avoiding bias. The goal is to understand what the data truly indicates, whether it aligns with the hypothesis or suggests a need for further investigation.
Steps to Effectively Interpret Experiment Data
- Examine Patterns: Look for recurring trends or correlations in the data. This can help identify the relationship between different factors being tested.
- Compare to Control Group: If applicable, compare the experimental results with a control group to assess the effect of the variable being tested.
- Use Statistical Tools: Apply statistical methods to determine whether the observed results are statistically significant and not due to chance.
- Identify Outliers: Pay attention to outliers or anomalies in the data. These can provide insights into factors that were not originally considered or could suggest errors in the experiment.
Drawing Conclusions from Data
Consider all possible explanations: Even if the results seem clear, it’s important to consider alternative explanations and test them if necessary.
Revise your hypothesis: If the data does not align with the expected outcome, use the findings to revise or refine your hypothesis and approach for further investigation.
Applying the Process of Inquiry in Everyday Life
The process of inquiry and problem-solving extends far beyond laboratory experiments and academic studies. In fact, we use similar techniques every day to make decisions, solve problems, and better understand the world around us. Whether we are trying to figure out why something isn’t working or testing a new method to improve a situation, the approach of gathering information, making assumptions, and testing those assumptions plays a crucial role in everyday problem-solving.
We often employ these steps without even realizing it, from deciding what to cook for dinner based on available ingredients, to troubleshooting a technical issue with a device. The key is recognizing that the process of forming hypotheses, testing them, and analyzing outcomes is something that can be applied to nearly all aspects of life.
Examples of Everyday Use of Inquiry

- Cooking a New Recipe: You might experiment with different ingredients or cooking techniques to see what works best and yields the best results.
- Fixing a Household Item: When something breaks, you might form a hypothesis about what went wrong, test possible fixes, and see which one works.
- Choosing the Best Route to Work: You might test different routes or methods of transportation to determine which one is fastest or most efficient.
- Improving Your Fitness Routine: Testing different workouts and tracking progress can help you find the best way to reach your fitness goals.
Benefits of Applying the Inquiry Process in Daily Life
- Improved Problem Solving: By systematically testing different approaches, you’re more likely to find effective solutions.
- Better Decision Making: When you analyze your choices and test their outcomes, you can make more informed decisions.
- Enhanced Critical Thinking: This approach encourages you to question assumptions, consider alternatives, and evaluate outcomes logically.
By incorporating the basic principles of inquiry into everyday situations, you can make more thoughtful, data-driven decisions and approach challenges with a greater sense of curiosity and confidence.
Benefits of Using the Inquiry Process

Adopting a structured approach to solving problems and testing ideas offers numerous advantages. By following a logical, step-by-step process, individuals can uncover insights, refine their understanding, and make more informed decisions. This approach helps to remove uncertainty and improve the accuracy of results, making it a powerful tool not just for scientific research, but for everyday challenges as well.
One of the primary benefits is the ability to make decisions based on evidence rather than assumptions. This systematic method encourages the collection of data, the testing of hypotheses, and the careful analysis of outcomes. It removes the guesswork and leads to more reliable conclusions. Whether you’re troubleshooting a technical issue, trying a new recipe, or making a business decision, using a methodical approach increases the chances of success.
Key Advantages of Following an Organized Process
- Improved Accuracy: Testing assumptions and gathering data ensures a more precise understanding of the problem.
- Better Problem Solving: Systematic investigation allows you to evaluate different solutions and identify the most effective one.
- Clearer Insights: By examining results, patterns become apparent, leading to a deeper understanding of the situation.
- Increased Confidence: With data supporting your conclusions, you can feel more confident in the decisions you make.
Real-Life Applications
- Making Better Choices: Whether it’s choosing the right tool for a task or determining the best route for travel, structured thinking helps weigh options effectively.
- Streamlining Processes: In professional environments, using a logical approach can optimize workflows, reduce inefficiencies, and improve outcomes.
- Innovating Solutions: By testing and iterating on ideas, new solutions and improvements are more likely to emerge.
Ultimately, using a well-organized inquiry process leads to more thoughtful, informed decisions, and fosters a deeper understanding of the world around us. Whether in personal or professional contexts, the ability to analyze, test, and refine ideas is invaluable in reaching the best possible outcomes.
How Spongebob Teaches Critical Thinking Skills
In many ways, the world of underwater adventures offers valuable lessons in developing strong problem-solving and reasoning abilities. Through challenges, experiments, and everyday situations, individuals in this world demonstrate how to approach complex issues and think critically. These examples can inspire viewers to apply similar thought processes in their own lives, improving their ability to analyze situations, weigh evidence, and come to sound conclusions.
By observing decisions and actions, viewers are encouraged to question assumptions, explore different perspectives, and assess the validity of various ideas. This type of learning environment fosters open-mindedness and creative problem-solving, key components of critical thinking. The characters’ willingness to test their ideas, embrace curiosity, and learn from their mistakes makes their world an engaging classroom for critical thinkers.
Key Lessons for Developing Analytical Skills
- Questioning Assumptions: By challenging the status quo and considering alternative explanations, critical thinkers avoid jumping to conclusions.
- Testing Ideas: Trying out different approaches and learning from the results helps to refine understanding and improve strategies.
- Learning from Mistakes: Mistakes are viewed as learning opportunities, encouraging the development of resilience and adaptability.
- Considering Different Perspectives: Understanding that there are multiple solutions to a problem enhances the ability to analyze situations from all angles.
Practical Applications in Everyday Life
- Decision Making: The ability to assess options and predict outcomes leads to more informed choices, whether at home or work.
- Problem Solving: Critical thinking allows for creative solutions to unexpected challenges, from technical issues to personal dilemmas.
- Conflict Resolution: By weighing all perspectives and considering possible outcomes, individuals can resolve conflicts more effectively.
Through the lessons learned from these characters, individuals can enhance their critical thinking abilities, applying these skills to real-world situations and challenges. Whether navigating social dynamics or approaching professional goals, the skills of questioning, testing, and analyzing are invaluable in making better, more thoughtful decisions.