Reading Plus Answers Level G See Reader Guide
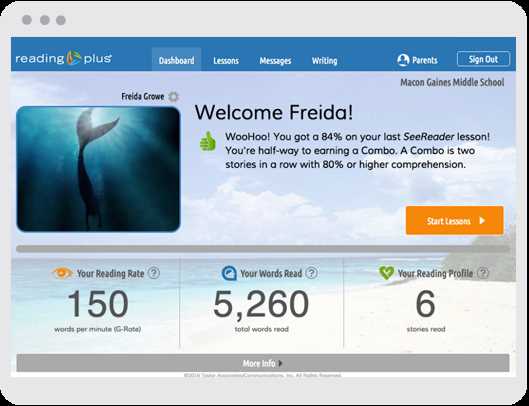
Improving comprehension and analytical abilities is crucial for mastering complex texts. The material presented in this section is designed to help readers develop deeper understanding and critical thinking skills through structured exercises. By engaging with challenging content, readers can enhance their capacity to interpret, analyze, and retain information more effectively.
Advanced exercises focus on building the necessary skills for tackling diverse texts, from identifying key concepts to exploring underlying themes. These practices promote attention to detail and encourage readers to think critically about what they read, sharpening both cognitive and interpretive abilities. This approach provides not only an academic advantage but also cultivates lifelong reading habits that are essential in navigating more complex ideas.
As you explore this section, you will encounter various tasks and challenges that require active engagement. Developing fluency and confidence in understanding texts will become second nature as you work through each segment, progressively advancing your skill set. The ultimate goal is to equip readers with the tools they need to succeed in more intricate material, fostering a strong foundation for future learning.
Reading Plus Level G Overview

The objective of this section is to enhance comprehension skills by providing a range of exercises that challenge readers with progressively complex texts. These tasks are designed to develop critical thinking and analytical abilities, equipping individuals with the tools they need to understand advanced material more efficiently. By engaging with carefully selected content, learners can build their cognitive strength and interpretive skills, ensuring they are prepared for a variety of intellectual challenges.
Key Features of the Program
Participants are guided through a structured learning process that emphasizes vocabulary expansion, contextual analysis, and comprehension retention. Each exercise focuses on specific areas, encouraging learners to engage actively with the material. The program’s design supports the development of higher-order thinking, such as drawing inferences and understanding subtle nuances in complex texts.
Effective Strategies for Success

To fully benefit from the exercises, it is essential to approach each task with a strategic mindset. By paying attention to details and maintaining focus, readers can improve their ability to process and understand intricate information. Utilizing techniques like summarization and questioning can significantly enhance the learning experience, ensuring long-term success and mastery over difficult reading materials.
Understanding the See Reader Feature
This feature is designed to enhance users’ interaction with texts, offering a more immersive and structured approach to comprehension exercises. It provides a range of interactive tools that facilitate deeper engagement with content, allowing learners to focus on key details and improve their interpretive skills. By guiding users through various text structures, this tool helps them better analyze and understand complex material.
How the Tool Enhances Comprehension
One of the main advantages of this feature is its ability to break down content into manageable sections, making it easier to grasp the main ideas. Learners are encouraged to reflect on what they’ve read, helping them develop critical analysis skills. Through interactive prompts, users are guided to identify important concepts, relationships, and themes, which boosts retention and understanding.
Interactive Elements for Active Learning
The feature also integrates various interactive elements that require active participation from the user. These tools help reinforce learning by offering real-time feedback, quizzes, and challenges. By actively responding to these prompts, learners can track their progress and pinpoint areas for further improvement, making the learning process both dynamic and personalized.
How Level G Improves Reading Skills
This section is designed to help individuals sharpen their understanding and analytical abilities through a carefully structured set of exercises. The goal is to challenge learners with more sophisticated material that encourages them to think critically, process complex information, and retain key details more effectively. By progressing through these activities, users will see noticeable improvements in their ability to interpret texts and draw insightful conclusions.
Key Areas of Improvement
- Comprehension Enhancement – Exercises focus on understanding central ideas, details, and the relationships between concepts, strengthening overall comprehension skills.
- Vocabulary Expansion – Through exposure to more diverse vocabulary, learners improve their ability to grasp unfamiliar terms and use context clues to determine meanings.
- Critical Thinking – Activities are designed to promote deeper analysis, helping users evaluate information, infer meaning, and make connections across different texts.
- Speed and Efficiency – Regular practice helps increase the pace of processing information, which is essential for tackling more advanced material.
Benefits of Structured Exercises
By consistently engaging with targeted exercises, learners gradually build confidence in their reading abilities. The structure of the tasks promotes active engagement and encourages users to practice important skills such as summarization, interpretation, and critical analysis. This approach not only prepares individuals for more challenging texts but also enhances their ability to retain and apply knowledge in different contexts.
Key Tips for Success in Level G
To excel in this section, learners need a combination of focus, strategy, and active participation. By adopting effective approaches and staying consistent with practice, individuals can enhance their comprehension, analytical abilities, and retention of key concepts. The following tips will help guide users toward success and ensure they are fully prepared to tackle complex content.
Effective Strategies for Improvement

- Break Down the Material – Approach each text by breaking it into smaller, manageable sections. This allows for better focus and understanding of each part before tackling the whole.
- Take Notes – Jot down key ideas, unfamiliar words, and important details while reading. This technique helps with retention and makes it easier to review concepts later.
- Stay Consistent – Regular practice is essential for continuous improvement. Set aside time each day to complete tasks and challenge yourself with new material.
- Utilize Context Clues – When encountering unfamiliar terms or phrases, try to infer their meaning based on the surrounding text. This builds vocabulary and comprehension skills.
- Review and Reflect – After completing each section, take a moment to reflect on what you’ve learned. Summarizing the content in your own words helps reinforce understanding.
Maintaining Focus and Motivation

- Set Goals – Establish clear, achievable goals for each session. This keeps you focused and gives you a sense of accomplishment as you progress.
- Track Your Progress – Monitor your performance to identify areas for improvement. Celebrate small milestones to maintain motivation throughout the process.
- Stay Engaged – Challenge yourself to think critically about the material. Ask questions and make connections to deepen your understanding and maintain interest.
Common Challenges in See Reader
While the interactive platform is designed to enhance comprehension and analysis, users may face several challenges along the way. These obstacles can vary in nature, ranging from difficulty in understanding complex vocabulary to struggling with maintaining focus during longer tasks. Identifying these common issues early on can help learners develop strategies to overcome them and make steady progress in their journey to mastery.
Common Obstacles to Overcome
- Difficulty with Complex Vocabulary – Encountering unfamiliar words can disrupt the flow of reading and hinder comprehension. It’s important to use context clues or look up definitions to maintain understanding.
- Struggling with Retention – Some readers may find it challenging to remember key details or the main ideas after completing a section. This can be mitigated by summarizing the material or revisiting it regularly.
- Time Management Issues – The structured exercises may feel overwhelming if not managed effectively. Setting a specific time for each task and breaking it into segments can help improve time management.
- Lack of Engagement – Long, dense passages can lead to loss of focus. Actively engaging with the content by asking questions or making predictions can help maintain interest and improve retention.
How to Overcome These Challenges
- Use Active Reading Techniques – Annotate key points, highlight important ideas, and take brief notes. This helps keep focus and improves comprehension.
- Practice Consistently – Regular interaction with the material helps reinforce learning. Short, frequent study sessions can be more effective than longer, irregular ones.
- Seek Support When Needed – Don’t hesitate to seek clarification or additional resources if certain concepts or vocabulary are challenging. Collaborative learning or using external references can help deepen understanding.
How to Approach Level G Questions
Successfully tackling the questions in this section requires a strategic approach. The key is to carefully read the material and then focus on understanding the core concepts before answering any questions. Taking the time to break down each task and using effective techniques will help in accurately interpreting the content and selecting the right answers. Below are some key steps to help you approach each question with confidence.
Steps to Effectively Answer Questions
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Skim the Text | Quickly go through the material to get a general idea of the content before diving into the details. |
| 2. Focus on Key Ideas | Identify the main concepts or arguments presented in the text. Pay attention to the introduction and conclusion sections. |
| 3. Analyze the Questions | Before answering, make sure you fully understand what each question is asking. Look for keywords that hint at the correct response. |
| 4. Refer Back to the Text | Use the text to support your answers. Find specific details or quotes that directly relate to the question. |
| 5. Eliminate Wrong Answers | Use the process of elimination to rule out any answers that are clearly incorrect based on the material you’ve read. |
| 6. Review Your Responses | Before finalizing your answers, review the questions and your responses to ensure they align with the text and make sense. |
Mastering Vocabulary in Level G
Building a strong vocabulary is essential for understanding complex texts and performing well in any reading task. Mastering new words not only enhances comprehension but also improves the ability to interpret nuanced meanings and ideas. This section explores effective techniques to expand your vocabulary and retain new terms that will help you excel in your tasks.
Effective Techniques for Vocabulary Building
- Contextual Learning – Pay close attention to how new words are used in sentences. Understanding their meaning within context makes it easier to remember and apply them in different situations.
- Use Flashcards – Create flashcards with new words and their meanings. Regularly review them to reinforce memory and ensure you can recall the terms quickly.
- Practice with Synonyms – Once you learn a new word, try finding its synonyms. This will help you expand your understanding and use of language in various contexts.
- Engage in Active Reading – While reading, underline or highlight unfamiliar words. Take the time to look them up and then re-read the passage to see how the word enhances the meaning.
Tips for Retaining New Vocabulary
- Use Words in Daily Conversations – Incorporating new vocabulary into your daily speech will help solidify your understanding and make the words more memorable.
- Write with New Vocabulary – Practice writing sentences or short paragraphs using newly learned words. This active engagement helps deepen your understanding.
- Group Words by Theme – Categorizing words into themes or subjects, such as nature, technology, or emotions, can make it easier to remember them as related terms.
- Review Regularly – Frequent revision of learned words is crucial for long-term retention. Set aside time each week to go over your vocabulary list.
Improving Retention with See Reader
Retention of information is a critical skill when it comes to mastering complex materials. The key to retaining what you’ve read lies in engaging with the content actively and revisiting it regularly. Utilizing interactive tools that promote active involvement helps reinforce the material and make it easier to recall. This section explores various strategies to improve retention and ensure that important details are not easily forgotten.
One effective method is to break down the material into smaller, manageable sections. This reduces the cognitive load and allows the brain to process the information in smaller chunks. Re-reading and reflecting on the text after each section can also enhance memory retention. Additionally, it is beneficial to relate new information to something already known, making it easier to remember and apply.
Regular review and self-testing are other important techniques. By testing yourself on key concepts and details from the material, you can gauge your understanding and reinforce the knowledge you have acquired. This technique, known as retrieval practice, has been shown to significantly improve long-term retention.
Engaging with the Reading Material Effectively

To fully understand and retain the content, it’s essential to engage with the material in a thoughtful and active way. Passive reading, where the text is simply absorbed without much thought, often leads to limited retention and understanding. Active engagement, on the other hand, encourages critical thinking, deeper analysis, and greater retention of key concepts.
One effective way to engage with the content is by asking questions as you read. By pondering what the author is trying to convey and how it relates to the larger picture, you can form a more personal connection with the material. This method not only deepens understanding but also enhances the ability to recall information later.
Another important strategy is to make predictions. Before diving into a section, try to predict what the text might cover. After reading, compare your predictions with the actual content. This technique helps to sharpen focus and gives context to the information, making it easier to remember.
Additionally, summarizing key points after each section is an effective way to reinforce learning. Writing a brief summary forces you to process and synthesize the information, ensuring that it sticks. It also helps to engage with the material by noting down unfamiliar terms and looking up their meanings, which contributes to building a stronger vocabulary.
Level G and Critical Thinking Development
Engaging with complex materials can significantly enhance critical thinking skills. By challenging the mind to analyze, question, and synthesize information, individuals can improve their ability to approach problems from multiple perspectives. This section explores how the tasks in this section foster the development of critical thinking by requiring readers to make connections, evaluate arguments, and think beyond the text.
How Critical Thinking is Fostered
- Analysis of Textual Content – Evaluating the structure, purpose, and arguments within the material encourages deeper thought and helps readers recognize patterns and inconsistencies.
- Questioning Assumptions – The material often presents ideas that challenge preconceived notions, prompting readers to question assumptions and consider alternative viewpoints.
- Synthesizing Information – Bringing together different pieces of information from various sections or sources helps develop the ability to synthesize and form cohesive ideas.
- Drawing Conclusions – Readers are often asked to infer meanings and conclusions based on evidence presented, promoting deductive reasoning skills.
Benefits of Critical Thinking in Learning

- Enhanced Problem-Solving – The ability to think critically improves the approach to solving problems both within and outside of academic contexts.
- Improved Decision-Making – The practice of evaluating evidence and considering multiple perspectives leads to better, more informed decision-making.
- Greater Analytical Skills – Developing the ability to break down complex information into smaller components fosters stronger analytical skills, beneficial for any field.
- Stronger Communication – Critical thinking leads to clearer articulation of ideas, as individuals are better equipped to defend their thoughts with reasoned arguments.
Time Management for Level G Success

Effective time management is crucial for achieving success in any learning program. The ability to plan, prioritize, and allocate sufficient time to different tasks enables individuals to stay organized and make consistent progress. In this section, we explore strategies for managing time efficiently while working through complex materials, ensuring that each task is completed without feeling overwhelmed.
Key Strategies for Effective Time Management
- Prioritize Tasks – Identify the most important tasks and allocate more time for them. Focus on completing high-priority assignments before moving to less critical tasks.
- Create a Schedule – Break down your tasks into manageable time slots. Creating a daily or weekly plan helps you stay on track and avoid procrastination.
- Set Realistic Goals – Set achievable goals for each study session. Avoid overloading yourself with too many tasks at once, as this can lead to burnout and decreased productivity.
- Avoid Distractions – Find a quiet space to work and eliminate distractions. Turn off notifications and set aside specific time for breaks to prevent interruptions.
Sample Time Management Schedule
| Time | Activity |
|---|---|
| 8:00 AM – 9:00 AM | Review key concepts from the previous day |
| 9:00 AM – 10:30 AM | Focus on the most challenging section |
| 10:30 AM – 10:45 AM | Take a short break |
| 10:45 AM – 12:00 PM | Work through practice exercises |
| 12:00 PM – 1:00 PM | Lunch break and relaxation |
| 1:00 PM – 2:30 PM | Review any difficult sections and test comprehension |
| 2:30 PM – 3:00 PM | Wrap-up and plan for the next session |
By sticking to a well-structured schedule, you can efficiently manage your time and maximize productivity, ensuring success without feeling overwhelmed.
Analyzing Themes in See Reader

Understanding the central themes of any narrative is key to gaining a deeper insight into the material. Themes often represent underlying messages, concepts, or ideas that the author seeks to explore. This section focuses on how to identify and analyze these themes effectively, providing tools to enhance comprehension and critical thinking while engaging with the content.
Identifying Common Themes
Themes are not always immediately apparent and may require careful reflection and analysis. Below are some common themes that frequently appear in many texts:
- Conflict – The struggles between opposing forces that drive the plot.
- Identity – The exploration of characters’ self-awareness and personal growth.
- Love and Relationships – Interpersonal dynamics that shape character motivations and outcomes.
- Justice – The pursuit of fairness and the consequences of moral choices.
- Change – The transformation of characters, settings, or situations over time.
Analyzing Themes with Examples
Once the themes are identified, it is essential to examine how they are developed throughout the text. The following table outlines a few examples of themes and their relevance within a narrative:
| Theme | Example from Text | Impact on the Story |
|---|---|---|
| Conflict | A character struggling with their inner fears and external challenges | Drives the plot forward and shapes character development |
| Identity | A protagonist questioning their purpose and place in society | Fosters emotional engagement and introspection in the audience |
| Justice | A character seeking retribution or fairness after an injustice | Highlights moral dilemmas and creates tension in the narrative |
By examining how these themes emerge and evolve, readers can appreciate the depth and complexity of the material, ultimately enhancing their understanding and engagement with the text.
Interpreting Key Ideas in Texts
Understanding the core concepts within a text is essential for gaining a full appreciation of its meaning. Whether the material is fictional or non-fictional, the ability to grasp its central messages, arguments, or themes is crucial. This section explores how to effectively interpret the most important ideas in any reading material and how these ideas contribute to the overall meaning.
Recognizing Main Ideas

The main idea of a passage is its central focus or the most important point that the author is trying to convey. Identifying these key concepts involves paying attention to:
- Topic Sentences – These often introduce the central theme of a paragraph or section.
- Repetition – Words or phrases that are repeated throughout the text often point to significant ideas.
- Supporting Details – Information that reinforces or explains the central concept is often key to understanding the broader message.
Evaluating the Significance of Ideas
Once the main ideas are identified, it is important to consider their significance. To do this, consider how these ideas:
- Relate to the Larger Message – How does the central concept connect with the overall theme or purpose of the text?
- Influence Character or Plot Development – In narrative texts, key ideas often drive character decisions and plot outcomes.
- Prompt Reflection – Think about how these ideas challenge, support, or enrich your own perspective.
By honing these skills, readers can better analyze and interpret the core ideas presented in any material, improving both comprehension and critical thinking.
Using Context Clues in Reading Plus
Understanding new words or phrases within a passage often requires more than just looking them up in a dictionary. Instead, readers can rely on context clues, which are hints found in the surrounding text that help clarify the meaning of unfamiliar terms. By analyzing these clues, one can make educated guesses about the meanings of unknown words and enhance overall comprehension.
Types of Context Clues
Context clues come in different forms. Recognizing and understanding these types can help readers quickly infer meanings without having to pause for a dictionary. Here are the most common types:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition Clue | When a word is defined directly within the sentence or paragraph. |
| Synonym Clue | When a synonym for the unfamiliar word is used nearby to provide clarification. |
| Antonym Clue | When the meaning of a word is contrasted with the meaning of another word, showing the opposite idea. |
| Example Clue | When examples are given to explain a concept or term, making it easier to deduce the meaning. |
| Inference Clue | When the meaning of a word can be inferred from the overall context of the sentence or paragraph. |
How to Apply Context Clues
To use context clues effectively, follow these steps:
- Read the surrounding sentences: Pay attention to how the unknown word fits into the larger passage.
- Look for familiar words: Identify words in the same sentence or nearby that might help explain the unknown word.
- Make an educated guess: Using the clues, try to form a reasonable meaning for the unknown word.
- Check consistency: Ensure that your guessed meaning makes sense within the overall context of the passage.
By mastering the use of context clues, readers can develop stronger vocabulary skills and improve comprehension, making reading a more efficient and enjoyable process.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When engaging with challenging texts, many learners encounter common pitfalls that can hinder their understanding and performance. These mistakes often stem from misconceptions, rushed reading, or overlooking key details. By recognizing these errors and learning strategies to avoid them, readers can significantly improve their comprehension and effectiveness in processing material.
One frequent mistake is misinterpreting the main idea of a passage. This occurs when the reader focuses too much on minor details and fails to grasp the overarching message. Another common issue is skipping over unfamiliar words or phrases, which may lead to confusion in understanding the full context. Additionally, some readers rush through passages without taking the time to reflect on the information presented, leading to missed connections and insights.
To avoid these mistakes, it is essential to slow down and read actively. Pay attention to the structure of the text and identify the main points. Make sure to pause when encountering unfamiliar terms and use context clues or other strategies to infer their meaning. Always revisit sections that seem unclear to ensure a complete understanding of the material. By practicing careful reading and developing these habits, learners can enhance their comprehension and avoid common errors that hinder progress.
Tracking Your Progress in Level G
Monitoring your advancement in any educational system is crucial for maintaining motivation and ensuring continuous improvement. When working with reading exercises, tracking progress helps you identify strengths and areas that require more focus. By keeping an eye on your development, you can set realistic goals and work more effectively toward achieving them.
One of the most efficient ways to track progress is by regularly assessing your comprehension skills and measuring your understanding of different topics. Here are some strategies to help track your growth:
- Record Your Scores: Keep track of your performance on quizzes and exercises to identify patterns in your strengths and weaknesses.
- Set Personal Milestones: Establish short-term goals and celebrate when you achieve them. These could be based on specific topics or improvement in your overall scores.
- Review Feedback: Pay attention to the feedback you receive after completing exercises. Constructive criticism can provide valuable insights into areas that need attention.
- Track Time Spent: Monitor how much time you spend on each reading task. This can help you gauge your efficiency and whether you need to adjust your pace.
As you continue to monitor your progress, make adjustments to your learning strategies as needed. Keeping a consistent record of your achievements and challenges will help you stay on track and achieve better results over time.