Basic Life Support Exam A Answers 25 Questions 2025

Preparing for an emergency response assessment requires a thorough understanding of critical procedures and the ability to perform under pressure. The ability to act swiftly and effectively can save lives in situations where immediate intervention is necessary. This section focuses on the essential techniques and knowledge required for successful certification in first aid and related practices.
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, new guidelines and practices are introduced regularly. Staying up-to-date with these updates is crucial for both professionals and individuals seeking to enhance their preparedness. In this article, we explore important concepts that form the core of any emergency response evaluation, offering valuable insights into the most effective approaches.
Mastering key principles through practice and understanding of standard procedures will help ensure confidence during assessment and in real-world scenarios. Whether you’re seeking initial certification or aiming to refine your skills, this guide provides the foundation necessary for success.
Emergency Response Certification Overview 2025
Achieving certification in emergency response practices requires a comprehensive understanding of key techniques used in critical situations. The evaluation focuses on the ability to assess, react, and apply lifesaving measures in urgent circumstances. It is designed to ensure that individuals are equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to handle emergencies effectively, both in professional environments and in daily life.
Key Components of the Certification
The assessment covers a range of essential topics, from performing effective chest compressions to operating automated defibrillators. Participants will be tested on their ability to recognize symptoms, make quick decisions, and execute vital actions under pressure. Mastery of these skills is crucial for both healthcare providers and everyday responders.
Important Updates for 2025
As guidelines evolve, staying informed about the latest procedures and recommendations is critical. For 2025, several updates have been introduced to improve the effectiveness and safety of emergency interventions. These changes reflect ongoing research and the refinement of established practices, ensuring that those certified are trained according to the most current standards.
Success in the evaluation requires not only knowledge but also practical application. The ability to remain calm and focused during high-stress situations is vital, as it directly impacts the outcome of emergency interventions.
Key Topics in Certification for Emergency Response
To achieve certification in emergency response practices, it is essential to cover a wide range of topics that equip individuals with the skills needed to manage crises effectively. From understanding the basics of first aid to mastering advanced procedures, these core subjects form the foundation of the certification process. This section explores the key areas that every candidate should focus on during their preparation.
Critical Skills and Procedures
One of the most important areas of focus is the ability to provide immediate assistance during a medical emergency. Mastering techniques such as performing chest compressions, managing airway obstructions, and assessing vital signs is essential. Additionally, proper use of equipment like defibrillators and oxygen devices plays a critical role in saving lives.
Updated Guidelines and Practices
As medical protocols evolve, so do the standards for emergency response. The latest updates ensure that responders are trained with the most current and evidence-based practices. Understanding these new guidelines, such as changes to compression depth or frequency, is crucial for passing the certification and performing optimally in real-world scenarios.
Familiarity with these topics ensures not only the ability to pass the certification process but also the confidence and competence required to act decisively when lives are at risk.
How to Prepare for Emergency Response Certification 2025
Successfully preparing for an emergency response certification requires both theoretical knowledge and practical skill development. Understanding key concepts and practicing techniques in realistic scenarios will ensure that candidates are confident and capable during their assessment. This section outlines effective strategies to help you prepare and perform at your best.
Study Key Procedures and Protocols
Familiarize yourself with the fundamental procedures involved in emergency interventions, such as CPR, airway management, and using defibrillators. Review the latest guidelines and recommended practices, as these may change periodically to reflect new research or medical advancements. Knowing the correct protocols ensures that you can apply the most effective methods during your assessment.
Practice in Simulated Environments
Theoretical knowledge alone is not enough to succeed. Hands-on practice in a controlled environment is crucial. Participate in training sessions that offer real-world simulations of emergency scenarios. Repetition of these techniques will help you develop muscle memory, which is essential for acting swiftly and accurately when it matters most.
Confidence and calmness are vital in high-pressure situations, and both can be cultivated through diligent practice and preparation. Approaching your certification with a structured study and practice plan will ensure you’re fully equipped to handle any challenge during the evaluation.
Common Mistakes in Emergency Response Assessments
During the process of certification, many individuals make avoidable mistakes that can hinder their success. These errors are often a result of inadequate preparation, rushed actions, or a lack of familiarity with key procedures. Understanding the most common pitfalls can help candidates avoid them and perform with confidence when it counts.
Top Mistakes to Avoid
- Inadequate chest compression depth – Not applying the correct amount of pressure during chest compressions can reduce the effectiveness of CPR and negatively impact the outcome.
- Failure to check for breathing – Neglecting to properly assess whether the person is breathing before proceeding with interventions can lead to unnecessary treatments.
- Incorrect AED usage – Not following the step-by-step instructions when using a defibrillator can delay the delivery of shocks, compromising the victim’s chances of survival.
- Panic or hesitation – Staying calm and focused is critical. Hesitation or panicking can lead to mistakes in applying interventions or missing critical steps.
- Improper hand placement – Incorrect hand positioning during chest compressions or rescue breathing can cause injury or reduce the effectiveness of the technique.
How to Avoid These Mistakes
To avoid these common errors, it’s essential to practice consistently and stay familiar with the most up-to-date guidelines. Regular hands-on training and simulated scenarios will help build muscle memory and increase confidence. Additionally, always remember to remain calm and follow protocols step by step, without rushing.
Thorough preparation and a calm, methodical approach are key to overcoming these challenges and excelling in the certification process.
Understanding CPR Guidelines for 2025
The guidelines for performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) are constantly evolving as medical research progresses. Staying up-to-date with the latest recommendations ensures that responders can provide the most effective care during critical situations. This section will explore the key updates and essential practices for performing CPR according to the most current protocols.
Key Updates in CPR Guidelines
- Compression-to-ventilation ratio – The recommended ratio for adults has been simplified in recent years. The current standard emphasizes high-quality chest compressions, with a focus on minimizing interruptions during the procedure.
- Compression depth and rate – It’s now recommended to compress the chest to a depth of at least 2 inches (5 cm) with a rate of 100 to 120 compressions per minute. This ensures optimal blood flow to vital organs.
- Minimizing interruptions – Interruptions in chest compressions should be as brief as possible. The longer the pauses, the lower the likelihood of successful resuscitation.
- Use of automated defibrillators (AEDs) – The integration of AEDs into CPR is emphasized. They should be used as soon as possible when available, with minimal delay after recognizing a cardiac arrest situation.
- Focus on hands-only CPR – For untrained bystanders, hands-only CPR is encouraged. Immediate chest compressions can significantly improve survival chances until professional help arrives.
How to Apply These Guidelines Effectively
To provide the most effective care, it’s crucial to practice the updated procedures regularly. Focus on proper hand placement, maintaining consistent compressions, and minimizing delays when applying defibrillation. Training courses often include simulations that help build the muscle memory necessary to perform CPR correctly in high-stress environments.
Adhering to the latest guidelines can greatly improve the chances of survival for individuals experiencing cardiac arrest, highlighting the importance of ongoing training and staying informed about current practices.
Importance of Chest Compression Depth
The depth of chest compressions is one of the most critical factors in performing effective resuscitation. It directly affects the blood flow to vital organs, particularly the brain and heart, during a cardiac emergency. Ensuring the proper compression depth helps maintain circulation and increases the likelihood of a positive outcome. In this section, we will explore why the correct depth is essential and how it impacts the success of interventions.
Why Compression Depth Matters

- Optimal blood flow – Proper chest compression depth ensures that enough blood is pumped to the heart and brain. If the depth is too shallow, circulation is inadequate, and the body’s organs may not receive the oxygen they need to survive.
- Improved survival rates – Studies show that compressions at the recommended depth significantly increase survival rates. Shallow compressions have been associated with poorer outcomes in patients experiencing cardiac arrest.
- Prevention of injury – While it’s important to apply sufficient pressure, excessive depth can cause damage to the ribcage or internal organs. It’s critical to balance adequate depth with proper technique to avoid harm.
How to Achieve Correct Compression Depth
- Positioning – Ensure that your hands are placed on the center of the chest, directly over the sternum. This positioning maximizes the efficiency of the compressions.
- Compression guidelines – For adults, compress the chest to a depth of at least 2 inches (5 cm), but no deeper than 2.4 inches (6 cm), at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute.
- Consistency – Maintain consistent depth and rhythm, avoiding interruptions in compressions whenever possible. This continuous flow of pressure is vital to sustaining circulation.
Achieving the correct compression depth is crucial for improving the chances of survival in an emergency. Regular practice and adherence to guidelines ensure that responders can act quickly and efficiently when faced with a cardiac arrest situation.
Effective Rescue Breathing Techniques
Rescue breathing is a vital technique used to provide oxygen to someone who is not breathing or has very low respiration. Properly delivering air to the lungs can help prevent brain damage and increase the chances of survival until further medical assistance arrives. This section covers the key aspects of performing rescue breathing and why it is so critical during an emergency.
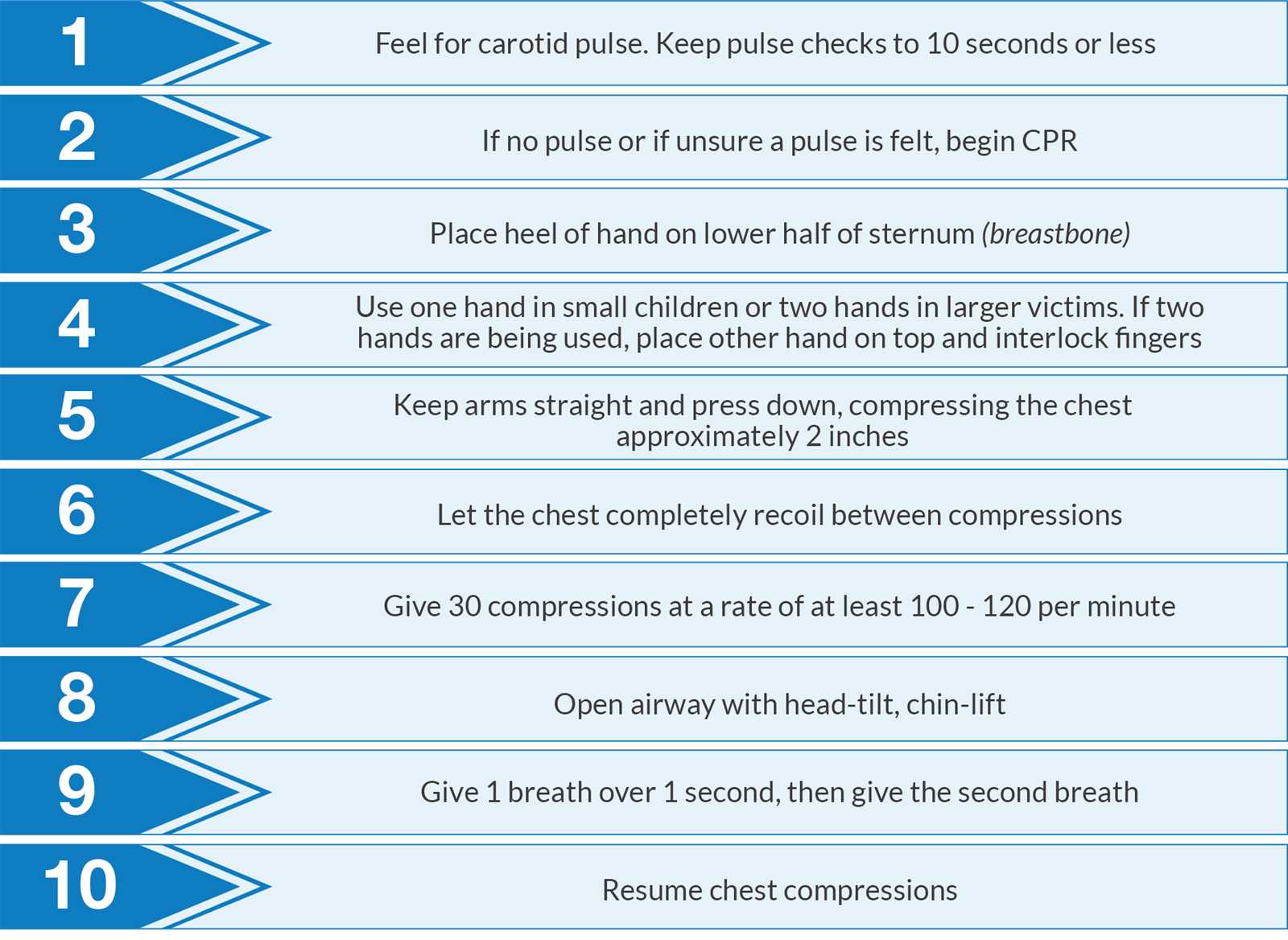
Steps for Proper Rescue Breathing
- Ensure an open airway – Before beginning rescue breaths, tilt the victim’s head back slightly to open the airway. This step is essential to ensure the air can reach the lungs without obstruction.
- Seal the mouth or nose – For mouth-to-mouth breathing, seal your lips over the victim’s mouth. If performing mouth-to-nose, seal the mouth and breathe into the nose. Make sure there is no air leakage to ensure effective ventilation.
- Breath delivery – Deliver each breath slowly and steadily, lasting about one second per breath. Watch for the chest to rise with each breath to confirm that air is entering the lungs.
- Regular assessment – After every two breaths, check for signs of breathing or pulse. If the person does not begin to breathe on their own, continue with rescue breaths and chest compressions as needed.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Over-inflation – Delivering air too forcefully can cause the stomach to inflate instead of the lungs, leading to potential complications such as vomiting.
- Inconsistent technique – Inconsistent or improper seal around the mouth or nose can cause air leakage, making the breaths less effective.
- Failure to monitor – Always assess the victim’s condition after each breath. Failing to do so can result in missed signs of recovery or deterioration.
Mastering rescue breathing is a crucial skill in emergency care. Practicing these techniques regularly ensures that you can act swiftly and effectively, significantly improving the chances of survival in respiratory emergencies.
Role of AED in Emergency Response
Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs) play a crucial role in emergency situations involving cardiac arrest. These devices are designed to analyze the heart’s rhythm and, if necessary, deliver a controlled electric shock to restore normal heart function. The timely use of an AED can significantly increase the chances of survival, especially when paired with other life-saving interventions like chest compressions.
AEDs are essential tools in both professional medical settings and public spaces, providing non-medical personnel with the ability to assist effectively in an emergency. The simplicity of operation–often guided by clear audio instructions–makes AEDs accessible even for individuals with no formal training. However, understanding when and how to use them correctly is key to ensuring their effectiveness.
Immediate use of an AED after cardiac arrest is crucial. Every minute without defibrillation decreases the survival rate by about 10%. Therefore, it’s vital to act quickly, retrieve the AED, and follow the device’s instructions without delay.
How to Handle Cardiac Arrest Cases
Cardiac arrest is a medical emergency where the heart unexpectedly stops beating, cutting off blood flow to the brain and other vital organs. Quick and decisive action is crucial in these situations, as the chances of survival decrease significantly with each passing minute. Understanding the steps to take during a cardiac arrest can make the difference between life and death.
When a person collapses and shows no signs of life, it’s essential to act immediately. The first priority is to assess the situation and call for emergency medical help. Simultaneously, initiating life-saving measures like chest compressions and using a defibrillator when available can increase survival rates.
Key Steps to Follow in Cardiac Arrest:
- Check responsiveness – Tap the person and shout to see if they respond. If there is no reaction, check for a pulse and breathing.
- Call for help – Immediately dial emergency services. The faster help arrives, the higher the chances of survival.
- Start chest compressions – If the person is not breathing, begin chest compressions. Push hard and fast at the center of the chest, aiming for a depth of at least 2 inches and a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute.
- Use an AED – If an automated external defibrillator (AED) is available, turn it on and follow the voice prompts to deliver a shock if needed. The AED can help reset the heart’s rhythm.
- Continue CPR – Continue performing chest compressions and rescue breaths (if trained) until emergency responders arrive or the person starts breathing on their own.
Remaining calm during a cardiac arrest situation is vital. By focusing on the correct procedures and maintaining composure, you can significantly improve the person’s chances of recovery before professional help arrives.
Recognizing Signs of Respiratory Failure
Respiratory failure occurs when the body is unable to adequately exchange gases, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, leading to insufficient oxygen levels in the blood. Early recognition of respiratory failure is critical for timely intervention and can prevent severe complications. This section focuses on the key signs and symptoms that indicate someone may be experiencing difficulty with breathing and oxygenation.
Identifying respiratory distress early can help initiate proper treatment, such as providing supplemental oxygen or initiating resuscitation efforts. The following signs are often indicative of impending or ongoing respiratory failure and should prompt immediate attention.
Signs to Watch For:
- Labored breathing – Rapid, shallow, or irregular breaths, especially with the use of accessory muscles (neck or chest muscles), can indicate difficulty in breathing.
- Decreased oxygen saturation – Low levels of oxygen in the blood (measured via pulse oximeter) can be a clear indicator of respiratory compromise.
- Blue or gray skin (cyanosis) – A bluish tint around the lips, fingertips, or extremities suggests inadequate oxygenation and is a severe sign of respiratory failure.
- Altered mental state – Confusion, dizziness, or difficulty staying awake can result from low oxygen levels affecting brain function.
- Struggling to speak or breathe – Difficulty in forming sentences or excessive pauses between breaths may indicate that the person is unable to maintain normal breathing on their own.
- Fatigue or exhaustion – As breathing becomes more difficult, the individual may become increasingly tired or unable to maintain normal respiratory effort.
Immediate action is necessary when respiratory failure is suspected. Providing emergency oxygen or initiating ventilation support can stabilize the patient and prevent further deterioration. Always seek professional medical help if you notice any of these signs.
What to Expect in BLS Exam A
When preparing for a certification assessment in emergency care, it’s important to understand the structure and content of the test. The assessment typically evaluates your knowledge and practical skills in providing immediate care during critical situations. Whether you are a first-time candidate or recertifying, knowing what to expect can help you perform with confidence.
This assessment will cover a variety of essential skills and theoretical knowledge needed to respond effectively to emergencies. From hands-on techniques to theoretical understanding of medical protocols, candidates are tested on their ability to perform under pressure while adhering to established procedures.
Key Topics Covered
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) – Understanding the correct techniques for chest compressions, rescue breathing, and their proper sequence.
- Use of AED – How to properly operate an automated external defibrillator and when to use it during emergencies.
- Choking and airway management – Procedures for clearing blocked airways in both adults and children.
- Recognition of medical emergencies – Identifying signs of cardiac arrest, respiratory distress, and other life-threatening conditions.
How the Assessment Works
Expect a combination of theoretical questions and practical simulations. The theoretical portion will test your understanding of medical procedures, while the practical component will assess your ability to apply these techniques in real-world scenarios. The hands-on portion may involve practicing CPR, using an AED, or performing other critical tasks in a controlled environment, often under timed conditions.
Preparation is key to success. Reviewing the latest guidelines, practicing techniques regularly, and ensuring you understand the protocols will increase your chances of passing with confidence.
Essential BLS Skills for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers are often the first responders in emergencies, and having the ability to perform critical procedures can make a life-saving difference. These essential skills help healthcare professionals provide immediate care, stabilize patients, and prevent further complications before advanced medical assistance arrives. Mastering these techniques is crucial for anyone working in medical settings, from hospitals to clinics and emergency services.
Below is a breakdown of the key skills that healthcare providers should be proficient in to handle emergencies effectively:
| Skill | Description |
|---|---|
| Chest Compressions | Proper technique for performing high-quality chest compressions to maintain circulation during cardiac arrest. |
| Rescue Breathing | Delivering breaths to a patient who is not breathing or breathing insufficiently, ensuring oxygen flow to vital organs. |
| Defibrillation | Properly using an automated external defibrillator (AED) to deliver a shock to the heart in cases of arrhythmia or cardiac arrest. |
| Airway Management | Techniques for clearing and securing the airway to ensure unobstructed breathing, including using tools like an airway adjunct. |
| Choking Relief | Administering abdominal thrusts or back blows to clear an obstructed airway in adults, children, and infants. |
By mastering these skills, healthcare providers ensure they are prepared to manage critical situations swiftly and effectively, improving patient outcomes and enhancing survival rates. Regular training and hands-on practice are essential to maintaining proficiency and ensuring the ability to perform these life-saving techniques under pressure.
Critical BLS Updates for 2025

As medical standards evolve, so do the guidelines for emergency care. In 2025, there have been several significant updates to protocols and recommendations aimed at improving the effectiveness of immediate interventions during critical situations. Staying up to date with these changes ensures that healthcare providers and first responders are equipped with the most current knowledge and tools to save lives.
Key revisions include changes to chest compression techniques, updated defibrillation protocols, and revised guidelines for airway management. These updates reflect ongoing research into improving patient outcomes and ensuring the highest level of care during emergencies.
Key Changes in CPR Guidelines
- Compression Depth – New recommendations emphasize deeper compressions, suggesting a depth of at least 2.4 inches (6 cm) for adults to optimize blood flow to vital organs.
- Compression-Only CPR – For untrained bystanders, the emphasis has shifted towards hands-only CPR, with research showing that uninterrupted chest compressions can improve survival rates.
- Ventilation Ratio – Adjustments have been made to the suggested compression-to-ventilation ratio, particularly in cases involving children and infants, to reduce potential complications.
Defibrillation Updates
- AED Use in Children – Guidelines now suggest the use of AEDs with pediatric pads in children under the age of 8, even in the absence of a trained professional, when available.
- Advanced Defibrillation Settings – New protocols emphasize higher shock doses and faster intervention time to improve the efficacy of defibrillation in adults and children.
These critical updates reflect the ongoing commitment to refining emergency care and improving patient outcomes. Staying current with the latest guidelines is essential for those responsible for responding to medical emergencies, ensuring that the care provided is as effective and impactful as possible.
How to Master BLS Test Questions
Preparing for an assessment in emergency medical techniques requires more than just knowing the procedures; it involves understanding the underlying principles and applying them to a variety of scenarios. Mastering test questions related to emergency care involves both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. This guide will help you focus on the key areas to ensure you perform confidently when it’s time to take the test.
Effective study methods include reviewing core concepts, practicing real-world scenarios, and familiarizing yourself with common question formats. The more you understand the principles of each intervention, the better equipped you will be to answer related questions accurately.
Key Areas to Focus On
| Area | Focus Points |
|---|---|
| Airway Management | Understand techniques for clearing and securing the airway, including the use of adjuncts and manual maneuvers. |
| Chest Compressions | Know the correct compression depth, rate, and the importance of uninterrupted compressions during resuscitation. |
| Defibrillation | Familiarize yourself with the proper use of an AED, recognizing when to use it, and the importance of correct pad placement. |
| Rescue Breathing | Understand when and how to administer breaths, including the appropriate rate and volume for adults and children. |
| Choking Relief | Know the appropriate steps for relieving choking in adults, children, and infants, including the use of abdominal thrusts and back blows. |
Study Tips for Success
- Understand the Guidelines – Make sure you are familiar with the most current protocols for emergency care, as these may have changed.
- Practice Scenarios – Use practice tests and scenario-based questions to strengthen your decision-making skills in real-life situations.
- Stay Calm Under Pressure – Many test questions simulate high-stress environments. Practice staying calm and thinking critically to apply what you’ve learned.
- Review and Repeat – Repetition is key in mastering emergency care techniques. Revisit areas where you feel less confident.
By focusing on these areas and adopting a strategic study approach, you’ll be better prepared to master the test and excel in emergency care scenarios. Always remember, hands-on practice combined with theoretical understanding is the key to mastering these skills.
Reviewing BLS Scenarios and Answers

In order to effectively respond to emergencies, it’s essential to practice and review realistic scenarios. These situations mimic what you may face in real life and require immediate, well-thought-out responses. By analyzing common emergency situations and reviewing the appropriate steps to take, you can better prepare yourself for when every second counts.
Reviewing scenarios helps to reinforce the correct sequence of actions, ensures understanding of protocols, and strengthens decision-making skills. It’s not enough to know the theory; you must be able to apply it confidently in stressful circumstances. Below are examples of some key scenarios and the recommended responses.
Scenario 1: Adult Cardiac Arrest
An adult collapses suddenly. You assess responsiveness and check for breathing. No response or abnormal breathing is detected. What steps should you take?
- Call for help or activate emergency services.
- Immediately begin chest compressions with a depth of at least 2 inches at a rate of 100–120 per minute.
- Use an AED as soon as available, following prompts to deliver a shock if necessary.
Scenario 2: Choking in a Child
A child is unable to breathe and is clutching their throat, indicating choking. What is the first step in this situation?
- Encourage the child to cough if they are still able to do so.
- If the child is unable to cough or breathe, perform 5 back blows followed by 5 abdominal thrusts.
- If the child becomes unresponsive, begin CPR and call for emergency medical assistance.
Scenario 3: Rescue Breathing for an Infant
An infant is found unconscious and not breathing. How do you proceed with rescue breathing?
- Position the infant’s head to open the airway and deliver gentle breaths using a barrier device or your mouth.
- Ensure each breath is given over 1 second, making the chest rise visibly.
- Continue with 2 breaths followed by chest compressions if the infant remains unresponsive and not breathing.
Scenario 4: AED Use in a Pregnant Woman
A pregnant woman collapses and is unresponsive. She is not breathing. What should you do?
- Immediately call for emergency medical help.
- Perform chest compressions without modification for the size of the body.
- If an AED is available, use it according to the usual instructions. There is no need to modify the AED pads; place them as you would for any adult.
Reviewing these scenarios regularly will help you become familiar with the required steps and ensure that, in an actual emergency, you will react quickly and appropriately. Each situation demands quick thinking and the ability to follow established protocols precisely. Practicing these skills will increase your confidence and efficiency in real-life situations.
Post-Exam Tips for BLS Success

After completing your certification test, it’s essential to focus on the next steps that ensure long-term success and mastery of the skills you’ve just been assessed on. The period following the test is an excellent opportunity to reflect, solidify your knowledge, and stay prepared for real-world emergencies. By implementing key post-assessment strategies, you can ensure that your skills remain sharp and your confidence grows as you progress in your career.
Whether you’ve passed the test or need to retake it, these tips will help you stay on track and continue refining your emergency care capabilities.
Review and Reflect on Your Performance
- Identify Weak Areas – Take note of any areas where you may have struggled or found challenging. This is your opportunity to focus more on these skills through additional study or practice.
- Evaluate Your Mistakes – If there were questions or scenarios where you were unsure, try to understand why. Reviewing these areas in-depth will help you avoid similar errors in the future.
- Stay Updated – Emergency care protocols can change. Make sure to stay informed about the latest updates to guidelines and practices to ensure that you’re always working with the most current information.
Practical Application and Continued Practice
- Hands-On Practice – Nothing beats practical experience. Keep practicing key skills like chest compressions, rescue breathing, and AED usage through simulations or hands-on training to stay proficient.
- Join a Refresher Course – Participating in a refresher course can help reinforce what you’ve learned, offer real-time feedback from instructors, and provide a chance to network with others in the field.
- Simulate Real-World Scenarios – Engage in scenario-based training to apply your knowledge in a realistic context. The more familiar you become with different emergency situations, the better prepared you’ll be when the need arises.
Remember, passing the test is just one step in your journey to becoming proficient in emergency care. By reflecting on your performance, continuing to practice, and staying updated on guidelines, you’ll not only excel in your certification but also be better prepared to handle emergencies with confidence and skill.