Normal HEENT Exam Documentation Guide
Accurate and detailed records play a crucial role in the healthcare process. Proper documentation ensures that essential information is preserved, allowing healthcare professionals to track a patient’s condition over time and make informed decisions about their care. It serves as a reliable reference point, offering insight into both current and past health evaluations.
Each clinical evaluation, particularly those related to the head and neck area, requires careful attention to detail. Clear and concise notes are essential for reflecting the findings during a patient’s visit. This record-keeping not only facilitates communication between different healthcare providers but also guarantees that important observations are not overlooked.
Maintaining comprehensive records is vital for ensuring that healthcare standards are met and that patient care is consistently accurate. A well-structured entry can significantly impact the quality of medical services provided, making it imperative for clinicians to adopt best practices for capturing and organizing key findings.
Complete Medical Record for Head and Neck Assessments

Properly capturing key findings from a thorough head and neck evaluation is essential for maintaining an accurate medical history. The process involves recording various observations about a patient’s overall condition, which serves as a foundation for ongoing care. This information is vital for both current treatment and future consultations, ensuring that healthcare professionals can make informed decisions.
When documenting the results of such an assessment, the clinician must ensure that each detail is captured comprehensively. These records not only provide a snapshot of the patient’s health but also facilitate communication between different medical specialists involved in the patient’s care.
- Observation of the head shape and structure
- Inspection of the skin for abnormalities or lesions
- Assessment of facial symmetry and movement
- Examination of the eyes, ears, nose, and throat
- Review of any visible abnormalities in the neck area
Each of these elements must be documented clearly and accurately to provide a complete picture of the patient’s health status. A systematic approach ensures that all relevant details are included and easily accessible for future reference. This methodical record-keeping enhances the quality of care and contributes to more effective patient management.
- Note any signs of tenderness, swelling, or irregularities
- Document eye reactions, hearing ability, and throat condition
- Record any issues related to breathing or swallowing
Ultimately, having a structured system in place for organizing these observations is key to ensuring that healthcare providers can easily interpret and follow up on any concerns. The clarity and completeness of these records play a significant role in achieving better outcomes for the patient.
Overview of Head and Neck Evaluation Process
The assessment of the head and neck region is a critical part of a comprehensive physical examination. This process involves a series of steps designed to evaluate the structure, function, and overall health of the areas that play key roles in daily activities such as breathing, seeing, hearing, and swallowing. A thorough evaluation ensures that any potential issues or abnormalities are identified early, providing the foundation for further investigation or treatment.
During the evaluation, the clinician observes and palpates various structures of the head, face, eyes, ears, nose, and throat. Each of these areas is carefully examined for signs of infection, injury, or disease. The goal is to document any deviations from normal and assess how they may impact the patient’s health.
The process typically includes:
- Inspection of facial symmetry and skin condition
- Assessment of vision, hearing, and nasal passage function
- Evaluation of the oral cavity, throat, and lymph nodes
- Palpation of the neck to check for swelling, masses, or tenderness
By systematically reviewing these areas, healthcare professionals can detect early signs of conditions that may require intervention. Accurate documentation of the findings helps in monitoring any changes over time, contributing to effective patient care and treatment planning.
Key Elements in Head and Neck Assessment Records
Effective record-keeping during a head and neck evaluation requires careful attention to detail, ensuring that all relevant findings are captured for future reference. The accuracy and clarity of these notes are essential for providing high-quality care and for facilitating communication among healthcare providers. Properly documenting key observations helps to track a patient’s progress and detect any emerging issues.
Essential Observations and Measurements
In any head and neck evaluation, specific observations must be recorded to provide a comprehensive picture of the patient’s health. These typically include the appearance and symmetry of the face, the condition of the skin, and any visible abnormalities in the eyes, ears, or throat. Additionally, the clinician should note any tenderness, swelling, or masses in the neck area, as well as document findings related to hearing and vision.
Functional Assessments
Along with structural observations, it is crucial to assess the functionality of the head and neck structures. This involves evaluating the patient’s ability to move the head, perform basic functions like swallowing, and assess the reflexes related to the facial and throat regions. Documenting these functional aspects ensures that any issues related to mobility or sensory perception are addressed promptly.
Step-by-Step Head and Neck Evaluation Procedure
A comprehensive head and neck assessment is an essential part of a physical examination, involving a series of steps to evaluate the health and functionality of various structures. Each step is designed to provide detailed observations that are crucial for identifying potential issues. This process helps healthcare professionals document any abnormalities and plan appropriate follow-up care.
Initial Inspection and Palpation
The procedure begins with a general inspection of the head and neck, followed by palpation to check for any abnormalities. The clinician carefully examines the patient’s facial features, skin, and overall symmetry.
- Check for any visible asymmetry in the face and skull.
- Examine the skin for lesions, discolorations, or unusual growths.
- Palpate the neck for tenderness, masses, or swollen lymph nodes.
Detailed Functional Assessment
- Assess vision and pupil reactions to light.
- Evaluate hearing by testing the response to sound from both sides.
- Check the patient’s ability to swallow, looking for any difficulty or discomfort.
- Test reflexes in the face and neck, noting any abnormal responses.
Each of these steps should be performed methodically to ensure that no detail is overlooked. Accurate documentation of the results at each stage is essential for tracking changes over time and identifying any health concerns early on.
Importance of Accurate Head and Neck Records
Maintaining precise and comprehensive records during a head and neck evaluation is critical for ensuring effective patient care. Accurate notes provide a detailed account of the patient’s condition, offering valuable insights for ongoing management and facilitating collaboration between healthcare providers. These records not only reflect the current state of health but also serve as a reference point for any future assessments or treatments.
Ensuring Consistency in Patient Care
Well-documented observations enable healthcare professionals to track changes over time, ensuring that any new symptoms or issues are promptly addressed. Consistency in record-keeping allows clinicians to compare current findings with past assessments, leading to more accurate diagnoses and better-informed treatment decisions.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Accurate record-keeping is also crucial from a legal perspective. Properly maintained records can protect both healthcare providers and patients by ensuring that all necessary information is available if questions arise regarding care. Inaccurate or incomplete notes may result in misunderstandings and potential liability issues.
Furthermore, accurate documentation is essential for maintaining patient trust and confidentiality, ensuring that sensitive health information is correctly managed and protected at all times.
Tools and Equipment for Head and Neck Assessment
To perform a comprehensive evaluation of the head and neck region, healthcare professionals rely on a variety of specialized tools. These instruments are essential for accurately observing and assessing the structure and function of the relevant areas. Using the right equipment ensures that important details are captured and that the examination process is thorough and efficient.
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Otoscope | Used to examine the ears, including the ear canal and eardrum. |
| Ophthalmoscope | Helps in evaluating the eyes, checking for abnormalities in the retina and optic nerve. |
| Tongue Depressor | Used to press down the tongue to examine the throat and oral cavity. |
| Stethoscope | Used for listening to sounds from the lungs, heart, and other organs during a thorough check of the neck and chest. |
| Penlight | Provides focused light to examine the eyes, throat, and oral cavity. |
| Reflex Hammer | Used to check for reflexes in the face and neck to assess neurological function. |
These tools help clinicians perform a detailed assessment by providing the necessary clarity and precision to detect any irregularities. Proper usage of each instrument ensures that no aspect of the head and neck is overlooked, leading to more accurate findings and better patient outcomes.
Documenting Patient History for Head and Neck Assessments

Accurate recording of a patient’s medical history is a critical component of the evaluation process. The history provides context for understanding any current symptoms or concerns and helps clinicians make informed decisions. By gathering detailed information about past health issues, treatments, and family medical histories, healthcare providers can identify potential risks and plan appropriate interventions.
The process of documenting the patient’s history involves asking relevant questions about both general health and specific conditions related to the head, face, ears, eyes, nose, and throat. This information can help pinpoint underlying causes of discomfort or irregularities in the examination.
Key elements to include in patient history:
- Previous conditions affecting the head or neck, such as infections or injuries
- Any recurring symptoms like headaches, dizziness, or difficulty swallowing
- History of allergies or respiratory issues
- Family history of genetic conditions related to the head and neck
- Medications or treatments that may impact sensory functions
Properly documenting these details helps create a clear picture of the patient’s health, allowing healthcare providers to tailor their examination and interventions to address specific concerns. It also ensures that all relevant factors are considered in the diagnosis and care plan.
Common Findings in Routine Head and Neck Assessments
During a standard assessment of the head and neck, several typical observations are expected that indicate healthy functioning of these areas. Identifying these common findings helps ensure that the patient’s structures are functioning optimally and without any apparent issues. Understanding these standard results provides a clear baseline for any future evaluations or potential interventions.
| Area Examined | Common Findings |
|---|---|
| Face | Symmetrical features, no swelling, redness, or visible abnormalities. |
| Eyes | Pupils equal and reactive to light, no redness, no discharge. |
| Ears | No tenderness, clear ear canals, intact tympanic membranes. |
| Nose | Clear nasal passages, no signs of congestion or abnormalities. |
| Throat | Normal mucosa, no redness or swelling in the tonsils or pharynx. |
| Neck | No swelling, tenderness, or lymph node enlargement. |
These findings are considered typical in a healthy individual and serve as a reference point for identifying any deviations that may require further investigation. Recording these observations helps build an accurate clinical picture and ensures that routine evaluations are thorough and reliable.
Recording Vital Signs During the Assessment
Accurate recording of vital signs is an essential part of any physical evaluation, providing key insights into a patient’s overall health. Monitoring parameters such as temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate helps clinicians identify potential health concerns early. By documenting these signs during the assessment, healthcare providers can establish a baseline and track changes over time, aiding in diagnosis and treatment decisions.
Key Vital Signs to Record
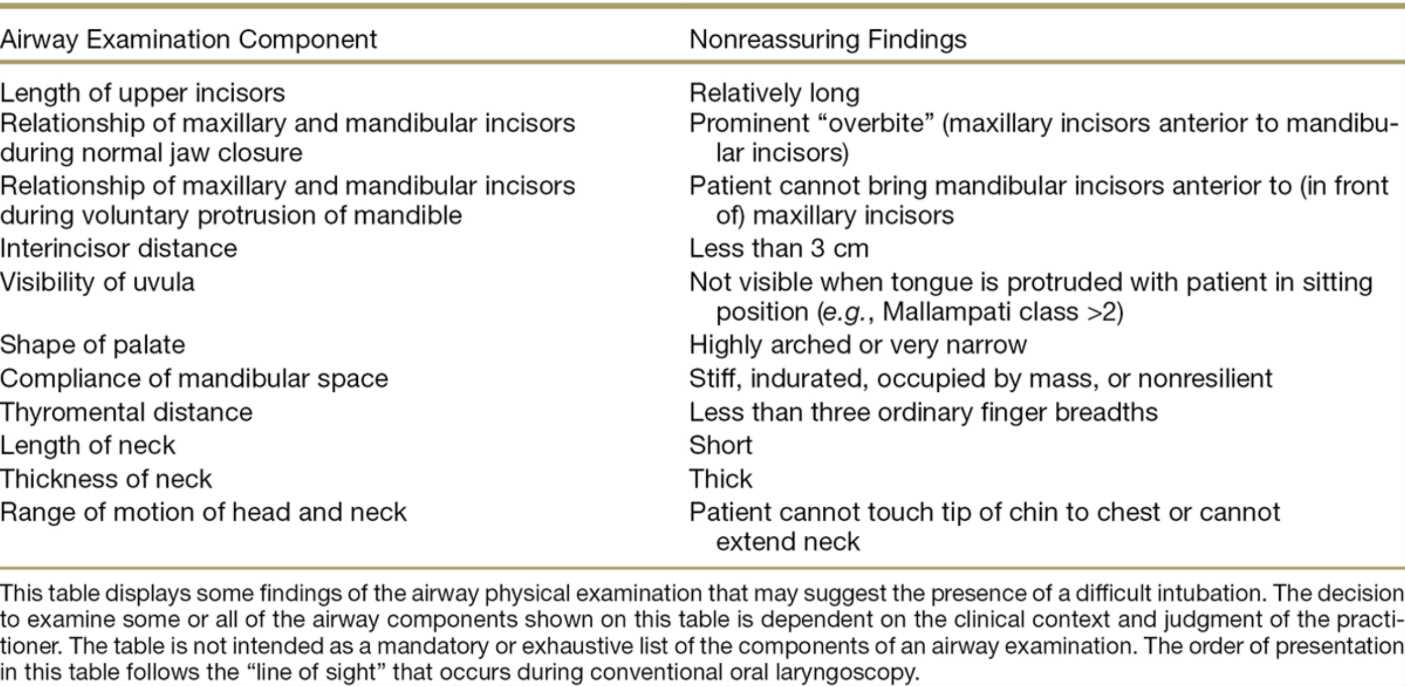
- Temperature: A measure of body heat, typically taken orally or via the ear, to check for signs of fever or infection.
- Heart Rate: The number of heartbeats per minute, evaluated to assess cardiovascular health.
- Blood Pressure: The force of blood against the arterial walls, used to identify hypertension or hypotension.
- Respiratory Rate: The number of breaths per minute, indicating the functioning of the lungs and respiratory system.
Importance of Accurate Recording
- Ensures all health parameters are closely monitored.
- Helps detect abnormal trends that may require immediate intervention.
- Provides essential data for longitudinal tracking of patient health.
- Facilitates communication between healthcare providers by having clear, consistent records.
Precise recording of these vital signs is crucial for making informed clinical decisions. It is an integral step in providing safe and effective care while offering a reliable reference for future visits or ongoing treatments.
How to Document Inspection Results

Recording the findings from a physical inspection is an important step in the evaluation process, providing a clear, objective account of observed conditions. These results serve as a vital reference for healthcare providers, helping to identify abnormalities or confirm a patient’s health status. Properly documenting inspection results ensures that all relevant details are captured, creating an accurate record for future assessments and treatment decisions.
Steps for Documenting Inspection Findings
- Observe Symmetry and Appearance: Note any visible asymmetries or abnormalities in the head, face, or neck. This could include swelling, discoloration, or structural irregularities.
- Record Skin and Tissue Conditions: Document any signs of rashes, lesions, or bruising. Pay attention to the skin texture, color, and overall health of the area.
- Check for Abnormalities: Report any unusual findings such as bulging, tenderness, or enlarged lymph nodes that may indicate an underlying issue.
- Detail Patient Behavior: If applicable, note how the patient responds to certain physical stimuli or their overall demeanor during the assessment.
Importance of Clear and Concise Documentation
- Facilitates communication between medical professionals, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
- Provides a reliable reference point for tracking any changes in the patient’s condition over time.
- Supports accurate diagnosis by documenting observable physical signs that may not be immediately obvious.
By adhering to a consistent approach to recording inspection findings, healthcare providers ensure that critical observations are not overlooked. These records serve not only as a reflection of the current health status but also as an essential tool for future medical decisions.
Best Practices for Maintaining Consistency in Records
Maintaining consistency in medical records is essential for ensuring accuracy, reliability, and clear communication among healthcare professionals. A standardized approach to recording observations, findings, and patient details enhances the quality of care and reduces the risk of errors. By following best practices, healthcare providers can ensure that their records are not only thorough but also aligned with professional standards.
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Use Standardized Terminology | Ensure that medical terms are used correctly and consistently to avoid ambiguity or confusion. |
| Document in Real Time | Record information immediately after the assessment to ensure accuracy and prevent forgetting key details. |
| Be Clear and Concise | Write clear and direct notes, avoiding unnecessary jargon or overly complex language. |
| Use Structured Formats | Adopt templates or checklists that standardize how findings are recorded, making it easier to compare records over time. |
| Review and Update Regularly | Ensure that records are reviewed for completeness and accuracy, and updated as needed based on new information. |
By adhering to these best practices, healthcare providers can improve the reliability of patient records, minimize the risk of misinterpretation, and ensure that the information can be easily shared across teams. Consistent documentation not only supports clinical decision-making but also facilitates better patient outcomes.
Examination Procedures and Patient Privacy
During any physical evaluation, maintaining patient privacy is of utmost importance. Ensuring that personal health information is protected, and that patients feel comfortable and secure, is essential for establishing trust. Healthcare providers must take extra precautions to ensure that sensitive details, especially those relating to personal health, are handled with the highest level of confidentiality.
Key Considerations for Protecting Privacy:
- Confidentiality of Health Records: All patient information, whether written or digital, must be kept secure and accessible only to authorized personnel.
- Informed Consent: Patients should be fully informed about the evaluation process and provide consent before any examination is performed.
- Respecting Physical Boundaries: Ensure that the examination is conducted in a respectful manner, with the patient’s comfort prioritized at all times.
- Proper Use of Technology: When using electronic devices to record findings, ensure that the software complies with privacy standards such as HIPAA or other relevant regulations.
Ensuring Comfort and Trust:
- Private Environment: Conduct the assessment in a quiet, private area where the patient can feel at ease.
- Patient’s Autonomy: Empower patients to ask questions and express concerns about the procedure, allowing them to remain in control of their personal space.
- Clear Communication: Explain every step of the process to the patient to reduce anxiety and reinforce the importance of their privacy.
Protecting patient privacy is not just a legal requirement but also a vital aspect of providing compassionate and ethical care. By prioritizing confidentiality and respect during any procedure, healthcare providers foster a safe environment where patients are more likely to share crucial health information and trust their providers with their well-being.
Using Templates for Recording Patient Evaluations
Templates are valuable tools for streamlining the process of recording patient assessments. By providing a standardized format, they ensure consistency and accuracy while saving time. When used effectively, templates allow healthcare professionals to focus on patient care rather than spending excessive time on documentation. These pre-structured formats guide clinicians in capturing essential information efficiently, ensuring no important details are overlooked.
Benefits of Using Templates
- Consistency: Templates help maintain uniformity across records, ensuring that all necessary information is documented consistently in every evaluation.
- Efficiency: With predefined fields and sections, templates reduce the time spent on note-taking, allowing for quicker completion without sacrificing accuracy.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Templates can be designed to include all relevant aspects of a patient assessment, ensuring that no critical information is missed.
- Reduced Errors: By following a structured format, templates help minimize the chances of missing key details or introducing inaccuracies into the record.
Effective Template Design
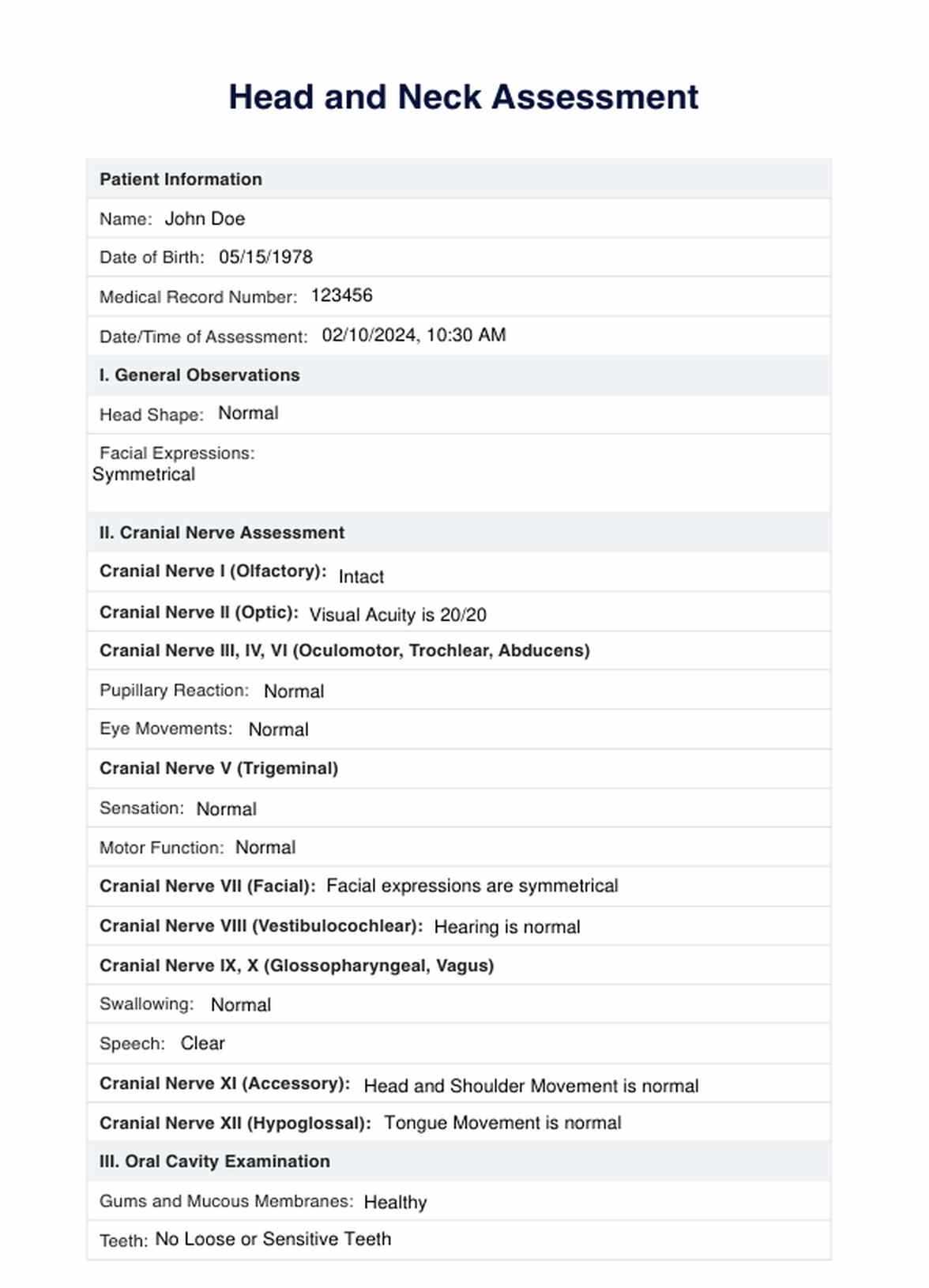
- Clear Sections: Design templates with distinct sections for each area of evaluation, ensuring clarity and ease of use during the recording process.
- Flexible Fields: Include adaptable fields that allow for customization based on individual patient needs, ensuring that templates are applicable in various situations.
- Simple Language: Use straightforward language and terms in templates to ensure ease of understanding for both healthcare providers and future readers of the record.
By integrating templates into patient evaluation processes, healthcare providers can enhance the quality and consistency of their records while reducing administrative burden. A well-designed template not only saves time but also contributes to better overall patient care by ensuring that all important aspects are consistently documented.
Reviewing the Records for Accuracy

Ensuring the precision of patient records is a crucial step in maintaining high-quality care. Inaccurate or incomplete information can lead to incorrect diagnoses, improper treatment plans, and potentially harm the patient. Regularly reviewing clinical entries for errors, inconsistencies, and omissions helps safeguard against such risks. This review process is an essential part of providing safe, effective healthcare and ensuring that patient information is both correct and comprehensive.
Key Steps in Reviewing Records
- Double-check for Completeness: Make sure all sections of the patient record are fully filled out, with no missing or ambiguous information.
- Cross-reference with Clinical Findings: Verify that all observations documented align with the physical findings and test results observed during the patient evaluation.
- Consistency Across Records: Ensure that the information recorded is consistent across all parts of the patient’s medical history and previous notes, preventing contradictions or discrepancies.
- Check for Accuracy in Terminology: Review the use of medical terminology to ensure that it is used correctly and consistently, avoiding confusion or misinterpretation.
Best Practices for Review
- Timely Review: Perform the accuracy check as soon as possible after the evaluation to ensure the information remains fresh and the context is clear.
- Peer Review: Involve other healthcare professionals in the review process, providing a second set of eyes to catch any potential errors that may have been overlooked.
- Use Technology for Support: Utilize electronic health record (EHR) systems that include built-in checks for common errors, such as missing fields or inconsistent data entries.
Regularly reviewing clinical records for accuracy not only improves patient care but also reduces the risk of medical errors and enhances the overall quality of healthcare services. By carefully ensuring that every detail is correct, healthcare providers can confidently rely on the records for informed decision-making and better patient outcomes.
Legal Considerations in HEENT Documentation
Properly recording patient interactions and findings is not only vital for clinical decision-making, but also for safeguarding against legal issues. Accurate and thorough medical records serve as a critical piece of evidence in case of disputes or legal claims. Health professionals must be aware of the legal implications of their written reports, as incomplete or incorrect documentation can lead to serious consequences, including malpractice suits. Ensuring adherence to legal standards is essential for protecting both the patient and the healthcare provider.
Key Legal Aspects to Consider
- Confidentiality: Patient information must be kept private and only shared with those who are authorized. Healthcare providers must comply with privacy laws such as HIPAA to protect patient data.
- Accuracy: Legal challenges can arise if the recorded information is inaccurate or misleading. Always ensure that findings are clearly documented, without alteration or omission.
- Timeliness: Records should be made promptly after a patient visit to ensure that details are fresh and accurately captured. Delays in documentation may lead to discrepancies that could harm the credibility of the record.
- Legibility: Records must be legible, whether handwritten or electronic, to prevent any misinterpretations that could affect patient care or legal outcomes.
Best Practices for Legal Compliance
- Use Standardized Terminology: Avoid ambiguous terms. Using accepted medical language reduces the risk of confusion and legal disputes.
- Document Decisions and Rationale: Always record the reasoning behind clinical decisions, including the consideration of alternative diagnoses and treatments, to demonstrate thoughtfulness and professional judgment.
- Ensure Patient Consent: Always document the patient’s informed consent, especially when performing procedures or sharing medical information with others.
Healthcare providers must understand the legal implications of their documentation practices. By following established guidelines for accuracy, privacy, and clarity, medical professionals can mitigate risks and ensure they are fully compliant with the law. This vigilance not only protects the provider but also ensures the patient’s rights and safety are upheld.
Common Mistakes in HEENT Documentation
Accurate record-keeping is essential for ensuring proper patient care and minimizing the risk of legal issues. However, healthcare professionals often make errors when documenting findings related to head, eyes, ears, nose, and throat assessments. These mistakes can compromise the clarity of the patient’s medical history, hinder diagnosis, and even lead to negative clinical outcomes. Understanding and avoiding common pitfalls can help improve the overall quality and reliability of health records.
Common Errors to Avoid
- Omitting Key Information: Failing to include vital details, such as specific symptoms or patient concerns, can lead to incomplete assessments. Always ensure that no critical information is left out during documentation.
- Using Ambiguous Language: Vague or non-specific terms can lead to confusion. It’s important to be clear and precise in describing symptoms, findings, and diagnoses to avoid misinterpretations.
- Inconsistent Terminology: Using different terminology for the same condition or symptom can create confusion. Standardizing the language used in medical records helps maintain clarity and consistency.
- Failure to Document Findings Promptly: Delayed documentation can result in forgotten details or inaccuracies. It’s essential to record findings immediately after the patient encounter to ensure accuracy.
Best Practices for Avoiding Mistakes
- Be Thorough: Document all relevant findings, including negative results. This ensures that a complete picture of the patient’s health is captured.
- Use Clear and Concise Language: Avoid jargon or unclear descriptions. Use precise and universally understood medical terms to document symptoms and findings.
- Review and Revise: Always double-check your documentation before finalizing it. Reviewing notes can help identify any overlooked details or unclear sections.
- Use Templates When Possible: Standardized templates can help reduce errors and ensure that all relevant information is included in the record.
By being mindful of these common mistakes and adopting best practices, healthcare professionals can improve the quality of their patient records and ensure that the documentation process supports effective clinical decision-making.
Benefits of Digital HEENT Documentation Systems
In modern healthcare, the transition from paper-based records to digital systems has significantly enhanced the efficiency and accuracy of medical record-keeping. Digital systems for capturing and managing patient assessments offer numerous advantages, ranging from improved accessibility to better data security. These systems streamline the process of recording, storing, and retrieving important patient information, enabling healthcare professionals to deliver more efficient and precise care.
The use of digital systems ensures that data is easily accessible and can be shared across different departments and facilities. This leads to faster decision-making and reduces the chances of errors or omissions in patient care. Below are some of the key benefits of using digital platforms for recording medical findings.
Key Advantages of Digital Systems
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Accuracy | Digital systems help reduce human errors by providing templates and pre-defined fields, ensuring that all necessary information is documented correctly. |
| Enhanced Accessibility | With digital records, healthcare professionals can quickly access patient information from anywhere, making it easier to provide timely care. |
| Better Organization | Electronic systems help organize records in a logical and structured way, making it easier to search and retrieve specific patient data when needed. |
| Improved Communication | Digital records can be easily shared among different departments or specialists, fostering better collaboration and coordination in patient care. |
| Data Security | Digital systems offer stronger security measures, including encryption and access controls, ensuring patient information is protected from unauthorized access. |
| Time Efficiency | Healthcare providers can save time by eliminating the need to manually search through paper records and can update patient information instantly. |
Adopting digital systems for patient assessments not only enhances the efficiency and accuracy of record-keeping but also contributes to higher quality care. These tools enable healthcare professionals to focus more on patient needs and less on administrative tasks, leading to improved outcomes and better patient satisfaction.