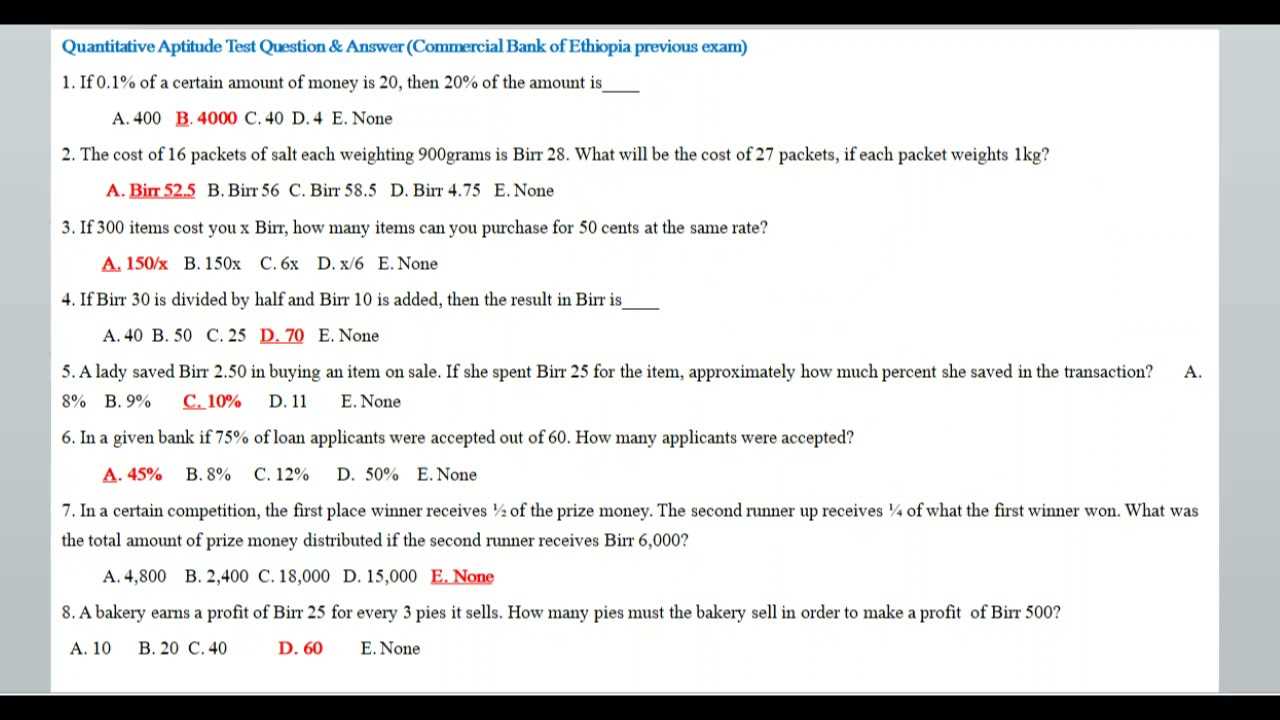
Aptitude Questions with Answers for Bank Exams

Mastering numerical reasoning and problem-solving is a key aspect of succeeding in competitive assessments. These skills are essential to tackle a variety of tasks that require quick thinking and a clear understanding of mathematical concepts. Preparing efficiently involves practicing a range of exercises that not only test your ability to solve problems but also your speed and accuracy under pressure.
Through consistent practice, candidates can improve their problem-solving skills and develop the mental agility needed to excel in timed challenges. It is crucial to understand different problem types and their solutions, as this helps in quickly recognizing patterns and applying the correct methods. Strong foundational knowledge, combined with strategic practice, can make a significant difference in performance.
Structured practice plays a significant role in building the confidence needed to tackle more complex challenges. Focusing on time management, precision, and problem-solving strategies can greatly enhance your ability to handle unexpected or tricky questions during the assessment process. With the right approach, success in these assessments becomes much more attainable.
Aptitude Questions with Answers for Bank Exams
Preparing for competitive assessments involves tackling a wide range of numerical problems that test your logical thinking and problem-solving skills. These tasks often require a solid understanding of mathematical principles and the ability to apply them quickly and accurately. Whether it’s dealing with basic calculations or more complex scenarios, each type of problem has a set of strategies that can lead to efficient solutions.
It is important to practice different problem types regularly to improve speed and accuracy. By solving similar exercises, you begin to recognize patterns and develop a systematic approach that can be applied to new challenges. Mastery of key concepts such as percentages, ratios, time, and distance allows you to approach any question with confidence and precision.
As you progress, it’s essential to test yourself under exam-like conditions to simulate the pressure of time constraints. This helps in managing stress and ensuring you can perform efficiently even in high-pressure situations. Success in such assessments comes down to understanding the principles behind the tasks and applying the right methods in the most efficient manner.
Understanding the Basics of Aptitude
At the core of every competitive assessment is the ability to think logically and solve mathematical challenges quickly. These tasks require a clear understanding of fundamental principles and the ability to apply them effectively in a time-sensitive environment. The foundation of such exercises often lies in basic arithmetic, number theory, and reasoning skills that need to be honed through regular practice.
Key Concepts to Master
To begin, one must first familiarize themselves with essential concepts such as ratios, percentages, and basic algebra. These form the building blocks for more complex problems and help in breaking down difficult scenarios into manageable parts. Recognizing the relationships between numbers and patterns is crucial to finding solutions efficiently.
Developing Logical Thinking
In addition to numerical skills, logical reasoning plays an equally important role. It involves recognizing patterns, drawing conclusions from given data, and applying deductive or inductive reasoning. Strengthening these cognitive abilities enables one to approach a wide variety of tasks, making the problem-solving process smoother and faster.
Regular practice and consistent learning are key to mastering the fundamentals. As one becomes more familiar with these principles, solving problems becomes more intuitive, leading to better performance under exam conditions.
Key Topics to Focus on for Bank Exams
To succeed in any competitive assessment, it’s essential to prioritize and focus on the most relevant subjects. While each test may have different patterns, certain topics tend to appear frequently and require a deeper understanding. By concentrating on these areas, candidates can significantly improve their performance and ensure that they are well-prepared for a wide range of scenarios.
| Topic | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Time and Work | Understanding how to calculate efficiency, work rates, and completing tasks in a given time frame. | High |
| Number Series | Recognizing patterns in sequences of numbers to predict the next term. | High |
| Data Interpretation | Analyzing charts, graphs, and tables to extract relevant information and solve problems. | High |
| Profit and Loss | Calculating gains, losses, and percentages in various financial scenarios. | Medium |
| Speed and Distance | Solving problems related to the movement of objects over time and distance. | Medium |
| Percentage Calculations | Understanding how to calculate percentage increases, decreases, and comparisons. | High |
| Ratio and Proportion | Solving problems involving the comparison of quantities and their relationships. | Medium |
| Simple and Compound Interest | Understanding the differences between simple and compound interest and calculating them effectively. | Medium |
Focusing on these critical subjects and practicing related problems regularly will help strengthen your problem-solving skills and boost your confidence in tackling complex tasks during the assessment.
Time and Work Questions Explained
Understanding the relationship between time and the amount of work completed is crucial for solving a wide range of problems in competitive assessments. These tasks typically involve calculating how long it takes to complete a task given a certain rate of work, or how work can be distributed among multiple people or machines. By mastering this concept, candidates can efficiently tackle related problems that often appear in assessments.
To solve such problems, one must know the basic formulas and how to apply them in different scenarios. For instance, if a person completes a task in a certain time, the rate of work can be determined by dividing the total work by the time taken. Similarly, combining the work rates of multiple people or machines involves finding their combined work rate and then calculating the time required to finish the task.
| Formula | Description |
|---|---|
| Work = Rate × Time | This basic formula calculates the total work done when the rate and time are known. |
| Time = Work / Rate | To find the time taken to complete a task, divide the total work by the rate of work. |
| Rate = Work / Time | The rate at which work is done can be found by dividing the total work by the time taken. |
In many problems, two or more people may be working together, each at a different rate. To find the total time taken when multiple workers are involved, the individual work rates are added. This combined rate is then used to calculate the time needed to complete the task. Understanding and practicing these calculations will greatly improve your ability to solve time-related work problems efficiently.
Practice Problems for Number Series
Number sequences often form an integral part of competitive assessments. Solving such problems requires the ability to identify patterns and apply the correct methods to determine the next number in the series. By practicing different types of sequences, you can sharpen your skills and increase your chances of success in assessments.
Common patterns in number series include arithmetic progressions, geometric progressions, alternating sequences, and more. Each type of series follows a specific rule or relationship between the numbers. Recognizing these patterns is key to solving these problems quickly and accurately.
Types of Series to Practice
- Arithmetic Series: A series where each number is obtained by adding or subtracting the same value.
- Geometric Series: A series where each term is found by multiplying or dividing the previous term by a constant factor.
- Fibonacci Series: A series where each term is the sum of the two preceding terms.
- Square and Cube Series: A series formed by squaring or cubing numbers in a specific order.
- Alternating Series: A series where terms follow an alternating pattern (e.g., adding and subtracting in turns).
Example Problems
- 2, 5, 8, 11, ? – What is the next number in the series?
- 3, 6, 12, 24, ? – Identify the next term.
- 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, ? – What follows next?
- 1, 4, 9, 16, ? – What comes after?
- 10, 15, 20, 25, ? – What is the next number?
By practicing these types of problems regularly, you will become more adept at spotting patterns and quickly solving number sequences. This skill will be invaluable in any competitive setting.
Data Interpretation Techniques and Tips
Interpreting data accurately is a critical skill in competitive assessments. Whether it involves charts, graphs, or tables, the ability to extract meaningful information quickly can greatly improve your performance. Mastering data analysis requires understanding how to read and manipulate different visual representations of information to solve problems efficiently.
Techniques for Effective Data Analysis
One of the most important steps in analyzing data is to first identify the type of information presented. Determine if you are dealing with percentages, averages, totals, or trends. Recognizing the structure of the data helps in focusing on the most relevant details. Once you have identified the key elements, it is essential to apply the correct mathematical methods, such as calculating differences, ratios, or proportions, to derive the necessary values.
Tips for Speed and Accuracy
- Read the question carefully: Ensure you understand exactly what is being asked before diving into the data.
- Focus on key numbers: Pay attention to the significant figures that directly influence your calculations.
- Estimate when possible: Use approximations to save time, especially when exact precision is not required.
- Practice mental math: Strengthen your ability to perform quick calculations without relying on a calculator.
- Check your assumptions: Verify that the data does not contain hidden variables or require additional analysis beyond the given values.
By practicing these techniques and tips, you can improve your ability to interpret data quickly and accurately, which is crucial in any competitive environment where time is of the essence.
Speed and Distance Problem Solving
Solving problems involving speed and distance requires understanding the fundamental relationship between the three key variables: speed, distance, and time. These types of problems often test your ability to calculate how fast something is moving, how far it travels, or how long it takes to cover a specific distance. The core formula for these problems is: Distance = Speed × Time. Understanding how to manipulate this formula is essential for tackling such challenges efficiently.
Key Concepts to Remember
When working on problems related to motion, it’s important to identify the variables given in the problem. Start by looking for information about the speed (rate), the time, or the total distance traveled. Once you have this data, you can use the core formula to solve for the unknown variable. Remember, if two objects are moving at different speeds, the time it takes for them to meet or overtake each other is another common type of problem you may encounter.
Common Problem Types
- Relative Speed: Problems where two objects are moving towards or away from each other.
- One-way Travel: Problems that involve calculating the time or distance for a single journey.
- Round Trip: Problems where the total time or distance involves traveling to a destination and then returning.
- Speed-Time-Distance Relationships: Problems that require solving for any one of the variables when the other two are known.
By practicing these types of problems regularly, you can improve your ability to quickly and accurately determine how speed, distance, and time are interrelated, making problem-solving much more intuitive.
How to Tackle Ratio and Proportion
Solving problems involving ratios and proportions is essential for many competitive assessments. These concepts are based on comparing quantities and determining how one quantity relates to another. A ratio expresses the relative sizes of two or more values, while a proportion helps to determine the relationship between them. Mastering these concepts will help you efficiently solve problems that require comparing parts to a whole or comparing different parts to each other.
Key Steps to Solve Ratio and Proportion Problems
To approach problems involving ratios and proportions, start by understanding the relationship between the given quantities. When dealing with ratios, ensure that the numbers are in the same units or can be converted into the same units. In proportion problems, the key is recognizing that the two ratios are equal. If two ratios are given as a:b and c:d, the proportion can be written as a/b = c/d. This equation can be solved by cross-multiplying to find the unknown value.
Common Techniques and Tips
- Simplify the Ratios: Always try to simplify the ratio to its lowest terms before proceeding with calculations.
- Cross-Multiplication: Use this technique for solving proportions, where cross-multiplying helps to eliminate fractions and makes calculations easier.
- Unitary Method: This method involves finding the value of one unit and then scaling it up to get the value of the desired quantity.
- Convert Units: Ensure that all quantities in a ratio are in the same unit before comparing them, as inconsistent units can lead to incorrect results.
By practicing these techniques and tips, you will gain confidence in handling ratio and proportion problems effectively, which is crucial in competitive environments where accuracy and speed are essential.
Simple and Compound Interest Questions
Interest calculations play a significant role in financial problems, often requiring you to compute the amount earned or paid over a given period. Understanding the difference between simple and compound interest is crucial in solving these types of problems. While simple interest is calculated only on the principal amount, compound interest considers both the principal and the accumulated interest over time. Mastering both concepts is essential for accurate calculations and effective problem-solving.
Key Concepts
- Simple Interest: This is calculated using the formula: SI = P × R × T / 100, where P is the principal, R is the rate of interest, and T is the time period.
- Compound Interest: Compound interest is calculated using the formula: CI = P × (1 + R/100)^T – P, where P is the principal, R is the rate of interest, and T is the time period. This calculation accounts for the interest earned on both the initial principal and any accumulated interest.
- Principal: The initial sum of money on which interest is calculated.
- Rate of Interest: The percentage at which interest is charged or earned over time.
- Time Period: The duration for which the money is invested or borrowed, typically measured in years.
Examples to Practice
- If $1000 is invested at a 5% simple interest rate for 3 years, what will be the total interest earned?
- A sum of $2000 is invested at a 4% compound interest rate for 2 years, compounded annually. What will be the total amount at the end of 2 years?
- If the principal is $1500 and the rate of interest is 6% per annum, calculate the simple interest for 5 years.
- Calculate the compound interest on $2500 for 4 years at 6% annual interest, compounded quarterly.
By practicing problems related to simple and compound interest, you will develop the ability to quickly and accurately determine the amount of interest in various financial situations.
Profit and Loss Questions Simplified
Understanding the concepts of profit and loss is essential for solving problems related to pricing, discounts, and business transactions. These problems typically involve determining how much profit is made or how much loss is incurred when selling goods or services. The key is understanding the relationship between cost price, selling price, and the percentage change in value. Once the fundamentals are clear, these problems can be solved with ease by using simple formulas.
Key Concepts
Profit occurs when the selling price exceeds the cost price, while a loss occurs when the selling price is less than the cost price. The formulas for calculating profit and loss are as follows:
| Concept | Formula | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Profit | Profit = Selling Price – Cost Price | Profit is the amount earned when the selling price is higher than the cost price. |
| Loss | Loss = Cost Price – Selling Price | Loss is the amount lost when the selling price is lower than the cost price. |
| Profit Percentage | Profit Percentage = (Profit / Cost Price) × 100 | The percentage of profit based on the cost price. |
| Loss Percentage | Loss Percentage = (Loss / Cost Price) × 100 | The percentage of loss based on the cost price. |
Tips for Solving Problems
- Understand the relationship: Identify whether the problem is dealing with a profit or a loss, then apply the appropriate formula.
- Percentage Calculations: Be mindful of converting the profit or loss into a percentage, as this is a common requirement in many problems.
- Work Backwards: In some cases, you may need to calculate the cost price or selling price when the percentage of profit or loss is given.
By practicing these concepts and solving various problems, you can quickly and accurately determine profit or loss in any given scenario.
Algebraic Problems for Bank Exams
Solving algebraic problems requires an understanding of variables, equations, and their relationships. These problems are designed to test your ability to manipulate mathematical expressions, simplify complex terms, and find unknown values. Algebra is an essential skill that helps in calculating rates, quantities, and other key financial figures. Mastering algebraic techniques is crucial for success in any competitive examination.
Important Concepts to Know
- Linear Equations: Equations that involve variables raised to the first power (e.g., ax + b = 0).
- Quadratic Equations: Equations that involve variables raised to the second power (e.g., ax² + bx + c = 0).
- Simple and Compound Interest: Algebra helps to compute financial values using formulas that involve interest calculations.
- Ratio and Proportion: Proportionality problems that require algebraic manipulation to find unknowns.
Solving Techniques
- Isolate the variable: Begin by simplifying the equation, moving terms to one side to isolate the unknown variable.
- Use substitution: If multiple equations are given, use substitution or elimination methods to solve for the unknown values.
- Check your solutions: Always substitute your final answers back into the original equation to verify the accuracy of your results.
By regularly practicing algebraic problems, you will enhance your problem-solving skills and improve your speed in finding solutions, which is vital for success in competitive assessments.
Logical Reasoning in Aptitude Tests
Logical reasoning is a critical component of any assessment that evaluates problem-solving skills. This area tests how well a person can analyze patterns, deduce conclusions, and apply logical rules to solve problems. Being able to think critically and follow a structured approach to reasoning is vital for answering complex problems efficiently. The goal is not just to find the answer but to develop a methodical way of thinking that can be applied to various situations.
Types of Logical Reasoning Problems
- Pattern Recognition: These problems involve identifying sequences or trends in a set of numbers, letters, or shapes and using them to predict the next element.
- Syllogisms: In these, conclusions are drawn from a given set of premises. The task is to determine whether the conclusion logically follows from the premises.
- Blood Relations: These problems deal with family relationships, where the goal is to identify the connection between individuals based on provided information.
- Seating Arrangement: These problems focus on placing individuals or objects in a specific order based on given conditions or constraints.
- Direction Sense: These problems require understanding spatial direction and movement based on certain instructions.
Tips for Success in Logical Reasoning
- Read the problem carefully: Pay attention to every detail in the given scenario, as small information can often lead to the correct answer.
- Practice different types: Consistent practice with different categories of logical reasoning problems helps improve pattern recognition and problem-solving speed.
- Break down complex problems: If the problem seems complicated, divide it into smaller parts and solve step by step.
- Elimination method: Use the process of elimination when faced with multiple options. This is especially useful in multiple-choice formats.
Mastering logical reasoning will not only enhance your problem-solving abilities but will also improve your decision-making skills in real-life situations, making it a crucial skill for success in competitive tests.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Aptitude
When preparing for any type of competitive evaluation, there are several common pitfalls that can affect performance. Many individuals make these errors due to a lack of attention to detail, poor time management, or overconfidence. Identifying these mistakes and working to avoid them can significantly improve problem-solving efficiency and accuracy.
Frequent Errors and How to Avoid Them
- Rushing Through the Problems: Often, candidates rush through problems without carefully reading the instructions or details. This leads to misinterpretations and careless mistakes. Always take a moment to understand the question before attempting to solve it.
- Skipping Steps: Sometimes, in an attempt to save time, individuals skip intermediate steps or attempt mental calculations. This can lead to errors. Always follow a systematic approach and show your work to ensure accuracy.
- Overlooking Units: In problems involving measurements or calculations, failing to keep track of units (like meters, seconds, percentages) can lead to incorrect answers. Ensure to check units at every step of the solution.
- Not Managing Time Effectively: Spending too much time on difficult problems while neglecting simpler ones can hinder performance. Time management is essential – allocate appropriate time to each question based on difficulty.
- Ignoring Approximation Techniques: Some problems can be solved faster using approximations rather than exact values. Learning when to approximate can save precious time, especially in complex calculations.
How to Improve Performance
- Practice Regularly: The more you practice, the more you can identify patterns and strategies that work, helping you avoid common errors.
- Read Carefully: Always read the problem thoroughly to ensure you don’t miss any crucial details or conditions provided in the question.
- Check Your Work: Before submitting or finalizing an answer, quickly review the steps to ensure no mistakes were made, especially in multi-step problems.
- Stay Calm and Focused: Stress can cloud your thinking and lead to errors. Take deep breaths, maintain a calm mindset, and focus on solving each problem step by step.
By avoiding these common mistakes and applying the right strategies, you can improve your ability to solve problems quickly and accurately, increasing your chances of success in any assessment.
Importance of Practice for Aptitude Success
Consistent practice plays a pivotal role in mastering various problem-solving techniques and enhancing one’s performance in competitive evaluations. The more one engages with different types of problems, the better prepared they are to handle unexpected challenges on the test. It allows individuals to identify patterns, refine their strategies, and build confidence over time.
Regular practice not only helps in improving speed but also in understanding the underlying concepts. It sharpens the mind, helps manage time efficiently, and reduces the chances of errors during the actual assessment. As problems become more familiar, individuals gain the ability to tackle them more quickly and accurately.
Benefits of Consistent Practice

- Improves Speed: The more you practice, the faster you become at identifying the right methods for solving problems.
- Builds Confidence: Solving problems regularly boosts your self-assurance and reduces the anxiety of facing unfamiliar challenges.
- Enhances Accuracy: Practice helps minimize careless errors, as it encourages a more thorough approach to problem-solving.
- Refines Problem-Solving Strategies: With frequent exposure to various problem types, individuals learn which strategies work best for them and can apply them effectively in timed conditions.
How to Maximize the Effectiveness of Practice
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Start with Basic Concepts | Begin by mastering fundamental concepts before moving on to more complex problems. This builds a strong foundation for tackling advanced challenges. |
| Practice Under Time Pressure | Simulate test conditions by practicing within time limits. This helps in improving speed and handling time management more effectively. |
| Review Mistakes | After each practice session, go over the mistakes made and understand why they happened. This helps in preventing them in the future. |
| Vary the Problem Types | Expose yourself to different categories of problems. This ensures that you are well-prepared for any kind of question that may appear. |
In conclusion, regular practice is the key to success in problem-solving challenges. By dedicating time to consistent practice, individuals not only sharpen their skills but also increase their ability to perform under pressure, leading to better outcomes in any competitive situation.
Time Management Strategies for Exams
Effective time management is essential for success in any competitive assessment. It ensures that candidates can complete all required tasks within the available time, without feeling rushed or overwhelmed. By organizing time efficiently, test-takers can allocate sufficient attention to each section and avoid wasting time on easier tasks at the expense of more challenging ones.
Implementing a strategic approach to time allocation not only enhances performance but also reduces stress during the assessment. It helps individuals maintain focus, optimize their efforts, and improve their overall ability to handle pressure.
Key Time Management Techniques
- Prioritize Tasks: Focus on questions that offer the most value in terms of points and difficulty level. Allocate time wisely based on the weightage of each section.
- Set a Time Limit for Each Question: Establish a specific time limit for each task to prevent spending too much time on any single one. Use a stopwatch to keep track.
- Start with Easy Questions: Begin with questions that are easier or more familiar to gain confidence and secure quick points before tackling more difficult ones.
- Skip and Return: If a question is taking too long to solve, move on and return to it later once you have tackled the others. This ensures that you don’t waste time on challenging questions.
- Practice Time-bound Mock Tests: Simulate real test conditions by practicing with a timer. This helps improve speed, manage distractions, and assess whether your time allocation strategy is effective.
Strategies to Avoid Time Wastage
- Don’t Overthink: Avoid getting stuck in the details of a question. If you feel unsure, make an educated guess and move on.
- Avoid Double-Checking Excessively: While it’s important to review answers, avoid spending too much time re-checking. A quick glance to ensure accuracy is sufficient.
- Minimize Distractions: In both practice sessions and the actual test, reduce distractions to stay focused on the task at hand. This will allow for more productive use of time.
- Track Time Regularly: Constantly monitor the clock and adjust your pace to stay on track. Regularly reassess how much time remains and make adjustments accordingly.
By incorporating these time management techniques, individuals can optimize their performance, reduce stress, and approach their assessments with a calm and organized mindset. Proper time allocation ensures that every task is given the attention it requires, ultimately leading to a more successful outcome.
How to Build Exam Confidence
Developing confidence for any competitive assessment is crucial in achieving success. Confidence not only helps in reducing anxiety but also improves decision-making and problem-solving abilities during the test. Building this self-assurance involves a combination of preparation, practice, and mental conditioning to ensure you can approach the assessment with a positive and calm mindset.
Confidence is built over time, and one of the most effective ways to achieve it is through repeated exposure to the types of challenges one might encounter. As you familiarize yourself with different task types, you develop a sense of mastery, which directly boosts your belief in your ability to perform well under pressure.
Effective Strategies to Boost Confidence
- Consistent Practice: Regular practice is the foundation of confidence. The more you practice solving tasks, the more comfortable you will become with the process, leading to improved efficiency and accuracy.
- Simulate Real Conditions: Take timed mock tests that replicate the actual testing environment. By doing this, you not only get accustomed to the format but also reduce the fear of the unknown, as you’ll know exactly what to expect.
- Break Down Difficult Tasks: When confronted with a challenging task, break it down into smaller, manageable parts. This makes it less overwhelming and easier to solve step by step.
- Celebrate Small Wins: Celebrate each step of progress, whether it’s mastering a particular type of problem or achieving a time-related goal. This reinforces a positive mindset and motivates you to continue improving.
- Stay Positive: Positive self-talk can work wonders. Replace thoughts of doubt with affirmations that remind you of your strengths and ability to succeed.
Mindset and Mental Conditioning

- Visualize Success: Before the test, take a moment to visualize yourself succeeding. This mental exercise can help create a positive expectation and reduce feelings of apprehension.
- Learn from Mistakes: Instead of being discouraged by errors, view them as opportunities for growth. Identifying weaknesses and addressing them head-on is key to continuous improvement.
- Stay Calm Under Pressure: Practice breathing exercises or mindfulness techniques to stay calm during the actual assessment. A clear mind is more capable of making sound decisions and solving problems effectively.
By applying these strategies, you will not only improve your abilities but also develop a strong sense of confidence that will help you perform at your best when it matters the most. Confidence is the result of hard work, practice, and maintaining a positive outlook, all of which can be achieved through consistent effort and focus.
Final Tips for Exam Preparation
As the assessment day approaches, it’s important to focus on refining your preparation strategy to ensure peak performance. This phase involves consolidating your knowledge, optimizing your approach to problem-solving, and fine-tuning your mental state to handle the pressure effectively. In these final stages, small adjustments can have a significant impact on your readiness and overall performance.
In addition to regular practice and thorough review, it’s essential to incorporate effective time management techniques and maintain a balanced approach to studying. Ensure that you take care of your physical and mental well-being, as this will have a direct influence on your focus and energy levels during the assessment.
- Focus on Weak Areas: Revisit topics where you feel less confident. Strengthening these areas will not only boost your overall score but will also enhance your self-assurance.
- Take Full-Length Mock Tests: Simulate the full assessment experience by taking practice tests under timed conditions. This will help you manage your time, avoid mistakes under pressure, and become more familiar with the format.
- Stay Consistent: Consistency is key to long-term retention and improvement. Set realistic goals and stick to a study schedule to ensure gradual progress leading up to the test day.
- Don’t Cram: Avoid cramming at the last minute. It’s important to review and reinforce your knowledge in advance, giving your brain the time to absorb and process the information.
- Relax Before the Test: Get a good night’s sleep before the test. Rest is essential for cognitive function, focus, and alertness during the assessment.
By following these final tips and maintaining a positive attitude, you will be well-prepared to face the challenge ahead. Remember, steady preparation, along with confidence and a calm mindset, will guide you to success when it’s time to perform.